1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY fuse box
[x] Cancel search: fuse boxPage 1244 of 1529
WIPERS AND WASHERS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 84-9
Front wash/ wipe switch
The front wash/ wipe switch is located on a stalk on the RH side of the steering column and allows the driver to control
the operation of the front wipers and the front washer pump.
Operating the washer switch provides battery voltage from fuse 19 in the passenger compartment fusebox to the
washer pump motor.
Operating the flick wipe function provides battery voltage from fuse 19 in the passenger compartment fuse box to the
high-speed brushes of the wiper motor.
Operating the intermittent function provides a battery voltage signal to the BCU. The BCU determines the wipe
interval from the variable delay switch and signals the IDM to activate the front wiper relay, which provides battery
voltage to the wiper motor.
Operating the low-speed function provides battery voltage from fuse 19 in the passenger compartment fuse box to
the low-speed brushes of the wiper motor.
Operating the high-speed function provides battery voltage from fuse 19 in the passenger compartment fuse box to
the high-speed brushes of the wiper motor
Page 1246 of 1529
WIPERS AND WASHERS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 84-11
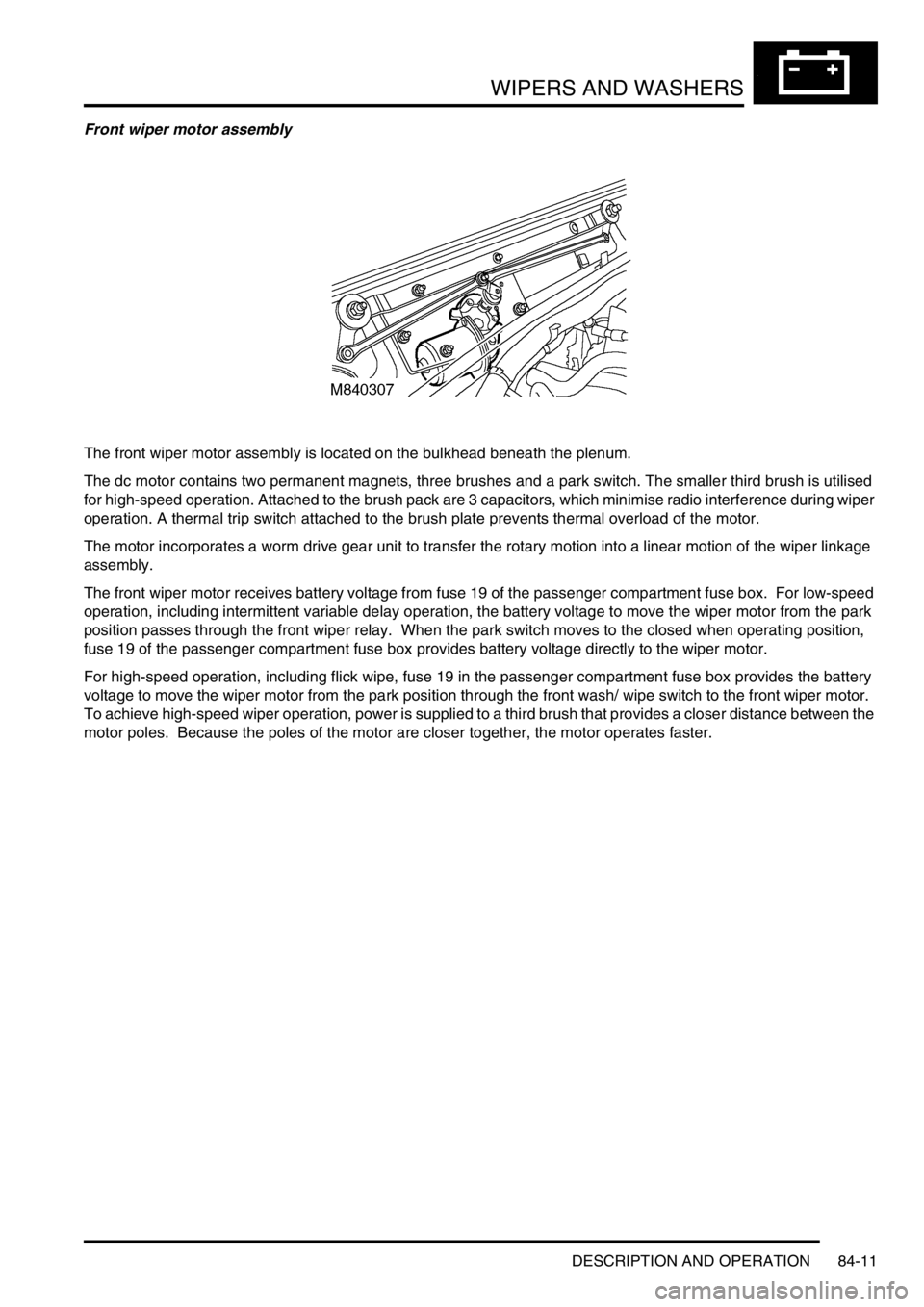
Front wiper motor assembly
The front wiper motor assembly is located on the bulkhead beneath the plenum.
The dc motor contains two permanent magnets, three brushes and a park switch. The smaller third brush is utilised
for high-speed operation. Attached to the brush pack are 3 capacitors, which minimise radio interference during wiper
operation. A thermal trip switch attached to the brush plate prevents thermal overload of the motor.
The motor incorporates a worm drive gear unit to transfer the rotary motion into a linear motion of the wiper linkage
assembly.
The front wiper motor receives battery voltage from fuse 19 of the passenger compartment fuse box. For low-speed
operation, including intermittent variable delay operation, the battery voltage to move the wiper motor from the park
position passes through the front wiper relay. When the park switch moves to the closed when operating position,
fuse 19 of the passenger compartment fuse box provides battery voltage directly to the wiper motor.
For high-speed operation, including flick wipe, fuse 19 in the passenger compartment fuse box provides the battery
voltage to move the wiper motor from the park position through the front wash/ wipe switch to the front wiper motor.
To achieve high-speed wiper operation, power is supplied to a third brush that provides a closer distance between the
motor poles. Because the poles of the motor are closer together, the motor operates faster.
Page 1249 of 1529
WIPERS AND WASHERS
84-14 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Rear screen washer jet
A single washer jet for the tail door window is fitted to the rear wiper blade. The jet has four spray orifices which direct
washer fluid to either side and along the length of the wiper blade. The jet is connected by a hose from the wiper blade,
through a sealing grommet in the tail door and connects with the rear washer hose from the rear washer pump. A non-
return valve is used to join the feed hose from the pump to the washer jet hose. The non-return valve prevents fluid
draining to the reservoir and ensures that the washer operates immediately the washer pump is operated. The hose
from the pump to the tail door is located inside the main harness.
Headlamp power washer jets
When fitted, a powerwash jet for each headlamp is located in a housing on the top surface of the front bumper. The
jets are fed with fluid at high pressure from the powerwash pump. A large diameter hose connects each jet to the
pump. Each connection is secured with a metal clip to secure the hose due to the high pressure from the pump. Each
jet directs the high pressure fluid in a wide spray onto the headlamp lens.
Rear washer switch
The rear washer switch is a non-latching pushbutton switch and is located on the RH side of the instrument pack.
Activating the rear washer switch provides battery voltage from fuse 30 in the passenger compartment fusebox to the
rear washer pump.
Page 1251 of 1529
WIPERS AND WASHERS
84-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
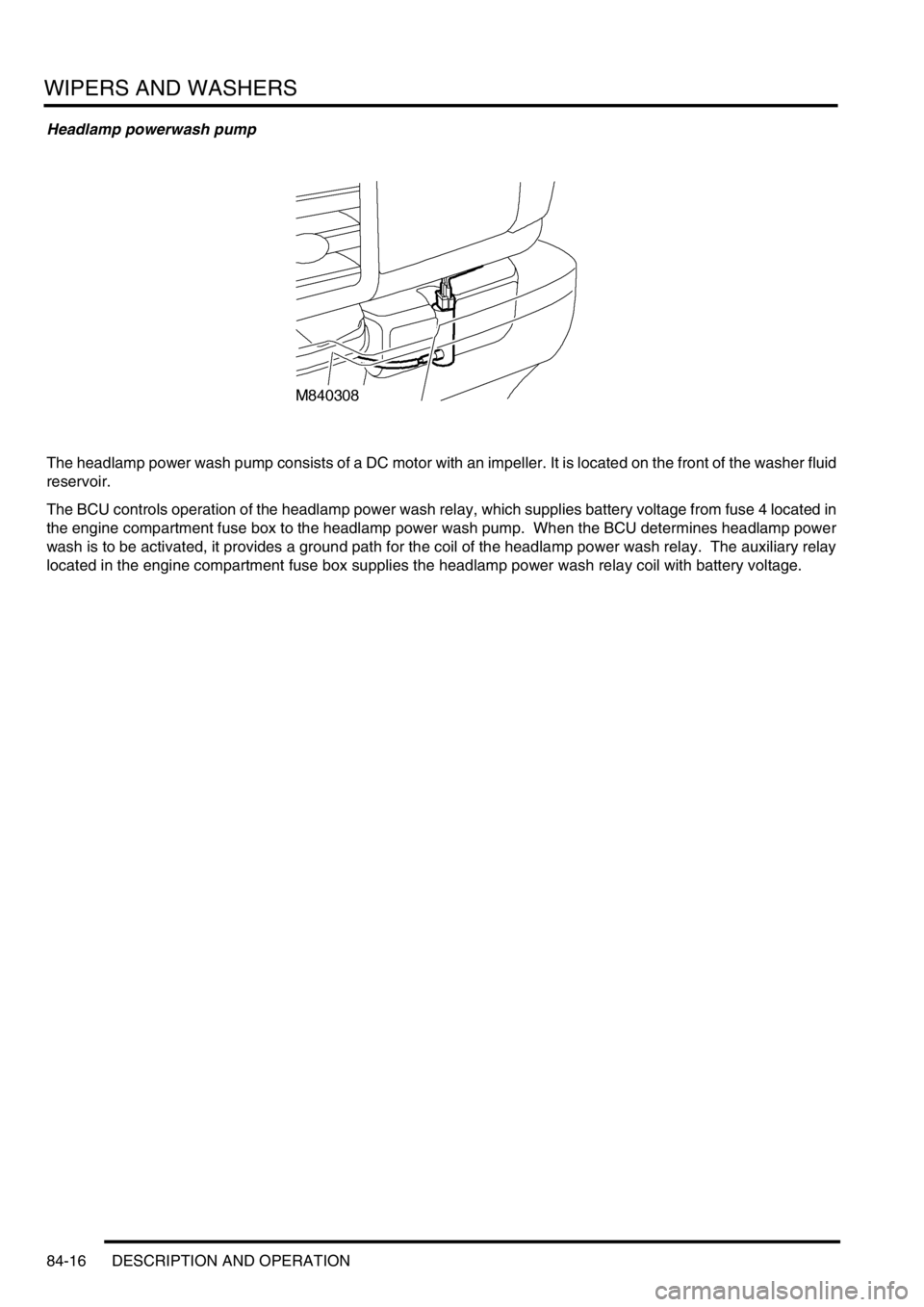
Headlamp powerwash pump
The headlamp power wash pump consists of a DC motor with an impeller. It is located on the front of the washer fluid
reservoir.
The BCU controls operation of the headlamp power wash relay, which supplies battery voltage from fuse 4 located in
the engine compartment fuse box to the headlamp power wash pump. When the BCU determines headlamp power
wash is to be activated, it provides a ground path for the coil of the headlamp power wash relay. The auxiliary relay
located in the engine compartment fuse box supplies the headlamp power wash relay coil with battery voltage.
Page 1288 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-1
BODY CONTROL UNIT DESCRIPTION AND OPERAT ION
Description
General
The Body Control Unit (BCU) is located behind the passenger glovebox and is connected to the main harness by four
connectors on its bottom edge and an additional connector located on the side of the BCU casing. Mounting the BCU
behind the fascia makes it reasonably inaccessible for intruders to disable the anti-theft system.
The BCU uses solid-state microprocessor control to perform logical operations and timing functions for a variety of
the vehicle's electrically operated systems, these include:
lDoor locking.
lAnti-theft alarm and immobilisation system.
lExterior lighting including direction indicators and hazard warning lamps.
lCourtesy lighting.
lWipers and washers.
lElectric windows and sunroof.
lHeated windows.
The BCU also communicates with several other electronically controlled systems such as the EAT ECU and SLABS
ECU and also has a datalink between the Intelligent Driver Module (IDM) and the instrument pack. The datalink is a
low speed bus capable of transmitting and receiving messages at a data rate of 10,400 bits per second. Additional
inputs and outputs to peripheral devices are included which are necessary for determining vehicle status for particular
logical operations e.g. crank, ignition key inserted, fuel flap enable etc.
The BCU receives its power supply from the engine compartment fuse box, and is protected by a 10 A fuse.
The BCU communicates with the IDM to provide the control signals to perform power switching operations in
conjunction with dedicated relays.
IDM
The IDM is integrated into the passenger compartment fuse box, which is mounted behind the fascia below the
steering column. There are no harnesses between the fuse box and the IDM. The IDM performs the power switching
operations for several of the vehicle's electrical systems.
The IDM communicates with the BCU and the instrument pack via a serial interface. If the BCU or the IDM is replaced,
the communications link between the two units has to be re-established. This can be done either by switching on the
ignition and leaving it on for five minutes, or by using TestBook. The vehicle immobilisation will remain active until the
communications link between the BCU and IDM has been re-established.
Transit mode
To prevent excessive battery drain during transit to overseas markets, the vehicle is placed in a transit mode. The
following functions are disabled when the vehicle is in transit mode:
lVolumetric sensors.
lPassive immobilisation.
lImmobilisation of the vehicle by use of door lock.
lIgnition key interlock.
lElectric seat enable time-out with driver's door open.
Page 1289 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
86-3-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Power supply
Battery supply to the BCU and the IDM is provided through a 10 A fuse located in the engine compartment fuse box.
The BCU unit receives an ignition switched power supply (ignition switch position II) input via a 10 A fuse in the
passenger compartment fuse box.
The BCU receives a signal when the ignition switch is turned to the crank position, it then supplies an earth path to
the starter relay coil, to enable the crank operation by supplying power through the starter relay contacts to the starter
motor.
Battery voltage is monitored and BCU operation will function normally between 8 and 18 volts. Between 5.7 and 8
volts the BCU is in the 'under volts' state. The status of the battery is used to determine which outputs may be driven.
If a voltage supply above 18 volts is experienced, outputs will not normally be driven except for those functions which
are required during cranking (robust immobilisation, antenna coil, crank enable relay and feed to gear position switch
contacts W, X, Y, Z). In the over voltage state the vehicle can be driven, but all other functions are disabled and
outputs are switched off (power windows, heated screen, direction indicators etc.).
All functions are disabled on power up until communications between the BCU and IDM have been established. If
communications cannot be established, operation will commence with degraded functionality.
Battery supply to the IDM is provided through the inertia switch and a 10 A fuse in the engine compartment fuse box.
If the inertia switch contacts are closed battery voltage is available at the IDM; if the inertia switch contacts are open
there is no battery supply to the IDM. The supply condition of the IDM is signalled to the BCU via the serial bus. If the
inertia switch is operated (contacts open) the change in state is detected by the BCU which unlocks the doors if the
ignition switch is in position II and the alarm is not set.
The BCU is earthed through a hard-wire connection.
Inputs and outputs
The BCU and IDM process inputs and provide the necessary outputs for control and operation of the vehicle's 'body'
systems.
BCU inputs
The BCU processes signals received from the following components:
lDoor latch switches.
lDriver's door key lock/ unlock switches.
lBonnet activated security system.
lVolumetric sensors.
lCentral Door Locking (CDL) switches.
lRemote transmitter (via receiver unit).
lInertia fuel cut-off switch.
lIgnition switch.
lFuel flap release switch.
The input voltages (V
in) for BCU digital signals are defined as follows:
lLogic 1 when V
in ≥ 6V.
lLogic 0 when V
in ≤ 2V.
BCU input voltages between 2 and 6 volts are indeterminate and cannot be guaranteed.
Analogue input voltages are measured as a ratio with respect to battery voltage.
Page 1292 of 1529
BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-5
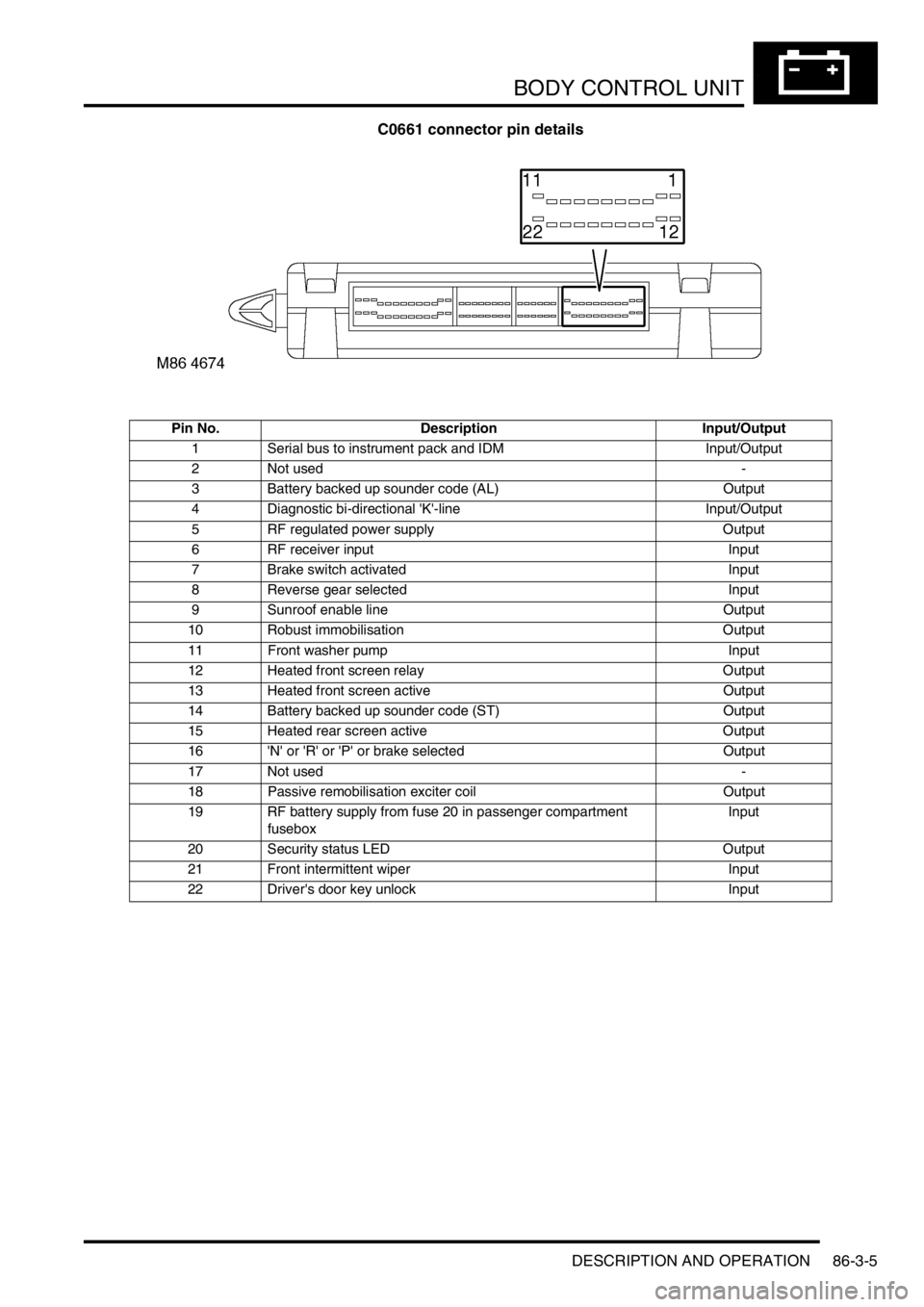
C0661 connector pin details
Pin No. Description Input/Output
1 Serial bus to instrument pack and IDM Input/Output
2 Not used -
3 Battery backed up sounder code (AL) Output
4 Diagnostic bi-directional 'K'-line Input/Output
5 RF regulated power supply Output
6 RF receiver input Input
7 Brake switch activated Input
8 Reverse gear selected Input
9 Sunroof enable line Output
10 Robust immobilisation Output
11 Front washer pump Input
12 Heated front screen relay Output
13 Heated front screen active Output
14 Battery backed up sounder code (ST) Output
15 Heated rear screen active Output
16 'N' or 'R' or 'P' or brake selected Output
17 Not used -
18 Passive remobilisation exciter coil Output
19 RF battery supply from fuse 20 in passenger compartment
fuseboxInput
20 Security status LED Output
21 Front intermittent wiper Input
22 Driver's door key unlock Input
Page 1300 of 1529
BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-13
Anti-theft system
The BCU controls the logical switching operations for enabling and activating the anti-theft system. Features include:
lPerimetric protection – monitors the condition of doors and hinged panels.
lVolumetric protection – monitors the vehicle's interior space.
lRemote locking, superlocking and unlocking functions.
lEngine immobilisation and remobilisation.
lAdvanced mislock detection and automatic compensation.
lEKA code functions.
lCustomer configuration options.
lMarket configuration options.
Immobilisation
The immobilisation system comprises the following components:
lRF receiver.
lRF transmitter/ transponder.
lTransponder coil.
lBCU.
lDoor switches, door lock switches and bonnet switch.
lIDM.
lECM.
lStarter solenoid relay.
lStatus LED.
Alarm system
The alarm system comprises the following components:
lRF receiver.
lRF transmitter.
lBCU.
lIDM.
lDoor switches, door lock switches and bonnet switch.
lBattery backed-up sounder (BBUS).
lStatus LED.
On non NAS vehicles, power supply for the alarm sounder and the battery BBUS is provided through two relays in the
passenger compartment fuse box. Each of the coils of the alarm relays are directly connected to the IDM which
controls their operation under the direction of BCU signals received via the serial data bus.
On NAS vehicles, an audible warning is provided through operation of the vehicle horns. The BCU provides an earth
path for the coil of the horn relay to initiate vehicle horn operation.
+ ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Acclimatisation locking Disabled The vehicle cannot be locked if the ignition is on.
Enabled The vehicle can be locked if the ignition is on and the engine is
running.
Alarm tamper Disabled The security system LED does not flash when the security system has
been tampered with.
Enabled The security system LED flashes when the security system has been
tampered with.
Engine immobilised LED off The security system LED does not flash when the engine is
immobilised.
LED flash The security system LED flashes when the engine is immobilised.
Low battery warning Disabled The security system LED does not flash when the remote transmitter
battery is low.
Enabled The security system LED flashes when the remote transmitter battery
is low.
Emergency Key Access
(EKA)Disabled EKA is disabled.
Enabled EKA is enabled and the door locks operate electrically.
No unlock EKA is enabled, but the door locks do not operate electrically. Function Option Details