1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 204 of 1529
ENGINE - V8
OVERHAUL 12-2-49
Seal - crankshaft - rear - automatic
models
$% 12.21.20.01
Disassembly
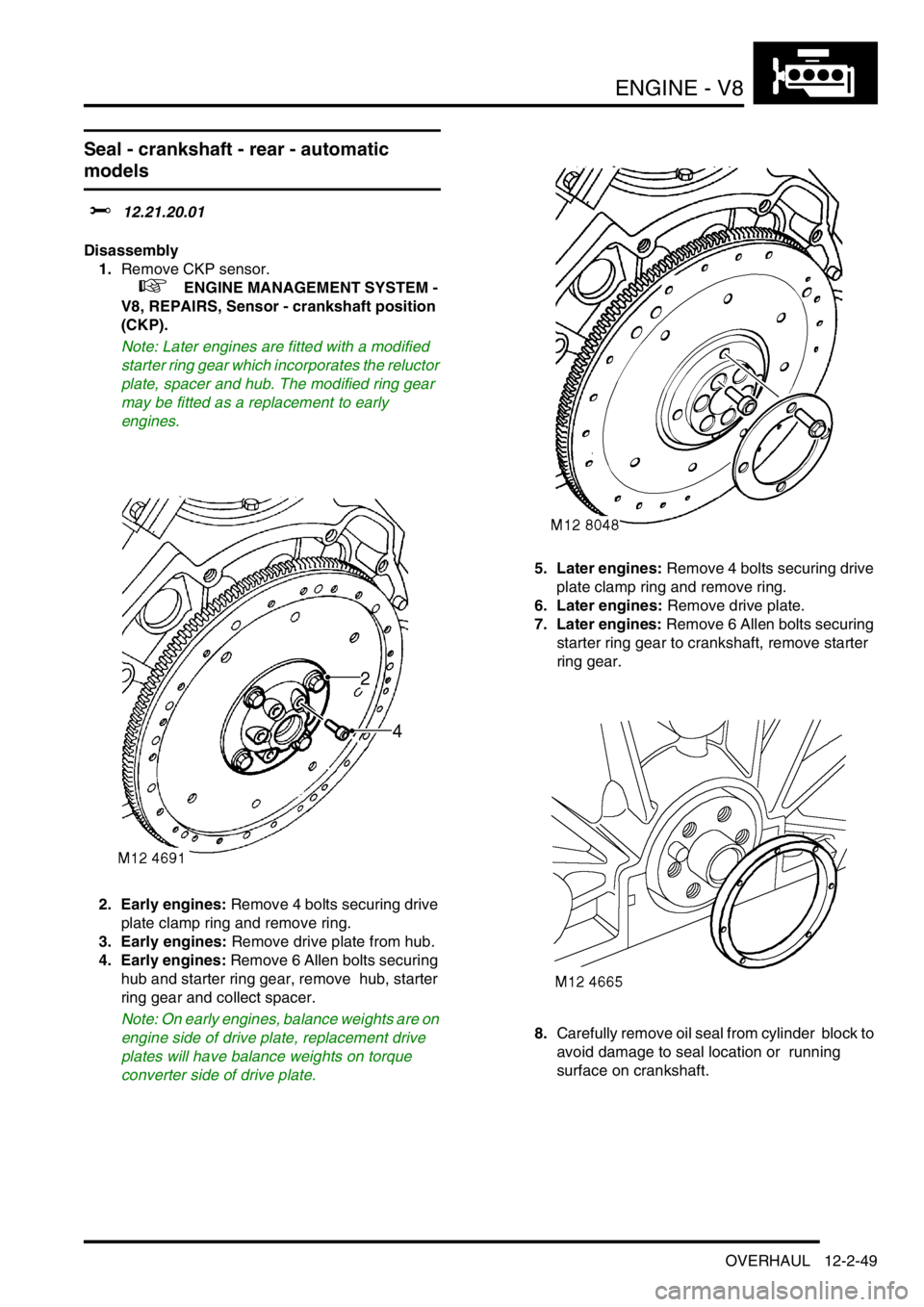
1.Remove CKP sensor.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, REPAIRS, Sensor - crankshaft position
(CKP).
Note: Later engines are fitted with a modified
starter ring gear which incorporates the reluctor
plate, spacer and hub. The modified ring gear
may be fitted as a replacement to early
engines.
2. Early engines: Remove 4 bolts securing drive
plate clamp ring and remove ring.
3. Early engines: Remove drive plate from hub.
4. Early engines: Remove 6 Allen bolts securing
hub and starter ring gear, remove hub, starter
ring gear and collect spacer.
Note: On early engines, balance weights are on
engine side of drive plate, replacement drive
plates will have balance weights on torque
converter side of drive plate.5. Later engines: Remove 4 bolts securing drive
plate clamp ring and remove ring.
6. Later engines: Remove drive plate.
7. Later engines: Remove 6 Allen bolts securing
starter ring gear to crankshaft, remove starter
ring gear.
8.Carefully remove oil seal from cylinder block to
avoid damage to seal location or running
surface on crankshaft.
Page 225 of 1529

ENGINE - V8
12-2-70 OVERHAUL
9.Fit gudgeon pin on to centre screw and into
piston bore up to connecting rod.
10.Fit remover/replacer bush LRT-12-126/1 with
flanged end towards gudgeon pin.
11.Screw the stop nut on to centre screw and
position piston against groove of tool LRT-12-
126/2.
CAUTION: Ensure that prongs of tool LRT-
12–126/2 remain in contact with piston and
do not contact gudgeon pin.
12.Lock the stop nut securely with the lockscrew.
13.Lubricate centre screw threads and thrust race
with graphite oil, screw large nut up to tool
LRT-12-013.
14.Set torque wrench to 16 Nm (12 lbf.ft) and using
socket on large nut, pull gudgeon pin in until
flange of remover/replacer bushLRT-12-126/1
is 0.40 mm (0.016 in), dimension 'A' from
face of piston. If torque is exceeded during this
procedure, fit of gudgeon pin to connecting rod
is not acceptable and components must be
replaced.
CAUTION: The centre screw and thrust race
must be kept well lubricated throughout the
operation.
15.Dismantle tool, remove piston and check no
damage has occurred during pressing and that
piston moves freely on gudgeon pin.
16.Remove compression rings, oil control rails
and expander from new piston.
17.Invert piston and with arrow pointing towards
rear of cylinder block, insert piston into cylinder
liner.
18.Position piston with bottom of skirt 30 mm (1.12
in) from top cylinder liner. 19.Using feeler gauges, measure and record
clearance between piston and left hand side of
cylinder- viewed from the front of cylinder
block.
lPiston to bore clearance = 0.020 to 0.045
mm (0.001 to 0.002 in).
20.Insert piston rings into cylinder bore, use the
piston to hold the rings square to bore and
check the ring gap.
l1st compression ring = 0.30 to 0.50 mm
(0.012 to 0.02 in).
l2nd compression ring = 0.40 to 0.65 mm
(0.016 to 0.026 in).
lOil control ring rails = 0.38 to 1.40 mm
(0.015 to 0.055 in).
21.Remove piston rings from bore.
22.Fit oil control ring rails and expander, ensuring
ends butt and do not overlap.
23.Fit 2nd compression ring marked 'TOP' with
marking uppermost in 2nd groove.
24.Fit 1st compression ring in first groove either
way round.
25.Check piston ring to groove clearance.
l1st compression ring = 0.05 to 0.10 mm
(0.002 to 0.004 in).
l2nd compression ring = 0.05 to 0.10 mm
(0.002 to 0.004 in).
26.Position oil control expander ring joint and ring
rail gaps all at one side, between gudgeon pin
and away from LH side of piston - viewed from
front of piston. Position the gaps in ring rails
approximately 25 mm (1.0 in) each side of
expander ring joint.
27.Position compression rings with gaps on
opposite side of piston between gudgeon pin
and RH side of piston - viewed from front of
piston.
28.Thoroughly clean cylinder bores.
29.Lubricate piston rings and gudgeon pin with
clean engine oil.
30.Lubricate cylinder bore with clean engine oil.
Page 230 of 1529

ENGINE - V8
OVERHAUL 12-2-75
Reassembly
1.Clean main bearing locations in cylinder block
and bearing caps; ensure bolt holes are clean
and dry.
2.Clean sealant from rear main bearing cap and
mating faces.
3.Fit key to keyway.
4.Check threads of main bearing cap bolts for
damage, renew bolts in pairs.
5.Lubricate grooved main bearing shells with
clean engine oil and fit to their locations in
cylinder block.
NOTE: Ensure that the flanged bearing is fitted
to the centre position.
6.Lubricate crankshaft journals with clean engine
oil.
7.Position crankshaft in cylinder block.
8.Lubricate plain bearing shells with clean
engine oil and fit to main bearing caps.
9.Fit main bearing caps 1 to 4 only at this stage,
ensuring that they are the correct way round
and in their fitted order.
10.Lightly lubricate threads of main bearing cap
bolts with clean engine oil.
11.Fit main bearing cap bolts but do not tighten at
this stage. Do not fit side bolts at this stage.12.Lubricate new cruciform seals with engine oil
and fit to rear main bearing cap.
CAUTION: Do not trim off excess from
cruciform seals at this stage.
13.Apply a 3 mm (0.12 in) wide bead of sealant,
Part No. STC 50550 to bearing cap rear mating
faces on cylinder block.
CAUTION: Ensure sealant does not enter
bolt holes.
14.Carefully fit rear main bearing cap assembly, fit
but do not tighten bolts.
CAUTION: Ensure engine oil does not enter
the side bolt holes in the bearing cap. Do
not trim off excess material from cruciform
seals at this stage.
15.Lubricate 'Dowty' washers with engine oil and
fit to side bolts.
16.Fit but do not tighten side bolts. Rear side
bolts are Allen headed.
17.Using the sequence shown, tighten main
bearing cap bolts as follows:
lInitial torque - all main bearing cap bolts and
side bolts - 13.5 Nm (10 lbf.ft).
lFinal torque - main bearing cap side bolts 11
to 15 - 45 Nm (34 lbf.ft).
lFinal torque - main bearing cap bolts 1 to 8
- 72 Nm (54 lbf.ft).
lFinal torque - main bearing cap bolts 9 and
10 - 92 Nm (68 lbf.ft).
lFinal torque - main bearing cap side bolts 16
to 20 - 45 Nm (34 lbf.ft).
18.Trim off excess material from cruciform seals.
Page 247 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-14 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The heated oxygen sensor is screwed into threaded mountings welded into the top of the front exhaust pipes at
suitable locations. They are used to detect the level of residual oxygen in the exhaust gas to provide an instantaneous
indication of whether combustion is complete. By positioning sensors in the stream of exhaust gases from each
separate bank of the exhaust manifold, the engine management system is better able to control the fuelling
requirements on each bank independently of the other, so allowing much closer control of the air:fuel ratio and
optimising catalytic converter efficiency.
Two pre-catalytic converter heated oxygen sensors are mounted in the front pipes for monitoring the oxygen content
of the exhaust gas. NAS models also have two additional post-catalytic converter heated oxygen sensors in the
exhaust front pipe.
CAUTION: HO2 sensors are easily damaged by dropping, over torquing, excessive heat or contamination.
Care must be taken not to damage the sensor housing or tip.
The oxygen sensors consist of a ceramic body (Galvanic cell) which is a practically pure oxygen-ion conductor made
from a mixed oxide of zirconium and yttrium. The ceramic is then coated with gas-permeable platinum, which when
heated to a sufficiently high temperature (≥ 350° C) generates a voltage which is proportional to the oxygen content
in the exhaust gas stream.
The heated oxygen sensor is protected by an outer tube with a restricted flow opening to prevent the sensor's
ceramics from being cooled by low temperature exhaust gases at start up. The post-catalytic sensors have improved
signal quality, but a slower response rate.
The pre-catalytic and post-catalytic converter sensors are not interchangeable, and although it is possible to mount
them in transposed positions, their harness connections are of different gender and colour. It is important not to
confuse the sensor signal pins; the signal pins are gold plated, whilst the heater supply pins are tinned,
mixing them up will cause contamination and adversely affect system performance.
Each of the heated oxygen sensors have a four pin connector with the following wiring details:
lSensor signal ground (grey wire – connects to engine management ECM)
lSensor signal (black wire – connects to engine management ECM)
lHeater drive (white wire – connects to engine management ECM)
lHeater supply (white wire – connects to fuse 2, underbonnet fuse box)
The ECM connector pins for exhaust emission control are listed in the following table:
ECM Connector 2 (C635) pin-out details for exhaust emission control system
The heated oxygen sensors should be treated with extreme care, since the ceramic material within them can be easily
cracked if dropped, banged or over-torqued; the sensors should be torqued to the recommended values indicated in
the repair procedures. Apply anti-seize compound to the sensor's threads when refitting.
WARNING: Some types of anti-seize compound used in service are a health hazard. Avoid skin contact.
WARNING: To prevent personal injury from a hot exhaust system, do not attempt to disconnect any
components until the exhaust system has cooled down.
CAUTION: Do not allow anti-seize compound to come into contact with tip of sensor or enter exhaust system.
NOTE: A new HO2 sensor is supplied pre-treated with anti-seize compound.
Pin Number Function Signal Type Control
2-01 Post-cat sensor heater (RH) - NAS only Output, Drive PWM, 12 - 0V
2-07 Post-cat sensor heater (LH) - NAS only Output, Drive PWM, 12 - 0V
2-08 Post-cat sensor (RH) - NAS only Ground, Signal 0V
2-09 Pre-cat sensor (LH) Ground, Signal 0V
2-10 Pre-cat sensor (RH) Ground, Signal 0V
2-11 Post-cat sensor (LH) - NAS only Ground, Signal 0V
2-13 Pre-cat sensor heater (RH) Output, Drive PWM, 12 - 0V
2-14 Post-cat sensor (RH) - NAS only Input, Signal Analogue, 0 - 1V
2-15 Pre-cat sensor (LH) Input, Signal Analogue, 0 - 1V
2-16 Pre-cat sensor (RH) Input, Signal Analogue, 0 - 1V
2-17 Post-cat sensor (LH) - NAS only Input, Signal Analogue, 0 - 1V
2-19 Pre-cat sensor heater (LH) Output, Drive PWM, 12 - 0V
Page 269 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-36 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Failure of the closed loop control of the exhaust emission system may be attributable to one of the failure modes
indicated below:
lMechanical fitting & integrity of the sensor.
lSensor open circuit / disconnected.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply or ground.
lLambda ratio outside operating band.
lCrossed sensors.
lContamination from leaded fuel or other sources.
lChange in sensor characteristic.
lHarness damage.
lAir leak into exhaust system (cracked pipe / weld or loose fixings).
System failure will be indicated by the following symptoms:
lMIL light on (NAS and EU-3 only).
lDefault to open-loop fuelling for the defective cylinder bank.
lIf sensors are crossed, engine will run normally after initial start and then become progressively unstable with
one bank going to its maximum rich clamp and the other bank going to its maximum lean clamp – the system will
then revert to open-loop fuelling.
lHigh CO reading
lStrong smell of H
2S (rotten eggs)
lExcessive emissions
Fuel Metering
When the engine is cold, additional fuel has to be provided to the air:fuel mixture to assist starting. This supplementary
fuel enrichment continues until the combustion chamber has heated up sufficiently during the warm-up phase.
Under normal part-throttle operating conditions the fuel mixture is adjusted to provide minimum fuel emissions and
the air:fuel mixture is held close to the optimum ratio (λ = 1). The engine management system monitors the changing
engine and environmental conditions and uses the data to determine the exact fuelling requirements necessary to
maintain the air:fuel ratio close to the optimum value that is needed to ensure effective exhaust emission treatment
through the three-way catalytic converters.
During full-throttle operation the air:fuel mixture needs to be made rich to provide maximum torque. During
acceleration, the mixture is enriched by an amount according to engine temperature, engine speed, change in throttle
position and change in manifold pressure, to provide good acceleration response.
When the vehicle is braking or travelling downhill the fuel supply can be interrupted to reduce fuel consumption and
eliminate exhaust emissions during this period of operation.
If the vehicle is being used at altitude, a decrease in the air density will be encountered which needs to be
compensated for to prevent a rich mixture being experienced. Without compensation for altitude, there would be an
increase in exhaust emissions and problems starting, poor driveability and black smoke from the exhaust pipe. For
open loop systems, higher fuel consumption may also occur.
Exhaust Emission System Diagnostics
The engine management ECM contains an on-board diagnostics (OBD) system which performs a number of
diagnostic routines for detecting problems associated with the closed loop emission control system. The diagnostic
unit monitors ECM commands and system responses and also checks the individual sensor signals for plausibility,
these include:
lLambda ratio outside of operating band
lLambda heater diagnostic
lLambda period diagnostic
lPost-catalytic converter lambda adaptation diagnostic (NAS only)
lCatalyst monitoring diagnostic
Lambda Ratio Outside Operating Band
The system checks to ensure that the system is operating in a defined range around the stoichiometric point. If the
system determines that the upper or lower limits for the air:fuel ratio are being exceeded, the error is stored as a fault
code in the ECM diagnostic memory (the MIL light is illuminated on NAS vehicles).
Page 332 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-33
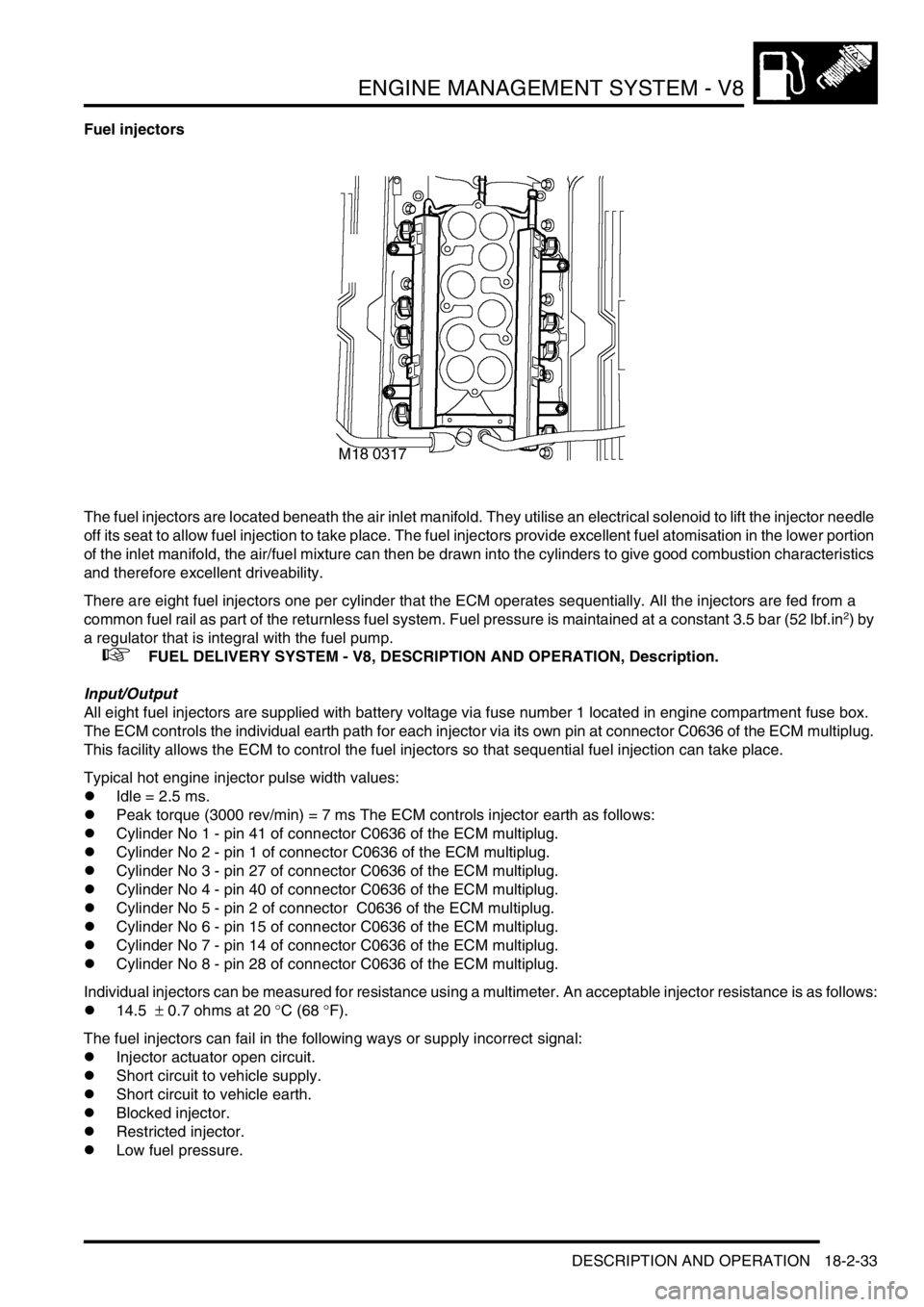
Fuel injectors
The fuel injectors are located beneath the air inlet manifold. They utilise an electrical solenoid to lift the injector needle
off its seat to allow fuel injection to take place. The fuel injectors provide excellent fuel atomisation in the lower portion
of the inlet manifold, the air/fuel mixture can then be drawn into the cylinders to give good combustion characteristics
and therefore excellent driveability.
There are eight fuel injectors one per cylinder that the ECM operates sequentially. All the injectors are fed from a
common fuel rail as part of the returnless fuel system. Fuel pressure is maintained at a constant 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in
2) by
a regulator that is integral with the fuel pump.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Input/Output
All eight fuel injectors are supplied with battery voltage via fuse number 1 located in engine compartment fuse box.
The ECM controls the individual earth path for each injector via its own pin at connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
This facility allows the ECM to control the fuel injectors so that sequential fuel injection can take place.
Typical hot engine injector pulse width values:
lIdle = 2.5 ms.
lPeak torque (3000 rev/min) = 7 ms The ECM controls injector earth as follows:
lCylinder No 1 - pin 41 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 2 - pin 1 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 3 - pin 27 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 4 - pin 40 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 5 - pin 2 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 6 - pin 15 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 7 - pin 14 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 8 - pin 28 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
Individual injectors can be measured for resistance using a multimeter. An acceptable injector resistance is as follows:
l14.5 ± 0.7 ohms at 20 °C (68 °F).
The fuel injectors can fail in the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lInjector actuator open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBlocked injector.
lRestricted injector.
lLow fuel pressure.
Page 355 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-56 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Function
Input for the rough road signal is measured via pin 34 of connector C0637 of the ECM. The SLABS ECU generates
a PWM signal that varies in accordance with changing road conditions. The rough road PWM signal operates at a
frequency of 2.33 Hz ± 10%. The significance of changes in the PWM signal are shown in the following table:
The rough road signal can fail in the following ways:
lHarness or connector damage
lSLABS failure — wheel speed sensor
A rough road signal failure may be evident from the following:
lHDC / ABS warning light on
Should a malfunction of the rough road signal occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved
by TestBook:
Hill Descent Control (HDC) signal
The ECM transmits throttle angle, engine torque, engine identification (Td5 or V8), and transmission type (automatic
or manual) data to the SLABS ECU to support the Hill Descent Control system. The information is transmitted via a
0 – 12V pulse width modulated (PWM) signal at a frequency of 179.27 Hz.
Function
The HDC signal output from the ECM is via pin 29 of connector C0636. The ECM generates a PWM signal that varies
in pulse width in accordance with changing throttle angle or engine torque. The throttle angle data is transmitted on
pulses 1, 3, 5 and 37. The engine torque data is transmitted on pulses 2,4,6 and 38. The engine and transmission
information is transmitted on pulse 39. A synchronising pulse is transmitted after every 39th pulse.
The HDC signal can fail in the following ways:
lHarness or connector damage
A HDC signal failure may be evident from the following:
lHDC / ABS warning light on
lHDC inoperative
lAudible warning
Should a malfunction of the HDC signal occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
PWM signal Indication
<10% Electrical short circuit to ground
25% ± 5 % Smooth road
50% ± 5 % SLABS error
75% ± 5% Rough road
>90% Electrical short circuit to battery voltage
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1590 ABS rough road signal circuit malfunction Hardware is OK, but SLABS ECU is sending an error
signal
P1591 ABS rough road signal circuit low Signal from SLABS ECU short circuit to earth
P1592 ABS rough road signal circuit high Signal from SLABS ECU short circuit to vehicle battery
supply
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1663 Throttle angle/Torque signal circuit malfunction SLABS HDC link open circuit
P1664 Throttle angle/Torque signal circuit low SLABS HDC link short circuit to ground
P1665 Throttle angle/Torque signal circuit high SLABS HDC link short circuit to battery voltage
Page 357 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-58 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Conditions
The CAN system is used by the EAT ECU and the ECM for transmission of the following information:
lGearshift torque control information.
lEAT OBD information.
lMIL request.
lVehicle speed signal.
lEngine temperature.
lEngine torque and speed.
lGear selected.
lGear change information.
lAltitude adaptation factor
lAir intake temperature
lThrottle angle / pedal position
Function
The CAN system uses a twisted pair of wires to form the 'data bus' to minimise electrical interference. This method of
serial interface is very reliable and very fast. The information messages are structured so that each of the receivers
(ECM or EAT ECU) is able to interpret and react to the messages sent.
The CAN 'data bus' is directly connected between pin 36 of connector C0637 of the ECM and pin 16 of connector
C0193 at the EAT ECU, and pin 37 of connector C0637 of the ECM and pin 44 of connector C0193 at the EAT ECU.
The CAN system can fail in the following ways:
lCAN data bus wiring open circuit.
lCAN data bus wiring short circuit.
In the event of a CAN data bus failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lMIL illuminated after 2 drive cycles (NAS only).
lEAT defaults to 3rd gear only.
lHarsh gearshifts.
l'Sport' and 'manual' lights flash alternately.
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Drive cycles
The following are the TestBook drive cycles:
⇒ Drive cycle A:
1Switch on the ignition for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
⇒ Drive cycle B:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Allow engine to idle for 2 minutes.
8Connect TestBook and with the engine still running, check for fault codes.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0600 Serial communication link malfunction CAN time out
P1776 Transmission control system torque interface
malfunctionEAT torque interface error