2001 DODGE RAM power steering
[x] Cancel search: power steeringPage 1628 of 2889

(9) Slide the steering pump from the bracket. Use
care not to damage the internal oil seal in the vac-
uum pump (Fig. 9).
(10) Remove the two pump body spacers.
INSTALLATION - GASOLINE ENGINE
(1) Install the front pump bracket and tighten
bolts to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.). On 8.0L engine install
rear pump bracket and tighten nut to 47 N´m (35 ft.
lbs.), tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install the pump pulley with Installer
C-4063±B, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP/PULLEY
- INSTALLATION).
(3) Install steering pump assembly on the engine
block. Install the upper stud and bolt in bracket.
(4) Pivot the pump down past the coolant tube and
install the lower bolts in bracket.(5) Tighten the bolts and nut to 41 N´m (30 ft.
lbs.).
(6) Connect the hoses to the pump.
(7) Install the serpentine drive belt, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION), (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCES-
SORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
(8) Fill the reservoir with power steering fluid,
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
INSTALLATION - DIESEL ENGINE
(1) Install the two pump body spacers.
(2) Rotate the drive gear until the steering pump
and vacuum pump drive dogs align. Install the steer-
ing pump onto the vacuum pump bracket. Use care
to avoid damaging the oil seal in the vacuum pump
during installation.The steering pump housing
and spacers must mate completely with the
vacuum pump bracket.
(3) Install the vacuum pump bracket to steering
pump nuts and tighten to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(4) Position new gasket on vacuum pump assem-
bly. Use sealer if necessary to retain the gasket.
(5) Align and install the pump assembly on the
engine. Ensure the steering pump stud is inserted
into the block bracket. Tighten the pump- to-engine
block attaching bolts to 77 N´m (57 ft. lbs.).
(6) Install the steering pump to attaching bracket
nut and tighten to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(7) Remove plug and install the oil pressure send-
ing unit and electrical connector.
(8) Install the oil feed line to the vacuum pump.
Tighten the oil line connection to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs./ 5
ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the fluid hoses to the power steering
pump. Tighten the pressure fitting at the pump to 31
N´m (23 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install and clamp the hose on the vacuum
pump.
(11) Install the serpentine belt, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(12) Fill the reservoir with power steering fluid,
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(13) Start the engine and check the operation of
the brakes.
Fig. 9 Steering Pump & Vacuum Pump
1 - PUMP SHAFT
2 - VACUUM FITTING
3 - VACUUM PUMP DRIVE
4 - OIL SEAL
5 - MOUNTING BRACKET
6 - DRIVE DOG
7 - PUMP SPACERS
BR/BEPUMP 19 - 35
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1629 of 2889
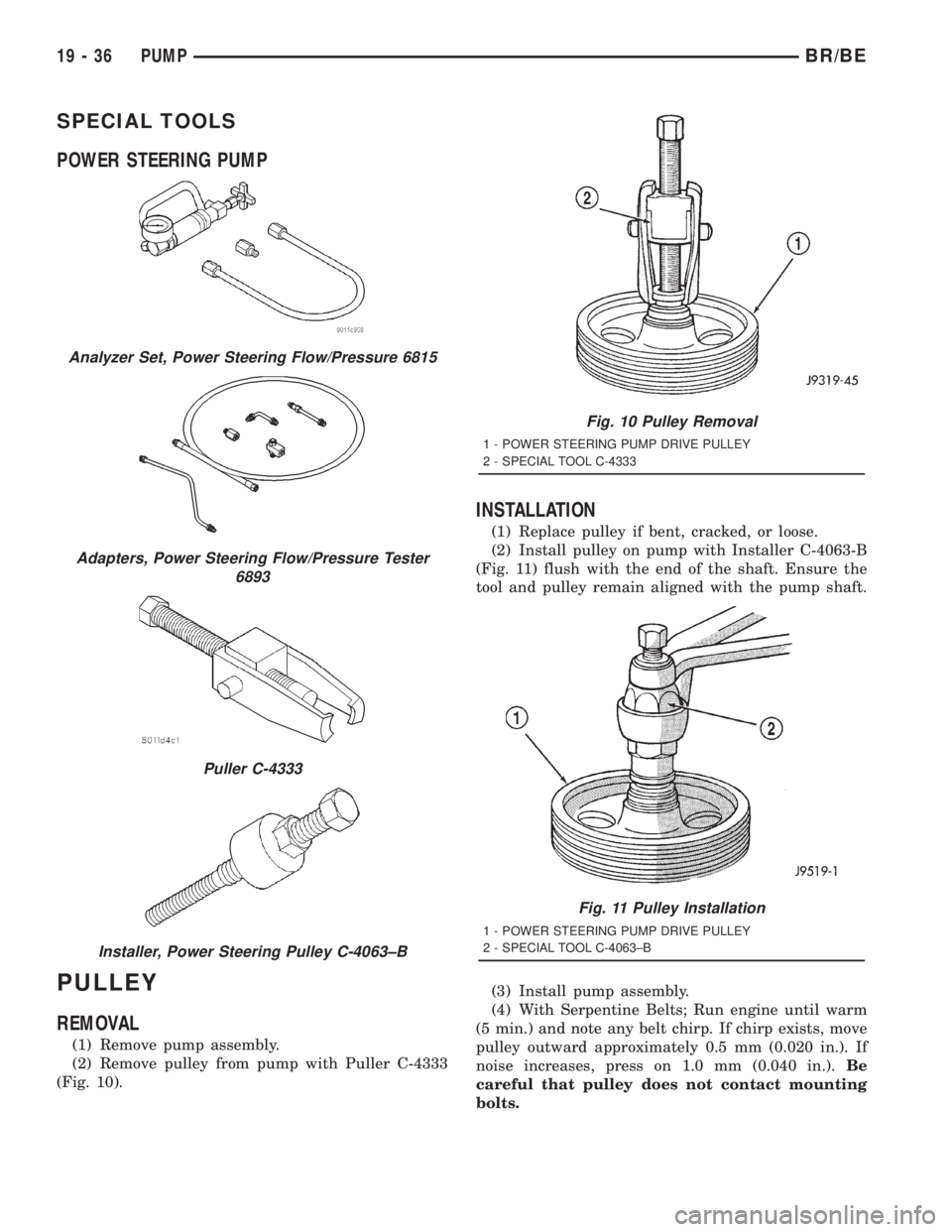
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING PUMP
PULLEY
REMOVAL
(1) Remove pump assembly.
(2) Remove pulley from pump with Puller C-4333
(Fig. 10).
INSTALLATION
(1) Replace pulley if bent, cracked, or loose.
(2) Install pulley on pump with Installer C-4063-B
(Fig. 11) flush with the end of the shaft. Ensure the
tool and pulley remain aligned with the pump shaft.
(3) Install pump assembly.
(4) With Serpentine Belts; Run engine until warm
(5 min.) and note any belt chirp. If chirp exists, move
pulley outward approximately 0.5 mm (0.020 in.). If
noise increases, press on 1.0 mm (0.040 in.).Be
careful that pulley does not contact mounting
bolts.
Analyzer Set, Power Steering Flow/Pressure 6815
Adapters, Power Steering Flow/Pressure Tester
6893
Puller C-4333
Installer, Power Steering Pulley C-4063±B
Fig. 10 Pulley Removal
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP DRIVE PULLEY
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4333
Fig. 11 Pulley Installation
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP DRIVE PULLEY
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4063±B
19 - 36 PUMPBR/BE
Page 1630 of 2889

HOSES - PRESSURE
DESCRIPTION
The hose consists of two metal ends and rubber
center section that contains a tuning cable.
OPERATION
Power steering pressure line, is used to transfer
high pressure power steering fluid, from the power
steering pump to the power steering gear.
HOSES - RETURN
DESCRIPTION
Power steering return line is a hose which is
clamped at the pump and the gear.
OPERATION
Power steering return line, is used to transfer low
pressure power steering fluid, from the power steer-
ing gear to the power steering pump.
BR/BEPUMP 19 - 37
Page 2677 of 2889

INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................104
OPERATION............................105
REMOVAL.............................106
INSTALLATION..........................107
ASH RECEIVER
REMOVAL.............................108
INSTALLATION..........................109
CLUSTER BEZEL
REMOVAL.............................109
INSTALLATION..........................110
CUBBY BIN
REMOVAL.............................110
INSTALLATION..........................110
CUP HOLDER
REMOVAL.............................110
INSTALLATION..........................111
GLOVE BOX
REMOVAL.............................112DISASSEMBLY..........................112
ASSEMBLY.............................112
INSTALLATION..........................113
GLOVE BOX LATCH STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................113
INSTALLATION..........................113
GLOVE BOX OPENING UPPER TRIM
REMOVAL.............................114
INSTALLATION..........................114
INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP COVER
REMOVAL.............................114
INSTALLATION..........................115
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER
REMOVAL.............................115
INSTALLATION..........................116
STORAGE BIN
REMOVAL.............................116
INSTALLATION..........................116
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The instrument panel is located at the front of the
passenger compartment. This instrument panel is
molded from a blend of various plastics that are
mechanically attached to the vehicle. Colors are
molded into the plastic components to minimize
appearance degradation from scratches or abrasions.
The panel components are internally ribbed and riv-
eted to steel reinforcements for additional structural
integrity and dimensional stability. The instrument
panel surface components are designed to deform
upon impact without breaking. This type of construc-
tion provides improved energy absorption which, in
conjunction with the dual airbags and seat belts,
helps to improve occupant protection.
The top of the instrument panel is secured to the
top of the dash panel near the base of the windshield
using screws. An end bracket integral to each end of
the instrument panel structure is secured to each
cowl side inner panel with a screw. A stamped metal
bracket supports the center of the instrument panel
by securing it to the top of the floor panel transmis-
sion tunnel below the instrument panel with screws.
The instrument cluster, radio, heater-air conditioner
control, passenger airbag, glove box, electrical junc-
tion block, Central Timer Module (CTM), accessoryswitches, ash receiver, cigar lighter, accessory power
outlet, park brake release handle, inside hood release
handle, as well as numerous other components are
secured to and supported by this unit.
The instrument panel for this vehicle includes the
following major features:
²Cluster Bezel- This molded plastic bezel is
secured with snap clips to the instrument panel sup-
porting structure. It trims out the edges of the head-
lamp switch, instrument cluster, radio, heater-air
conditioner controls, passenger airbag on-off switch,
and the heated seat switches on vehicles so equipped.
On vehicles without the heated seat option, a small
storage cubby bin is provided in the cluster bezel.
This bezel also incorporates three completely adjust-
able panel outlets for the climate control system, and
fills the opening between the instrument cluster and
the top of the steering column where it passes
through the instrument panel.
²Cup Holder/Storage Bin- Vehicles equipped
with an automatic transmission feature a latching
fold-down, adjustable cup holder located on the lower
instrument panel between the glove box and the ash
receiver. Vehicles equipped with a manual transmis-
sion have a lighted storage bin on the instrument
panel in place of the cup holder.
²Glove Box- The hinged bin-type glove box in
the passenger side of the instrument panel features a
recessed paddle-operated latch handle. Three molded
23 - 104 INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMBR/BE
Page 2678 of 2889

hook formations on the lower edge of the glove box
door are engaged with and pivot on three hinge pins
integral to the lower edge of the instrument panel
support structure. The glove box door also serves as
the passenger side knee blocker. A honeycomb struc-
ture between the inner and outer glove box door pan-
els helps to absorb the impact load and distribute it
to the instrument panel structure.
²Steering Column Opening Cover- The steer-
ing column opening cover serves as the driver side
knee blocker. This molded plastic cover has an inte-
gral ribbed plastic liner concealed behind it, for
increased strength and integrity. The steering column
opening cover transfers impact loads to the instru-
ment panel structural support.
²Top Cover- The instrument panel top cover or
base trim is the molded, grained, and color impreg-
nated plastic outer skin of the instrument panel
structural support.
Hard wired circuitry connects the electrical compo-
nents on the instrument panel to each other through
the electrical system of the vehicle. These hard wired
circuits are integral to several wire harnesses, which
are routed throughout the vehicle and retained by
many different methods. These circuits may be con-
nected to each other, to the vehicle electrical system
and to the instrument panel components through the
use of a combination of soldered splices, splice block
connectors and many different types of wire harness
terminal connectors and insulators. Refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes complete circuit diagrams, proper wire
and connector repair procedures, further details on
wire harness routing and retention, as well as pin-
out and location views for the various wire harness
connectors, splices, and grounds.
OPERATION
The instrument panel serves as the command cen-
ter of the vehicle, which necessarily makes it a very
complex unit. The instrument panel is designed to
house the controls and monitors for standard and
optional powertrains, climate control systems, audio
systems, safety systems, and many other comfort or
convenience items. When the components of the
instrument panel structural support are properly
assembled and secured in the vehicle they provide
superior instrument panel stiffness and integrity to
help reduce buzzes, squeaks, and rattles. This type of
construction also provides improved energy absorp-
tion which, in conjunction with the dual airbags and
seat belts, helps to improve occupant protection.
The instrument panel is also designed so that all of
the various controls can be safely reached and the
monitors can be easily viewed by the vehicle operator
when driving, while still allowing relative ease ofaccess to each of these items for service. Modular
instrument panel construction allows all of the
gauges and controls to be serviced from the front of
the panel. In addition, most of the instrument panel
electrical components can be accessed without com-
plete instrument panel removal. However, if neces-
sary, the instrument panel can be removed from the
vehicle as an assembly.
The steering column opening cover with its inte-
gral knee blocker located on the driver side of the
instrument panel works in conjunction with the air-
bag system in a frontal vehicle impact to keep the
driver properly positioned for an airbag deployment.
In addition, removal of this component provides
access to the steering column mounts, the steering
column wiring, the Junction Block (JB) (removal of a
snap-fit fuse access panel on the left end of the
instrument panel allows access to the fuses and cir-
cuit breakers), the Central Timer Module (CTM), the
Infinity speaker filter choke and relay unit, much of
the instrument panel wiring, and the gear selector
indicator cable (automatic transmission).
In a frontal collision, the glove box door on the pas-
senger side of the instrument panel provides the
same function for the front seat passenger as the
knee blocker does for the driver. The glove box door
also incorporates a recessed latch handle. Removal of
the glove box provides access to the passenger airbag,
the glove box lamp and switch, the radio antenna
coaxial cable, the heating and air conditioning vac-
uum harness connector, and additional instrument
panel wiring.
Removal of the instrument panel cluster bezel
allows access to the headlamp switch, instrument
cluster, radio, passenger airbag on-off switch, heated
seat switches (if equipped), and the heating and air
conditioning control. Removal of the instrument clus-
ter allows access to the cluster illumination and indi-
cator bulbs, and more of the instrument panel
wiring. Complete instrument panel removal is
required for service of most components internal to
the heating and air conditioning system housing,
including the heater core and the evaporator.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of all of the components and systems mounted on or
in the instrument panel.
BR/BEINSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM 23 - 105
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 2754 of 2889

motor speeds, but can only be turned off by selecting
the Off position with the heater-only or a/c heater
control switch knob.
OPERATION
The blower motor switch directs the blower motor
ground path through the mode control switch to the
blower motor resistor, or directly to ground, as
required to achieve the selected blower motor speed.
The blower motor switch cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, the entire heater-only or a/c
heater control unit must be replaced. The blower
motor switch knob is serviced separately.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
SWITCH
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Check for battery voltage at the fuse in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Remove the a/c heater control from the instrument
panel. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CONTROLS/A/C HEATER CONTROL -
REMOVAL) Check for continuity between the ground
circuit cavity of the a/c heater control wire harness
connector and a good ground. There should be conti-
nuity. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to ground as required.
(3) With the a/c heater control wire harness con-
nector unplugged, place the a/c heater mode control
switch knob in any position except the Off position.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit ter-
minal and each of the blower motor driver circuit ter-
minals of the a/c heater control as you move the
blower motor switch knob to each of the four speed
positions. There should be continuity at each drivercircuit terminal in only one blower motor switch
speed position. If OK, test and repair the blower
driver circuits between the a/c heater control connec-
tor and the blower motor resistor as required. If not
OK, replace the faulty a/c heater control unit.
REMOVAL
The blower motor switch cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, the entire heater-only or a/c
heater control unit must be replaced. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C
HEATER CONTROL - REMOVAL) The blower motor
switch knob is serviced separately.
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the run position.
(2) Locate the temperature control knob in the mid
(12 o'clock) position.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the off position.
(4) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(5) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle.
Refer to Instrument Panel System for the procedures.
(6) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(7) Unplug the wire harness connector from the
blend door actuator (Fig. 24).
(8) Remove the two mounting screws which secure
the actuator to the housing.
(9) Slide the blend door actuator off the blend door
shaft.
NOTE: A black plastic coupler may be attached to
the blend door shaft. Remove the coupler and
inspect for damage. Reinstall if there is no damage
found.
BR/BECONTROLS 24 - 25
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2755 of 2889

INSTALLATION
NOTE: Before installing the blend door actuator, be
certain that the blend door is not binding and is
capable of full travel in both directions.
(1) Align the actuator with the blend door shaft
and rotate the actuator to align it to the mounting
bosses on the HVAC housing.
(2) Align and install the actuator screws. Tighten
the mounting screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Plug in the wire harness connector to the blend
door actuator.
(4) Install the HVAC housing in the vehicle. (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRI-
BUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLATION)
(5) Install the instrument panel in the vehicle.
Refer to Instrument Panel System for the procedures.
(6) Make sure the Temperature Control Knob is in
the mid (12 o'clock) position to allow the actuator to
automatically position itself in the mid position and
come to a complete stop when powered up.
(7) Connect the battery negative cable.
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
REMOVAL - HEAT/DEFROST DOOR ACTUATOR
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle
and place it on a work bench. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC
HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(3) Unplug the two vacuum harness connectors
from the heat/defrost door actuator (Fig. 25).
(4) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry the heat/defrost door
crank arm off the heat/defrost door pivot.
(5) Remove the two screws that secure the heat/de-
frost door actuator to the HVAC housing.
(6) Remove the heat/defrost door actuator from the
HVAC housing.
Fig. 24 BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR REMOVE/
INSTALL
1 - DUCT
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
3 - UNIT HOUSING
4 - HARNESS AND CONNECTOR
5 - BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
Fig. 25 HEAT/DEFROST DOOR ACTUATOR
1 - VACUUM LINE
2 - DOOR PIVOT CONNECTION
3 - HEAT/DEFROST DOOR ACTUATOR
24 - 26 CONTROLSBR/BE
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 2795 of 2889

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0505 (M) Idle Air Control Motor Circuits SBEC II
P0522 Oil Pressure Voltage Too Low Oil pressure sending unit (sensor) voltage input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0523 Oil Pressure Voltage Too High Oil pressure sending unit (sensor) voltage input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0524 Oil Pressure Too Low Engine oil pressure is low. Engine power derated.
P0545 A/C Clutch Relay Circuit Problem detected in air conditioning clutch relay control
circuit.
P0551 Power Steering Switch Failure Incorrect input state detected for the power steering
switch circuit. PL: High pressure seen at high speed.
P0562 Charging System Voltage Too Low Supply voltage sensed at ECM too low.
P0563 Charging System Voltage Too High Supply voltage sensed at ECM too high.
P0600 PCM Failure SPI Communications No communication detected between co-processors in the
control module.
P0601 (M) Internal Controller Failure Internal control module fault condition (check sum)
detected.
P0602 (M) ECM Fueling Calibration Error ECM Internal fault condition detected.
P0604 RAM Check Failure Transmission control module RAM self test fault detected.
-Aisin transmission
P0605 ROM Check Falure Transmission control module ROM self test fault detected
-Aisin transmission
P0606 (M) ECM Failure ECM Internal fault condition detected.
P0615 Starter Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the starter relay
control circuit.
P0622 (G) Generator Field Not Switching
ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the generator
field control circuit.
P0645 A/C Clutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C clutch
relay control circuit.
P0700 EATX Controller DTC Present This SBEC III or JTEC DTC indicates that the EATX or
Aisin controller has an active fault and has illuminated the
MIL via a CCD (EATX) or SCI (Aisin) message. The
specific fault must be acquired from the EATX via CCD or
from the Aisin via ISO-9141.
P0703 Brake Switch Stuck Pressed or
ReleasedIncorrect input state detected in the brake switch circuit.
(Changed from P1595)
P0711 (M) Trans Temp Sensor, No Temp Rise
After StartRelationship between the transmission temperature and
overdrive operation and/or TCC operation indicates a
failure of the Transmission Temperature Sensor. OBD II
Rationality. Was MIL code 37.
P0712 Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too Low Transmission fluid temperature sensor input below
acceptable voltage. Was MIL code 37.
P0712 (M) Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too Low Voltage less than 1.55 volts (4-speed auto. trans. only).
25 - 8 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)