Page 332 of 557
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-37
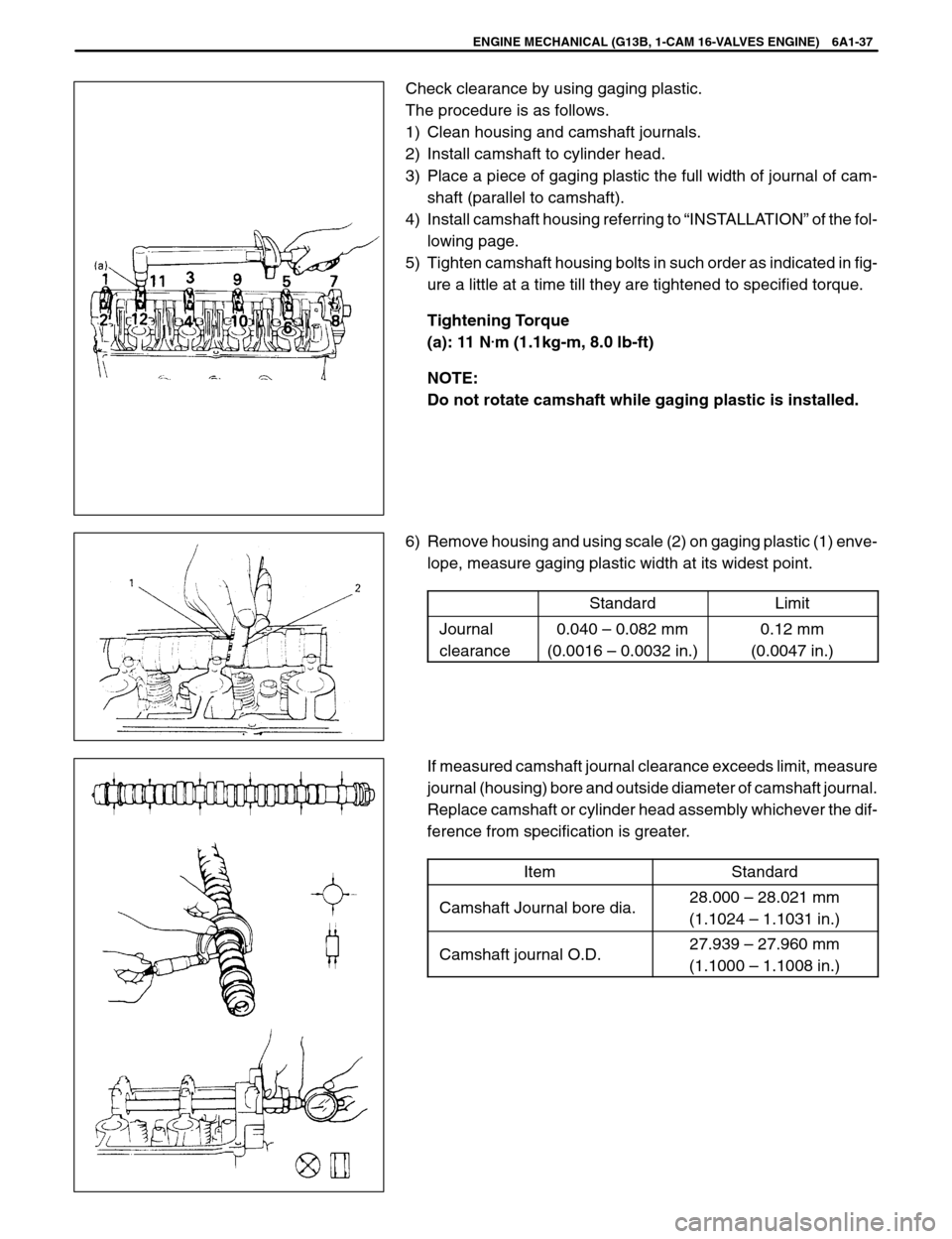
Check clearance by using gaging plastic.
The procedure is as follows.
1) Clean housing and camshaft journals.
2) Install camshaft to cylinder head.
3) Place a piece of gaging plastic the full width of journal of cam-
shaft (parallel to camshaft).
4) Install camshaft housing referring to “INSTALLATION” of the fol-
lowing page.
5) Tighten camshaft housing bolts in such order as indicated in fig-
ure a little at a time till they are tightened to specified torque.
Tightening Torque
(a): 11 N
.m (1.1kg-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
NOTE:
Do not rotate camshaft while gaging plastic is installed.
6) Remove housing and using scale (2) on gaging plastic (1) enve-
lope, measure gaging plastic width at its widest point.
StandardLimit
Journal
clearance0.040 – 0.082 mm
(0.0016 – 0.0032 in.)0.12 mm
(0.0047 in.)
If measured camshaft journal clearance exceeds limit, measure
journal (housing) bore and outside diameter of camshaft journal.
Replace camshaft or cylinder head assembly whichever the dif-
ference from specification is greater.
Item
Standard
Camshaft Journal bore dia.28.000 – 28.021 mm
(1.1024 – 1.1031 in.)
Camshaft journal O.D.27.939 – 27.960 mm
(1.1000 – 1.1008 in.)
Page 333 of 557
A: Timing belt side
B: Flywheel side
6A1-38 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
INSTALLATION
1) Apply engine oil to rocker arm shaft and rocker arms.
2) Check O-ring for damage or deterioration. Install O-ring to rock-
er arm shaft.
3) Install rocker arm shaft (3) with shaft bolt holes (4) facing up,
rocker arm (exhaust side) (2) and rocker arm spring (1).
4) Install rocker arm shaft bolts and tighten them to specified
torque.
Tightening Torque
(a): 11 N
.m (1.1 kg-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
5) Fill small amount of engine oil into arm pivot holding part (3) of
rocker arm shaft. Install rocker arm (intake side) (1) with clips (2)
to rocker arm shaft.
6) Apply engine oil to cams and journals on camshaft and put cam-
shaft on cylinder head. Install camshaft housing to camshaft and
cylinder head.
�Apply engine oil to sliding surface of each housing against
camshaft journal.
�Apply sealant to mating surface of No.6 housing which will
mate with cylinder head.
“A” Sealant: 99000-31110
Page 335 of 557
6A1-40 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
1. O-ring2
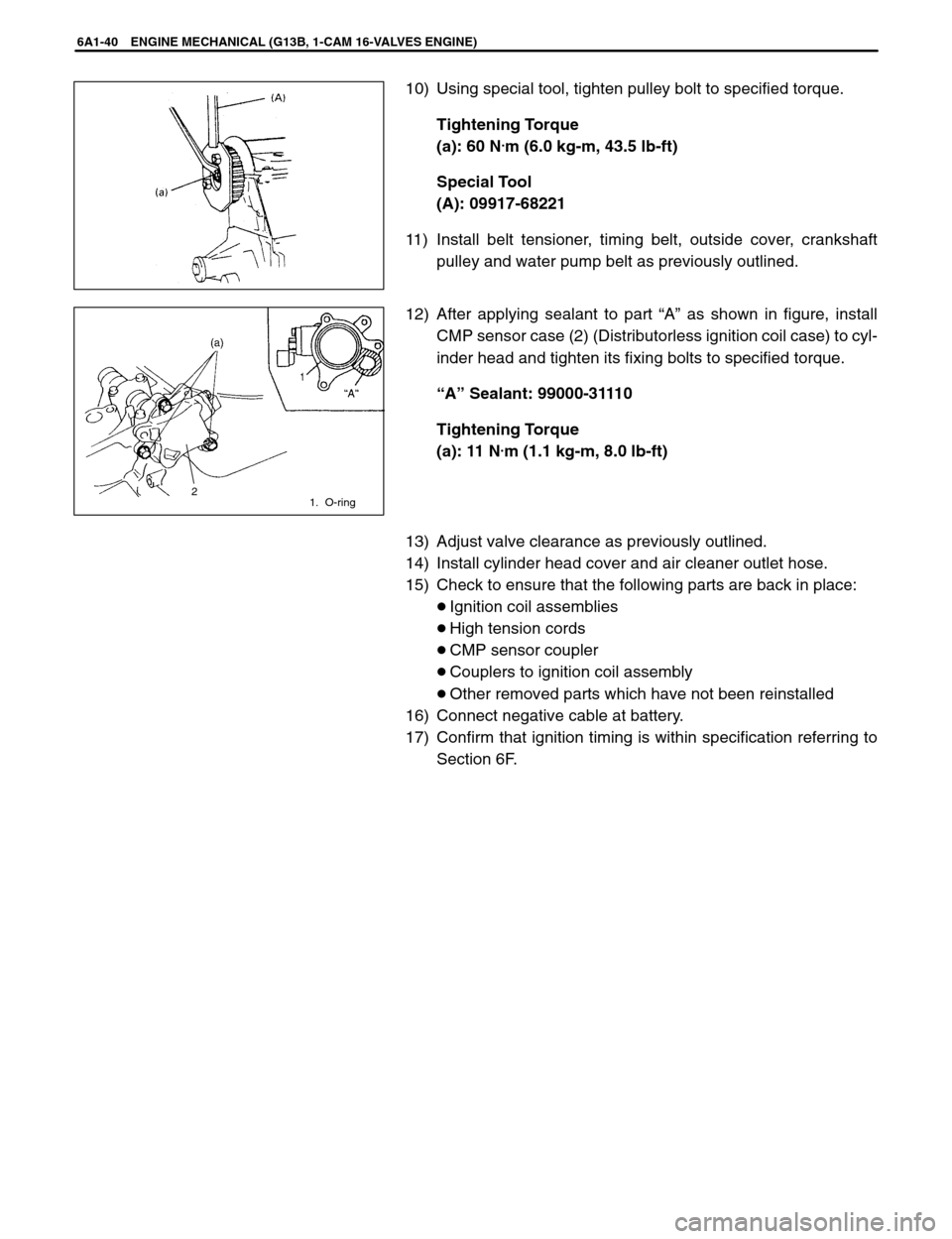
10) Using special tool, tighten pulley bolt to specified torque.
Tightening Torque
(a): 60 N
.m (6.0 kg-m, 43.5 lb-ft)
Special Tool
(A): 09917-68221
11) Install belt tensioner, timing belt, outside cover, crankshaft
pulley and water pump belt as previously outlined.
12) After applying sealant to part “A” as shown in figure, install
CMP sensor case (2) (Distributorless ignition coil case) to cyl-
inder head and tighten its fixing bolts to specified torque.
“A” Sealant: 99000-31110
Tightening Torque
(a): 11 N
.m (1.1 kg-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
13) Adjust valve clearance as previously outlined.
14) Install cylinder head cover and air cleaner outlet hose.
15) Check to ensure that the following parts are back in place:
�Ignition coil assemblies
�High tension cords
�CMP sensor coupler
�Couplers to ignition coil assembly
�Other removed parts which have not been reinstalled
16) Connect negative cable at battery.
17) Confirm that ignition timing is within specification referring to
Section 6F.
Page 338 of 557
3
2. Breather hose
3. PCV valve4. High-tension cords
5. Ignition coil assembly
6. Ignition coil coupler
A: Camshaft pulley side
B: CMP sensor case side
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-43
9) Remove cylinder head cover (1) as previously outlined.
Loosen all valve lash adjusting screws fully.
10) Remove timing belt and camshaft as previously outlined.
11) Disconnect exhaust pipe from exhaust manifold and remove
exhaust manifold stiffener (if equipped).
12) Loosen cylinder head bolts in such order as indicated in figure
and remove them.
13) Check all around cylinder head for any other parts required to
be removed or disconnected and remove or disconnect what-
ever necessary.
14) Remove cylinder head with intake manifold, exhaust manifold
CMP sensor case, using lifting device if necessary.
Page 340 of 557
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-45
INSPECTION
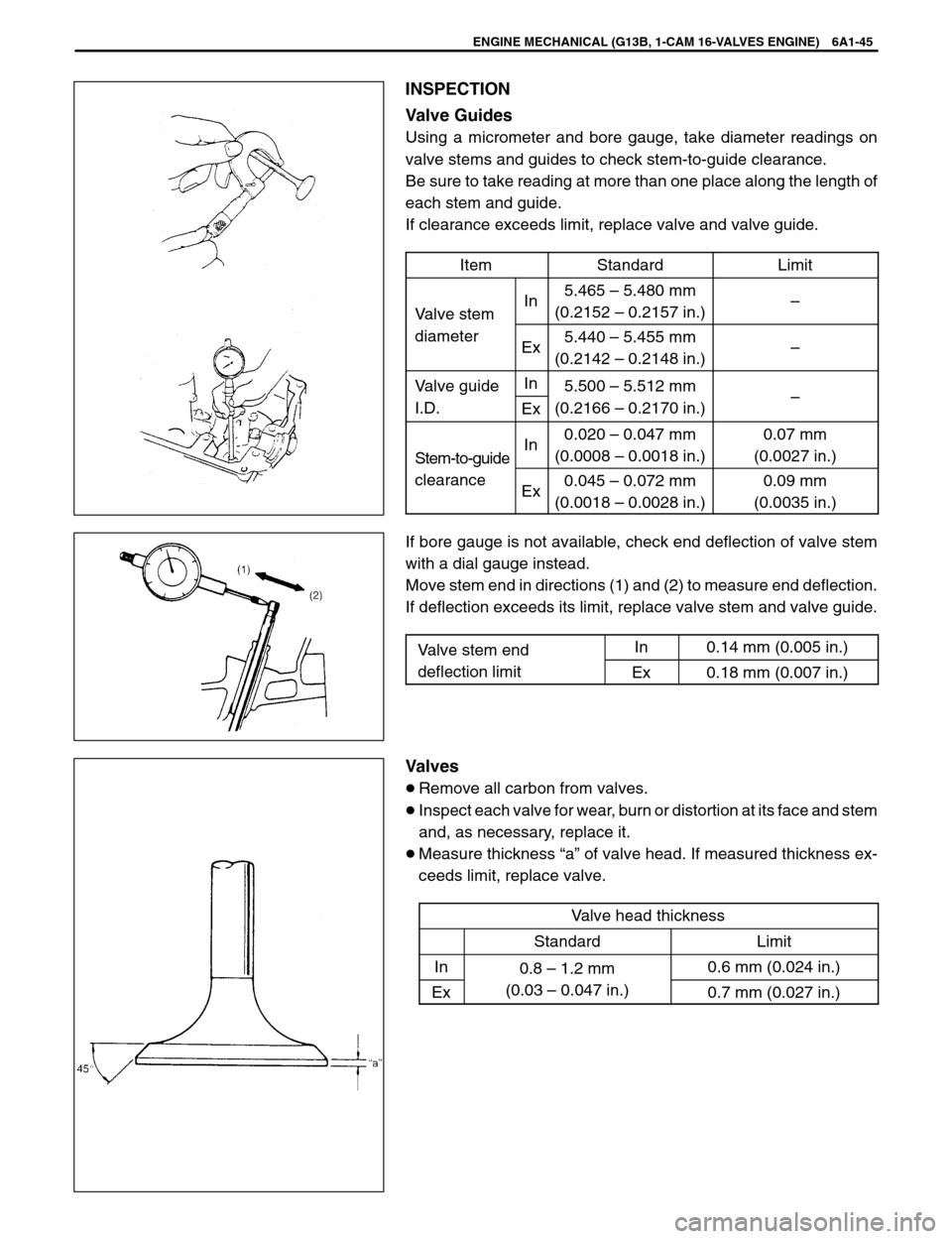
Valve Guides
Using a micrometer and bore gauge, take diameter readings on
valve stems and guides to check stem-to-guide clearance.
Be sure to take reading at more than one place along the length of
each stem and guide.
If clearance exceeds limit, replace valve and valve guide.
Item
StandardLimit
Valve stemIn5.465 – 5.480 mm
(0.2152 – 0.2157 in.)–
diameterEx5.440 – 5.455 mm
(0.2142 – 0.2148 in.)–
Valve guideIn5.500 – 5.512 mmg
I.D.Ex(0.2166 – 0.2170 in.)–
Stem-to-guideIn0.020 – 0.047 mm
(0.0008 – 0.0018 in.)0.07 mm
(0.0027 in.)
g
clearanceEx0.045 – 0.072 mm
(0.0018 – 0.0028 in.)0.09 mm
(0.0035 in.)
If bore gauge is not available, check end deflection of valve stem
with a dial gauge instead.
Move stem end in directions (1) and (2) to measure end deflection.
If deflection exceeds its limit, replace valve stem and valve guide.
Valve stem end
In0.14 mm (0.005 in.)
deflection limitEx0.18 mm (0.007 in.)
Valves
�Remove all carbon from valves.
�Inspect each valve for wear, burn or distortion at its face and stem
and, as necessary, replace it.
�Measure thickness “a” of valve head. If measured thickness ex-
ceeds limit, replace valve.
Valve head thickness
StandardLimit
In0.8 – 1.2 mm0.6 mm (0.024 in.)
Ex(0.03 – 0.047 in.)0.7 mm (0.027 in.)
Page 342 of 557
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-47
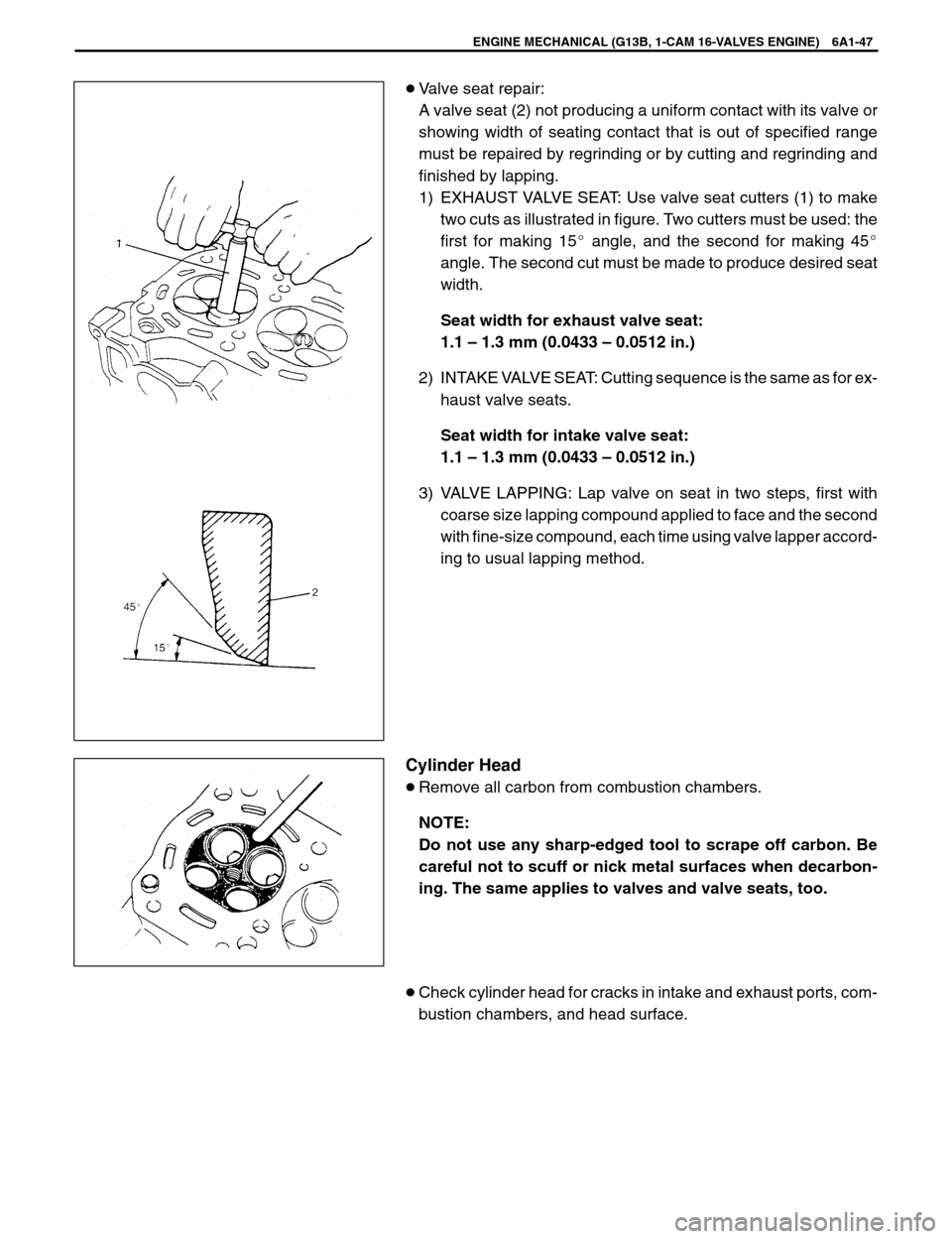
�Valve seat repair:
A valve seat (2) not producing a uniform contact with its valve or
showing width of seating contact that is out of specified range
must be repaired by regrinding or by cutting and regrinding and
finished by lapping.
1) EXHAUST VALVE SEAT: Use valve seat cutters (1) to make
two cuts as illustrated in figure. Two cutters must be used: the
first for making 15� angle, and the second for making 45�
angle. The second cut must be made to produce desired seat
width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat:
1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
2) INTAKE VALVE SEAT: Cutting sequence is the same as for ex-
haust valve seats.
Seat width for intake valve seat:
1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
3) VALVE LAPPING: Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with
coarse size lapping compound applied to face and the second
with fine-size compound, each time using valve lapper accord-
ing to usual lapping method.
Cylinder Head
�Remove all carbon from combustion chambers.
NOTE:
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to scrape off carbon. Be
careful not to scuff or nick metal surfaces when decarbon-
ing. The same applies to valves and valve seats, too.
�Check cylinder head for cracks in intake and exhaust ports, com-
bustion chambers, and head surface.
Page 343 of 557
6A1-48 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
�Flatness of gasketed surface:
Using a straightedge and thickness gauge, check surface at a to-
tal of 6 locations. If distortion limit, given below, is exceeded, cor-
rect gasketed surface with a surface plate and abrasive paper of
about #400 (Waterproof silicon carbide abrasive paper): place
paper on and over surface plate, and rub gasketed surface
against paper to grind off high spots. Should this fail to reduce
thickness gauge readings to within limit, replace cylinder head.
Leakage of combustion gases from this gasketed joint is often
due to warped gasketed surface: such leakage results in reduced
power output.
Limit of distortion: 0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
�Distortion of manifold seating faces:
Check seating faces of cylinder head for manifolds, using a
straightedge and thickness gauge, in order to determine whether
these faces should be corrected or cylinder head replaced.
Limit of distortion: 0.10 mm (0.004 in.)
Page 344 of 557
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-49
Valve Springs
�Referring to data given below, check to be sure that each spring
is in sound condition, free of any evidence of breakage or weak-
ening. Remember, weakened valve springs can cause chatter,
not to mention possibility of reducing power output due to gas
leakage caused by decreased seating pressure.
Item
StandardLimit
Valve spring
free length36.83 mm
(1.4500 in.)35.67 mm
(1.4043 in.)
Valve spring
preload10.7 – 12.5 kg for
31.5 mm (23.6 –
27.5 lb / 1.24 in.)9.3 kg for 31.5 mm
(20.5 lb / 1.24 in.)
�Spring squareness:
Use a square and surface plate to check each spring for square-
ness in terms of clearance between end of valve spring and
square. Valve springs found to exhibit a larger clearance than limit
given below must be replaced.
Valve spring squareness limit: 1.6 mm (0.063 in.)