Page 483 of 698

6-114 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1717 A/T DRIVE RANGE (PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION) SIGNAL CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Start engine and shift selector lever to “D” range.
4) Increase vehicle speed to higher than 20 mph, 32 km/h and then stop vehicle.
5) Repeat above step 4) 9 times.
6) Shift selector lever to “2” range and repeat above step 4) and 5).
7) Shift selector lever to “L” range and repeat above step 4) and 5).
8) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
1. From ignition switch 2. Transmission range switch
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
TCMECMIG1
12V P
R
N
D
2
L
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
IG11
C44-8
REDGRN/ORN1
2G02-6 [B] C41-14 [A]
C41-15 [A]
G02-2 [B] GRN RED [B]LT BLU [A]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
“D” range signal not inputted (Park/Neutral position
signal inputted) to ECM while vehicle running
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitor-
ing.“LT BLU” circuit open
Transmission range switch malfunction
“R”, “D”, “2” or “L” range signal circuit open
TCM power or ground circuit open
TCM malfunction
ECM malfunction
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
Page 484 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-115
INSPECTION
Fig. 1 for Step 3Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Is SUZUKI scan tool available? Go to Step 3. Go to Step 4.
3 Check PNP Signal (“D” range signal).
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with igni-
tion switch OFF. See Fig. 1.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and check PNP sig-
nal (“P/N” or “D” range) on display when
shifting selector lever to each range.
Is “D” range on display (Is 0 – 1 V indicated) no
matter which of “R”, “D”, “2” and “L” range posi-
tions selector lever may be at? See Table 1.Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM. Check for
intermittent referring to
“Intermittent and poor
connection” in Section 0A.Go to Step 5.
4 Check PNP Signal (“D” range signal).
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check voltage at terminal C41-14 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or G02-6 (Case of
TYPE B. See NOTE) of ECM connector
connected. See Fig. 2.
Is “D” range on display (Is 0 – 1 V indicated) no
matter which of “R”, “D”, “2” and “L” range posi-
tions selector lever may be at? See Table 1.Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM. Check for
intermittent referring to
“Intermittent and poor
connection” in Section 0A.Go to Step 5.
5Is “P/N range on display (Is 10 – 14 V indicated)
when selector lever is at one of “R”, “D”, “2” and
“L” range positions only?Check transmission range
switch and circuits refer-
ring to section 7B.Go to Step 6.
6 Check PNP Signal Circuit.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect TCM connectors.
3) Check for proper connection to TCM at ter-
minal C44-8.
4) If OK, then check voltage at terminal
C44-8 in TCM connector disconnected, with
ignition switch ON.
Is it 10 – 14 V? See Fig. 3“GRN/ORN” circuit open,
poor transmission range
switch connector connec-
tion, select cable malad-
justed, transmission
range sensor malad-
justed or transmission
range sensor malfunction.
If all above are OK, sub-
stitute a known-good
TCM and recheck.“LT BLU” (Case of TYPE
A. See NOTE) or “GRN
RED” (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE) circuit open or
poor C41-14 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or
G02-6 (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE) connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Page 485 of 698
6-116 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Fig. 2 for Step 4
Table 1 for Step 3 and 4
Fig. 3 for Step 6
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE)
[B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
Scan tool or voltmeter
SUZUKI SCAN TOOL VOLTAGE AT C41-14
Selector lever
position“P” and “N” range P/N range 10 – 14V
“R”, “D”, “2” and “L” range D range 0 – 1V
Page 486 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-117
TABLE B-1 FUEL INJECTOR CIRCUIT CHECK
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION
1. No.1 injector 3. No.3 injector
2. No.2 injector 4. No.4 injector
ECM
1
2
3
4
+B
C42-9
C42-21
C42-8 C42-31 BLU/YEL
BLU/WHT
BLU/RED
BLU/ORN
BLK/RED
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check Injector for operating sound.
Using sound scope, check each injector for
operating sound at engine cranking.
Do all 4 injector make operating sound?Fuel injector circuit is in
good condition.Go to Step 3.
3 Dose none of 4 injectors make operating sound
at Step 2?Go to Step 4. Check coupler connec-
tion and wire harness of
injector not making oper-
ating sound and injector
itself (Refer to Section
6E1).
4 Check power circuit of injectors for open and
short.
Is it normal?Check all 4 injectors for
resistance respectively.
If resistance is OK, substi-
tute a known-good ECM
and recheck.Power circuit open or
short.
Page 488 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-119
Fig. 1 for Step 2
Fig. 2 for Step 3
Fig. 3 for Step 44 Check Fuel Pump Relay for operation.
1) Check resistance between each two termi-
nals of fuel pump relay. See Fig.3.
Between terminals “c” and “d” : Infinity
Between terminals “a” and “b” : 56 – 146
Ω
2) Check that there is continuity between ter-
minals “c” and “d” when battery is con-
nected to terminals “a” and “b”. See Fig. 3.
Is fuel pump relay in good condition?“PNK” circuit open or poor
C41-19 connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.Replace fuel pump
relay. Step Action Yes No
Page 489 of 698
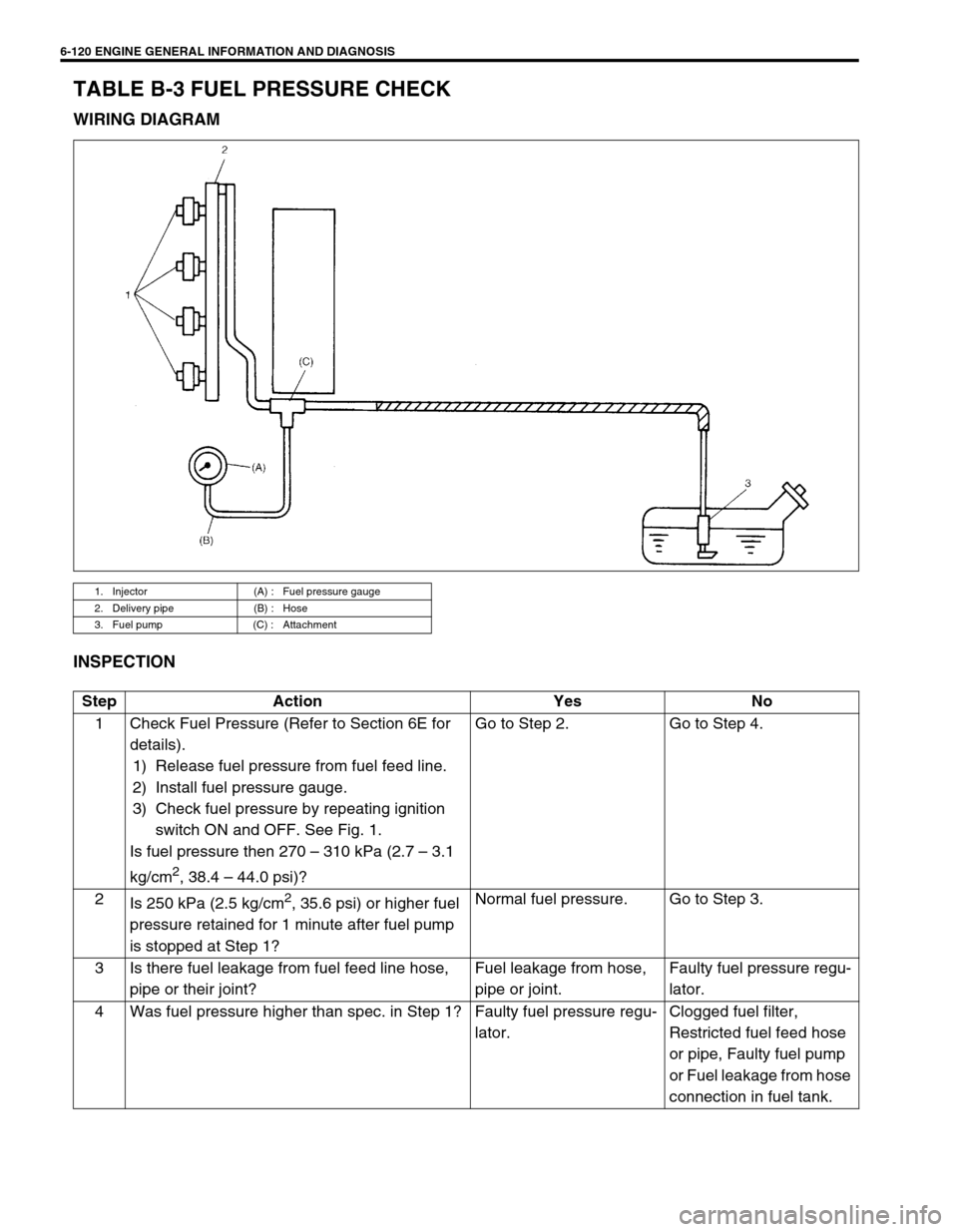
6-120 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-3 FUEL PRESSURE CHECK
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION
1. Injector (A) : Fuel pressure gauge
2. Delivery pipe (B) : Hose
3. Fuel pump (C) : Attachment
Step Action Yes No
1 Check Fuel Pressure (Refer to Section 6E for
details).
1) Release fuel pressure from fuel feed line.
2) Install fuel pressure gauge.
3) Check fuel pressure by repeating ignition
switch ON and OFF. See Fig. 1.
Is fuel pressure then 270 – 310 kPa (2.7 – 3.1
kg/cm
2, 38.4 – 44.0 psi)?Go to Step 2. Go to Step 4.
2
Is 250 kPa (2.5 kg/cm
2, 35.6 psi) or higher fuel
pressure retained for 1 minute after fuel pump
is stopped at Step 1?Normal fuel pressure. Go to Step 3.
3 Is there fuel leakage from fuel feed line hose,
pipe or their joint?Fuel leakage from hose,
pipe or joint.Faulty fuel pressure regu-
lator.
4 Was fuel pressure higher than spec. in Step 1? Faulty fuel pressure regu-
lator.Clogged fuel filter,
Restricted fuel feed hose
or pipe, Faulty fuel pump
or Fuel leakage from hose
connection in fuel tank.
Page 490 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-121
Fig. 1 for Step 1
Special tool
(A) : 09912-58441
(B) : 09912-58490
1. Fuel pressure gauge
2. 3 way joint1, (A)
2, (B)
Page 491 of 698
![SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual 6-122 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-4 IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
INSPECTION
1. IAC valve 2. Main relay 3. To TCM
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual 6-122 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-4 IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
INSPECTION
1. IAC valve 2. Main relay 3. To TCM
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is](/manual-img/20/7606/w960_7606-490.png)
6-122 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-4 IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
INSPECTION
1. IAC valve 2. Main relay 3. To TCM
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
GRN/RED
BLK/YEL
BRN/WHT
BLK/RED
BLK/RED
ECM
C41-10
C41-6
C41-5
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
3
1
2
C42-6 C41-14 [A]
G02-6 [B]
LT BLU [A]
GRN RED [B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
Step Action Yes No
1 Check engine idle speed and IAC duty referring
to “Idle Speed/IAC Duty Inspection” in Section
6E1.
Is idle speed within specification?Go to Step 2. Go to Step 4.
2 Is IAC duty within specification in Step 1? Go to Step 3. Check for followings :
Vacuum leak
EVAP canister purge con-
trol system
Clog of IAC air passage
Accessory engine load
Closed throttle position
(TP sensor)
Stuck of PCV valve
3 Is engine idle speed kept specified speed even
with headlight ON?System is in good condi-
tion.Check IAC system for
operation referring to Step
2 of DTC P0505 Diag.
Flow Table.
4 Was idle speed higher than specification in
Step 1?Go to Step 5. Go to Step 8.