2001 DODGE RAM length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 432 of 2889

There should now be battery voltage. If OK, repair
the open amplified speaker (+) circuits to the speak-
er-mounted amplifiers as required. If not OK, replace
the faulty filter, choke and speaker relay unit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Reach under the driver side of the instrument
panel near the 16-way data link connector and
inboard of the ash receiver to access the filter, choke,
and speaker relay (Fig. 6) .
(3) Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the filter, choke and speaker relay
wire harness connector.
(4) Remove the two screws that secure the filter,
choke, and speaker relay mounting bracket to the
instrument panel center brace.
(5) Remove the filter, choke, and speaker relay
unit from under the instrument panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the filter, choke, and speaker relay
unit under the instrument panel.(2) Install and tighten the two screws that secure
the filter, choke, and speaker relay mounting bracket
to the instrument panel center brace. Tighten the
screws to 2.7 N´m (24 in. lbs.).
(3) Reconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector to the filter, choke and speaker relay wire
harness connector.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
INSTRUMENT PANEL
ANTENNA CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Reach under the passenger side of the instru-
ment panel near the right cowl side inner panel to
disengage the coaxial cable connector from the
retainer clip located on the bottom of the heater-A/C
housing .
(3) Remove the foam tape to access the coaxial
cable connector. Disconnect the connector by pulling
it apart while twisting the metal connector halves.
Do not pull on the cable.
(4) Securely tie a suitable length of cord or twine
to the instrument panel half of the antenna coaxial
cable connector. This cord will be used to pull or
ªfishº the cable back into position during installation.
(5) Roll down the glove box from the instrument
panel. Refer to Body, Instrument Panel for the proce-
dures.
(6) Reach through the glove box opening to disen-
gage the antenna cable from the retainer clips on the
back of the instrument panel (Fig. 7).
Fig. 6 Filter, Choke, and Speaker Relay Remove/
Install
1 - ASH RECEIVER HOUSING
2 - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
3 - CENTER BRACE
4 - SCREW
5 - CHOKE AND RELAY
6 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
Fig. 7 ANTENNA CABLE ROUTING
1 - RETAINER CLIPS
2 - TO RADIO
3 - TO ANTENNA
BR/BEAUDIO 8A - 9
RADIO CHOKE RELAY (Continued)
Page 459 of 2889

Once a message is broadcast over the CCD data
bus, all electronic control modules on the data bus
have the ability to receive it through their CCD chip.
Reception of CCD messages is also carried out by the
transceiver in the CCD chip. The transceiver moni-
tors the voltage on the data bus for any fluctuations.
When data bus voltage fluctuations are detected,
they are interpreted by the transceiver as binary
messages and sent to the electronic control module's
microprocessor.
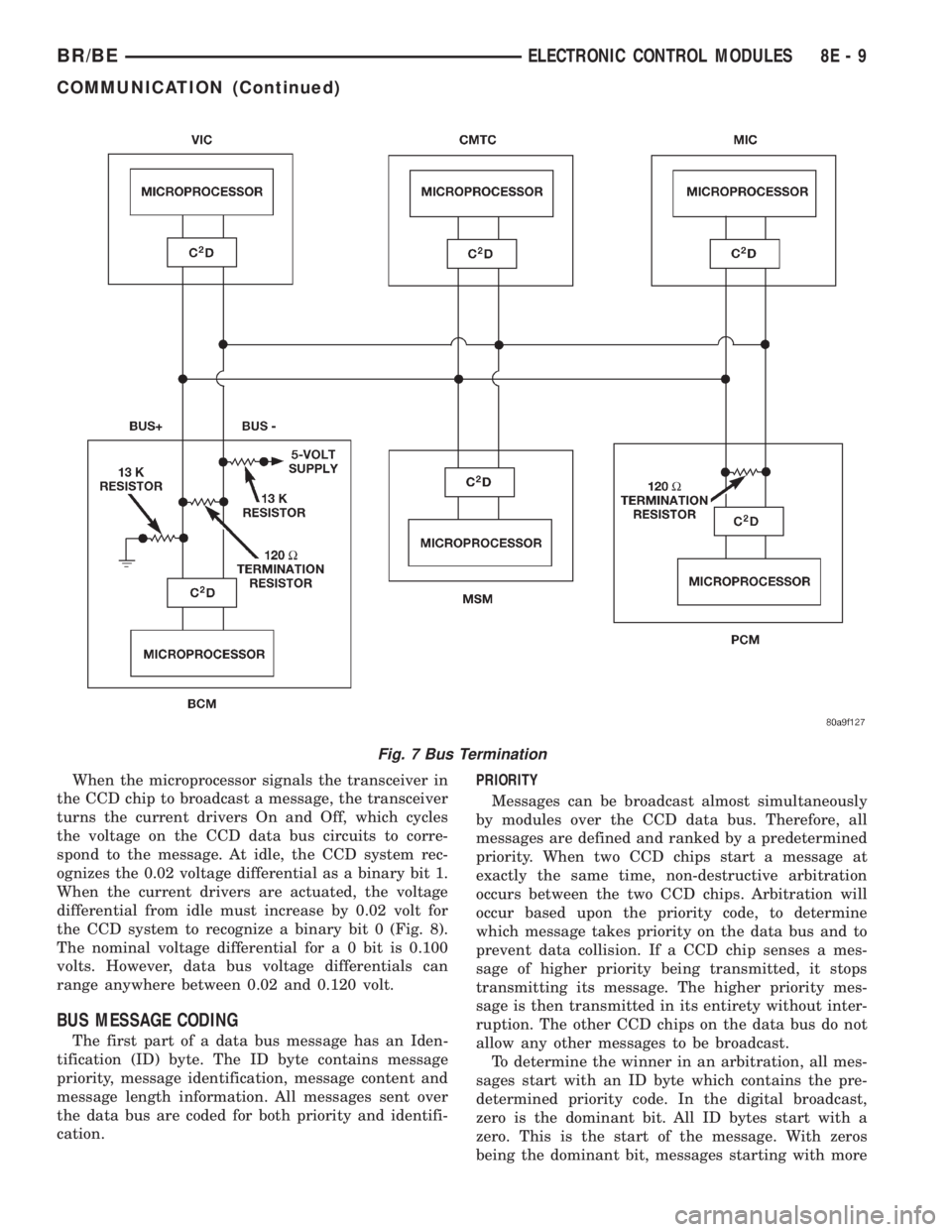
BUS BIAS AND TERMINATION
The voltage network used by the CCD data bus to
transmit messages requires both bias and termina-
tion. At least one electronic control module on the
data bus must provide a voltage source for the CCD
data bus network known as bus bias, and there must
be at least one bus termination point for the data bus
circuit to be complete. However, while bias and ter-
mination are both required for data bus operation,
they both do not have to be within the same elec-
tronic control module. The CCD data bus is biased to
approximately 2.5 volts. With each of the electronic
control modules wired in parallel to the data bus, all
modules utilize the same bus bias. Therefore, based
upon vehicle options, the data bus can accommodate
two or twenty electronic control modules without
affecting bus voltage.
The power supplied to the data bus is known as
bus biasing. Bus bias is provided through a series cir-
cuit. To properly bias the data bus circuits, a 5 volt
supply is provided through a 13 kilohm resistor to
the Bus (±) circuit (Fig. 6). Voltage from the Bus (±)
circuit flows through a 120 ohm termination resistor
to the Bus (+) circuit. The Bus (+) circuit is grounded
through another 13 kilohm resistor. While at least
one termination resistor is required for the system to
operate, most Chrysler systems use two. The second
termination resistor serves as a backup (Fig. 7). The
termination resistor provides a path for the bus bias
voltage. Without a termination point, voltage biasing
would not occur. Voltage would go to 5 volts on one
bus wire and 0 volts on the other bus wire.
The voltage drop through the termination resistor
creates 2.51 volts on Bus (±), and 2.49 volts on Bus
(+). The voltage difference between the two circuits is
0.02 volts. When the data bus voltage differential is a
steady 0.02 volts, the CCD system is considered
ªidle.º When no input is received from any module
and the ignition switch is in the Off position for a
pre-programmed length of time, the bus data
becomes inactive or enters the ºsleep mode.º Elec-
tronic control modules that provide bus bias can be
programmed to ºwake upº the data bus and becomeactive upon receiving any predetermined input or
when the ignition switch is turned to the On posi-
tion.
BUS MESSAGING
The electronic control modules used in the CCD
data bus system contain microprocessors. Digital sig-
nals are the means by which microprocessors operate
internally and communicate messages to other micro-
processors. Digital signals are limited to two states,
voltage high or voltage low, corresponding to either a
one or a zero. Unlike conventional binary code, the
CCD data bus systems translate a small voltage dif-
ference as a one (1), and a larger voltage difference
as a zero (0). The use of the 0 and 1 is referred to as
binary coding. Each binary number is called a bit,
and eight bits make up a byte. For example:
01011101 represents a message. The controllers in
the multiplex system are able to send thousands of
these bytes strung together to communicate a variety
of messages. Through the use of binary data trans-
mission, all electronic control modules on the data
bus can communicate with each other.
The microprocessors in the CCD data bus system
translate the binary messages into Hexadecimal
Code (or Hex Code). Hex code is the means by which
microprocessors communicate and interpret mes-
sages. When fault codes are received by the DRBIIIt
scan tool, they are translated into text for display on
the DRBIIItscreen. Although not displayed by the
DRBIIItfor Body Systems, hex codes are shown by
the DRBIIItfor Engine System faults.
Fig. 6 Bus Biasing
8E - 8 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESBR/BE
COMMUNICATION (Continued)
Page 460 of 2889
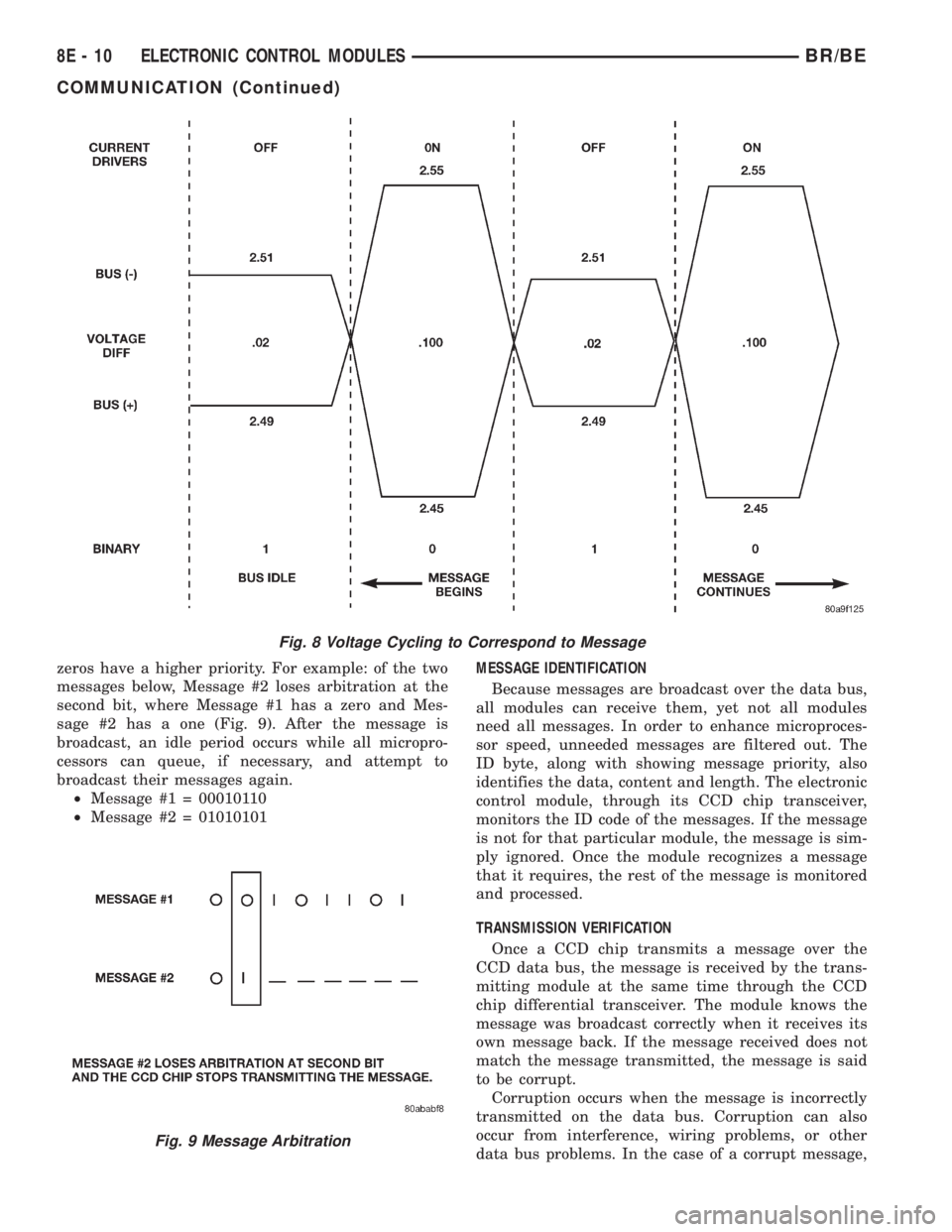
When the microprocessor signals the transceiver in
the CCD chip to broadcast a message, the transceiver
turns the current drivers On and Off, which cycles
the voltage on the CCD data bus circuits to corre-
spond to the message. At idle, the CCD system rec-
ognizes the 0.02 voltage differential as a binary bit 1.
When the current drivers are actuated, the voltage
differential from idle must increase by 0.02 volt for
the CCD system to recognize a binary bit 0 (Fig. 8).
The nominal voltage differential for a 0 bit is 0.100
volts. However, data bus voltage differentials can
range anywhere between 0.02 and 0.120 volt.
BUS MESSAGE CODING
The first part of a data bus message has an Iden-
tification (ID) byte. The ID byte contains message
priority, message identification, message content and
message length information. All messages sent over
the data bus are coded for both priority and identifi-
cation.PRIORITY
Messages can be broadcast almost simultaneously
by modules over the CCD data bus. Therefore, all
messages are defined and ranked by a predetermined
priority. When two CCD chips start a message at
exactly the same time, non-destructive arbitration
occurs between the two CCD chips. Arbitration will
occur based upon the priority code, to determine
which message takes priority on the data bus and to
prevent data collision. If a CCD chip senses a mes-
sage of higher priority being transmitted, it stops
transmitting its message. The higher priority mes-
sage is then transmitted in its entirety without inter-
ruption. The other CCD chips on the data bus do not
allow any other messages to be broadcast.
To determine the winner in an arbitration, all mes-
sages start with an ID byte which contains the pre-
determined priority code. In the digital broadcast,
zero is the dominant bit. All ID bytes start with a
zero. This is the start of the message. With zeros
being the dominant bit, messages starting with more
Fig. 7 Bus Termination
BR/BEELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 9
COMMUNICATION (Continued)
Page 461 of 2889
zeros have a higher priority. For example: of the two
messages below, Message #2 loses arbitration at the
second bit, where Message #1 has a zero and Mes-
sage #2 has a one (Fig. 9). After the message is
broadcast, an idle period occurs while all micropro-
cessors can queue, if necessary, and attempt to
broadcast their messages again.
²Message #1 = 00010110
²Message #2 = 01010101MESSAGE IDENTIFICATION
Because messages are broadcast over the data bus,
all modules can receive them, yet not all modules
need all messages. In order to enhance microproces-
sor speed, unneeded messages are filtered out. The
ID byte, along with showing message priority, also
identifies the data, content and length. The electronic
control module, through its CCD chip transceiver,
monitors the ID code of the messages. If the message
is not for that particular module, the message is sim-
ply ignored. Once the module recognizes a message
that it requires, the rest of the message is monitored
and processed.
TRANSMISSION VERIFICATION
Once a CCD chip transmits a message over the
CCD data bus, the message is received by the trans-
mitting module at the same time through the CCD
chip differential transceiver. The module knows the
message was broadcast correctly when it receives its
own message back. If the message received does not
match the message transmitted, the message is said
to be corrupt.
Corruption occurs when the message is incorrectly
transmitted on the data bus. Corruption can also
occur from interference, wiring problems, or other
data bus problems. In the case of a corrupt message,
Fig. 8 Voltage Cycling to Correspond to Message
Fig. 9 Message Arbitration
8E - 10 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESBR/BE
COMMUNICATION (Continued)
Page 519 of 2889

(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the 3-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the heated mirror switch from
the heated mirror switch connector receptacle on the
back of the a/c heater control. Check for continuity
between the ground circuit cavity of the wire harness
connector and a good ground. There should be conti-
nuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit to ground as required.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Check for battery
voltage at the fused ignition switch output (run/start)
circuit cavity of the 3-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the heated mirror switch. If
OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the open fused
ignition switch output (run/start) circuit to the fuse
in the JB as required.
(5) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Reconnect the 3-way instrument panel wire harness
connector for the heated mirror switch to the heated
mirror switch connector receptacle on the back of the
a/c heater control. Reconnect the battery negative
cable. Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Depress and release the heated mirror switch. The
amber heated mirror system indicator lamp next to
the heated mirror switch button should light. If OK,
go to Step 6. If not OK, replace the faulty a/c heater
control.
(6) Back probe the fused heated mirror relay out-
put circuit cavity of the 3-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the heated mirror switch on
the back of the a/c heater control and check for volt-
age (battery voltage less the resistance in both out-
side mirror heating grids). If OK, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/HEATED MIRRORS/HEATED MIR-
ROR GRID - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
HEATED MIRROR GRID
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the optional heated mirror
system have an electrically operated heating grid
located behind the mirror glass of each power oper-
ated outside rear view mirror. The outside mirror
heating grid consists of two thin laminations of plas-
tic that approximate the outer dimensions and shape
of the mirror glass. A single length of resistor wire
weaves in a back and forth pattern between, and is
held in place by the two thin laminations of plastic.
The two ends of the resistor wire terminate near the
inboard edge of the grid, where they are soldered to
the ground feed and battery current feed wires con-
tained in the power mirror wire harness. The heating
grid is then sandwiched between the back of themolded plastic mirror glass case and the mirror
glass, where it remains in direct contact with the
back of the mirror glass at all times.
The outside mirror heating grids cannot be
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the entire outside
power mirror unit must be replaced. Refer to Power
Mirrors for the service procedures.
OPERATION
One end of the outside mirror heating grid resistor
wire is connected to a ground feed at all times
through a body ground screw located inside the left
rear corner of the truck cab. Battery current is
directed to the other end of the outside mirror heat-
ing grid resistor wire by the energized heated mirror
relay when the heated mirror switch is in the On
position. As electrical current passes through the
heating grid, the resistance of the wire in the heating
grid converts some of that electrical current into
heat. The heat produced by the heating grid is then
conducted through the back of the mirror glass to
help keep the glass clear of ice, snow or fog.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED MIRROR
GRID
For circuit descriptions and diagrams (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the door wire harness connector
from the power mirror wire harness connector at the
power mirror with the inoperative heating grid.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit cav-
ity in the door wire harness connector for the power
mirror and a good ground. If OK, go to Step 2. If not
OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground as
required.
(2) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Turn on the
heated mirror system. Check for voltage (battery
voltage less the resistance in the outside mirror heat-
ing grid that is still connected) at the fused heated
mirror relay output circuit cavity in the door wire
harness connector for the power mirror. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, repair the open fused heated mir-
ror relay output circuit to the heater and air condi-
tioner control unit as required.
(3) Check the outside mirror heating grid by test-
ing for continuity between the ground circuit and the
fused heated mirror relay output circuit cavities in
the power mirror wire harness connector. There
should be continuity. If not OK, replace the faulty
power mirror. If OK, check the resistance through
the outside mirror heating grid. The correct resis-
tance should be from 10 to 16 ohms when measured
at an ambient temperature of 21É C (70É F). If not
OK, replace the faulty power mirror.
8G - 4 HEATED MIRRORSBR/BE
MIRROR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 525 of 2889

(3) Reconnect the two instrument panel wire har-
ness connectors to the connector receptacles on the
backs of the heated seat switches.
(4) Position the heated seat switch bezel and both
switches in the instrument panel mounting hole as a
unit.
(5) Install and tighten the three screws that secure
the heated seat switch bezel to the instrument panel.
Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the cluster bezel onto the instrument
panel. Refer toCluster Bezelin the index of this
service manual for the location of the proper cluster
bezel installation procedures.
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
HEATED SEAT ELEMENT
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the optional heated seat
system have two sets of electrically operated heating
element grids located in each outboard seating posi-
tion of the front seat, one set for the seat cushion
and the other set for the seat back. Each of the
heated seat element grids consists of a single length
of resistor wire that is routed in a zigzag pattern and
captured between the leather trim cover and the
foam rubber backing on the underside of its respec-
tive seat cushion trim cover and seat back trim cover
assembly. Short pigtail wires with connectors (Fig. 5)
are soldered to each end of each resistor wire ele-
ment grid, which connect all of the element grids foreach seating position to each other in series with the
heated seat module through the seat wire harness.
One temperature sensor is used for each outboard
seating position of the front seat, and it is located in
the center insert area of the seat cushion cover. The
heated seat sensors and their pigtail wires are also
captured between the leather trim cover and the
foam rubber backing on the underside of their
respective seat cushion trim cover assemblies. The
heated seat sensors are Negative Thermal Coefficient
(NTC) thermistors. The sensors for both front seats
receive a voltage feed from a single output of the
heated seat module, but the module receives individ-
ual sensor inputs from the driver side and passenger
side sensors.
The heated seat elements and sensors cannot be
repaired. If damaged or faulty, the front seat cushion
trim cover or front seat back trim cover assembly
must be replaced. Refer toFront Seat Cushion
Cover - Quad CaborFront Seat Back Cover -
Quad Cabin the index of this service manual for
the location of the proper front seat trim cover
removal and installation procedures.
OPERATION
One end of the heated seat element resistor wire is
connected to a ground feed at all times through a
splice in the heated seat module ground circuit. Bat-
tery current is directed to the other end of the heated
seat element resistor wire by the energized N-chan-
nel Field Effect Transistor (N-FET) located within
the heated seat module. The heated seat module will
energize the N-FET only when the heated seat
switch is in the Low or High position and the heated
seat sensor indicates that the seat cushion surface
temperature is below the selected (Low or High) tem-
perature set point. As electrical current passes
through the heating element grid, the resistance of
the wire used in the element disperses some of that
electrical current in the form of heat. The heat pro-
duced by the heated seat element grid then radiates
through the underside of the seat cushion and seat
back trim covers, warming the seat cover and its
occupant.
The resistance of the heated seat sensor increases
and decreases as the surface temperature of the seat
cushion cover changes. The heated seat module sup-
plies each sensor with a voltage feed, then detects
the sensor resistance by monitoring the voltage of the
separate sensor return circuits. The heated seat mod-
ule compares the heated seat sensor resistance (seat
cushion surface temperature) with the heated seat
switch resistance (Low or High set point) to deter-
mine when the heated seat element grids need to be
cycled on or off in order to maintain the selected tem-
perature set point.
Fig. 5 Heated Seat Cushion Trim Cover
1 - TO SEAT BACK COVER
2 - TO SEAT WIRE HARNESS
3 - FOAM PADDING
4 - HEATED SEAT CUSHION TRIM COVER
5 - TO ELEMENT GRIDS
6 - TO ELEMENT GRIDS AND SENSOR
8G - 10 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMBR/BE
DRIVER SEAT HEATER SWITCH (Continued)
Page 555 of 2889

CHIPPED ELECTRODE INSULATOR
A chipped electrode insulator usually results from
bending the center electrode while adjusting the
spark plug electrode gap. Under certain conditions,
severe detonation can also separate the insulator
from the center electrode (Fig. 33). Spark plugs with
this condition must be replaced.
PREIGNITION DAMAGE
Preignition damage is usually caused by excessive
combustion chamber temperature. The center elec-
trode dissolves first and the ground electrode dis-
solves somewhat latter (Fig. 34). Insulators appear
relatively deposit free. Determine if the spark plug
has the correct heat range rating for the engine.
Determine if ignition timing is over advanced or if
other operating conditions are causing engine over-
heating. (The heat range rating refers to the operat-
ing temperature of a particular type spark plug.
Spark plugs are designed to operate within specific
temperature ranges. This depends upon the thick-
ness and length of the center electrodes porcelain
insulator.)
SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING
Overheating is indicated by a white or gray center
electrode insulator that also appears blistered (Fig.
35). The increase in electrode gap will be consider-
ably in excess of 0.001 inch per 2000 miles of opera-
tion. This suggests that a plug with a cooler heat
range rating should be used. Over advanced ignition
timing, detonation and cooling system malfunctions
can also cause spark plug overheating.
REMOVAL
On 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L engines, spark plug cable heat
shields are pressed into the cylinder head to sur-
round each cable boot and spark plug (Fig. 36).
(1) Always remove spark plug or ignition coil
cables by grasping at the cable boot (Fig. 38). Turn
the cable boot 1/2 turn and pull straight back in a
steady motion. Never pull directly on the cable.
Internal damage to cable will result.
(2) Prior to removing the spark plug, spray com-
pressed air around the spark plug hole and the area
around the spark plug. This will help prevent foreign
material from entering the combustion chamber.
(3) Remove the spark plug using a quality socket
with a rubber or foam insert.
(4) Inspect the spark plug condition. Refer to
Spark Plug Condition in the Diagnostics and Testing
section of this group.
Fig. 33 Chipped Electrode Insulator
1 - GROUND ELECTRODE
2 - CENTER ELECTRODE
3 - CHIPPED INSULATOR
Fig. 34 Preignition Damage
1 - GROUND ELECTRODE STARTING TO DISSOLVE
2 - CENTER ELECTRODE DISSOLVED
Fig. 35 Spark Plug Overheating
1 - BLISTERED WHITE OR GRAY COLORED INSULATOR
8I - 18 IGNITION CONTROLBR/BE
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 557 of 2889

With the engine running, remove spark plug cable
from spark plug (one at a time) and hold next to a
good engine ground. If the cable and spark plug are
in good condition, the engine rpm should drop and
the engine will run poorly. If engine rpm does not
drop, the cable and/or spark plug may not be operat-
ing properly and should be replaced. Also check
engine cylinder compression.
With the engine not running, connect one end of a
test probe to a good ground. Start the engine and run
the other end of the test probe along the entire
length of all spark plug cables. If cables are cracked
or punctured, there will be a noticeable spark jump
from the damaged area to the test probe. The cable
running from the ignition coil to the distributor cap
can be checked in the same manner. Cracked, dam-
aged or faulty cables should be replaced with resis-
tance type cable. This can be identified by the words
ELECTRONIC SUPPRESSION printed on the cable
jacket.
Use an ohmmeter to test for open circuits, exces-
sive resistance or loose terminals. If equipped,
remove the distributor cap from the distributor.Do
not remove cables from cap.Remove cable from
spark plug. Connect ohmmeter to spark plug termi-
nal end of cable and to corresponding electrode in
distributor cap. Resistance should be 250 to 1000
Ohms per inch of cable. If not, remove cable from dis-
tributor cap tower and connect ohmmeter to the ter-
minal ends of cable. If resistance is not within
specifications as found in the SPARK PLUG CABLE
RESISTANCE chart, replace the cable. Test all spark
plug cables in this manner.
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE
MINIMUM MAXIMUM
250 Ohms Per Inch 1000 Ohms Per Inch
3000 Ohms Per Foot 12,000 Ohms Per Foot
To test ignition coil-to-distributor cap cable, do not
remove the cable from the cap. Connect ohmmeter to
rotor button (center contact) of distributor cap and
terminal at ignition coil end of cable. If resistance is
not within specifications as found in the Spark Plug
Cable Resistance chart, remove the cable from the
distributor cap. Connect the ohmmeter to the termi-
nal ends of the cable. If resistance is not within spec-
ifications as found in the Spark Plug Cable
Resistance chart, replace the cable. Inspect the igni-
tion coil tower for cracks, burns or corrosion.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: When disconnecting a high voltage cable
from a spark plug or from the distributor cap, twist
the rubber boot slightly (1/2 turn) to break it loose
(Fig. 38). Grasp the boot (not the cable) and pull it
off with a steady, even force.
INSTALLATION
Install cables into the proper engine cylinder firing
order (Fig. 39), (Fig. 40) or (Fig. 41).
When replacing the spark plug and coil cables,
route the cables correctly and secure in the proper
retainers. Failure to route the cables properly can
cause the radio to reproduce ignition noise. It could
also cause cross ignition of the plugs or short circuit
the cables to ground.
Fig. 37 Heat ShieldsÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L Engines
1 - AIR GAP
2 - SPARK PLUG BOOT HEAT SHIELD
Fig. 38 Cable Removal
1 - SPARK PLUG CABLE AND BOOT
2 - SPARK PLUG BOOT PULLER
3 - TWIST AND PULL
4 - SPARK PLUG
8I - 20 IGNITION CONTROLBR/BE
SPARK PLUG CABLE (Continued)