2001 DODGE RAM light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 1185 of 2889

HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN
BLOCK)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐHYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length,
which allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on
intake side of oil pump through which air can be
drawn will create the same tappet action. Check the
lubrication system from the intake strainer to the
pump cover, including the relief valve retainer cap.
When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be
intermittent or constant, and usually more than one
tappet will be noisy. When oil level and leaks have
been corrected, operate the engine at fast idle. Run
engine for a sufficient time to allow all of the air
inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in thetappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3) Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger, or by the
plunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder.
The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click is
caused by a tappet check valve not seating, or by for-
eign particles wedged between the plunger and the
tappet body. This will cause the plunger to stick in
the down position. This heavy click will be accompa-
nied by excessive clearance between the valve stem
and rocker arm as valve closes. In either case, tappet
assembly should be removed for inspection and clean-
ing.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
ing the noise. If more than one tappet seems to be
noisy, it's probably not the tappets.
LEAK-DOWN TEST
After cleaning and inspection, test each tappet for
specified leak-down rate tolerance to ensure zero-lash
operation (Fig. 38).
Swing the weighted arm of the hydraulic valve tap-
pet tester away from the ram of the Universal Leak-
Down Tester.
(1) Place a 7.925-7.950 mm (0.312-0.313 inch)
diameter ball bearing on the plunger cap of the tap-
pet.
(2) Lift the ram and position the tappet (with the
ball bearing) inside the tester cup.
(3) Lower the ram, then adjust the nose of the ram
until it contacts the ball bearing. DO NOT tighten
the hex nut on the ram.
(4) Fill the tester cup with hydraulic valve tappet
test oil until the tappet is completely submerged.
(5) Swing the weighted arm onto the push rod and
pump the tappet plunger up and down to remove air.
When the air bubbles cease, swing the weighted arm
away and allow the plunger to rise to the normal
position.
(6) Adjust the nose of the ram to align the pointer
with the SET mark on the scale of the tester and
tighten the hex nut.
(7) Slowly swing the weighted arm onto the push
rod.
(8) Rotate the cup by turning the handle at the
base of the tester clockwise one revolution every 2
seconds.
(9) Observe the leak-down time interval from the
instant the pointer aligns with the START mark on
the scale until the pointer aligns with the 0.125
mark. A normally functioning tappet will require
9 - 38 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
Page 1190 of 2889

(3) Install the crankshaft bolt and washer. Tighten
the bolt to 244 N´m (180 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install the crankshaft pulley. Tighten the pul-
ley bolts to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.(5) Install the serpentine belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
(6) Install viscous fan drive and fan (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install the fan shroud.
(8) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Position fan to ensure clearance for radiator
top tank and hose.
CAUTION: DO NOT lift the engine by the intake
manifold.
(3) Install engine support/lifting fixture.
(4) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(5) Lift the engine SLIGHTLY and remove the
thru-bolt and nut (Fig. 47).
(6) Remove engine support bracket/cushion bolts
(Fig. 47). Remove the support bracket/cushion and
heat shields.
INSTALLATION
(1) With engine raised SLIGHTLY, position the
engine support bracket/cushion and heat shields to
the block. Install new bolts and tighten to 81 N´m (60
ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the through-bolt into the engine support
bracket/cushion.
Fig. 44 Proper Ring Installation
1 - OIL RING SPACER GAP
2 - SECOND COMPRESSION RING GAP OIL RING RAIL GAP
(TOP)
3 - OIL RING RAIL GAP (BOTTOM)
4 - TOP COMPRESSION RING GAP
Fig. 45 Vibration Damper Assembly
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3688
Fig. 46 Installing Vibration Damper
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3688
Fig. 47 Engine Front Mounts
1 - ENGINE MOUNT HEAT SHIELD
2 - THRU-BOLT
3 - RESTRICTION PADS
4 - ENGINE SUPPORT BRACKET/CUSHION
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 43
VIBRATION DAMPER (Continued)
Page 1191 of 2889
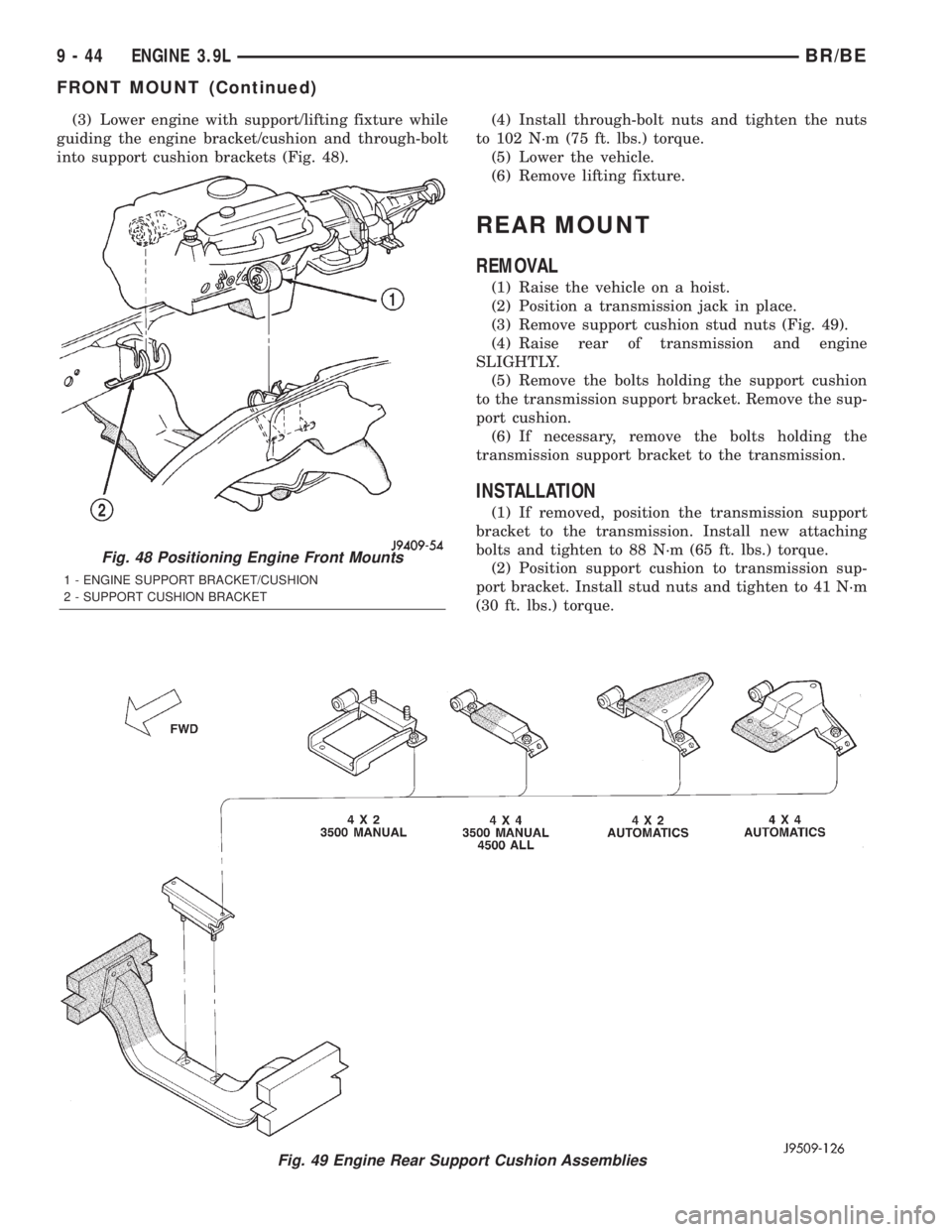
(3) Lower engine with support/lifting fixture while
guiding the engine bracket/cushion and through-bolt
into support cushion brackets (Fig. 48).(4) Install through-bolt nuts and tighten the nuts
to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove lifting fixture.
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(2) Position a transmission jack in place.
(3) Remove support cushion stud nuts (Fig. 49).
(4) Raise rear of transmission and engine
SLIGHTLY.
(5) Remove the bolts holding the support cushion
to the transmission support bracket. Remove the sup-
port cushion.
(6) If necessary, remove the bolts holding the
transmission support bracket to the transmission.
INSTALLATION
(1) If removed, position the transmission support
bracket to the transmission. Install new attaching
bolts and tighten to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Position support cushion to transmission sup-
port bracket. Install stud nuts and tighten to 41 N´m
(30 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 49 Engine Rear Support Cushion Assemblies
Fig. 48 Positioning Engine Front Mounts
1 - ENGINE SUPPORT BRACKET/CUSHION
2 - SUPPORT CUSHION BRACKET
9 - 44 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
FRONT MOUNT (Continued)
Page 1193 of 2889
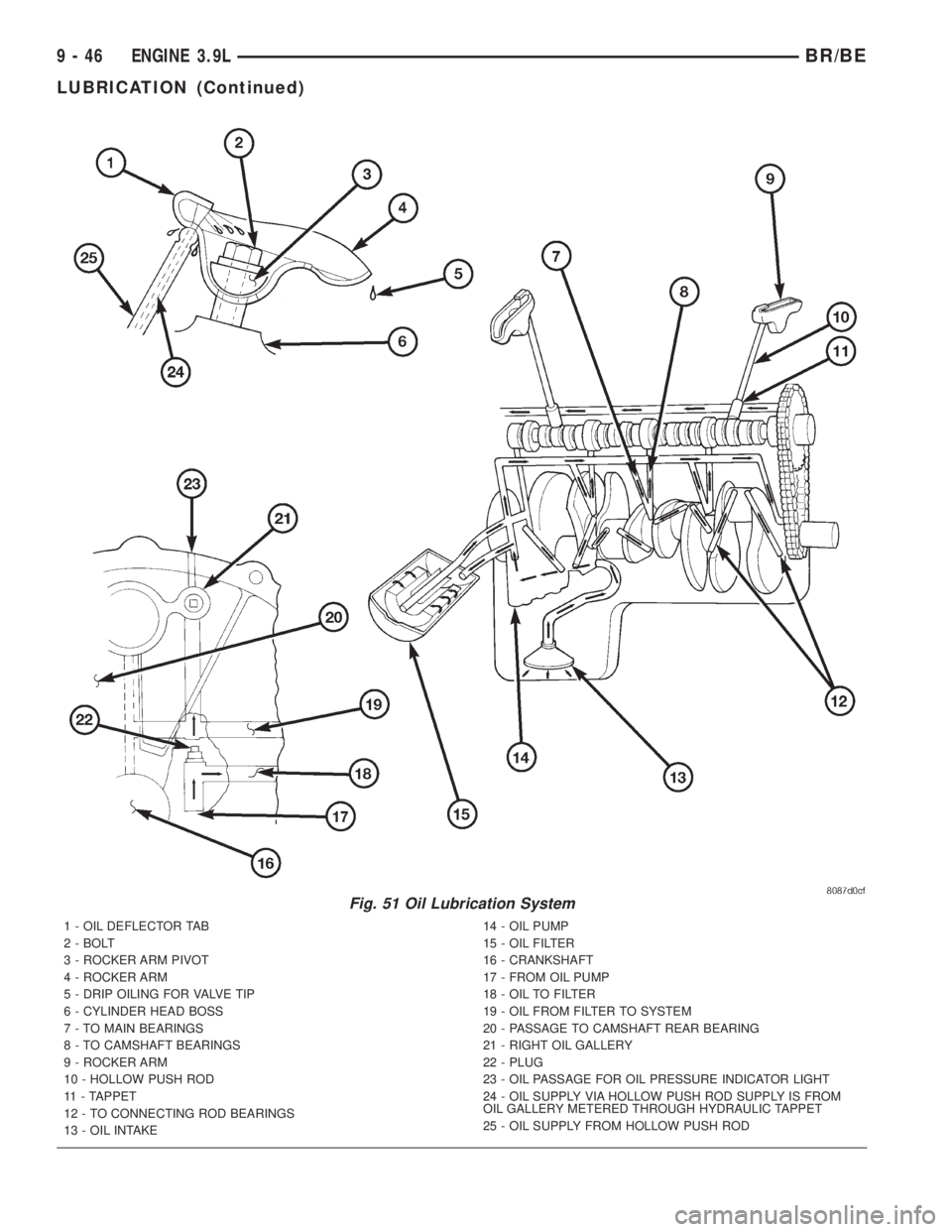
Fig. 51 Oil Lubrication System
1 - OIL DEFLECTOR TAB
2 - BOLT
3 - ROCKER ARM PIVOT
4 - ROCKER ARM
5 - DRIP OILING FOR VALVE TIP
6 - CYLINDER HEAD BOSS
7 - TO MAIN BEARINGS
8 - TO CAMSHAFT BEARINGS
9 - ROCKER ARM
10 - HOLLOW PUSH ROD
11 - TAPPET
12 - TO CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
13 - OIL INTAKE14 - OIL PUMP
15 - OIL FILTER
16 - CRANKSHAFT
17 - FROM OIL PUMP
18 - OIL TO FILTER
19 - OIL FROM FILTER TO SYSTEM
20 - PASSAGE TO CAMSHAFT REAR BEARING
21 - RIGHT OIL GALLERY
22 - PLUG
23 - OIL PASSAGE FOR OIL PRESSURE INDICATOR LIGHT
24 - OIL SUPPLY VIA HOLLOW PUSH ROD SUPPLY IS FROM
OIL GALLERY METERED THROUGH HYDRAULIC TAPPET
25 - OIL SUPPLY FROM HOLLOW PUSH ROD
9 - 46 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1194 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292. Start engine and record pressure. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
LEAKS
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil-soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
be sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light source.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat previous step.
(5) If the oil leak source is not positively identified
at this time, proceed with the air leak detection test
method as follows:
(6) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(7) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(8) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(9) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(10) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(11) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air sup-
ply and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose. Proceed
to next step.(12) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area
using a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐENGINE OIL
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located at the right
front of the engine, left of the generator on 3.9L
engines (Fig. 52).
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
Fig. 52 Oil Level Indicator Location
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP
3 - DIPSTICK
4 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
5 - FILTER BOSS
BR/BEENGINE 3.9L 9 - 47
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1195 of 2889

(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE:
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. This infor-
mation can be found in the owner's manual.
TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist vehicle.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Change oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL).
(8) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/
FLUID TYPES - DESCRIPTION) and amount of
engine oil (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTE-
NANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(9) Install oil fill cap.
(10) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(11) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-
flow, disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Cor-
poration recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil
filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise to remove
it from the cylinder block oil filter boss (Fig. 53).
(4) When filter separates from adapter nipple, tip
gasket end upward to minimize oil spill. Remove fil-
ter from vehicle.
(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface (Fig. 54) of oil and grime.
(6) Install new filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION).
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil or chassis grease.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 54) hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.
(3) Add oil (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/
OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Remove engine oil dipstick.
(3) Raise vehicle.
(4) Drain engine oil.
(5) Remove exhaust pipe.
(6) Remove left engine to transmission strut.
(7) Loosen the right side engine support bracket
cushion through-bolt nut and raise the engine
slightly. Remove oil pan by sliding backward and out.
(8) Remove the one-piece gasket.
Fig. 53 Oil Filter RemovalÐTypical
1 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
2 - OIL FILTER WRENCH
Fig. 54 Oil Filter Sealing SurfaceÐTypical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
9 - 48 ENGINE 3.9LBR/BE
OIL (Continued)
Page 1207 of 2889

FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................100
INSTALLATION..........................100
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................101
INSTALLATION..........................101
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION..........................102
OPERATION............................102
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................104
ENGINE OIL LEAKS....................104
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE................104
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................104
ENGINE OIL..........................104
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL.............................105
INSTALLATION..........................105
OIL PAN
REMOVAL.............................105
CLEANING.............................106
INSPECTION...........................106
INSTALLATION..........................106
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL.............................107
DISASSEMBLY..........................107INSPECTION...........................107
ASSEMBLY............................109
INSTALLATION..........................109
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION..........................109
OPERATION............................109
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................110
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE............110
REMOVAL.............................110
CLEANING.............................110
INSPECTION...........................110
INSTALLATION..........................111
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION..........................112
OPERATION............................112
REMOVAL.............................112
CLEANING.............................112
INSPECTION...........................112
INSTALLATION..........................113
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
REMOVAL.............................113
INSTALLATION..........................113
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL.............................114
INSPECTION...........................114
INSTALLATION..........................115
ENGINE 5.2L
DESCRIPTION
The 5.2 Liter (318 CID) eight-cylinder engine is a
V-Type lightweight, single cam, overhead valve
engine with hydraulic roller tappets. This engine is
designed for unleaded fuel.
Engine lubrication system consists of a rotor type
oil pump and a full flow oil filter.The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5, 7 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right
bank. The firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2 (Fig. 1).
The engine serial number is stamped into a
machined pad located on the left, front corner of the
cylinder block. When component part replacement is
necessary, use the engine type and serial number for
reference (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 Firing Order
Fig. 2 Engine Identification (Serial) Number
9 - 60 ENGINE 5.2LBR/BE
Page 1216 of 2889

(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1) Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round, as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing
oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, available from
major oil distributors.
CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 50É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Recover refrigerant from a/c system, if
equipped (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Remove the a/c condenser, if equipped (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL).
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
BR/BEENGINE 5.2L 9 - 69
ENGINE 5.2L (Continued)