2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 1276 of 2321

OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dipstick, it is
possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil
while engine is running and create foaming. Foam in
oil pan would be fed to the hydraulic lifters by the oil
pump causing them to become soft and allow valves
to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the lifters it causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump, through which air can be drawn, will
create the same lifter noise. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the oil pump
cover, including the relief valve retainer cap. When
lifter noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent
or constant, and usually more than one lifter will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
the engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all
of the air inside of the lifters to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy lifters. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
Valve lifter noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger which will
necessitate replacing the lifter, or by the plunger par-
tially sticking in the lifter body cylinder. A heavy
click is caused either by a lifter check valve not seat-
ing, or by foreign particles becoming wedged between
the plunger and the lifter body causing the plunger
to stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the
valve stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either
case, lifter assembly should be removed for inspec-
tion.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the yoke retainer and aligning yokes
(Fig. 71).
(3) Remove the hydraulic lifters. If necessary use
Special Tool C-4129, or equivalent to remove liftersfrom bores. If lifters are to be reused, identify each
lifter to ensure installation in original location.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the lifters with engine oil.
NOTE: Position the lifter in bore with the lubrication
hole facing upward (Fig. 70).
(2) Install the hydraulic lifters with the lubrication
hole facing upward towards middle of block (Fig. 70).
Install lifters in original positions, if reused.
(3) Install lifter aligning yokes (Fig. 71).
(4) Install yoke retainer and torque screws to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 71).
(5) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(6) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all
hydraulic lifters have filled with oil and have
become quiet.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of cast aluminum alloy and
are a strutless, short skirt design. The piston rings
consist of two compression rings and a three piece oil
ring. Piston pins connect the piston to the forged
steel connecting rods. The piston pins are a press fit
into the connecting rod.
Fig. 70 LIFTER LUBRICATION HOLE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 119
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK) (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1277 of 2321

OPERATION
The piston and connecting rod is the link between
the combustion force to the crankshaft.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - FITTING
CONNECTING RODS
The bearing caps are not interchangeable or
reversible, and should be marked at removal to
ensure correct reassembly. The bearing shells must
be installed with the tangs inserted into the
machined grooves in the rods and caps. Install cap
with the tangs on the same side as the rod. For con-
necting rod bearing fitting (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Fit all connecting rods
on one bank until complete.NOTE: The connecting rod cap bolts should be
examined before reuse. Bolt stretch can be checked
by holding a scale or straight edge against the
threads. If all the threads do not contact the scale
the bolt must be replaced (Fig. 72).
(1) Before installing the nuts the threads should
be oiled with engine oil.
(2) Install nuts finger tight on each bolt then alter-
nately torque each nut to assemble the cap properly.
(3) Tighten the nuts to 54 N´m PLUS 1/4 turn (40
ft. lbs. PLUS 1/4 turn).
(4) Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 73). Refer to Engine Specifications
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
Fig. 71 Lifter Aligning Yoke and Retainer
1 - YOKE RETAINER
2 - BOLT - YOKE RETAINER
3 - ALIGNING YOKE
4 - HYDRAULIC LIFTER
Fig. 72 Check for Stretched (Necked) Bolts
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 73 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance
9 - 120 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1284 of 2321
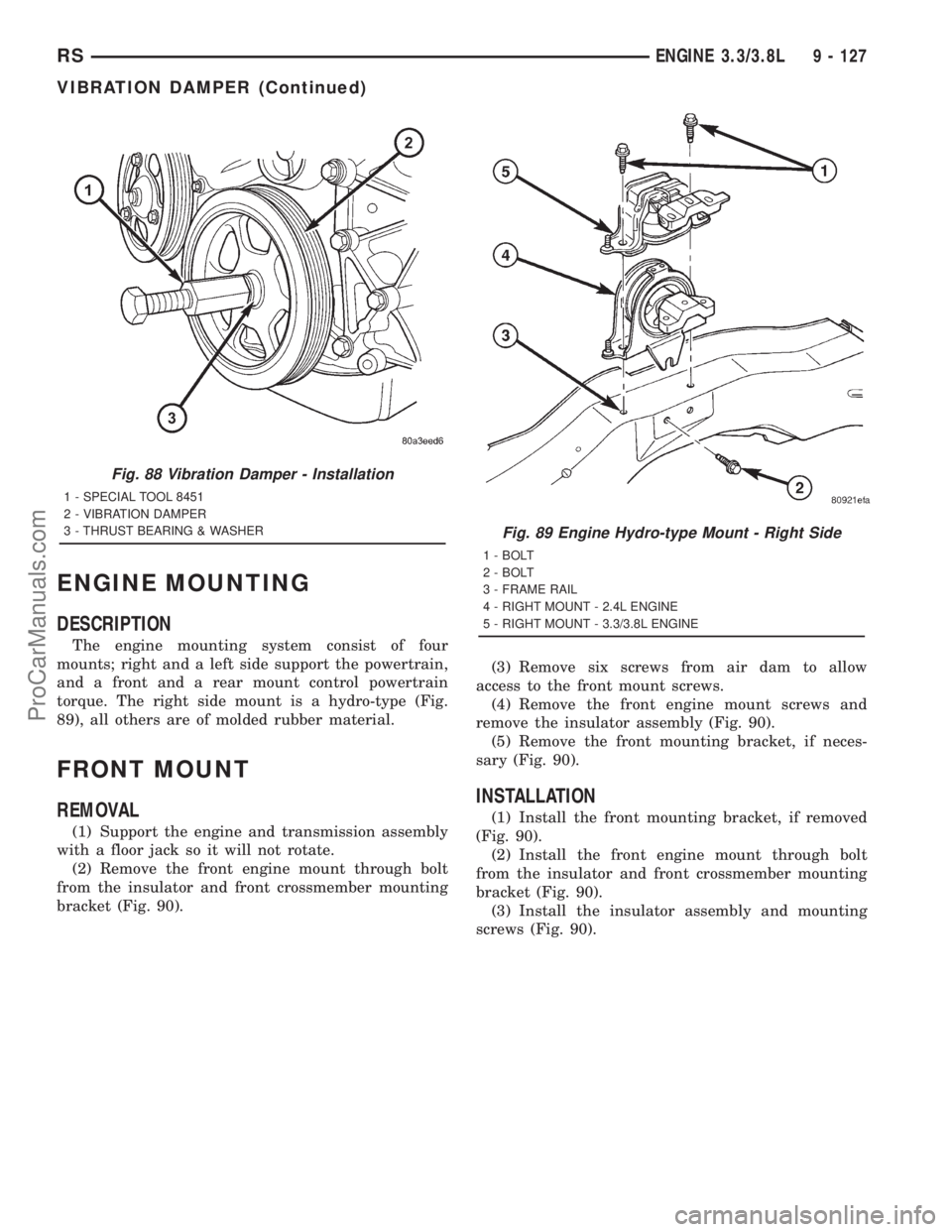
ENGINE MOUNTING
DESCRIPTION
The engine mounting system consist of four
mounts; right and a left side support the powertrain,
and a front and a rear mount control powertrain
torque. The right side mount is a hydro-type (Fig.
89), all others are of molded rubber material.
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL
(1) Support the engine and transmission assembly
with a floor jack so it will not rotate.
(2) Remove the front engine mount through bolt
from the insulator and front crossmember mounting
bracket (Fig. 90).(3) Remove six screws from air dam to allow
access to the front mount screws.
(4) Remove the front engine mount screws and
remove the insulator assembly (Fig. 90).
(5) Remove the front mounting bracket, if neces-
sary (Fig. 90).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the front mounting bracket, if removed
(Fig. 90).
(2) Install the front engine mount through bolt
from the insulator and front crossmember mounting
bracket (Fig. 90).
(3) Install the insulator assembly and mounting
screws (Fig. 90).
Fig. 88 Vibration Damper - Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8451
2 - VIBRATION DAMPER
3 - THRUST BEARING & WASHER
Fig. 89 Engine Hydro-type Mount - Right Side
1 - BOLT
2 - BOLT
3 - FRAME RAIL
4 - RIGHT MOUNT - 2.4L ENGINE
5 - RIGHT MOUNT - 3.3/3.8L ENGINE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 127
VIBRATION DAMPER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1298 of 2321

between cylinder heads and houses the coolant ther-
mostat (Fig. 121).
The intake manifold utilizes a compact design with
very low restriction and outstanding flow balance.
This design allows the engine to perform with a wide
torque curve while increasing higher rpm horse-
power.
The composite upper intake for the 3.3L engine has
a unique cover over the upper portion of the manifold
(Fig. 119). This cover is designed to absorb intake
noises and also offers styling to the engine. This
cover, under any circumstance, should never be
removed. The fasteners attaching the upper intake
manifold can be accessed without removing this
cover. If, for some reason, the molded-in vacuum
ports break, the composite manifold can salvaged.
The vacuum ports are designed to break at the shoul-
der, if overloaded. Additional material in the shoulder
area provides sufficient stock to repair. For more
information and procedure, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - STANDARD
PROCEDURE). Also, if the special screws that attach
the MAP sensor, power steering reservoir, throttle
cable bracket, and the EGR tube become stripped, an
oversized screw is available to repair the stripped-out
condition. For more information and procedure,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
OPERATION
The intake manifold delivers air to the combustion
chambers. This air allows the fuel delivered by the
fuel injectors to ignite when the spark plug fire.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If engine RPM'S change, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
3.3L
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANIFOLD
STRIPPED THREAD REPAIR
The composite upper intake manifold thread
bosses, if stripped out, can be repaired by utilizing a
repair screw available through Mopartparts. Repair
screws are available for the following manifold
attached components:
²MAP sensor
²Power steering reservoir
²EGR tube
²Throttle cable bracket
The repair screws require a unique tightening
torque specification from the original screw. Refer to
the following chart for specification.
Fig. 119 INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.3L
1 - BOLT
2 - MAP SENSOR
3 - SCREW
4 - MANIFOLD - UPPER
5 - WIRE HARNESS
6 - GASKET (3 PER CYL. BANK)
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 141
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1299 of 2321
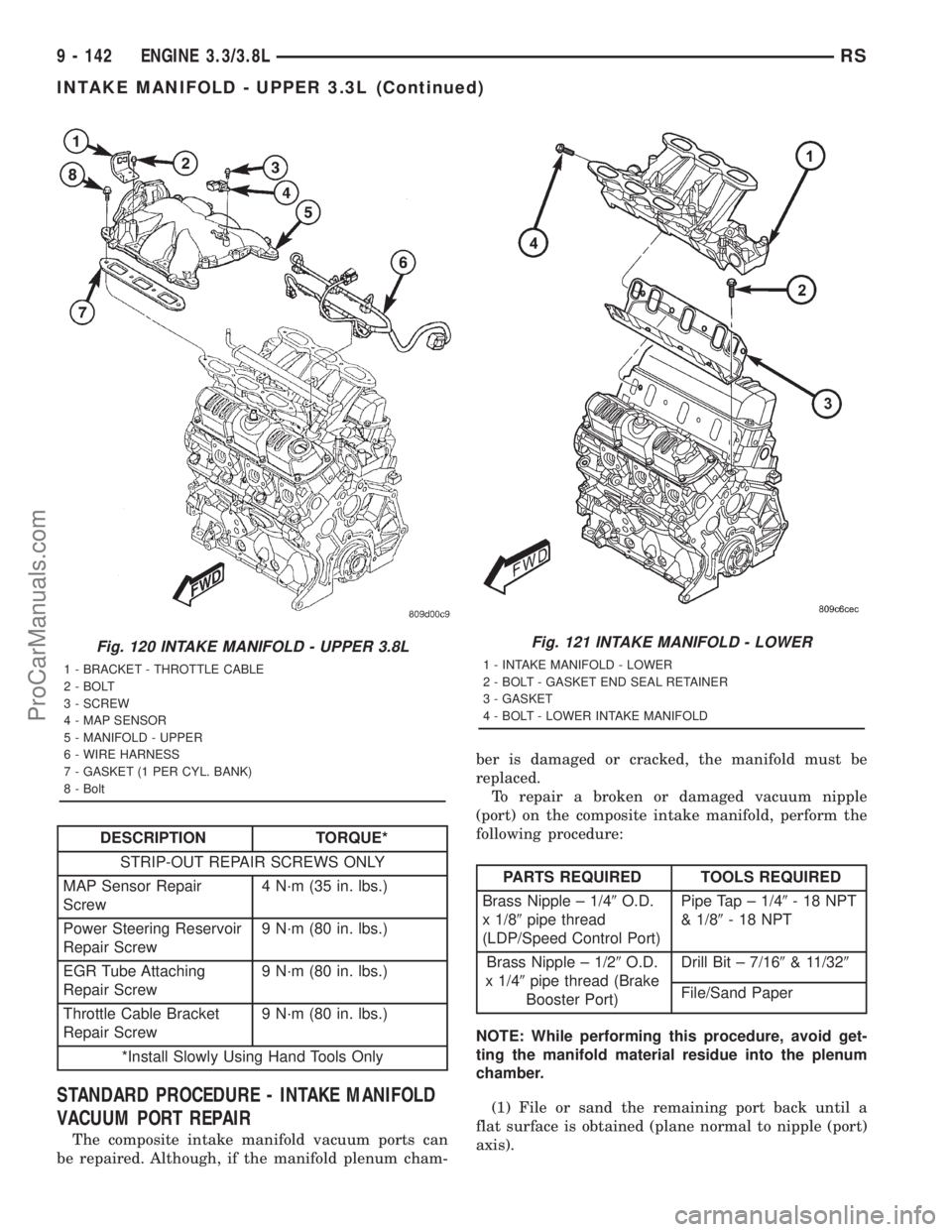
DESCRIPTION TORQUE*
STRIP-OUT REPAIR SCREWS ONLY
MAP Sensor Repair
Screw4 N´m (35 in. lbs.)
Power Steering Reservoir
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
EGR Tube Attaching
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
Throttle Cable Bracket
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
*Install Slowly Using Hand Tools Only
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INTAKE MANIFOLD
VACUUM PORT REPAIR
The composite intake manifold vacuum ports can
be repaired. Although, if the manifold plenum cham-ber is damaged or cracked, the manifold must be
replaced.
To repair a broken or damaged vacuum nipple
(port) on the composite intake manifold, perform the
following procedure:
PARTS REQUIRED TOOLS REQUIRED
Brass Nipple ± 1/49O.D.
x 1/89pipe thread
(LDP/Speed Control Port)Pipe Tap ± 1/49-18NPT
& 1/89-18NPT
Brass Nipple ± 1/29O.D.
x 1/49pipe thread (Brake
Booster Port)Drill Bit ± 7/169& 11/329
File/Sand Paper
NOTE: While performing this procedure, avoid get-
ting the manifold material residue into the plenum
chamber.
(1) File or sand the remaining port back until a
flat surface is obtained (plane normal to nipple (port)
axis).
Fig. 120 INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.8L
1 - BRACKET - THROTTLE CABLE
2 - BOLT
3 - SCREW
4 - MAP SENSOR
5 - MANIFOLD - UPPER
6 - WIRE HARNESS
7 - GASKET (1 PER CYL. BANK)
8 - Bolt
Fig. 121 INTAKE MANIFOLD - LOWER
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD - LOWER
2 - BOLT - GASKET END SEAL RETAINER
3 - GASKET
4 - BOLT - LOWER INTAKE MANIFOLD
9 - 142 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.3L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1300 of 2321
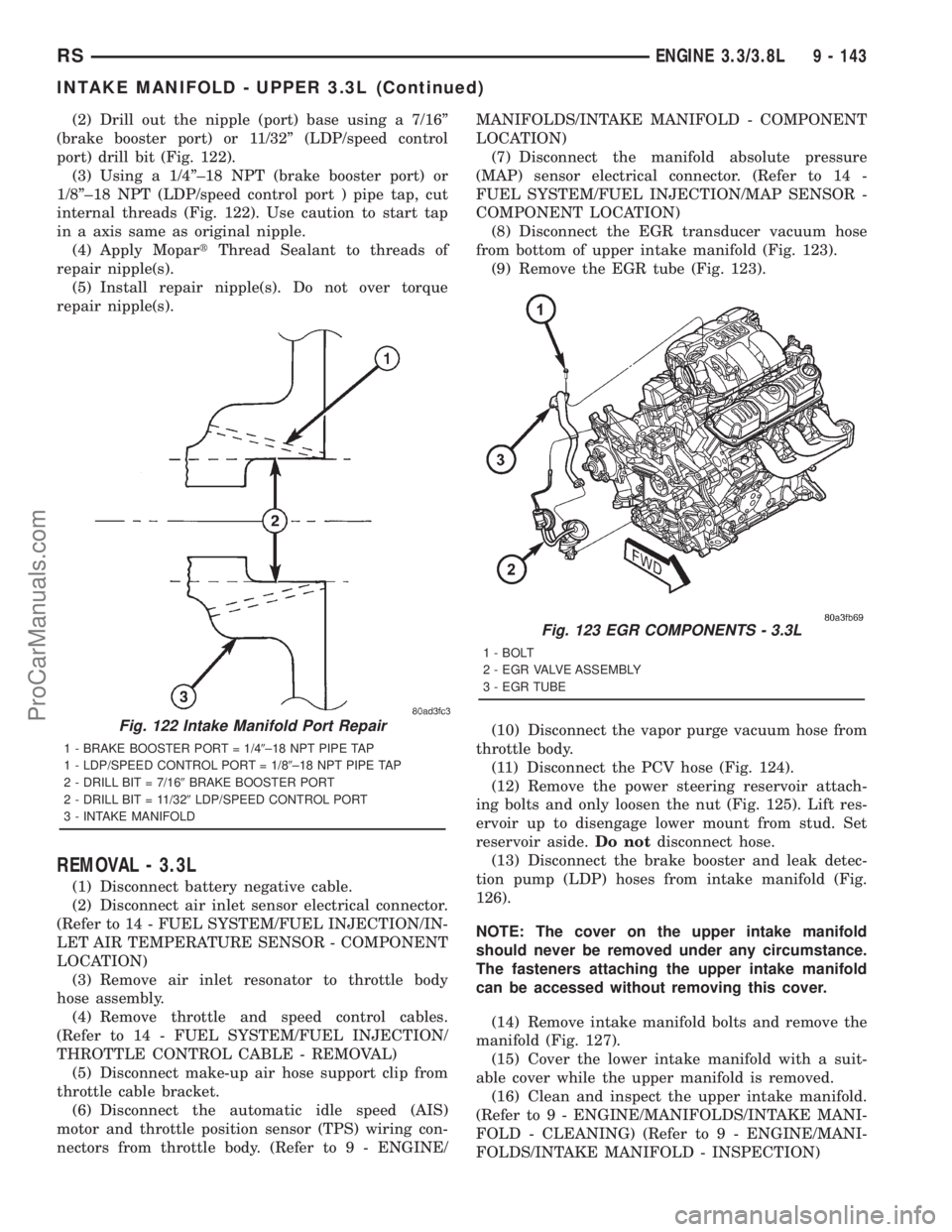
(2) Drill out the nipple (port) base using a 7/16º
(brake booster port) or 11/32º (LDP/speed control
port) drill bit (Fig. 122).
(3) Using a 1/4º±18 NPT (brake booster port) or
1/8º±18 NPT (LDP/speed control port ) pipe tap, cut
internal threads (Fig. 122). Use caution to start tap
in a axis same as original nipple.
(4) Apply MopartThread Sealant to threads of
repair nipple(s).
(5) Install repair nipple(s). Do not over torque
repair nipple(s).
REMOVAL - 3.3L
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect air inlet sensor electrical connector.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/IN-
LET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR - COMPONENT
LOCATION)
(3) Remove air inlet resonator to throttle body
hose assembly.
(4) Remove throttle and speed control cables.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE - REMOVAL)
(5) Disconnect make-up air hose support clip from
throttle cable bracket.
(6) Disconnect the automatic idle speed (AIS)
motor and throttle position sensor (TPS) wiring con-
nectors from throttle body. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - COMPONENT
LOCATION)
(7) Disconnect the manifold absolute pressure
(MAP) sensor electrical connector. (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/MAP SENSOR -
COMPONENT LOCATION)
(8) Disconnect the EGR transducer vacuum hose
from bottom of upper intake manifold (Fig. 123).
(9) Remove the EGR tube (Fig. 123).
(10) Disconnect the vapor purge vacuum hose from
throttle body.
(11) Disconnect the PCV hose (Fig. 124).
(12) Remove the power steering reservoir attach-
ing bolts and only loosen the nut (Fig. 125). Lift res-
ervoir up to disengage lower mount from stud. Set
reservoir aside.Do notdisconnect hose.
(13) Disconnect the brake booster and leak detec-
tion pump (LDP) hoses from intake manifold (Fig.
126).
NOTE: The cover on the upper intake manifold
should never be removed under any circumstance.
The fasteners attaching the upper intake manifold
can be accessed without removing this cover.
(14) Remove intake manifold bolts and remove the
manifold (Fig. 127).
(15) Cover the lower intake manifold with a suit-
able cover while the upper manifold is removed.
(16) Clean and inspect the upper intake manifold.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - CLEANING) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANI-
FOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - INSPECTION)
Fig. 122 Intake Manifold Port Repair
1 - BRAKE BOOSTER PORT = 1/49±18 NPT PIPE TAP
1 - LDP/SPEED CONTROL PORT = 1/89±18 NPT PIPE TAP
2 - DRILL BIT = 7/169BRAKE BOOSTER PORT
2 - DRILL BIT = 11/329LDP/SPEED CONTROL PORT
3 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
Fig. 123 EGR COMPONENTS - 3.3L
1 - BOLT
2 - EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY
3 - EGR TUBE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 143
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.3L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1302 of 2321

(4) Position upper manifold on lower manifold (Fig.
127). Install and tighten bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
following torque sequence in (Fig. 128).(5) Connect the MAP sensor electrical connector.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
MAP SENSOR - COMPONENT LOCATION)
(6) Connect the brake booster and LDP vacuum
hose to intake manifold (Fig. 126).
CAUTION: The special screws used for attaching
the EGR tube and power steering reservoir to the
manifold must be installed slowly using hand tools
only. This requirement is to prevent the melting of
material that causes stripped threads. If threads
become stripped, an oversize repair screw is avail-
able. For more information and procedure (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Install the power steering reservoir (Fig. 125).
Tighten screws to manifold to 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
(8) Using new gaskets, install the EGR tube and
torque bolts to 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
(9) Connect the EGR transducer vacuum hose.
(10) Install throttle and speed control cables.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE - INSTALLATION)
(11) Attach make up air hose clip into the hole in
the throttle cable bracket.
(12) Connect the wiring connectors to the throttle
position sensor (TPS) and Automatic Idle Speed (AIS)
motor. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE
MANIFOLD - COMPONENT LOCATION)
(13) Install air cleaner and air inlet hose assembly.
(14) Connect the inlet air sensor electrical connec-
tor. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJEC-
TION/INLET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
COMPONENT LOCATION)
(15) Connect battery negative cable.
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
3.8L
REMOVAL - 3.8L
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect air inlet sensor electrical connector.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/IN-
LET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR - COMPONENT
LOCATION)
(3) Remove air inlet resonator to throttle body
hose assembly.
(4) Remove throttle and speed control cables.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE - REMOVAL)
(5) Disconnect make-up air hose support clip from
throttle cable bracket.
(6) Disconnect the automatic idle speed (AIS)
motor and throttle position sensor (TPS) wiring con-
Fig. 127 INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.3L
1 - BOLT
2 - MAP SENSOR
3 - SCREW
4 - MANIFOLD - UPPER
5 - WIRE HARNESS
6 - GASKET (3 PER CYL. BANK)
Fig. 128 UPPER MANIFOLD TIGHTENING
SEQUENCE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 145
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.3L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1304 of 2321

INSPECTION
Check manifold for:
²Damage and cracks.
²Mounting surface distortion by using a straight-
edge and thickness gauge.
INSTALLATION - 3.8L
(1) If the following components were removed from
manifold, install and tighten to specifications:
²MAP sensor - 3.4 N´m (30 in. lbs.)
²Throttle cable bracket - 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
(2) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surfaces.
(3) Position the new intake manifold gasket on
lower manifold.
(4) Position upper manifold on lower manifold (Fig.
133). Install and tighten bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
following torque sequence in (Fig. 134).
(5) Connect the MAP sensor electrical connector.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
MAP SENSOR - COMPONENT LOCATION)
(6) Connect the brake booster and LDP vacuum
hose to intake manifold (Fig. 132).
(7) Connect the PCV hose (Fig. 130).
(8) Install the power steering reservoir (Fig. 131)
and torque fasteners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(9) Connect the EGR transducer vacuum hose.
(10) Using new gaskets, install the EGR tube (Fig.
129) and torque bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
Fig. 132 BRAKE BOOSTER & LDP VACUUM HOSES
1 - LDP & SPEED CONTROL VACUUM HOSE
2 - BRAKE BOOSTER VACUUM HOSE
3 - MAP SENSOR
Fig. 133 INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.8L
1 - BRACKET - THROTTLE CABLE
2 - BOLT
3 - SCREW
4 - MAP SENSOR
5 - MANIFOLD - UPPER
6 - WIRE HARNESS
7 - GASKET (1 PER CYL. BANK)
8 - BOLT
Fig. 134 UPPER MANIFOLD TIGHTENING
SEQUENCE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 147
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER 3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com