2001 DODGE RAM display
[x] Cancel search: displayPage 711 of 2889

to enter the servo and pull open the throttle plate
using the cable. When the PCM breaks the ground,
the solenoid closes and no more vacuum is allowed to
enter the servo. The PCM also operates the vent sole-
noid via ground. The vent solenoid opens and closes a
passage to bleed or hold vacuum in the servo as
required.
The PCM duty cycles the vacuum and vent sole-
noids to maintain the set speed, or to accelerate and
decelerate the vehicle. To increase throttle opening,
the PCM grounds the vacuum and vent solenoids. To
decrease throttle opening, the PCM removes the
grounds from the vacuum and vent solenoids. When
the brake is released, if vehicle speed exceeds 30
mph to resume, 35 mph to set, and the RES/ACCEL
switch has been depressed, ground for the vent and
vacuum circuits is restored.
REMOVAL
V-6/V-8 ENGINES
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector at servo (Fig. 4).
(3) Disconnect vacuum hose at servo.
(4) Disconnect servo cable at throttle body. Refer to
Servo Cable Removal/Installation in this group.(5) Remove three bolts retaining servo/servo
mounting bracket to side of battery tray (Fig. 5).
(6) Position servo assembly to gain access to 2
servo mounting nuts (Fig. 5) or (Fig. 6).
(7) Remove 2 mounting nuts holding servo cable
sleeve to bracket (Fig. 6).
(8) Pull speed control cable sleeve and servo away
from servo mounting bracket to expose cable retain-
ing clip (Fig. 6) and remove clip. Note: The servo
mounting bracket displayed in (Fig. 6) is a typical
bracket and may/may not be applicable to this model
vehicle.
(9) Remove servo from mounting bracket. While
removing, note orientation of servo to bracket.
8.0L V-10 ENGINE
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Disconnect positive battery cable at battery.
(3) Remove 2 bolts and battery holddown (Fig. 7).
(4) If equipped, pull up on battery heat shield to
remove it (Fig. 8).
(5) Remove battery from vehicle.
Fig. 3 Servo Cable at Throttle Lever
1 - PINCH (2) TABS
2 - CABLE MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - PINCH TABS (2)
4 - OFF
5 - THROTTLE CABLE
6 - THROTTLE LEVER
7 - THROTTLE LEVER PIN
8 - OFF
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
Fig. 4 Servo LocationÐRemoval/Installation
1 - BATTERY TRAY
2 - SERVO ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - SERVO BRACKET SCREWS (3)
8P - 6 SPEED CONTROLBR/BE
SPEED CONTROL SERVO (Continued)
Page 713 of 2889
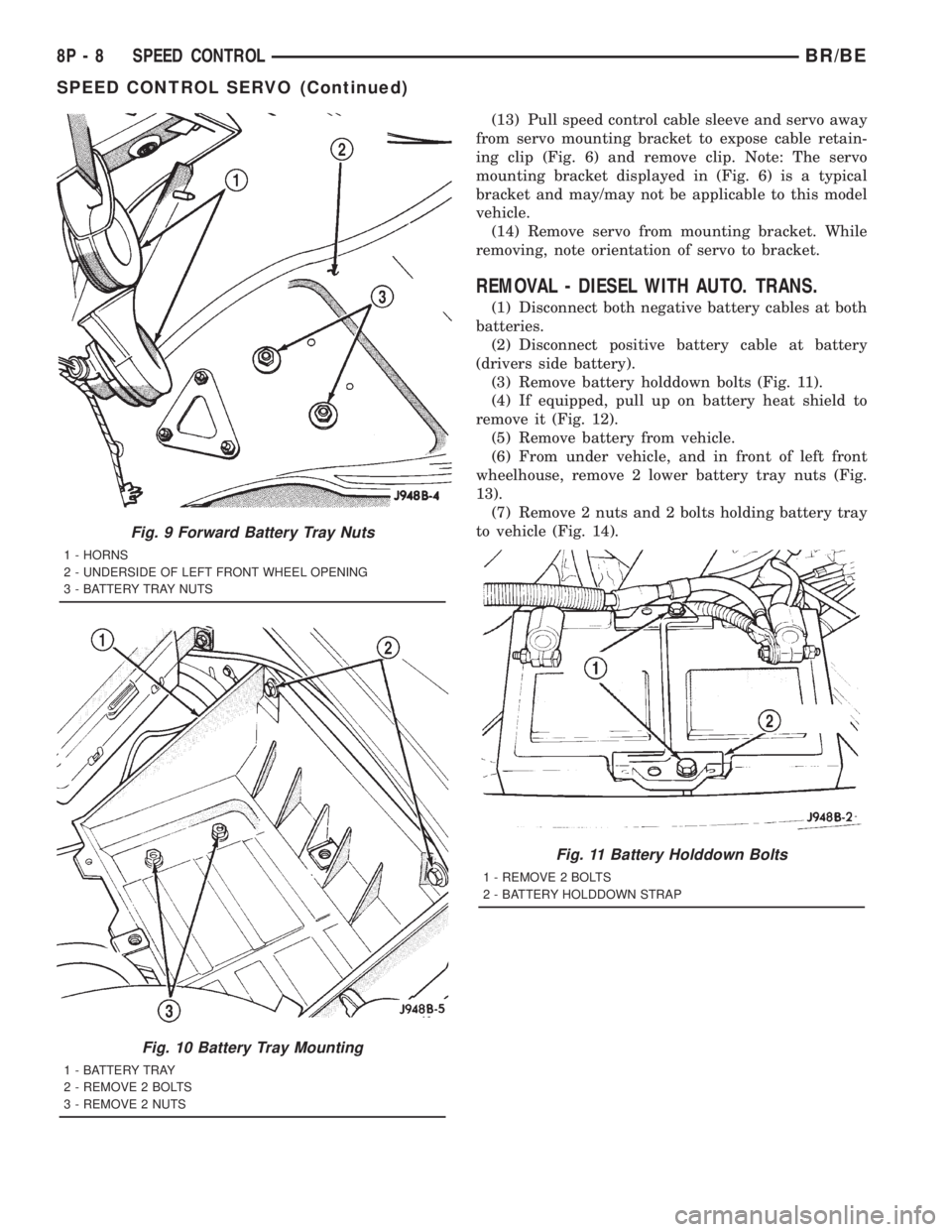
(13) Pull speed control cable sleeve and servo away
from servo mounting bracket to expose cable retain-
ing clip (Fig. 6) and remove clip. Note: The servo
mounting bracket displayed in (Fig. 6) is a typical
bracket and may/may not be applicable to this model
vehicle.
(14) Remove servo from mounting bracket. While
removing, note orientation of servo to bracket.
REMOVAL - DIESEL WITH AUTO. TRANS.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Disconnect positive battery cable at battery
(drivers side battery).
(3) Remove battery holddown bolts (Fig. 11).
(4) If equipped, pull up on battery heat shield to
remove it (Fig. 12).
(5) Remove battery from vehicle.
(6) From under vehicle, and in front of left front
wheelhouse, remove 2 lower battery tray nuts (Fig.
13).
(7) Remove 2 nuts and 2 bolts holding battery tray
to vehicle (Fig. 14).
Fig. 9 Forward Battery Tray Nuts
1 - HORNS
2 - UNDERSIDE OF LEFT FRONT WHEEL OPENING
3 - BATTERY TRAY NUTS
Fig. 10 Battery Tray Mounting
1 - BATTERY TRAY
2 - REMOVE 2 BOLTS
3 - REMOVE 2 NUTS
Fig. 11 Battery Holddown Bolts
1 - REMOVE 2 BOLTS
2 - BATTERY HOLDDOWN STRAP
8P - 8 SPEED CONTROLBR/BE
SPEED CONTROL SERVO (Continued)
Page 715 of 2889

(9) Using finger pressure only, disconnect end of
servo cable from throttle lever pin by pulling forward
on connector while holding lever rearward (Fig. 16).
DO NOT try to pull connector off perpendicular
to lever pin. Connector will be broken.
(10) Position battery tray up far enough for access
to speed control servo electrical connector and vac-
uum line.
(11) Disconnect electrical connector and vacuum
line at servo.
(12) Position battery tray with attached servo
assembly to gain access to 2 servo mounting nuts
(Fig. 18) or (Fig. 19).
(13) Remove 2 mounting nuts holding servo cable
sleeve to bracket (Fig. 19).
(14) Pull speed control cable sleeve and servo away
from servo mounting bracket to expose cable retain-
ing clip (Fig. 19) and remove clip. Note: The servo
mounting bracket displayed in (Fig. 19) is a typical
bracket and may/may not be applicable to this model
vehicle.
(15) Remove servo from mounting bracket. While
removing, note orientation of servo to bracket.
INSTALLATION
V-6/V-8 ENGINES
(1) Position servo to mounting bracket.
(2) Align hole in cable connector with hole in servo
pin. Install cable-to-servo retaining clip.
(3) Insert servo studs through holes in servo
mounting bracket.
(4) Insert servo studs through holes in servo cable
sleeve.
(5) Install servo mounting nuts and tighten to 8.5
N´m (75 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect vacuum line to servo.
(7) Connect electrical connector to servo terminals.
(8) Install three bolts retaining servo/servo mount-
ing bracket to battery tray.
(9) Connect servo cable to throttle body. Refer to
Servo Cable Removal/Installation in this group.
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(11) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
Fig. 16 Servo Cable at Throttle Lever
1 - PINCH (2) TABS
2 - CABLE MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - PINCH TABS (2)
4 - OFF
5 - THROTTLE CABLE
6 - THROTTLE LEVER
7 - THROTTLE LEVER PIN
8 - OFF
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
Fig. 17 Servo LocationÐRemoval/Installation
1 - BATTERY TRAY
2 - SERVO ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - SERVO BRACKET SCREWS (3)
8P - 10 SPEED CONTROLBR/BE
SPEED CONTROL SERVO (Continued)
Page 733 of 2889

REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disconnect the headlamp and dash wire har-
ness connector for the washer pump/motor from the
motor connector receptacle (Fig. 3).
(3) Disconnect the washer hose from the barbed
outlet nipple of the washer pump/motor and allow
the washer fluid to drain into a clean container for
reuse.
(4) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry the barbed inlet nipple of
the washer pump out of the rubber grommet seal in
the reservoir. Care must be taken not to damage the
reservoir.
(5) Remove the rubber grommet seal from the
washer pump mounting hole in the washer reservoir
and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new rubber grommet seal into the
washer pump mounting hole in the washer reservoir.
Always use a new rubber grommet seal on the reser-
voir.
(2) Position the barbed inlet nipple of the washer
pump to the rubber grommet seal in the reservoir.
(3) Press firmly and evenly on the washer pump
until the barbed inlet nipple is fully seated in the
rubber grommet seal in the washer reservoir mount-
ing hole.
(4) Reconnect the washer hose to the barbed outlet
nipple of the washer pump.(5) Reconnect the headlamp and dash wire harness
connector for the washer pump/motor unit to the
motor connector receptacle (Fig. 3).
(6) Refill the washer reservoir with the washer
fluid drained from the reservoir during the removal
procedure.
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
WASHER RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION
The molded plastic washer fluid reservoir is
secured with integral mounting tabs to keyed slots
on the left side of the radiator fan shroud in the left
front corner of the engine compartment. A bright yel-
low plastic filler cap with a rubber seal and an Inter-
national Control and Display Symbol icon for
ªWindshield Washerº and the text ªWasher Fluid
Onlyº molded into it snaps over the open end of the
filler neck. A bail strap that is integral to the cap
secures the cap to the reservoir filler neck when it is
removed for inspecting or adjusting the fluid level in
the reservoir. There are separate, dedicated holes on
the rear side of the reservoir provided for the mount-
ing of the washer/pump motor unit and the washer
fluid level switch.
The washer reservoir cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced. The washer
reservoir, the grommet seals for the washer pump/
motor unit and the washer fluid level switch, and the
filler cap are each available for service replacement.
OPERATION
The washer fluid reservoir provides a secure,
on-vehicle storage location for a large reserve of
washer fluid for operation of the washer system. The
washer reservoir filler neck provides a clearly
marked and readily accessible point from which to
add washer fluid to the reservoir. The washer/pump
motor unit is located in a sump area near the bottom
of the reservoir to be certain that washer fluid will
be available to the pump as the fluid level in the res-
ervoir becomes depleted. The washer fluid level
switch is mounted just above the sump area of the
reservoir so that there will be adequate warning to
the vehicle operator that the washer fluid level is
low, before the washer system will no longer operate.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Drain the engine cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAIN/
ALL EXCEPT DIESEL ENGINE) or (Refer to 7 -
Fig. 3 Washer Reservoir
1 - FAN SHROUD
2 - WASHER FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
3 - WASHER PUMP/MOTOR
4 - WASHER RESERVOIR
8R - 10 WIPERS/WASHERSBR/BE
WASHER PUMP/MOTOR (Continued)
Page 2788 of 2889

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................18AIR INJECTION..........................25
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS.................31
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL
Two different modules are used for powertrain con-
trol with the diesel engine. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) is used primarily for charging system,
transmission, A/C compressor clutch operation and
speed control functions. The Engine Control Module
(ECM) is used to control thefuel and emissions
systems.The PCM is located in the right/rear of
engine compartment (Fig. 1). The ECM is bolted to
the left side of the engine cylinder block (Fig. 2).
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connectthe DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Location
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
Fig. 2 Engine Control Module (ECM) Location
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - HEX HEADED BOLT
3 - FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
4 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
5 - 50±WAY CONNECTOR
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 1
Page 2789 of 2889

DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.
Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Relay Circuit Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Relay Circuit Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0106 Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0121 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Low Throttle position sensor input below the acceptable
voltage range.
P0122 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2790 of 2889
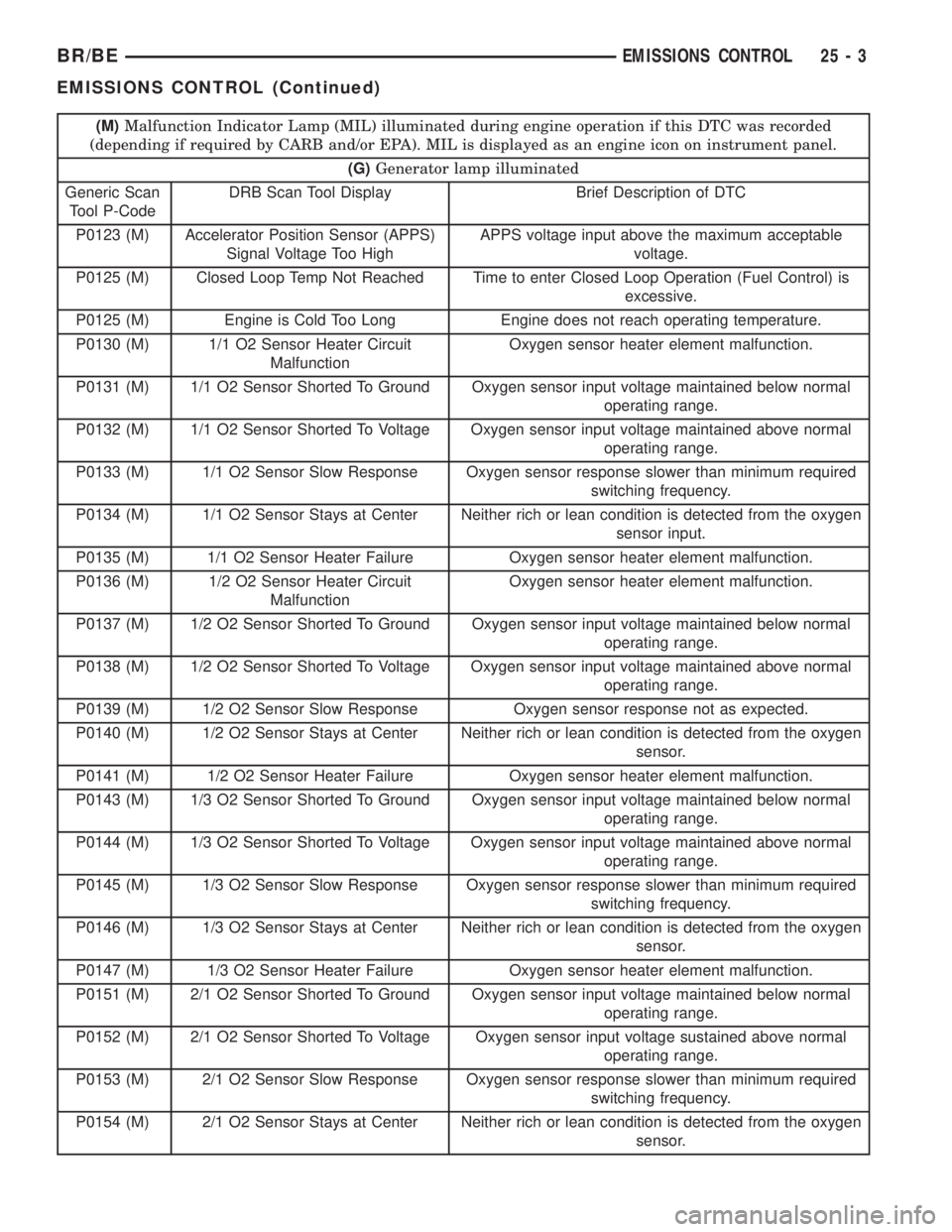
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0123 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too HighAPPS voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
P0125 (M) Closed Loop Temp Not Reached Time to enter Closed Loop Operation (Fuel Control) is
excessive.
P0125 (M) Engine is Cold Too Long Engine does not reach operating temperature.
P0130 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0131 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0132 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0133 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0134 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor input.
P0135 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0136 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0137 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0138 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0139 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response not as expected.
P0140 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0141 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0143 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0144 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0145 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0146 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0147 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0151 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0152 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage sustained above normal
operating range.
P0153 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0154 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2791 of 2889

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0155 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0157 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0158 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0159 2/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0160 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0161 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0168 Decreased Engine Performance Due
To High Injection Pump Fuel TempFuel temperature is above the engine protection limit.
Engine power will be derated.
P0171 (M) 1/1 Fuel System Lean A lean air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an
abnormally rich correction factor.
P0172 (M) 1/1 Fuel System Rich A rich air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an
abnormally lean correction factor.
P0174 (M) 2/1 Fuel System Lean A lean air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an
abnormally rich correction factor.
P0175 (M) 2/1 Fuel System Rich A rich air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an
abnormally lean correction factor.
P0176 Loss of Flex Fuel Calibration Signal No calibration voltage present from flex fuel sensor.
P0177 Water In Fuel Excess water found in fuel by water-in-fuel sensor.
P0178 Flex Fuel Sensor Volts Too Low Flex fuel sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0178 Water In Fuel Sensor Voltage Too
LowLoss of water-in-fuel circuit or sensor.
P0179 Flex Fuel Sensor Volts Too High Flex fuel sensor input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
P0181 Fuel Injection Pump Failure Low power, engine derated, or engine stops.
P0182 (M) CNG Temp Sensor Voltage Too Low Compressed natural gas temperature sensor voltage
below acceptable voltage.
P0183 (M) CNG Temp Sensor Voltage Too High Compressed natural gas temperature sensor voltage
above acceptable voltage.
P0201 (M) Injector #1 Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit for
injector #1 or the INJ 1 injector bank.
P0202 (M) Injector #2 Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit for
injector #2 or the INJ 2 injector bank.
P0203 (M) Injector #3 Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit for
injector #3 or the INJ 3 injector bank.
P0204 (M) Injector #4 Control Circuit Injector #4 or INJ 4 injector bank output driver stage does
not respond properly to the control signal.
P0205 (M) Injector #5 Control Circuit Injector #5 output driver stage does not respond properly
to the control signal.
25 - 4 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)