2000 SUZUKI SWIFT Electric system
[x] Cancel search: Electric systemPage 640 of 698

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E1-19
5) Disconnect electric connector from TP sensor (1) and IAC
valve (2).
6) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
7) Disconnect engine coolant hoses from throttle body.
DISASSEMBLY
Remove TP sensor and IAC valve from throttle body.
CLEANING
Clean throttle body bore (1) and idle air passage (2) by blowing
compressed air.
REASSEMBLY
1) Install IAC valve to throttle body referring to “IAC valve Instal-
lation” section.
2) Install TP sensor to throttle body referring to “TP sensor
Installation” section.
INSTALLATION
1) Clean mating surfaces and install throttle body gasket to
intake manifold.
Use new gasket.
2) Connect engine coolant hoses.
NOTE:
While disassembling and assembling throttle body, use
special care not to deform levers on throttle valve shaft
or cause damage to any other parts.
NOTE:
TP sensor, idle air control valve or other components
containing rubber must not be placed in a solvent or
cleaner bath. A chemical reaction will cause these parts
to swell, harden or get distorted.
Page 655 of 698
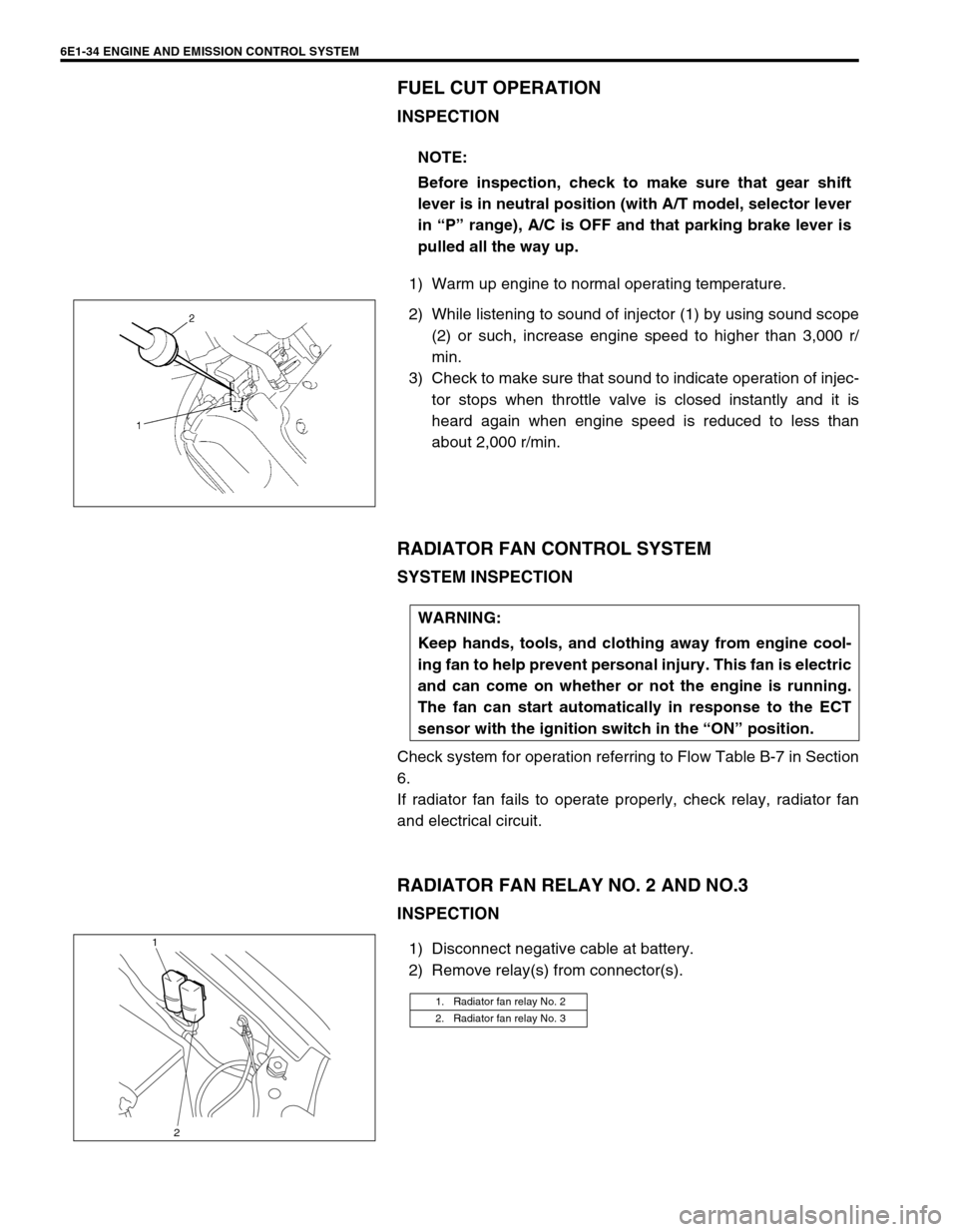
6E1-34 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
FUEL CUT OPERATION
INSPECTION
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) While listening to sound of injector (1) by using sound scope
(2) or such, increase engine speed to higher than 3,000 r/
min.
3) Check to make sure that sound to indicate operation of injec-
tor stops when throttle valve is closed instantly and it is
heard again when engine speed is reduced to less than
about 2,000 r/min.
RADIATOR FAN CONTROL SYSTEM
SYSTEM INSPECTION
Check system for operation referring to Flow Table B-7 in Section
6.
If radiator fan fails to operate properly, check relay, radiator fan
and electrical circuit.
RADIATOR FAN RELAY NO. 2 AND NO.3
INSPECTION
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Remove relay(s) from connector(s).NOTE:
Before inspection, check to make sure that gear shift
lever is in neutral position (with A/T model, selector lever
in “P” range), A/C is OFF and that parking brake lever is
pulled all the way up.
WARNING:
Keep hands, tools, and clothing away from engine cool-
ing fan to help prevent personal injury. This fan is electric
and can come on whether or not the engine is running.
The fan can start automatically in response to the ECT
sensor with the ignition switch in the “ON” position.
1. Radiator fan relay No. 2
2. Radiator fan relay No. 3
1
2
Page 664 of 698
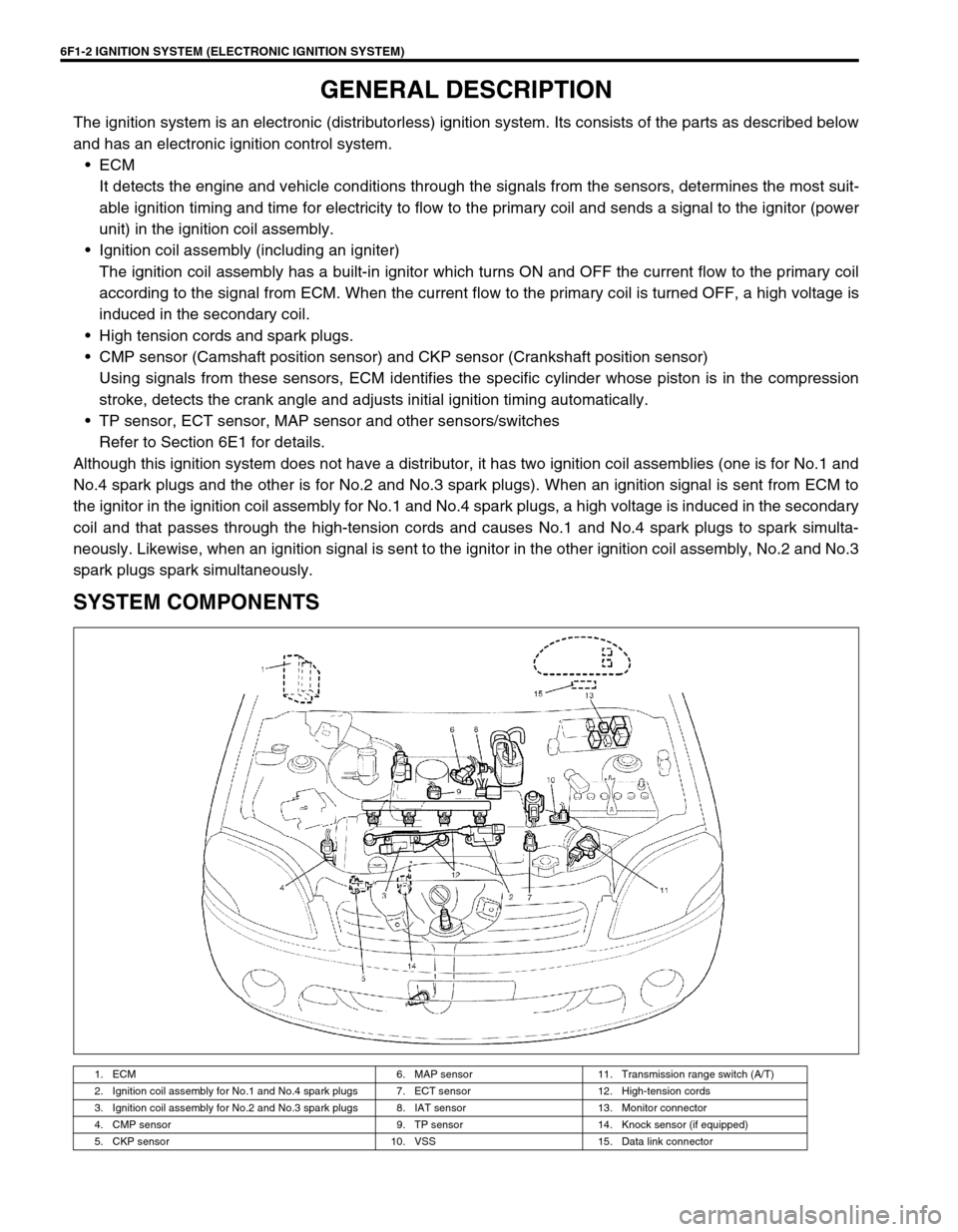
6F1-2 IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ignition system is an electronic (distributorless) ignition system. Its consists of the parts as described below
and has an electronic ignition control system.
ECM
It detects the engine and vehicle conditions through the signals from the sensors, determines the most suit-
able ignition timing and time for electricity to flow to the primary coil and sends a signal to the ignitor (power
unit) in the ignition coil assembly.
Ignition coil assembly (including an igniter)
The ignition coil assembly has a built-in ignitor which turns ON and OFF the current flow to the primary coil
according to the signal from ECM. When the current flow to the primary coil is turned OFF, a high voltage is
induced in the secondary coil.
High tension cords and spark plugs.
CMP sensor (Camshaft position sensor) and CKP sensor (Crankshaft position sensor)
Using signals from these sensors, ECM identifies the specific cylinder whose piston is in the compression
stroke, detects the crank angle and adjusts initial ignition timing automatically.
TP sensor, ECT sensor, MAP sensor and other sensors/switches
Refer to Section 6E1 for details.
Although this ignition system does not have a distributor, it has two ignition coil assemblies (one is for No.1 and
No.4 spark plugs and the other is for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs). When an ignition signal is sent from ECM to
the ignitor in the ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs, a high voltage is induced in the secondary
coil and that passes through the high-tension cords and causes No.1 and No.4 spark plugs to spark simulta-
neously. Likewise, when an ignition signal is sent to the ignitor in the other ignition coil assembly, No.2 and No.3
spark plugs spark simultaneously.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1. ECM 6. MAP sensor 11. Transmission range switch (A/T)
2. Ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs 7. ECT sensor 12. High-tension cords
3. Ignition coil assembly for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs 8. IAT sensor 13. Monitor connector
4. CMP sensor 9. TP sensor 14. Knock sensor (if equipped)
5. CKP sensor 10. VSS 15. Data link connector
Page 665 of 698
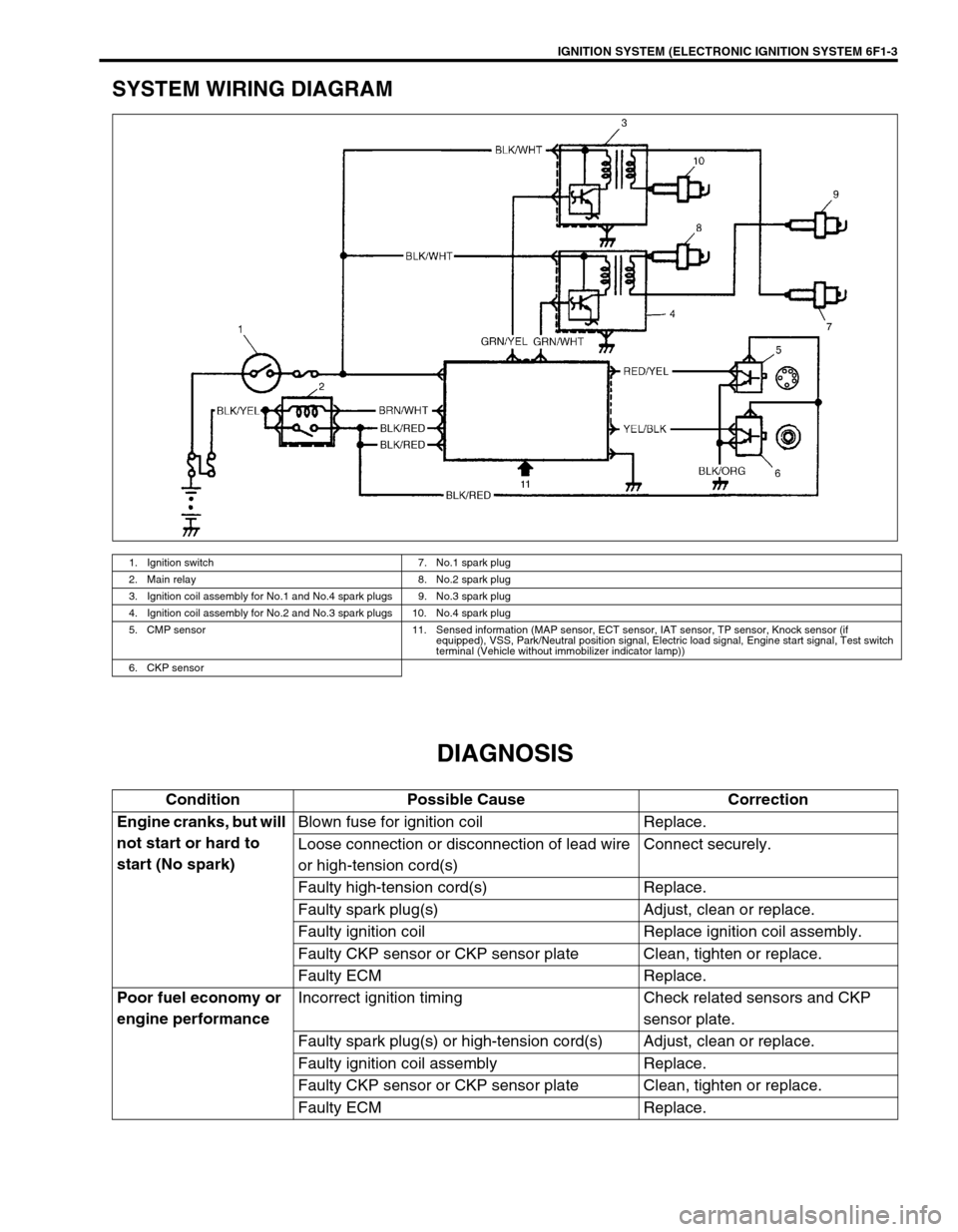
IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM 6F1-3
SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAM
DIAGNOSIS
1. Ignition switch 7. No.1 spark plug
2. Main relay 8. No.2 spark plug
3. Ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs 9. No.3 spark plug
4. Ignition coil assembly for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs 10. No.4 spark plug
5. CMP sensor 11. Sensed information (MAP sensor, ECT sensor, IAT sensor, TP sensor, Knock sensor (if
equipped), VSS, Park/Neutral position signal, Electric load signal, Engine start signal, Test switch
terminal (Vehicle without immobilizer indicator lamp))
6. CKP sensor
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Engine cranks, but will
not start or hard to
start (No spark)Blown fuse for ignition coil Replace.
Loose connection or disconnection of lead wire
or high-tension cord(s)Connect securely.
Faulty high-tension cord(s) Replace.
Faulty spark plug(s) Adjust, clean or replace.
Faulty ignition coil Replace ignition coil assembly.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
Poor fuel economy or
engine performanceIncorrect ignition timing Check related sensors and CKP
sensor plate.
Faulty spark plug(s) or high-tension cord(s) Adjust, clean or replace.
Faulty ignition coil assembly Replace.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
Page 666 of 698
6F1-4 IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
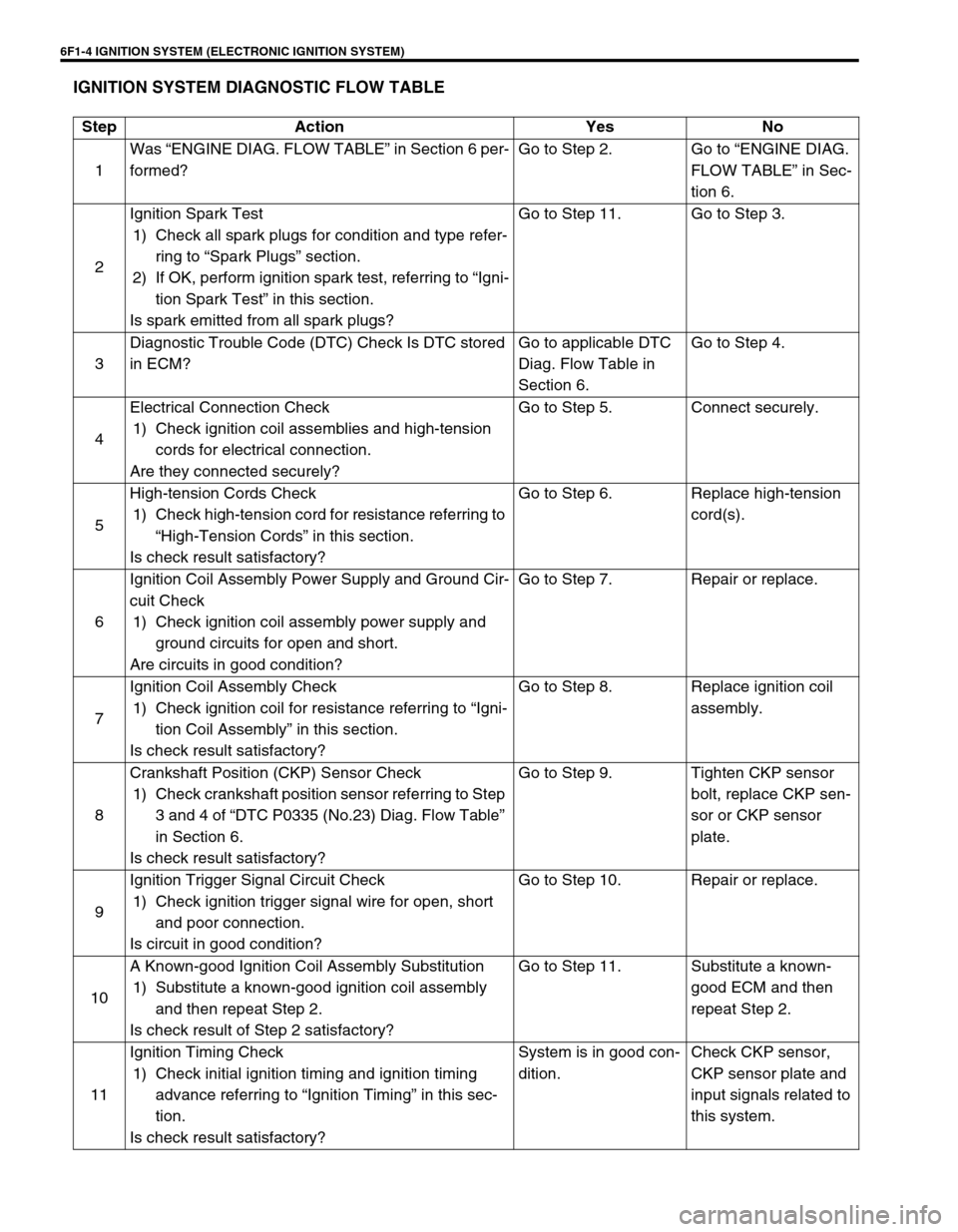
IGNITION SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” in Section 6 per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE” in Sec-
tion 6.
2Ignition Spark Test
1) Check all spark plugs for condition and type refer-
ring to “Spark Plugs” section.
2) If OK, perform ignition spark test, referring to “Igni-
tion Spark Test” in this section.
Is spark emitted from all spark plugs?Go to Step 11. Go to Step 3.
3Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check Is DTC stored
in ECM?Go to applicable DTC
Diag. Flow Table in
Section 6.Go to Step 4.
4Electrical Connection Check
1) Check ignition coil assemblies and high-tension
cords for electrical connection.
Are they connected securely?Go to Step 5. Connect securely.
5High-tension Cords Check
1) Check high-tension cord for resistance referring to
“High-Tension Cords” in this section.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 6. Replace high-tension
cord(s).
6Ignition Coil Assembly Power Supply and Ground Cir-
cuit Check
1) Check ignition coil assembly power supply and
ground circuits for open and short.
Are circuits in good condition?Go to Step 7. Repair or replace.
7Ignition Coil Assembly Check
1) Check ignition coil for resistance referring to “Igni-
tion Coil Assembly” in this section.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 8. Replace ignition coil
assembly.
8Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Check
1) Check crankshaft position sensor referring to Step
3 and 4 of “DTC P0335 (No.23) Diag. Flow Table”
in Section 6.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 9. Tighten CKP sensor
bolt, replace CKP sen-
sor or CKP sensor
plate.
9Ignition Trigger Signal Circuit Check
1) Check ignition trigger signal wire for open, short
and poor connection.
Is circuit in good condition?Go to Step 10. Repair or replace.
10A Known-good Ignition Coil Assembly Substitution
1) Substitute a known-good ignition coil assembly
and then repeat Step 2.
Is check result of Step 2 satisfactory?Go to Step 11. Substitute a known-
good ECM and then
repeat Step 2.
11Ignition Timing Check
1) Check initial ignition timing and ignition timing
advance referring to “Ignition Timing” in this sec-
tion.
Is check result satisfactory?System is in good con-
dition.Check CKP sensor,
CKP sensor plate and
input signals related to
this system.
Page 670 of 698

6F1-8 IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
IGNITION TIMING
INSPECTION
1) When using SUZUKI scan tool, connect SUZUKI scan tool to
DLC with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A) : 09931-76011 (SUZUKI scan tool)
(B) : Mass storage cartridge
(C) : 09931-76030 (16/14 pin DLC cable)
2) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating tempera-
ture.
3) Make sure that all of electrical loads except ignition are
switched off.
4) Check to be sure that idle speed is within specification.
(Refer to Section 6E1)
5) Fix ignition timing to initial one as follows.
Select “MISC” mode on SUZUKI scan tool and fix ignition
timing to initial one.
If scan tool is not available (vehicle without immobilizer indi-
cator lamp), connect D and E terminals of monitor connector
(1) by using service wire so that ignition timing is fixed on ini-
tial one.
6) Using timing light (1), check that ignition timing is within
specification.
Initial ignition timing (test switch terminal grounded or
fixed with SUZUKI scan tool)
: 5
± 3° BTDC at idle speed
Ignition order
: 1-3-4-2 NOTE:
Ignition timing is not adjustable. If ignition timing is
out of specification, check system related parts.
Before starting engine, place transmission gear shift
lever in “Neutral” (shift selector lever to “P” range for
A/T model), and set parking brake.
(C)
(A)
(B)
D
E1
Page 682 of 698

6H-2 CHARGING SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
BATTERY
The battery has three major functions in the electrical system.
It is a source of electrical energy for cranking the engine.
It acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system.
It can, for a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load exceeds the output of the generator.
CARRIER AND HOLD-DOWN
The battery carrier should be in good condition so that it will support the battery securely and keep it level.
Before installing the battery, the battery carrier and hold-down clamp should be clean and free from corrosion
and make certain there are no parts in carrier.
To prevent the battery from shaking in its carrier, the hold-down bolts should be tight enough but not over-tight-
ened.
ELECTROLYTE FREEZING
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on its specific gravity. Since freezing may ruin a battery, it should be
protected against freezing by keeping it in a fully charged condition. If a battery is frozen accidentally, it should
not be charged until it is warmed.
SULFATION
If the battery is allowed to stand for a long period in discharged condition, the lead sulfate becomes converted
into a hard, crystalline substance, which will not easily turn back to the active material again during the subse-
quent recharging. “Sulfation” means the result as well as the process of that reaction. Such a battery can be
revived by very slow charging and may be restored to usable condition but its capacity is lower than before.
BUILT-IN INDICATOR (IF EQUIPPED)
The battery has a built-in temperature compensated indicator in the top of the battery. This indicator is to be
used with the following diagnostic procedure. When checking the indicator, make sure that the battery has a
clean top. A light may be needed in some poorly-lit areas.
Three types of indication available under normal operation are as
follows.
Green Dot
Battery is sufficiently charged for testing.
Dark
Battery must be charged before testing.
If there is a cranking complaint, battery should be tested as
described in Diagnosis section. Charging and electrical sys-
tems should also be checked at this time.
Clear or Light Yellow
This means that fluid level is below the bottom of hydrome-
ter. Its possible cause is excessive or prolonged charging, a
broken case, excessive tipping or normal battery deteriora-
tion. When the battery is found in such condition, it is possi-
ble that high charging voltage is caused by the faulty
charging system and therefore, charging and electrical sys-
tems need to be checked. If there is a trouble in cranking
and its cause lies in the battery, it should be replaced.
Page 683 of 698

CHARGING SYSTEM 6H-3
CARE OF BATTERY
1) The battery is a very reliable component, but needs periodical attentions.
Keep the battery carrier clean
Prevent rust formation on the terminal posts
Keep the electrolyte up to the upper level uniformly in all cells.
When keeping battery on vehicle over a long period of time, follow instructions given below.
–Weekly, start the engine and run it until it reaches normal operating temperature with engine speed of
2000 to 3000 rpm. Make sure all electric switches are off before storing the vehicle.
–Recharge the battery twice a month to prevent it from discharging excessively. This is especially impor-
tant when ambient temperature is low.
The battery discharges even when it is not used, while vehicles are being stored. Battery electrolyte can
freeze and battery case can crack at cold ambient condition if battery is not properly charged.
2) Keep the battery cable connections clean.
The cable connections, particularly at the positive (+) terminal post, tend to become corroded. The product
of corrosion, or rust, on the mating faces of conductors resists the flow of current.
Clean the terminals and fittings periodically to ensure good metal-to-metal contact, and grease the connec-
tions after each cleaning to protect them against rusting.
3) Be always in the know as to the state of charge of the battery. The simplest way to tell the state of charge is
to carry out a hydrometer test. The hydrometer is an instrument for measuring the specific gravity (S.G.) of
the battery electrolyte. The S.G. of the electrolyte is indicative of the state of charge. Refer to “DIAGNOSIS”
of BATTERY in this section. WARNING:
Never expose battery to open flame or electric spark because of battery generate gas which is flam-
mable and explosive.
Do not allow battery fluid to contact eyes, skin, fabrics, or painted surfaces as fluid is a corrosive
acid. Flush any contacted area with water immediately and thoroughly.
Batteries should always be kept out of reach of children.