2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: transmission fluidPage 1745 of 2321
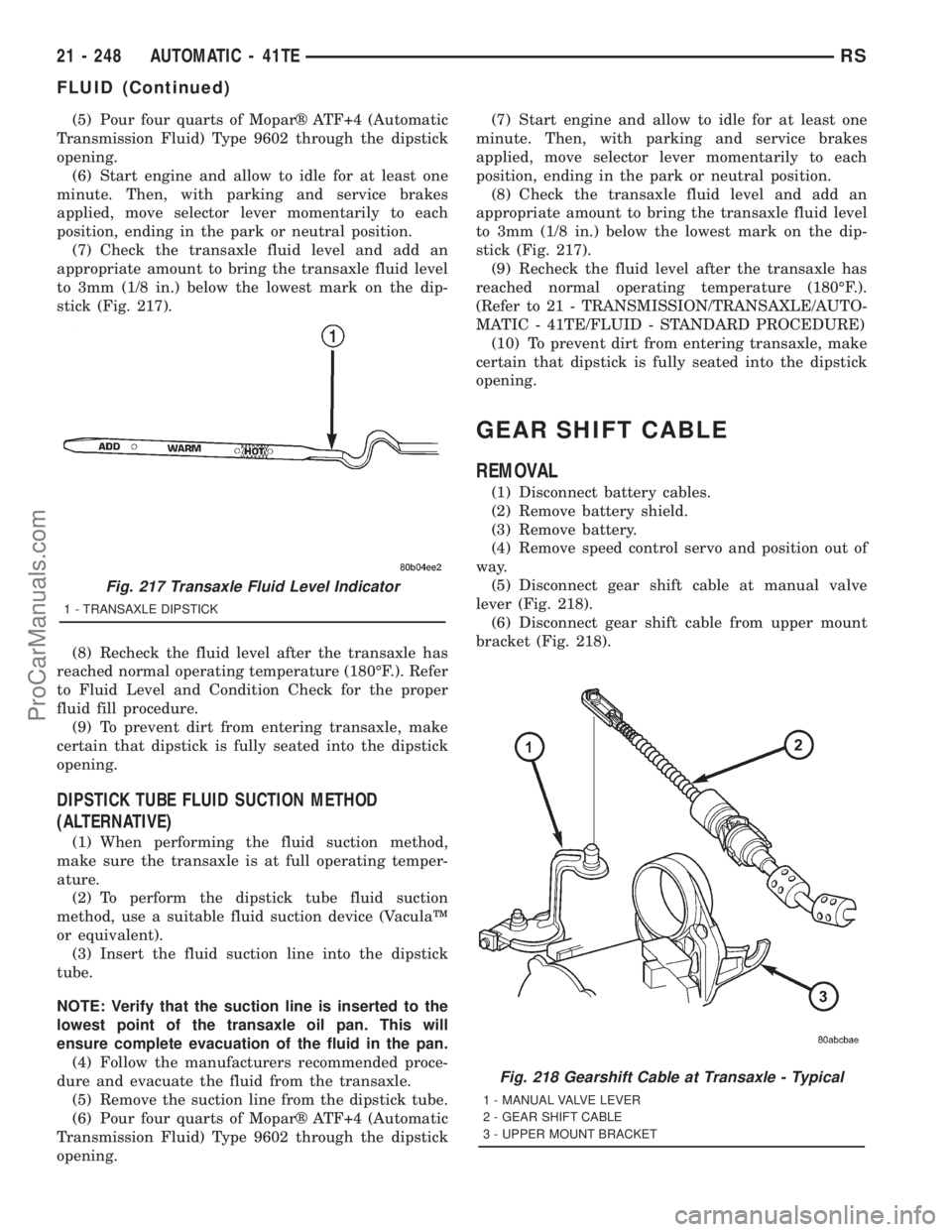
(5) Pour four quarts of Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) Type 9602 through the dipstick
opening.
(6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(7) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 217).
(8) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.). Refer
to Fluid Level and Condition Check for the proper
fluid fill procedure.
(9) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature.
(2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent).
(3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
(5) Remove the suction line from the dipstick tube.
(6) Pour four quarts of Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) Type 9602 through the dipstick
opening.(7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 217).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield.
(3) Remove battery.
(4) Remove speed control servo and position out of
way.
(5) Disconnect gear shift cable at manual valve
lever (Fig. 218).
(6) Disconnect gear shift cable from upper mount
bracket (Fig. 218).
Fig. 217 Transaxle Fluid Level Indicator
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
Fig. 218 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
21 - 248 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
FLUID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1766 of 2321
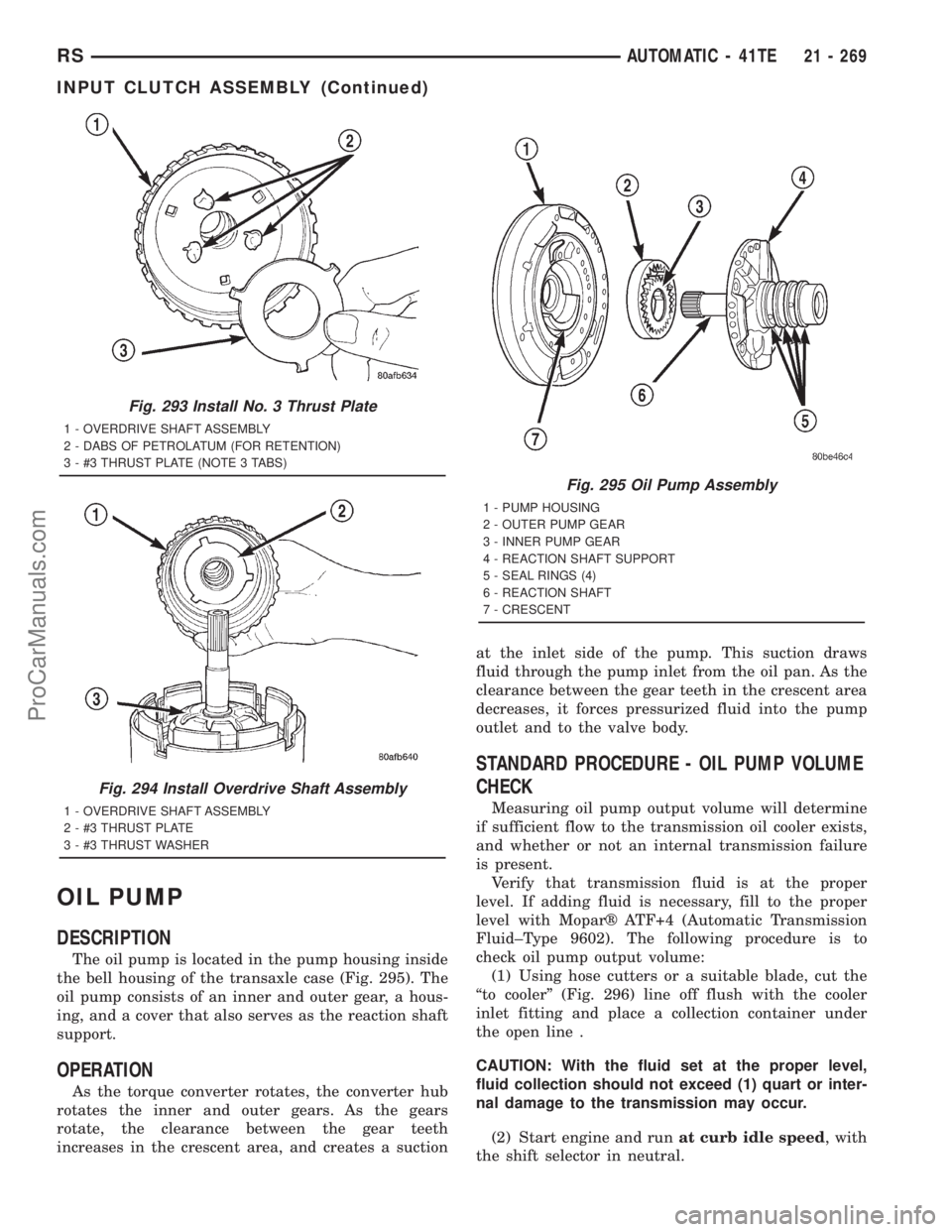
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump is located in the pump housing inside
the bell housing of the transaxle case (Fig. 295). The
oil pump consists of an inner and outer gear, a hous-
ing, and a cover that also serves as the reaction shaft
support.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the inner and outer gears. As the gears
rotate, the clearance between the gear teeth
increases in the crescent area, and creates a suctionat the inlet side of the pump. This suction draws
fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
clearance between the gear teeth in the crescent area
decreases, it forces pressurized fluid into the pump
outlet and to the valve body.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP VOLUME
CHECK
Measuring oil pump output volume will determine
if sufficient flow to the transmission oil cooler exists,
and whether or not an internal transmission failure
is present.
Verify that transmission fluid is at the proper
level. If adding fluid is necessary, fill to the proper
level with Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission
Fluid±Type 9602). The following procedure is to
check oil pump output volume:
(1) Using hose cutters or a suitable blade, cut the
ªto coolerº (Fig. 296) line off flush with the cooler
inlet fitting and place a collection container under
the open line .
CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(2) Start engine and runat curb idle speed, with
the shift selector in neutral.
Fig. 293 Install No. 3 Thrust Plate
1 - OVERDRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
2 - DABS OF PETROLATUM (FOR RETENTION)
3 - #3 THRUST PLATE (NOTE 3 TABS)
Fig. 294 Install Overdrive Shaft Assembly
1 - OVERDRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
2 - #3 THRUST PLATE
3 - #3 THRUST WASHER
Fig. 295 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - OUTER PUMP GEAR
3 - INNER PUMP GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 269
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1767 of 2321
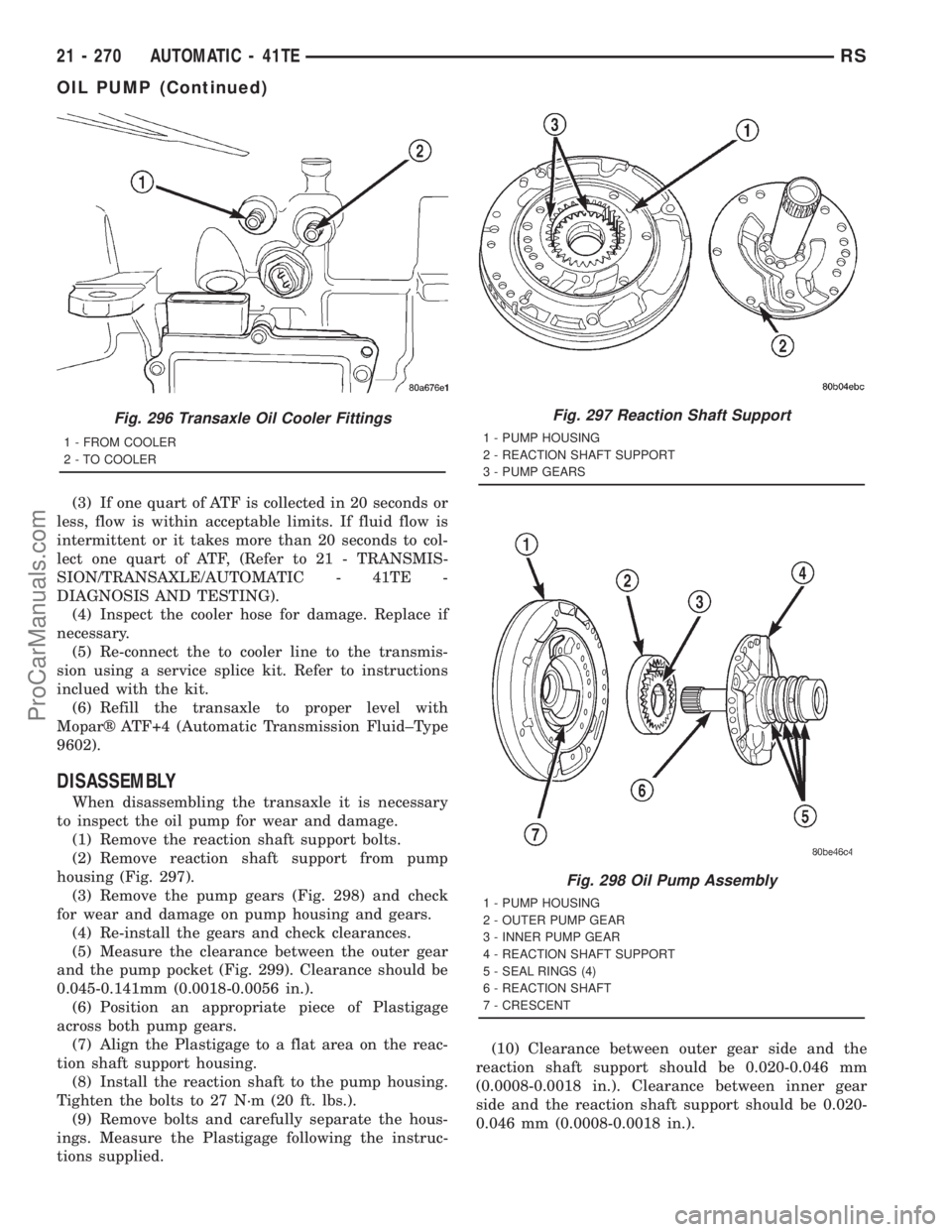
(3) If one quart of ATF is collected in 20 seconds or
less, flow is within acceptable limits. If fluid flow is
intermittent or it takes more than 20 seconds to col-
lect one quart of ATF, (Refer to 21 - TRANSMIS-
SION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(4) Inspect the cooler hose for damage. Replace if
necessary.
(5) Re-connect the to cooler line to the transmis-
sion using a service splice kit. Refer to instructions
inclued with the kit.
(6) Refill the transaxle to proper level with
Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid±Type
9602).
DISASSEMBLY
When disassembling the transaxle it is necessary
to inspect the oil pump for wear and damage.
(1) Remove the reaction shaft support bolts.
(2) Remove reaction shaft support from pump
housing (Fig. 297).
(3) Remove the pump gears (Fig. 298) and check
for wear and damage on pump housing and gears.
(4) Re-install the gears and check clearances.
(5) Measure the clearance between the outer gear
and the pump pocket (Fig. 299). Clearance should be
0.045-0.141mm (0.0018-0.0056 in.).
(6) Position an appropriate piece of Plastigage
across both pump gears.
(7) Align the Plastigage to a flat area on the reac-
tion shaft support housing.
(8) Install the reaction shaft to the pump housing.
Tighten the bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(9) Remove bolts and carefully separate the hous-
ings. Measure the Plastigage following the instruc-
tions supplied.(10) Clearance between outer gear side and the
reaction shaft support should be 0.020-0.046 mm
(0.0008-0.0018 in.). Clearance between inner gear
side and the reaction shaft support should be 0.020-
0.046 mm (0.0008-0.0018 in.).
Fig. 296 Transaxle Oil Cooler Fittings
1 - FROM COOLER
2 - TO COOLER
Fig. 297 Reaction Shaft Support
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - PUMP GEARS
Fig. 298 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - OUTER PUMP GEAR
3 - INNER PUMP GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
21 - 270 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
OIL PUMP (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1773 of 2321
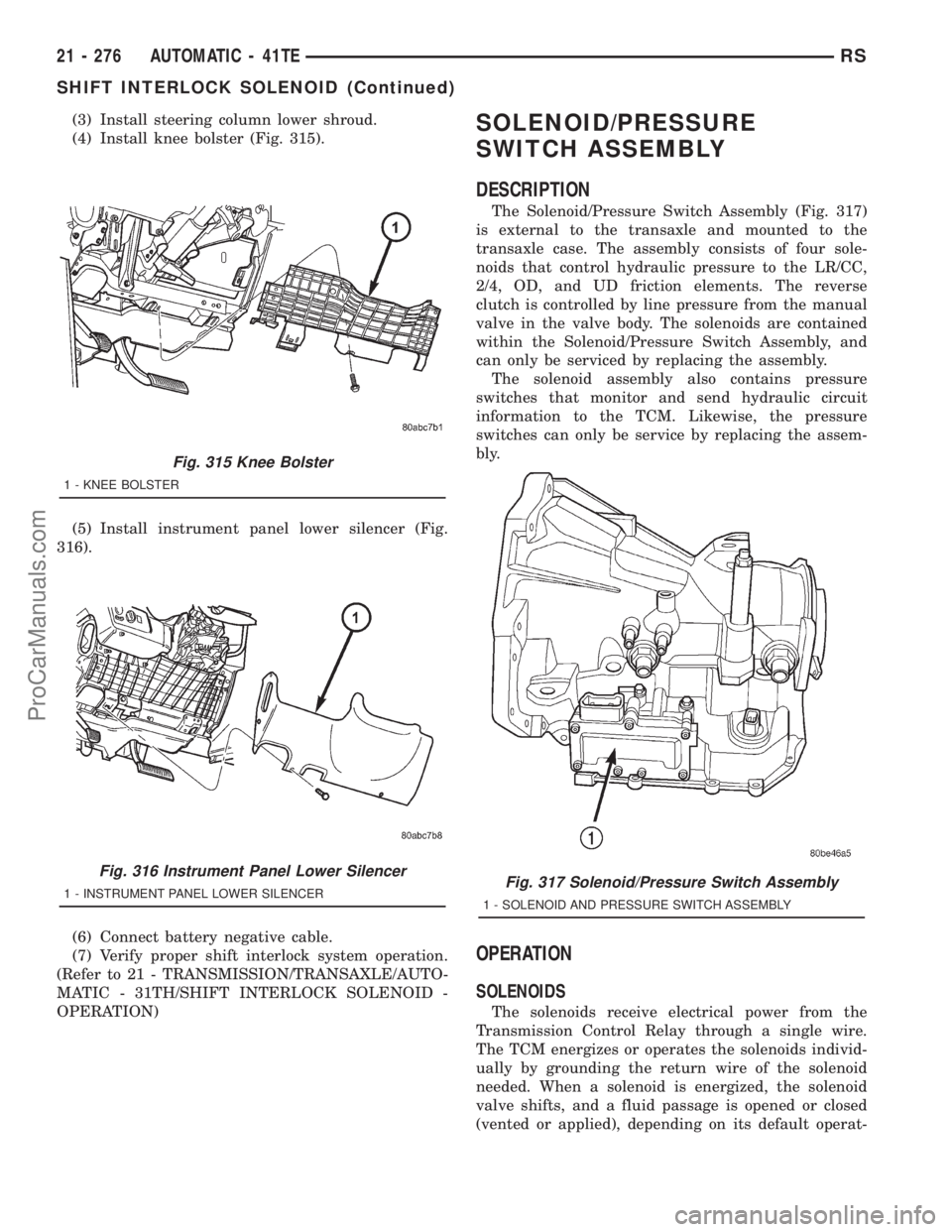
(3) Install steering column lower shroud.
(4) Install knee bolster (Fig. 315).
(5) Install instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
316).
(6) Connect battery negative cable.
(7) Verify proper shift interlock system operation.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID -
OPERATION)SOLENOID/PRESSURE
SWITCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly (Fig. 317)
is external to the transaxle and mounted to the
transaxle case. The assembly consists of four sole-
noids that control hydraulic pressure to the LR/CC,
2/4, OD, and UD friction elements. The reverse
clutch is controlled by line pressure from the manual
valve in the valve body. The solenoids are contained
within the Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly, and
can only be serviced by replacing the assembly.
The solenoid assembly also contains pressure
switches that monitor and send hydraulic circuit
information to the TCM. Likewise, the pressure
switches can only be service by replacing the assem-
bly.
OPERATION
SOLENOIDS
The solenoids receive electrical power from the
Transmission Control Relay through a single wire.
The TCM energizes or operates the solenoids individ-
ually by grounding the return wire of the solenoid
needed. When a solenoid is energized, the solenoid
valve shifts, and a fluid passage is opened or closed
(vented or applied), depending on its default operat-
Fig. 315 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 316 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCERFig. 317 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly
1 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
21 - 276 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1774 of 2321

ing state. The result is an apply or release of a fric-
tional element.
The 2/4 and UD solenoids are normally applied,
which by design allow fluid to pass through in their
relaxed or ªoffº state. This allows transaxle limp-in
(P,R,N,2) in the event of an electrical failure.
The continuity of the solenoids and circuits are
periodically tested. Each solenoid is turned on or off
depending on its current state. An inductive spike
should be detected by the TCM during this test. It no
spike is detected, the circuit is tested again to verify
the failure. In addition to the periodic testing, the
solenoid circuits are tested if a speed ratio or pres-
sure switch error occurs.
PRESSURE SWITCHES
The TCM relies on three pressure switches to mon-
itor fluid pressure in the L/R, 2/4, and OD hydraulic
circuits. The primary purpose of these switches is to
help the TCM detect when clutch circuit hydraulic
failures occur. The range for the pressure switch clos-
ing and opening points is 11-23 psi. Typically the
switch opening point will be approximately one psi
lower than the closing point. For example, a switch
may close at 18 psi and open at 17 psi. The switches
are continuously monitored by the TCM for the cor-
rect states (open or closed) in each gear as shown in
the following chart:
PRESSURE SWITCH STATES
GEAR L/R 2/4 OD
ROPOPOP
P/N CL OP OP
1st CL OP OP
2nd OP CL OP
DOPOPCL
OD OP CL CL
OP = OPEN
CL = CLOSED
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will set if the
TCM senses any switch open or closed at the wrong
time in a given gear.
The TCM also tests the 2/4 and OD pressure
switches when they are normally off (OD and 2/4 are
tested in 1st gear, OD in 2nd gear, and 2/4 in 3rd
gear). The test simply verifies that they are opera-
tional, by looking for a closed state when the corre-
sponding element is applied. Immediately after a
shift into 1st, 2nd, or 3rd gear with the engine speed
above 1000 rpm, the TCM momentarily turns on ele-
ment pressure to the 2/4 and/or OD clutch circuits to
identify that the appropriate switch has closed. If it
doesn't close, it is tested again. If the switch fails toclose the second time, the appropriate Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) will set.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If solenoid/pressure switch assembly is
being replaced, it is necessary to perform the TCM
Quick Learn Procedure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(3) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector.
(4) Disconnect input speed sensor connector.
(5) Remove input speed sensor (Fig. 318).
(6) Remove three (3) solenoid/pressure switch
assembly-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 319).
(7) Remove solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
gasket (Fig. 320). Use care to prevent gasket mate-
rial and foreign objects from become lodged in the
transaxle case ports.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If solenoid/pressure switch assembly is
being replaced, it is necessary to perform the TCM
Quick Learn Procedure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Install solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
new gasket to transaxle (Fig. 320).
Fig. 318 Input Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 277
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1778 of 2321
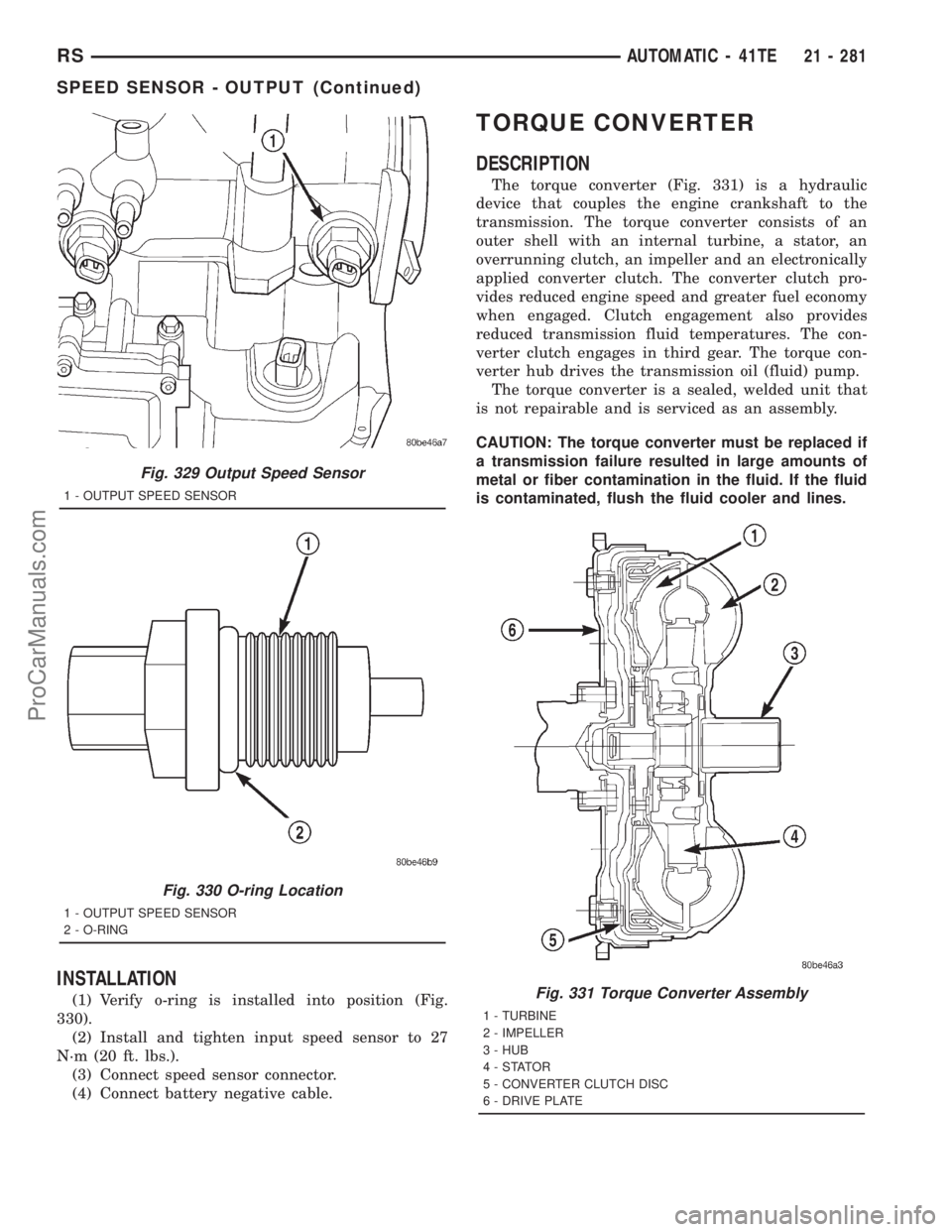
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
330).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector.
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 331) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the fluid cooler and lines.
Fig. 329 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 330 O-ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 331 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
6 - DRIVE PLATE
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 281
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1781 of 2321
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 337) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
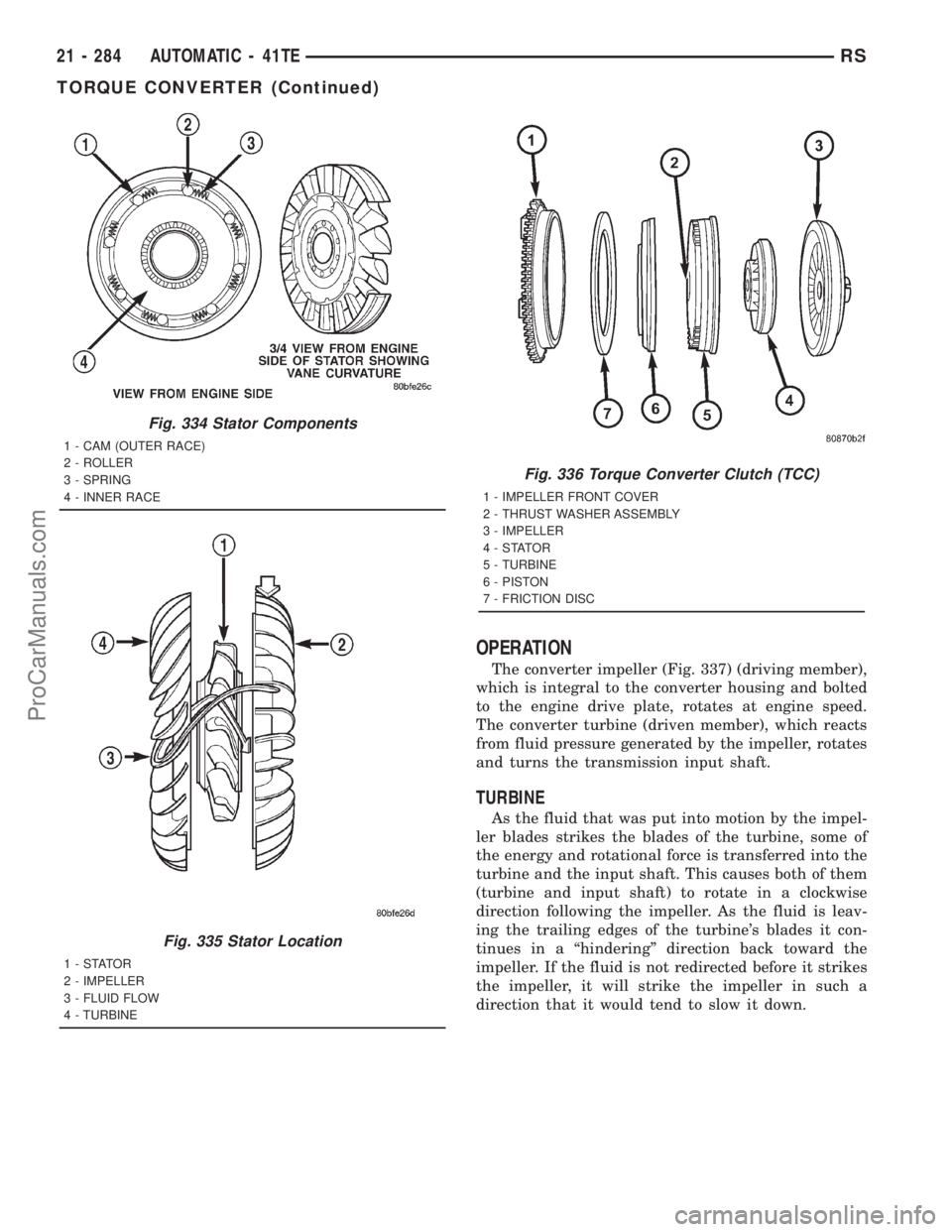
Fig. 334 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 335 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 336 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 284 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1782 of 2321
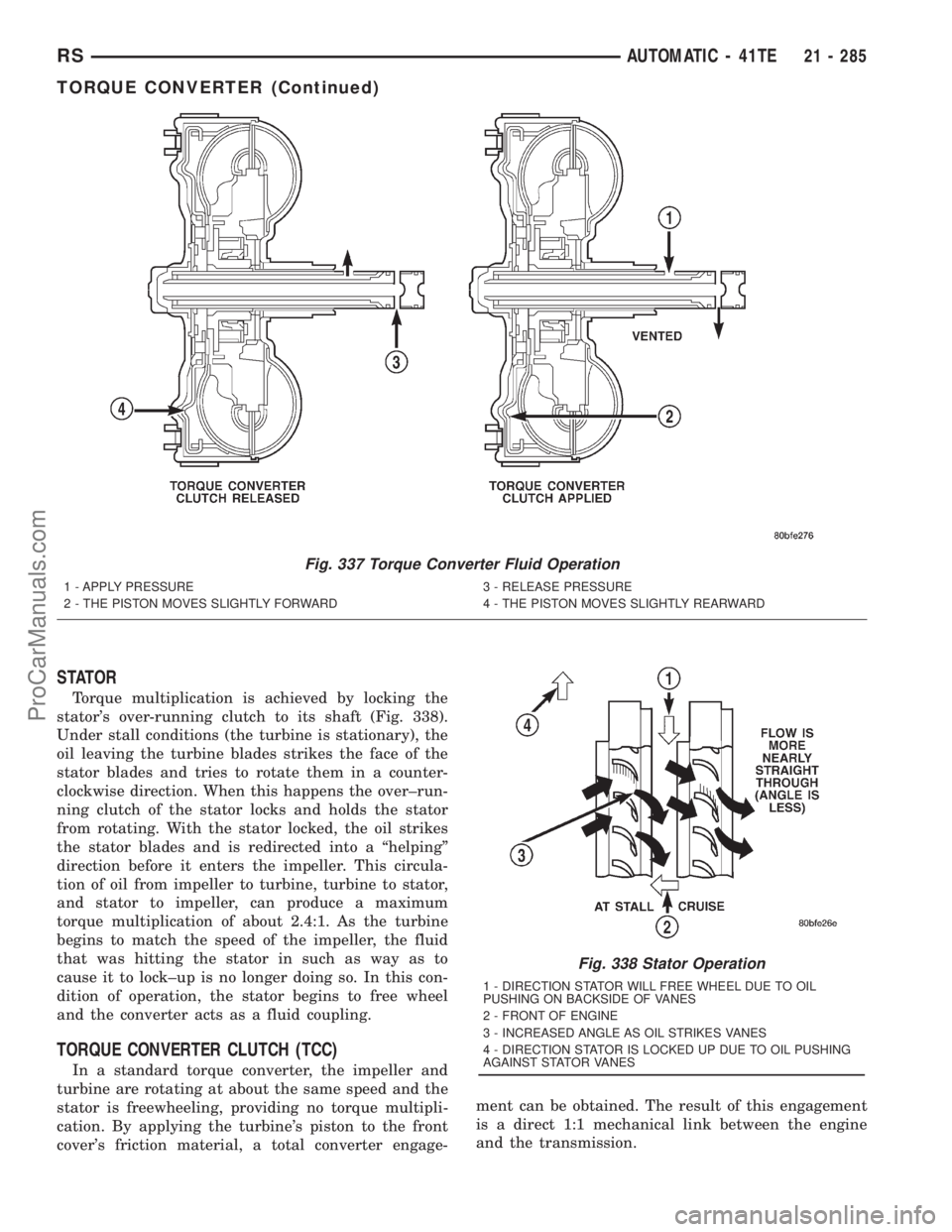
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 338).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over±run-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock±up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
Fig. 337 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
Fig. 338 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 285
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com