1999 SUZUKI GRAND VITARA Crankshaft
[x] Cancel search: CrankshaftPage 202 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-41
C51-2-1 Fuel injector No.2
10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
C51-2-2 Fuel injector No.1
C51-2-3 – – –
C51-2-4Heater of HO2S-1 (bank 1)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
0 – 2 VAt specified idle speed after engine
warmed up
C51-2-5Heater of HO2S-1 (bank 2)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
0 – 2 VAt specified idle speed after engine
warmed up
C51-2-6 – – –
C51-2-7 Ground – –
C51-2-8 Fuel injector No.4
10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
C51-2-9 Fuel injector No.3
C51-2-10 – – –
C51-2-11 – – –
C51-2-12EGR valve (stepper motor coil 4)
(if equipped)0 – 1 V
Ignition switch ON C51-2-13EGR valve (stepper motor coil 3)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V
C51-2-14EGR valve (stepper motor coil 2)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V
C51-2-15EGR valve (stepper motor coil 1)
(if equipped)0 – 1 V
C51-2-16Heater of HO2S-2 (bank 1)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
0 – 1 VAt specified idle speed after engine
warmed up
C51-2-17Heater of HO2S-2 (bank 2)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
0 – 1 VAt specified idle speed after engine
warmed up
C51-2-18 – – –
C51-2-19Crankshaft position sensor (+)
(if equipped)––
C51-2-20Crankshaft position sensor (–)
(if equipped)––
C51-2-21 Fuel injector No.6
10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
C51-2-22 Fuel injector No.5
C51-2-23 Ignition coil assembly for No.6 – –
C51-2-24 Ignition coil assembly for No.5 – –
C51-2-25 Ignition coil assembly for No.4 – –
C51-2-26 Ignition coil assembly for No.3 – –
C51-2-27 Ignition coil assembly for No.2 – –
C51-2-28 Ignition coil assembly for No.1 – –
C51-2-29 – – –
C51-2-30Ground for CKP sensor shield wire
(if equipped)–– TERMINAL CIRCUIT NORMAL VOLTAGE CONDITION
Page 241 of 656

6-1-80 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
DTC P0300/P0301/P0302/P0303/P0304/P0305/P0306 Random Misfire/Cylinder
1 Misfire/Cylinder 2 Misfire/Cylinder 3 Misfire/Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected/Cyl-
inder 5 Misfire Detected/Cylinder 6 Misfire Detected
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
ECM (PCM) measures the angle speed of the crankshaft based on the pulse signal from the CKP sensor and
CMP sensor for each cylinder. If it detects a large change in the angle speed of the crankshaft, it concludes
occurrence of a misfire. When the number of misfire is counted by the ECM (PCM) beyond the DTC detecting
condition, it determines the cylinder where the misfire occurred and outputs it as DTC.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION AND TROUBLE AREA
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC, pending DTC and freeze frame data by using scan tool and start
engine.
3) Increase vehicle speed to speed recorded as freeze frame data (V) ± 5 km/h when detecting misfire.
4) Keep driving above vehicle speed for 5 min.
5) Stop vehicle and check DTC (or pending DTC) by using scan tool.DTC DETECTING CONDITION TROUBLE AREA
DTC P0300 :
• Misfire which causes catalyst to overheat during 200 engine
revolutions is detected at 2 or more cylinders. (MIL flashes as
long as this misfire occurs continuously.)
• Misfire which affects exhaust emission adversely during 1000
engine revolutions is detected at 2 or more cylinders (2 driving
cycle detection logic)• Ignition system
• Fuel injector and its circuit
• Fuel line pressure
• Engine compression
• Abnormal air drawn in
• EGR system
• Fuel level sensor
• Valve lash adjuster
• Valve timing DTC P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306 :
• Misfire which causes catalyst to overheat during 200 engine
revolutions is detected at 1 cylinder. (MIL flashes as long as
this misfire occurs continuously.)
• Misfire which affects exhaust emission adversely during 1000
engine revolutions is detected at 1 cylinder
(2 driving cycle detection logic)
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
NOTE:
Check to make sure that following conditions are satisfied when using this “DTC CONFIRMATION
PROCEDURE”.
Intake air temp. : – 8 – 70°C (18 – 158°F)
Engine coolant temp. : – 8°C (18°F) or higher
Altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg (75 kPa) or more)
Page 245 of 656

6-1-84 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
WIRING DIAGRAM
DTC DETECTING CONDITION AND TROUBLE AREA
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC, pending DTC and freeze frame data by using scan tool and run
engine at idle speed for 10 sec.
3) Check DTC by using scan tool.
1. CKP sensor
2. ECM (PCM)
DTC DETECTING CONDITION TROUBLE AREA
CKP sensor signal is not input while 100 pulses of
CMP sensor signal are input after engine start.CKP sensor circuit
CKP sensor
ECM (PCM)
NOTE:
Check to make sure that following condition is satisfied when using this “DTC CONFIRMATION PRO-
CEDURE”.
Intake air temp. : – 8°C (18°F) or higher
Engine coolant temp. : – 8 – 110°C (18 – 230°F)
Altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg (75 kPa) or more)
Page 249 of 656

6-1-88 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Fig. for Step 45 CMP sensor (REF) signal check :
1) With ignition switch OFF, connect CMP sensor
coupler.
2) Disconnect couplers from ignition coil assembly
and fuel injectors.
3) With ignition switch ON and crankshaft turned
slowly, check voltage between C51-1-13 and
C51-3-26 terminal.
Does voltmeter indicator deflect between 0 – 1 V
and 3 – 5.25 V 4 times while crankshaft turned two
revolutions?Go to Step 6. Faulty “YEL/GRN” wire
or CMP sensor.
If OK, substitute a
known-good ECM
(PCM) and recheck.
6 CMP sensor (POS) signal check :
1) With ignition switch ON and crankshaft turned
slowly, check voltage between C51-1-12 and
C51-3-26 terminal.
Does voltmeter indicator deflect between 0 – 1 V
and 3 – 5.25 V 6 times while crankshaft turned two
revolutions?Poor C51-1-12 and/or
C51-3-13 terminal of
ECM (PCM) coupler con-
nection.
If OK, substitute a
known-good ECM (PCM)
and recheck.Faulty “YEL/BLU” wire
or CMP sensor.
If OK, substitute a
known-good ECM
(PCM) and recheck. Step Action Yes No
1. Disconnected CMP sensor coupler
2. “BLU/BLK” wire (C09-2) terminal
3. “GRY/YEL” wire (C09-1) terminal
Page 288 of 656

ENGINE MECHANICAL (H27 ENGINE) 6A2-1
6A2
SECTION 6A2
ENGINE MECHANICAL (H27 ENGINE)
CONTENTS
On-Vehicle Service........................................6A2-2
Throttle Body and Intake Manifold .............. 6A2-2
Exhaust Manifold ......................................... 6A2-9
LH (No.1) Bank 2nd Timing Chain
and Chain Tensioner ................................. 6A2-13
Camshaft and Valve Lash Adjuster ........... 6A2-14
Valves and Cylinder Heads ....................... 6A2-17
Piston, Piston Rings, Connecting Rodsand Cylinders ............................................ 6A2-21
Unit Repair Overhaul .................................. 6A2-26
Engine Assembly ...................................... 6A2-26
Main Bearings, Crankshaft
and Cylinder Block .................................... 6A2-30
Special Tool ................................................. 6A2-36
WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
For the descriptions (items) not found in this section, refer to the same section of service manual
mentioned in the FOREWORD of this manual.
Whether following systems (parts) are used in the particular vehicle or not depends on specifica-
tions. Be sure to bear this in mind when performing service work.
–EGR valve
–Warm up three way catalytic converter
–Heated oxygen sensor(s)
–Three way catalytic converter
–CKP sensor
–MAP sensor
Page 305 of 656
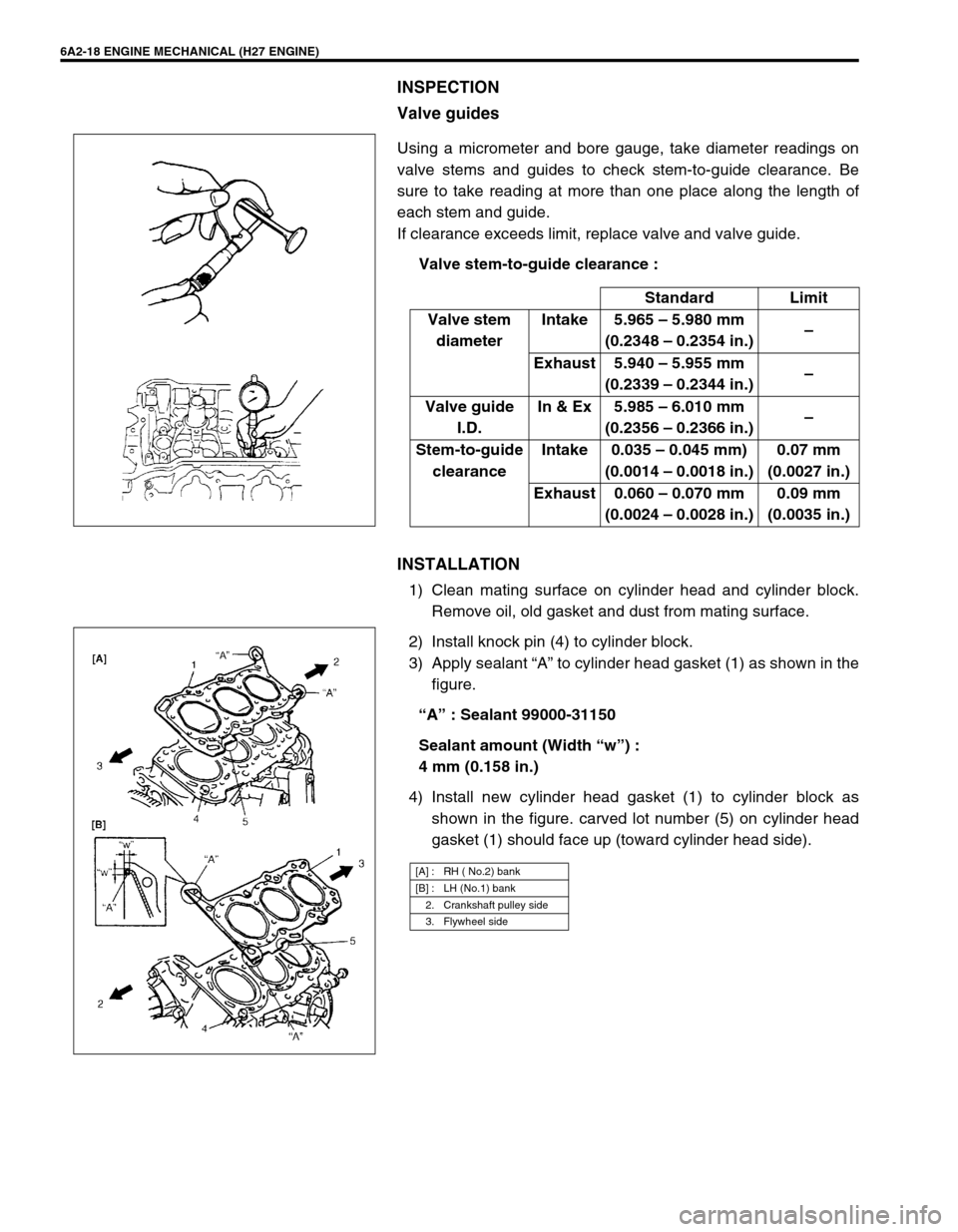
6A2-18 ENGINE MECHANICAL (H27 ENGINE)
INSPECTION
Valve guides
Using a micrometer and bore gauge, take diameter readings on
valve stems and guides to check stem-to-guide clearance. Be
sure to take reading at more than one place along the length of
each stem and guide.
If clearance exceeds limit, replace valve and valve guide.
Valve stem-to-guide clearance :
INSTALLATION
1) Clean mating surface on cylinder head and cylinder block.
Remove oil, old gasket and dust from mating surface.
2) Install knock pin (4) to cylinder block.
3) Apply sealant “A” to cylinder head gasket (1) as shown in the
figure.
“A” : Sealant 99000-31150
Sealant amount (Width “w”) :
4 mm (0.158 in.)
4) Install new cylinder head gasket (1) to cylinder block as
shown in the figure. carved lot number (5) on cylinder head
gasket (1) should face up (toward cylinder head side).Standard Limit
Valve stem
diameterIntake 5.965 – 5.980 mm
(0.2348 – 0.2354 in.)–
Exhaust 5.940 – 5.955 mm
(0.2339 – 0.2344 in.)–
Valve guide
I.D.In & Ex 5.985 – 6.010 mm
(0.2356 – 0.2366 in.)–
Stem-to-guide
clearanceIntake 0.035 – 0.045 mm)
(0.0014 – 0.0018 in.)0.07 mm
(0.0027 in.)
Exhaust 0.060 – 0.070 mm
(0.0024 – 0.0028 in.)0.09 mm
(0.0035 in.)
[A] : RH ( No.2) bank
[B] : LH (No.1) bank
2. Crankshaft pulley side
3. Flywheel side
Page 306 of 656

ENGINE MECHANICAL (H27 ENGINE) 6A2-19
5) Install cylinder head to block.
After applying oil to cylinder head bolts, tighten them gradu-
ally as follows.
a) Tighten all bolts to 53 N·m (5.3 kg-m, 38.5 lb-ft) according
to numerical order in the figure.
b) In the same manner as in a), tighten them to 84 N·m (8.4
kg-m, 61.0 lb-ft).
c) Loosen all bolts until tightening torque is reduced to 0 in
reverse order of tightening.
d) In the same manner as in a), tighten them to 53 N·m (5.3
kg-m, 38.5 lb-ft).
e) In the same manner as in a) again, tighten them to speci-
fied torque.
Tightening torque
Cylinder head bolt (a) : 105 N·m (10.5 kg-m, 76.0 lb-ft)
Cylinder head bolt (hex hole bolt) (b) :
11 N·m (1.1 kg-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
6) Install water outlet cap.
7) Check timing mark on crankshaft as shown in the figure.
8) Install valve lash adjuster, camshaft, CMP sensor and RH
bank 2nd timing chain.
Refer to “CAMSHAFT AND VALVE LASH ADJUSTER” and
“RH (NO.2) BANK 2ND TIMING CHAIN AND CHAIN TEN-
SIONER” in this section. For CMP sensor, refer to “CMP
SENSOR” in Section 6F2.
9) Install 1st timing chain.
Refer to “1ST TIMING CHAIN AND CHAIN TENSIONER” in
this section.
10) Install LH bank 2nd timing chain.
Refer to “LH (NO.1) BANK 2ND TIMING CHAIN AND CHAIN
TENSIONER” in this section.
11) Install timing chain cover.
Refer to “TIMING CHAIN COVER” in this section. NOTE:
Don’t forget to install (b) bolts as shown in the figure.
1. Hex hole bolt
2. Crankshaft pulley side
3. Flywheel side
[A] RH bank
[B] LH bank
1. Crank timing pulley key
2. Oil jet
Page 312 of 656
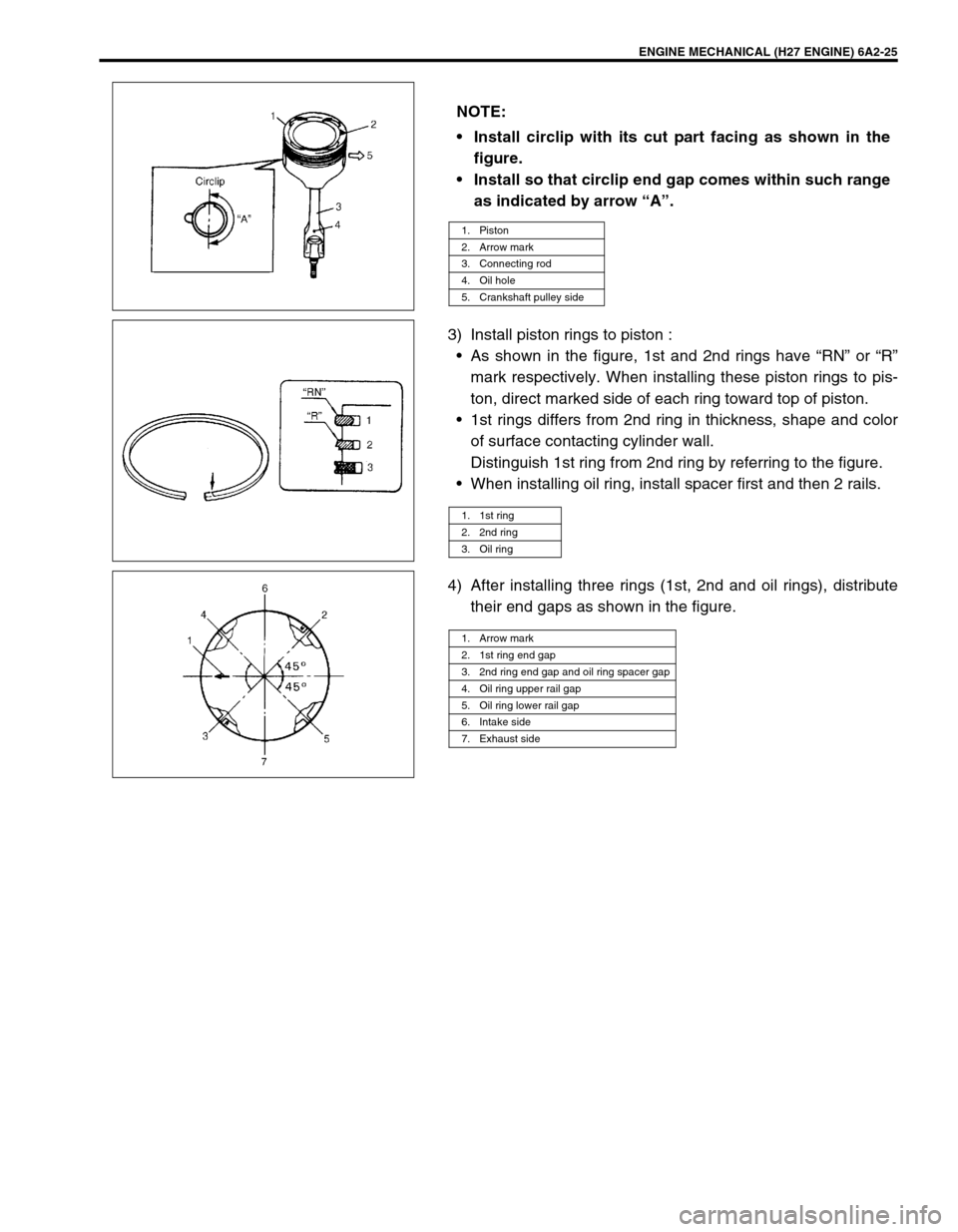
ENGINE MECHANICAL (H27 ENGINE) 6A2-25
3) Install piston rings to piston :
•As shown in the figure, 1st and 2nd rings have “RN” or “R”
mark respectively. When installing these piston rings to pis-
ton, direct marked side of each ring toward top of piston.
•1st rings differs from 2nd ring in thickness, shape and color
of surface contacting cylinder wall.
Distinguish 1st ring from 2nd ring by referring to the figure.
•When installing oil ring, install spacer first and then 2 rails.
4) After installing three rings (1st, 2nd and oil rings), distribute
their end gaps as shown in the figure. NOTE:
Install circlip with its cut part facing as shown in the
figure.
Install so that circlip end gap comes within such range
as indicated by arrow “A”.
1. Piston
2. Arrow mark
3. Connecting rod
4. Oil hole
5. Crankshaft pulley side
1. 1st ring
2. 2nd ring
3. Oil ring
1. Arrow mark
2. 1st ring end gap
3. 2nd ring end gap and oil ring spacer gap
4. Oil ring upper rail gap
5. Oil ring lower rail gap
6. Intake side
7. Exhaust side