2001 DODGE RAM transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 2016 of 2889

(7) Remove front clutch thrust washer from sup-
port hub (Fig. 102).
OIL PUMP BUSHING REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove pump bushing with Tool Handle
C-4171 and Bushing Remover SP-3551 from Tool Set
C-3887-J (Fig. 103).
(2) Install new pump bushing with Tool Handle
C-4171 and Bushing Installer SP-5117 (Fig. 103).
Bushing should be flush with pump housing bore.
(3) Stake new pump bushing in two places with
blunt punch (Fig. 104). Remove burrs from stake
points with knife blade afterward.
REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT BUSHING REMOVAL
(1) Assemble Bushing Remover Tools SP-1191,
3633 and 5324 (Fig. 105). Do not clamp any part of
reaction shaft or support in vise.
(2) Hold Cup Tool SP-3633 firmly against reaction
shaft and thread remover SP-5324 into bushing as
far as possible by hand. Then thread remover tool 3-4
additional turns into bushing with a wrench.
(3) Turn remover tool hex nut down against
remover cup to pull bushing from shaft. Clean all
chips from shaft after bushing removal.
(4) Lightly grip old bushing in vise or with pliers
and back remover tool out of bushing.
(5) Assemble Bushing Installer Tools C-4171 and
SP-5325 (Fig. 105).
(6) Slide new bushing onto Installer Tool SP-5325.
(7) Position reaction shaft support upright on a
clean smooth surface.
(8) Align bushing in bore. Then tap bushing into
place until Bushing Installer SP-5325 bottoms.(9) Clean reaction shaft support thoroughly after
installing bushing.
CLEANING
Clean pump and support components with solvent
and dry them with compressed air.
Fig. 102 Support Hub Thrust Washer
1 - BUSHING
2 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - THRUST WASHER
4 - HUB
Fig. 103 Removing Oil Pump Bushing
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL SP-3551
3 - BUSHING
4 - SPECIAL TOOL SP-5117
5 - BUSHING
6 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
7 - PUMP HOUSING
Fig. 104 Staking Oil Pump Bushing
1 - NARROW BLADE
2 - BLUNT PUNCH
3 - TWO STAKES
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44RE 21 - 381
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2017 of 2889
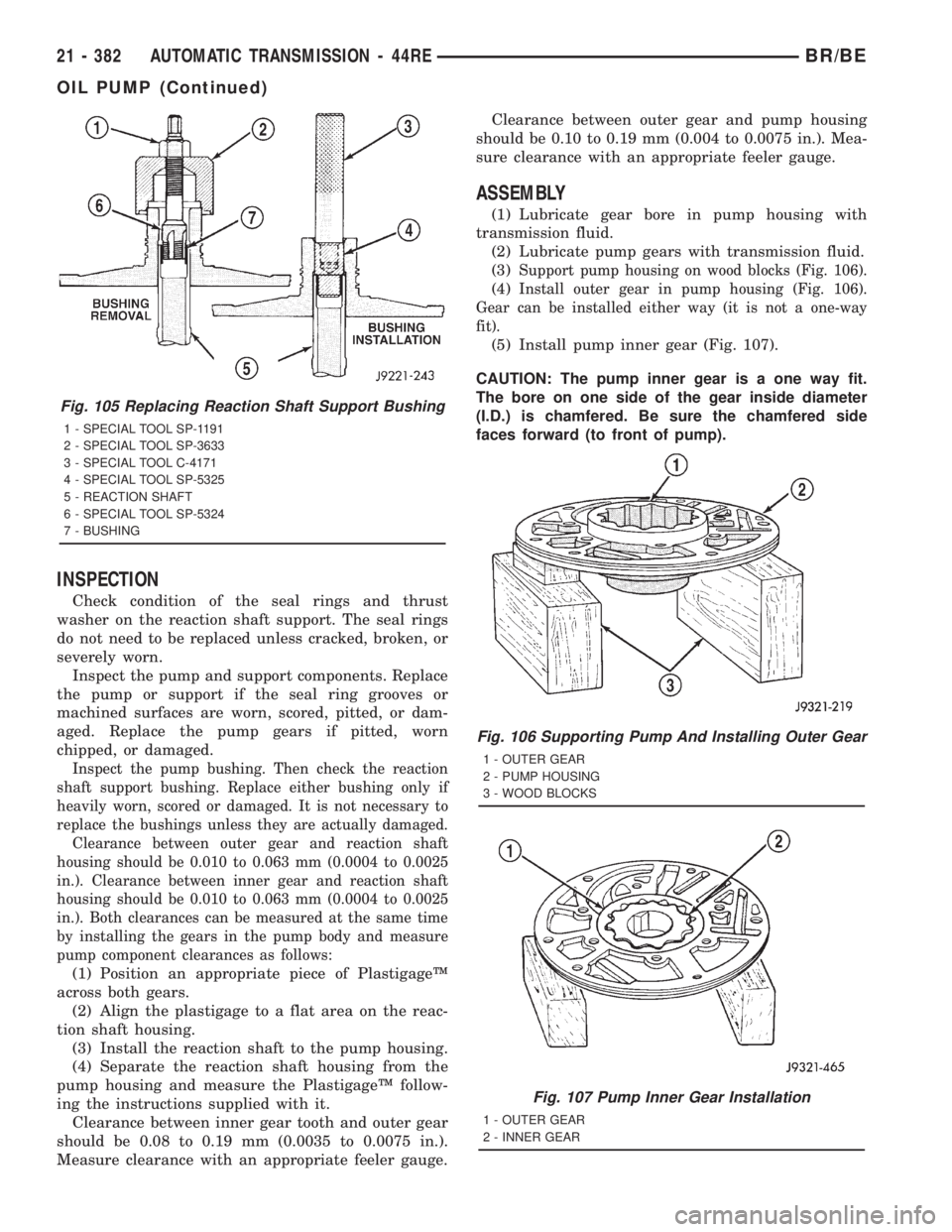
INSPECTION
Check condition of the seal rings and thrust
washer on the reaction shaft support. The seal rings
do not need to be replaced unless cracked, broken, or
severely worn.
Inspect the pump and support components. Replace
the pump or support if the seal ring grooves or
machined surfaces are worn, scored, pitted, or dam-
aged. Replace the pump gears if pitted, worn
chipped, or damaged.
Inspect the pump bushing. Then check the reaction
shaft support bushing. Replace either bushing only if
heavily worn, scored or damaged. It is not necessary to
replace the bushings unless they are actually damaged.
Clearance between outer gear and reaction shaft
housing should be 0.010 to 0.063 mm (0.0004 to 0.0025
in.). Clearance between inner gear and reaction shaft
housing should be 0.010 to 0.063 mm (0.0004 to 0.0025
in.). Both clearances can be measured at the same time
by installing the gears in the pump body and measure
pump component clearances as follows:
(1) Position an appropriate piece of PlastigageŸ
across both gears.
(2) Align the plastigage to a flat area on the reac-
tion shaft housing.
(3) Install the reaction shaft to the pump housing.
(4) Separate the reaction shaft housing from the
pump housing and measure the PlastigageŸ follow-
ing the instructions supplied with it.
Clearance between inner gear tooth and outer gear
should be 0.08 to 0.19 mm (0.0035 to 0.0075 in.).
Measure clearance with an appropriate feeler gauge.Clearance between outer gear and pump housing
should be 0.10 to 0.19 mm (0.004 to 0.0075 in.). Mea-
sure clearance with an appropriate feeler gauge.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate gear bore in pump housing with
transmission fluid.
(2) Lubricate pump gears with transmission fluid.
(3)
Support pump housing on wood blocks (Fig. 106).
(4)Install outer gear in pump housing (Fig. 106).
Gear can be installed either way (it is not a one-way
fit).
(5) Install pump inner gear (Fig. 107).
CAUTION: The pump inner gear is a one way fit.
The bore on one side of the gear inside diameter
(I.D.) is chamfered. Be sure the chamfered side
faces forward (to front of pump).
Fig. 105 Replacing Reaction Shaft Support Bushing
1 - SPECIAL TOOL SP-1191
2 - SPECIAL TOOL SP-3633
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
4 - SPECIAL TOOL SP-5325
5 - REACTION SHAFT
6 - SPECIAL TOOL SP-5324
7 - BUSHING
Fig. 106 Supporting Pump And Installing Outer Gear
1 - OUTER GEAR
2 - PUMP HOUSING
3 - WOOD BLOCKS
Fig. 107 Pump Inner Gear Installation
1 - OUTER GEAR
2 - INNER GEAR
21 - 382 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44REBR/BE
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2018 of 2889

(6) Install new thrust washer on hub of reaction
shaft support. Lubricate washer with transmission
fluid or petroleum jelly.
(7) If reaction shaft seal rings are being replaced,
install new seal rings on support hub (Fig. 108).
Lubricate seal rings with transmission fluid or petro-
leum jelly after installation. Squeeze each ring until
ring ends are securely hooked together.
CAUTION: The reaction shaft support seal rings will
break if overspread, or twisted. If new rings are
being installed, spread them only enough for instal-
lation. Also be very sure the ring ends are securely
hooked together after installation. Otherwise, the
rings will either prevent pump installation, or break
during installation.
(8) Install reaction shaft support on pump housing
(Fig. 109).
(9) Align reaction support on pump housing. Use
alignment marks made at disassembly. Or, rotate
support until bolt holes in support and pump housing
are all aligned (holes are offset for one-way fit).(10) Install all bolts that attach support to pump
housing. Then tighten bolts finger tight.
(11) Tighten support-to-pump bolts to required
torque as follows:
(a) Reverse pump assembly and install it in
transmission case. Position pump so bolts are fac-
ing out and are accessible.
(b) Secure pump assembly in case with 2 or 3
bolts, or with pilot studs.
(c) Tighten support-to-pump bolts to 20 N´m (15
ft. lbs.).
(d) Remove pump assembly from transmission
case.
(12) Install new oil seal in pump with Special Tool
C-4193 and Tool Handle C-4171 (Fig. 110). Be sure
seal lip faces inward.
(13) Install new seal ring around pump housing.
Be sure seal is properly seated in groove.
(14) Lubricate lip of pump oil seal and O-ring seal
with transmission fluid.
Fig. 108 Hub Seal Ring Position
1 - SEAL RINGS
2 - SUPPORT HUB
Fig. 109 Assembling Reaction Shaft Support And
Pump Housing
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
Fig. 110 Pump Oil Seal Installation
1 - PUMP BODY
2 - PUMP SEAL
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4193
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44RE 21 - 383
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2020 of 2889

OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive clutch (Fig. 113) is composed of the
pressure plate, clutch plates, holding discs, overdrive
piston retainer, piston, piston spacer, and snap-rings.
The overdrive clutch is the forwardmost component
in the transmission overdrive unit and is considered
a holding component. The overdrive piston retainer,
piston, and piston spacer are located on the rear of
the main transmission case.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between the
piston retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is pro-
vided by the oil pump, transferred through the control
valves and passageways, and enters the clutch through
passages at the lower rear portion of the valve body
area. With pressure applied between the piston retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the piston
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This action
applies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow through
the intermediate shaft into the overdrive planetary gear
set. The overdrive clutch discs are attached to the over-
drive clutch hub while the overdrive clutch plates, reac-
tion plate, and pressure plate are lugged to the
overdrive housing. This allows the intermediate shaft totransfer the engine torque to the planetary gear and
overrunning clutch. This drives the planetary gear
inside the annulus, which is attached to the overdrive
clutch drum and output shaft, creating the desired gear
ratio. The waved snap-ring is used to cushion the appli-
cation of the clutch pack.
OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive OFF (control) switch is located in
the shift lever arm (Fig. 114). The switch is a
momentary contact device that signals the PCM to
toggle current status of the overdrive function.
OPERATION
At key-on, overdrive operation is allowed. Pressing
the switch once causes the overdrive OFF mode to be
entered and the overdrive OFF switch lamp to be illu-
minated. Pressing the switch a second time causes nor-
mal overdrive operation to be restored and the overdrive
lamp to be turned off. The overdrive OFF mode defaults
to ON after the ignition switch is cycled OFF and ON.
The normal position for the control switch is the ON
position. The switch must be in this position to energize
the solenoid and allow a 3-4 upshift. The control switch
indicator light illuminates only when the overdrive
switch is turned to the OFF position, or when illumi-
nated by the transmission control module.
Fig. 113 Overdrive Clutch
1 - REACTION PLATE 2 - PRESSURE PLATE
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44RE 21 - 385
Page 2022 of 2889
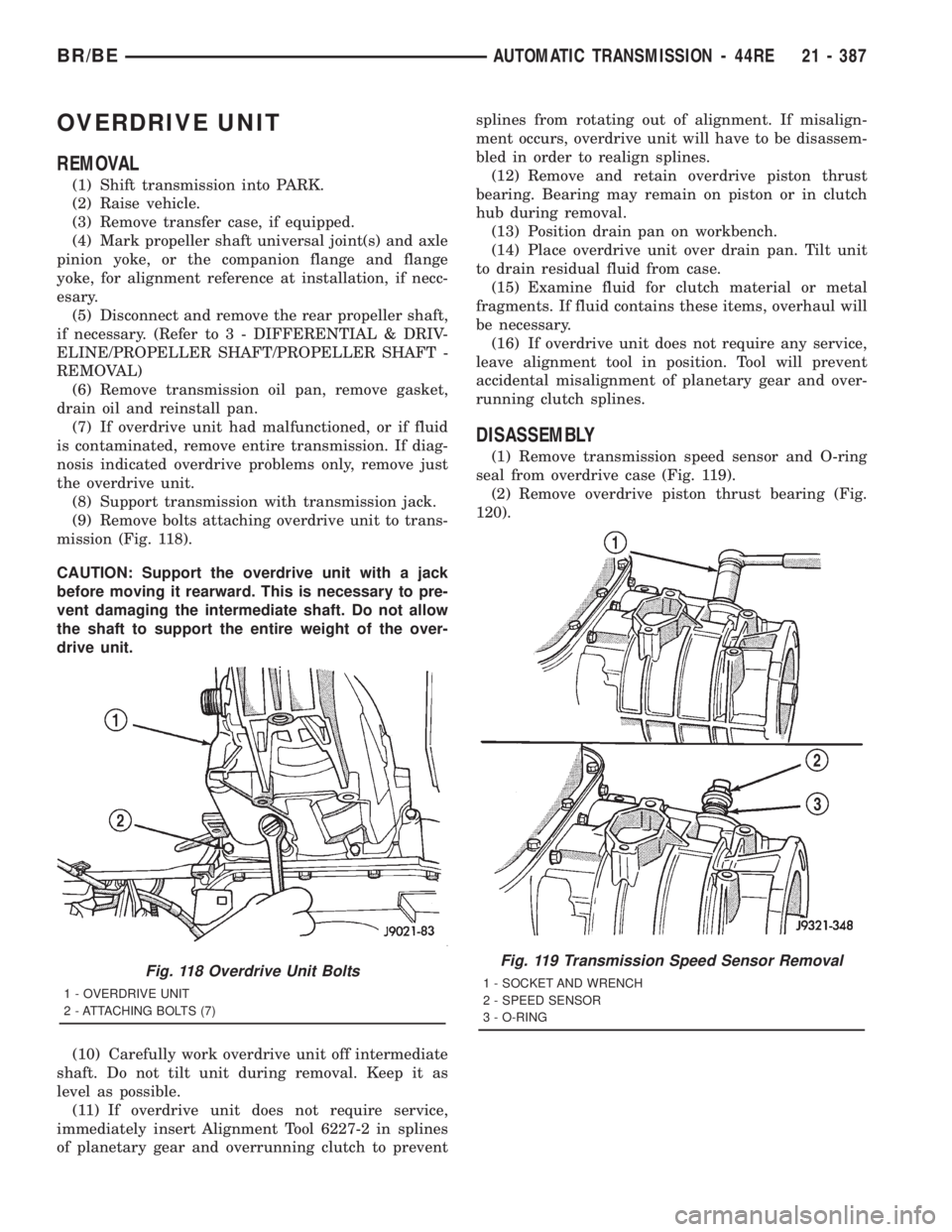
OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove transfer case, if equipped.
(4) Mark propeller shaft universal joint(s) and axle
pinion yoke, or the companion flange and flange
yoke, for alignment reference at installation, if necc-
esary.
(5) Disconnect and remove the rear propeller shaft,
if necessary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(6) Remove transmission oil pan, remove gasket,
drain oil and reinstall pan.
(7) If overdrive unit had malfunctioned, or if fluid
is contaminated, remove entire transmission. If diag-
nosis indicated overdrive problems only, remove just
the overdrive unit.
(8) Support transmission with transmission jack.
(9) Remove bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission (Fig. 118).
CAUTION: Support the overdrive unit with a jack
before moving it rearward. This is necessary to pre-
vent damaging the intermediate shaft. Do not allow
the shaft to support the entire weight of the over-
drive unit.
(10) Carefully work overdrive unit off intermediate
shaft. Do not tilt unit during removal. Keep it as
level as possible.
(11) If overdrive unit does not require service,
immediately insert Alignment Tool 6227-2 in splines
of planetary gear and overrunning clutch to preventsplines from rotating out of alignment. If misalign-
ment occurs, overdrive unit will have to be disassem-
bled in order to realign splines.
(12) Remove and retain overdrive piston thrust
bearing. Bearing may remain on piston or in clutch
hub during removal.
(13) Position drain pan on workbench.
(14) Place overdrive unit over drain pan. Tilt unit
to drain residual fluid from case.
(15) Examine fluid for clutch material or metal
fragments. If fluid contains these items, overhaul will
be necessary.
(16) If overdrive unit does not require any service,
leave alignment tool in position. Tool will prevent
accidental misalignment of planetary gear and over-
running clutch splines.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove transmission speed sensor and O-ring
seal from overdrive case (Fig. 119).
(2) Remove overdrive piston thrust bearing (Fig.
120).
Fig. 118 Overdrive Unit Bolts
1 - OVERDRIVE UNIT
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS (7)
Fig. 119 Transmission Speed Sensor Removal
1 - SOCKET AND WRENCH
2 - SPEED SENSOR
3 - O-RING
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44RE 21 - 387
Page 2052 of 2889

REAR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The rear clutch assembly (Fig. 213) is composed of
the rear clutch retainer, pressure plate, clutch plates,
driving discs, piston, Belleville spring, and snap-
rings. The Belleville spring acts as a lever to multi-
ply the force applied on to it by the apply piston. The
increased apply force on the rear clutch pack, in com-
parison to the front clutch pack, is needed to hold
against the greater torque load imposed onto the rear
pack. The rear clutch is directly behind the front
clutch and is considered a driving component.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This action
applies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved spring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack.
The snap-ring is selective and used to adjust clutch
pack clearance.
Fig. 213 Rear Clutch
1 - PISTON SPRING 10 - TOP PRESSURE PLATE
2 - REAR CLUTCH PISTON 11 - CLUTCH DISCS (4)
3 - CLUTCH PISTON SEALS 12 - BOTTOM PRESSURE PLATE
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT THRUST WASHER (METAL) 13 - WAVE SPRING
5 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING 14 - CLUTCH PLATES (3)
6 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER 15 - RETAINER SEAL RING
7 - INPUT SHAFT 16 - SHAFT REAR SEAL RING (PLASTIC)
8 - REAR CLUTCH THRUST WASHER (FIBER) 17 - SHAFT FRONT SEAL RING (TEFLON)
9 - CLUTCH PACK SNAP-RING (SELECTIVE)
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44RE 21 - 417
Page 2058 of 2889

ADJUSTMENT
Check linkage adjustment by starting engine in
PARK and NEUTRAL. Adjustment is acceptable if
the engine starts in only these two positions. Adjust-
ment is incorrect if the engine starts in one position
but not both positions
If the engine starts in any other position, or if the
engine will not start in any position, the park/neutral
switch is probably faulty.
LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
Check condition of the shift linkage (Fig. 225). Do
not attempt adjustment if any component is loose,
worn, or bent. Replace any suspect components.
Replace the grommet securing the shift rod or
torque rod in place if either rod was removed from
the grommet. Remove the old grommet as necessary
and use suitable pliers to install the new grommet.
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Loosen lock bolt in front shift rod adjusting
swivel (Fig. 225).
(4) Ensure that the shift rod slides freely in the
swivel. Lube rod and swivel as necessary.
(5) Move transmission shift lever fully rearward to
the Park detent.
(6) Center adjusting swivel on shift rod.
(7) Tighten swivel lock bolt to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(8) Lower vehicle and verify proper adjustment.
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
²Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
²Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
Fig. 225 Linkage Adjustment Components
1 - FRONT SHIFT ROD
2 - TORQUE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - TORQUE SHAFT ARM
4 - ADJUSTING SWIVEL
5 - LOCK BOLT
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44RE 21 - 423
SHIFT MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 2059 of 2889

where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The speed sensor (Fig. 226) is located in the over-
drive gear case. The sensor is positioned over the
park gear and monitors transmission output shaft
rotating speed.
OPERATION
Speed sensor signals are triggered by the park
gear lugs as they rotate past the sensor pickup face.
Input signals from the sensor are sent to the trans-
mission control module for processing. Signals from
this sensor are shared with the powertrain control
module.
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Transmission throttle valve cable (Fig. 227) adjust-
ment is extremely important to proper operation.
This adjustment positions the throttle valve, which
controls shift speed, quality, and part-throttle down-
shift sensitivity.
If cable setting is too loose, early shifts and slip-
page between shifts may occur. If the setting is too
tight, shifts may be delayed and part throttle down-
shifts may be very sensitive.
The transmission throttle valve is operated by a
cam on the throttle lever. The throttle lever is oper-
ated by an adjustable cable (Fig. 228). The cable is
attached to an arm mounted on the throttle lever
shaft. A retaining clip at the engine-end of the cable
is removed to provide for cable adjustment. The
retaining clip is then installed back onto the throttle
valve cable to lock in the adjustment.
Fig. 226 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED SENSOR
2 - SEAL
Fig. 227 Throttle Valve Cable Attachment - At
Engine
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - CABLE BRACKET
3 - THROTTLE BODY LEVER
4 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
5 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
21 - 424 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 44REBR/BE
SOLENOID (Continued)