2000 SUZUKI SWIFT fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 11 of 698

0A-8 GENERAL INFORMATION
Make sure that all parts used in reassembly are perfectly
clean.
When use of a certain type of lubricant, bond or sealant
is specified, be sure to use the specified type.
“A” : Sealant 99000-31150
Be sure to use special tools when instructed.
Special Tool
(A) : 09917-98221
(B) : 09916-58210
When disconnecting vacuum hoses, attach a tag
describing the correct installation positions so that the
hoses can be reinstalled correctly.
After servicing fuel, oil, coolant, vacuum, exhaust or
brake systems, check all lines related to the system for
leaks.
For vehicles equipped with fuel injection systems, never
disconnect the fuel line between the fuel pump and
injector without first releasing the fuel pressure, or fuel
can be sprayed out under pressure.
When performing a work that produces a heat exceeding
80°C (176°F) in the vicinity of the electrical parts, remove
the heat sensitive electrical part(s) beforehand.
Page 40 of 698

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION 0B-11
4) Install air cleaner filter fitting protrusion (1) of filter into
groove (2) of case and clamp upper case securely.
REPLACEMENT
Replace air cleaner filter with new one according to steps 1), 2)
and 4) of inspection procedure.
FUEL LINES AND CONNECTIONS
INSPECTION
Visually inspect fuel lines and connections for evidence of fuel
leakage, hose cracking and damage. Make sure all clamps are
secure.
Repair leaky joints, if any.
Replace hoses that are suspected of being cracked.
FUEL FILTER
REPLACEMENT
Fuel filter (1) is installed in fuel pump assembly (2) in fuel tank.
Replace fuel filter with new one, referring to “FUEL PUMP
ASSEMBLY” in Section 6C for proper procedure.
WARNING:
This work must be performed in a well ventilated area
and away from any open flames (such as gas hot water
heaters).
Page 372 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-3
DTC P1500 ENGINE STARTER SIGNAL
CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION ........................... 6-110
DTC P1510 ECM BACK-UP POWER
SUPPLY MALFUNCTION ........................... 6-111
DTC P1600 SERIAL COMMUNICATION
PROBLEM BETWEEN ECM AND TCM...... 6-112
DTC P1717 A/T DRIVE RANGE (PARK/
NEUTRAL POSITION) SIGNAL CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION .......................................... 6-114
TABLE B-1 FUEL INJECTOR CIRCUIT
CHECK ........................................................ 6-117
TABLE B-2 FUEL PUMP AND ITS CIRCUIT CHECK ....................................................... 6-118
TABLE B-3 FUEL PRESSURE CHECK ..... 6-120
TABLE B-4 IDLE AIR CONTROL
SYSTEM CHECK........................................ 6-122
TABLE B-5 A/C SIGNAL CIRCUITS
CHECK (VEHICLE WITH A/C) ................... 6-124
TABLE B-6 ELECTRIC LOAD SIGNAL
CIRCUIT CHECK ........................................ 6-126
TABLE B-7 RADIATOR FAN CONTROL
SYSTEM CHECK........................................ 6-128
SPECIAL TOOL ............................................. 6-130
Page 374 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-5
PRECAUTION ON FUEL SYSTEM SERVICE
Work must be done with no smoking, in a well-ventilated
area and away from any open flames.
As fuel feed line (between fuel pump and fuel delivery pipe)
is still under high fuel pressure even after engine was
stopped, loosening or disconnecting fuel feed line directly
may cause dangerous spout of fuel to occur where loosened
or disconnected.
Before loosening or disconnecting fuel feed line, make sure
to release fuel pressure according to “FUEL PRESSURE
RELIEF PROCEDURE”. A small amount of fuel may be
released after the fuel line is disconnected. In order to
reduce the chance of personal injury, cover the fitting to be
disconnected with a shop cloth. Put that cloth in an approved
container when disconnection is completed.
Never run engine with fuel pump relay disconnected when
engine and exhaust system are hot.
Fuel or fuel vapor hose connection varies with each type of
pipe. When reconnecting fuel or fuel vapor hose, be sure to
connect and clamp each hose correctly referring to figure
Hose Connection.
After connecting, make sure that it has no twist or kink.
When installing injector or fuel delivery pipe, lubricate its O-
ring with spindle oil or gasoline.
When connecting fuel pipe flare nut, first tighten flare nut by
hand and then tighten it to specified torque.
[A] : With short pipe, fit hose as far as it reaches pipe joint as shown.
[B] : With following type pipe, fit hose as far as its peripheral projection as shown.
[C] : With bent pipe, fit hose as its bent part as shown or till pipe is about 20 to 30 mm
(0.79–1.18 in.) into the hose.
[D] : With straight pipe, fit hose till pipe is, about 20 to 30 mm (0.79–1.18 in.) into the
hose.
1. Hose
2. Pipe
3. Clamp
4. Clamp securely at a position 3 to 7 mm (0.1 2–0.27 in.) from hose end.
5. 20 to 30 mm (0.79–1.18 in.)
Page 375 of 698

6-6 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF PROCEDURE
After making sure that engine is cold, release fuel pressure as fol-
lows.
1) Place transmission gear shift lever in “Neutral” (Shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T model), set parking brake, and
block drive wheels.
2) Remove relay box cover.
3) Disconnect fuel pump relay (1) from relay box.
4) Remove fuel filler cap to release fuel vapor pressure in fuel
tank and then reinstall it.
5) Start engine and run it till it stops for lack of fuel. Repeat
cranking engine 2-3 times for about 3 seconds each time to
dissipate fuel pressure in lines. Fuel connections are now
safe for servicing.
6) Upon completion of servicing, connect fuel pump relay (1) to
relay box and install relay box cover.
FUEL LEAKAGE CHECK PROCEDURE
After performing any service on fuel system, check to make sure
that there are no fuel leakages as follows.
1) Turn ON ignition switch for 3 seconds (to operate fuel pump)
and then turn it OFF.
Repeat this (ON and OFF) 3 or 4 times and apply fuel pres-
sure to fuel line. (till fuel pressure is felt by hand placed on
fuel feed hose.)
2) In this state, check to see that there are no fuel leakages
from any part of fuel system.
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ECM.
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ECM. ECM has an On-Board Diagnos-
tic system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of those parts that influence the engine
exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the outline of “On-
Board Diagnostic System” and each item in “Precaution in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute diagnosis accord-
ing to “ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE”.
There is a close relationship between the engine mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system, exhaust
system, etc. and the engine and emission control system in their structure and operation. In case of an engine
trouble, even when the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed according to
this flow table.CAUTION:
This work must not be done when engine is hot. If done
so, it may cause adverse effect to catalyst.
1
Page 391 of 698
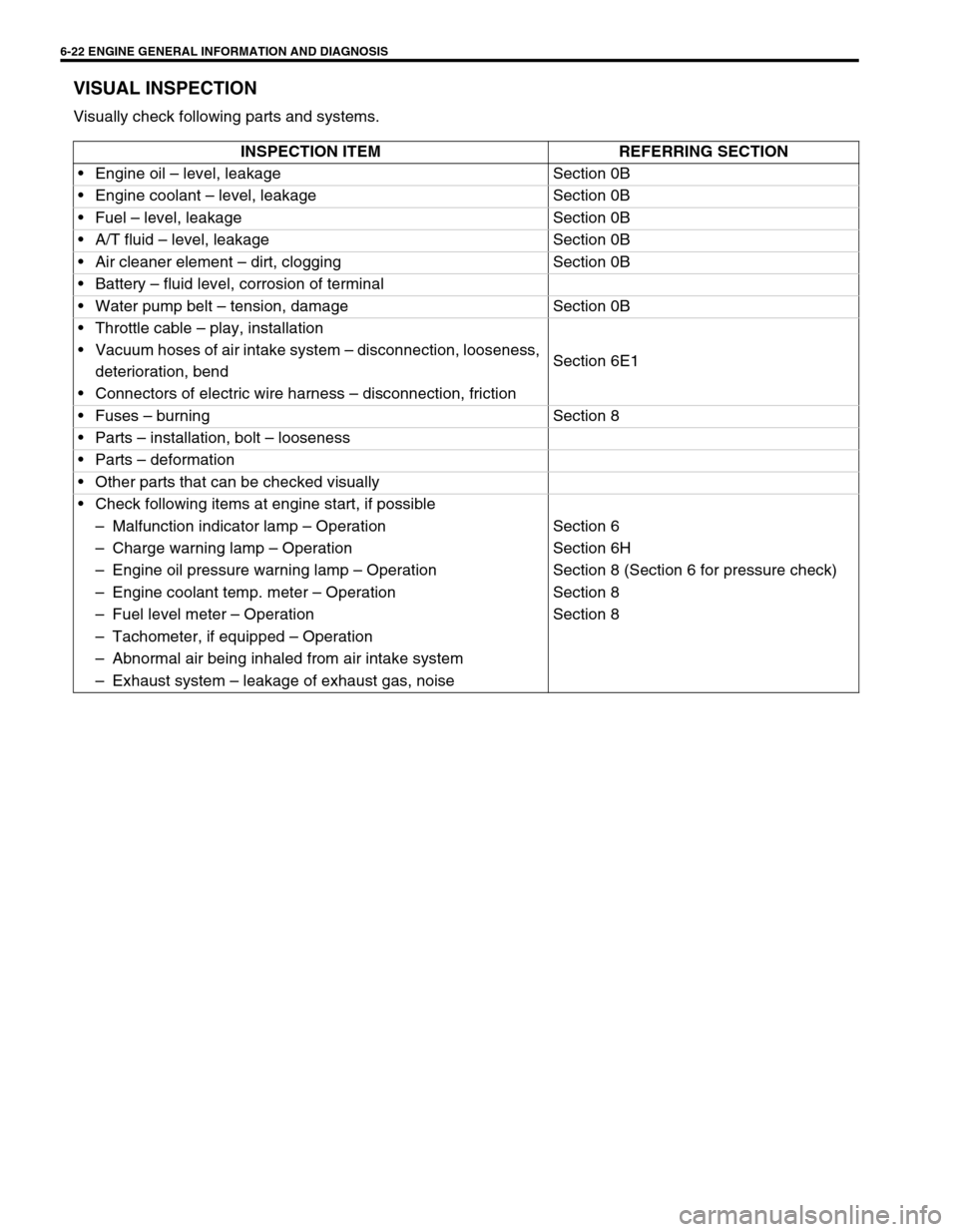
6-22 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
VISUAL INSPECTION
Visually check following parts and systems.
INSPECTION ITEM REFERRING SECTION
Engine oil – level, leakage Section 0B
Engine coolant – level, leakage Section 0B
Fuel – level, leakage Section 0B
A/T fluid – level, leakage Section 0B
Air cleaner element – dirt, clogging Section 0B
Battery – fluid level, corrosion of terminal
Water pump belt – tension, damage Section 0B
Throttle cable – play, installation
Section 6E1 Vacuum hoses of air intake system – disconnection, looseness,
deterioration, bend
Connectors of electric wire harness – disconnection, friction
Fuses – burning Section 8
Parts – installation, bolt – looseness
Parts – deformation
Other parts that can be checked visually
Check following items at engine start, if possible
–Malfunction indicator lamp – Operation Section 6
–Charge warning lamp – Operation Section 6H
–Engine oil pressure warning lamp – Operation Section 8 (Section 6 for pressure check)
–Engine coolant temp. meter – Operation Section 8
–Fuel level meter – Operation Section 8
–Tachometer, if equipped – Operation
–Abnormal air being inhaled from air intake system
–Exhaust system – leakage of exhaust gas, noise
Page 392 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-23
ENGINE BASIC INSPECTION
This check is very important for troubleshooting when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in visual inspection.
Follow the flow table carefully.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check battery voltage.
Is it 11 V or more?Go to Step 3. Charge or replace battery.
3 Is engine cranked? Go to Step 4. Go to “DIAGNOSIS” in
Section 6G.
4 Does engine start? Go to Step 5. Go to Step 7.
5 Check idle speed as follows :
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temp.
2) Shift transmission to neutral position for M/T
(“P” position for A/T).
3) All of electrical loads are switched off.
4) Check engine idle speed with scan tool.
See Fig. 1.
Is it 650 – 750 r/min (700 – 800 r/min. for A/T
vehicle)?Go to Step 6. Go to “ENGINE DIAGNO-
SIS TABLE”.
6 Check ignition timing as follows :
1) When SUZUKI scan tool is not available,
disconnect scan tool from DLC and connect
test switch terminal of monitor connector to
ground. See Fig. 2.
When using SUZUKI scan tool, select
“MISC” mode on SUZUKI scan tool and fix
ignition timing to initial one. See Fig. 3.
2) Using timing light (1), check initial ignition
timing. See Fig. 4.
Is it 5° ± 3° BTDC at specified idle speed?Go to “ENGINE DIAGNO-
SIS TABLE”.Check ignition control
related parts referring to
Section 6F1.
7 Is immobilizer control system equipped? Go to Step 8. Go to Step 9.
8 Check immobilizer system malfunction as fol-
lows.
1) Check immobilizer indicator lamp or MIL
(malfunction indicator lamp) for flashing.
Is it flashing when ignition switch is turned to
ON position?Go to “DIAGNOSIS” in
Section 8G.Go to Step 9.
9 Check fuel supply as follows :
1) Check to make sure that enough fuel is
filled in fuel tank.
2) Turn ON ignition switch for 2 seconds and
then OFF. See Fig. 5.
Is fuel pressure felt from fuel feed hose (1)
when ignition switch is turned ON?Go to Step 11. Go to Step 10.
10 Check fuel pump for operating.
Was fuel pump operating sound heard from fuel
filler for about 10 seconds after ignition switch
ON and stop?Go to “DIAG. FLOW
TABLE B-3”.Go to “DIAG. FLOW
TABLE B-2”.
Page 395 of 698

6-26 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS TABLE
Perform troubleshooting referring to following table when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has
been found in visual inspection and engine basic inspection previously.
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Hard Starting
(Engine cranks OK) Faulty spark plug Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Leaky high-tension cord High-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Loose connection or disconnection of high-
tension cords or lead wiresHigh-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Faulty ignition coil Ignition coil in Section 6F1.
Dirty or clogged fuel hose or pipe Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Malfunctioning fuel pump Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Air inhaling from intake manifold gasket or
throttle body gasket
Faulty idle air control system Diagnostic Flow Table B-4.
Faulty ECT sensor or MAP sensor ECT sensor or MAP sensor in Section
6E1.
Faulty ECM
Hard Starting
(Engine cranks OK) Poor spark plug tightening or faulty gasket Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Compression leak from valve seat Valves inspection in Section 6A1.
Sticky valve stem Valves inspection in Section 6A1.
Weak or damaged valve springs Valve springs inspection in Section
6A1.
Compression leak at cylinder head gasket Cylinder head inspection in Section
6A1.
Sticking or damaged piston ring Cylinders, pistons and piston rings
inspection in Section 6A1.
Worn piston, ring or cylinder Cylinders, pistons and piston rings
inspection in Section 6A1.
Malfunctioning PCV valve PCV system in Section 6E1.
Low compression Compression check in Section 6A1.
Low oil pressure
Improper oil viscosity Engine oil and oil filter change in Sec-
tion 0B.
Malfunctioning oil pressure switch Oil pressure switch inspection in Sec-
tion 8.
Clogged oil strainer Oil pan and oil pump strainer cleaning
in Section 6A1.
Functional deterioration of oil pump Oil pump in Section 6A1.
Worn oil pump relief valve Oil pump in Section 6A1.
Excessive clearance in various sliding parts