1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY trailer
[x] Cancel search: trailerPage 1313 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
86-3-26 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Electric seats
The BCU can be programmed to operate the electric seats according to one of three options:
lOption 1 – no electric seats.
lOption 2 – normal.
lOption 3 – operates with ignition only.
To determine when to provide an output to the passenger and drivers seat enable relay, the BCU checks the condition
of the following inputs:
lIgnition state.
lTransit mode.
lDriver's door open.
The electrically controlled seats are operated when the ignition switch is in position I or II or for a predetermined period
when the driver's door is open. If the ignition state is in crank, the seat enable relay is off. If the ignition state is off and
the driver's door open input is off, the seat enable relay is off. If the ignition state is off and the driver's door open input
is on and transit mode is on, the seat enable relay output is off.
The power supply to each seat switch pack is powered from a power seat relay located on the underside of each seat
frame. The feed from the relay is protected by a fuse located in a satellite fuse block located adjacent to the power
seat relay. The fuse block also contains two additional fuses which are used to protect the feeds to the lumbar pump
and solenoid.
With the ignition switch in position I or II or the driver's door open, the BCU provides an earth path for the coils of the
LH and RH power seat relays, energising the relays and closing the contacts. If the driver's door input signal is on for
longer than 45 seconds with the ignition switched off, the seat enable relay is switched off.
Direction indicators and hazard warning lamps
The BCU supplies reference voltages for the LH and RH indicators. When the direction indicator switch is used to
select the LH or RH indicator position, an earth path is completed which signals the BCU that a request for direction
indicator operation has been made. The BCU then communicates this request to the IDM which supplies an earth
path for the coil of the relevant relay (LH or RH indicator relay). When the relay coil is energised, the relay contacts
close and a voltage supply is provided via a resistor to the relevant direction indicators. The IDM controls the timing
of the flash operations by continually removing and restoring the earth path to the direction indicator relay coil.
The BCU checks for the following inputs for performing the logic operations associated with the direction indicator
lamps:
lIgnition state.
lRH indicators selected.
lLH indicators selected.
lHazards selected.
lInertia switch hazard request.
lOne short indicator flash request (anti-theft system arming).
lTwo short indicator flash request (superlocking).
lOne long indicator flash request (anti-theft system disarming).
lAlarm flashing indicators (anti-theft alarm triggered).
The following outputs are provided by the BCU as a result of the inputs received and the logical operations performed:
lRH indicators enable.
lLH indicators enable.
lDirection indicator left message (link to IDM).
lDirection indicator right message (link to IDM).
Direction indicator lamp failure detection
The BCU uses the following logic inputs to determine if there is a direction indicator bulb failure or if the presence of
a trailer is detected. The BCU uses the information to decide which output to enable at any particular instance:
lRight direction indicators requested.
lLeft direction indicators requested.
lRH indicators current sense.
lLH indicators current sense.
Page 1314 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-27
If a direction indicator bulb failure or a trailer presence is detected, the following outputs can be generated depending
on the BCU logic states:
lTrailer detected.
lBulb failure detected.
lDirection indicator short circuit.
lDirection indicator relay stuck.
The BCU can be configured whether or not to provide bulb failure warnings.
When the direction indicators are operating, instrument pack direction indicators flash in sequence with the exterior
direction indicators. If a failure of an indicator bulb occurs, the corresponding instrument pack indication lamp will flash
quickly to warn of the problem.
The IDM monitors the current drawn through the circuit to detect for the occurrence of a lamp failure. If an indicator
lamp fails, the IDM detects the drop in current drawn through the resistor and operates the indicator relay at a faster
speed. The fast flash is demonstrated on the instrument pack direction indicator warning lamps to bring attention to
the driver that a direction indicator bulb failure has occurred. The current sense for the related indicator lamps (RH or
LH) are checked when a direction indicator request has been made that lasts for at least 160 ms. The current level
sensed is relative to the number of working bulbs and determines the request generated by the BCU.
The output is signalled to the instrument pack using the serial communications link. If the hazard warning lamps are
operating, both sets of direction indicators are checked using the current sensing functions to check the number of
bulbs on each side of the vehicle.
If the BCU detects that a direction indicator request has not been made, but one or other of the current sense inputs
indicate that current is flowing, a 'Relay stuck' output is generated.
Hazard lamps
The BCU controls the operation of the hazard warning lamps via the IDM and dedicated relays. The hazard warning
lamps are activated under the following conditions:
lThe vehicle is locked and the security system is set (the hazard warning lamps flash three times if the
superlocking feature is used, once if not).
lThe vehicle is unlocked (the hazard warning lamps flash once for a duration of two seconds).
lThe anti-theft alarm system is triggered (the hazard warning lamps flash in phase with and for the duration of the
audible warning).
lThe hazard warning switch is pressed (the hazard warning lamps flash until the hazard warning switch is pressed
for a second time).
lThe inertia switch is triggered (the hazard warning lamps flash until the inertia switch has been reset).
The hazard warning lamp operation may differ dependent on market and customer configuration options.
The hazard warning lamps are operated from a latching pushbutton switch located on the fascia. When the switch is
pressed, both left and right indicator lamps in the instrument pack flash to show that the hazard warning lamps are
operating and all hazard warning lamps flash simultaneously. If a trailer is fitted, the ICM detects this and a trailer
symbol in the instrument pack also flashes to show correct operation of the trailer direction indicators and hazard
warning lamps.
The BCU supplies a reference voltage to the hazard warning switch. When the hazard warning switch is operated an
earth path is completed which signals the BCU that a request for hazard lamp operation has been made. The BCU
then sends a signal to the IDM via the serial data bus to communicate the request. The IDM supplies an earth path
for both direction indicator relay coils simultaneously so that the hazard warning lamps are turned on concurrently.
The IDM controls the timing of the flash operations by continually removing and restoring the earth path to both
direction indicator relay coils simultaneously.
Number of working bulbs Request generated
3 Trailer detected
2 None (bulbs okay)
1 Bulb failure detected
0 Direction indicator short circuit detected
Page 1441 of 1529

DRIVING AIDS
86-8-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
Park Distance Control (PDC) is introduced on vehicles from 03 model year. PDC provides an audible warning to the
driver when any obstacles are in the path of the vehicle during a reversing manoeuvre. The purpose of the system is
to assist the driver when parking and is not designed as a crash avoidance system or a replacement for visual
interpretation by the driver.
The system comprises four ultrasonic sensors in the rear bumper, an ECU, a fascia mounted momentary switch and
a sounder unit. The system operates using ultrasonic signals which are transmitted by the sensors. The reflected echo
from this output is received by the sensors and used by the PDC ECU to calculate the distance from an object.
The fascia mounted switch allows the driver to de-activate the PDC system if operation is not required or the vehicle
has a trailer attached.
Page 1480 of 1529

NAVIGATION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 87-27
Sensor Check Menu
TestBook/T4 Diagnostics
No serial diagnostic link is provided with the CARiN III navigation system, so TestBook/T4 cannot interact with the
system.
Vehicle Position
If the vehicle’s battery has been disconnected, or if the vehicle has been transported to a new location on another
vehicle (e.g. by trailer or train), the navigation system will require up to 15 minutes to identify the new position. Entering
the vehicle’s position manually, reduces this delay. To enter the vehicle's position manually:
1Highlight and select Information.
2From the information menu, scroll down to the next screen and highlight and select Vehicle position.
NOTE: If the correct CD is in the navigation computer, the country is automatically entered. If you have travelled
to a new country, a new CD may be needed.
3From the vehicle position menu, highlight and select City, then use the typewriter menu to enter the vehicle’s
position (town, road, etc.) in the same way that you would enter a destination.
4Once the town and road names are entered, the navigation computer asks for a junction. This is the name of the
road that forms the next junction ahead of the vehicle.
5Highlight and select Junction, then enter the name using the typewriter, or select the correct road name if a list
of names is displayed. Crossing the junction will be highlighted. Drive the vehicle in the direction of the junction
and press the rotary controller when you reach the junction.
NOTE: The vehicle position menu provides a street map facility which enables you to check your vehicle’s current
position and assists in identifying the name of the next road junction.
Provided that the information entered into the computer is correct, the navigation system requires approximately 1
minute to determine the vehicle's position.
Navigation and Trafficmaster
Road navigation and off-road navigation are accessed from the main menu by highlighting and selecting the
appropriate title with the rotary controller. In both modes of navigation, this brings up a safety notice on the display
unit. Pushing the rotary controller again accepts the safety notice and replaces it with a menu screen, which is the
entry point for operation of the navigation function. The Trafficmaster function only operates in the road navigation
mode, and is activated and de-activated by pushing and holding the menu switch for more than 0.5 second. When
activating the Trafficmaster function, the system returns to the navigation mode if the menu switch is not released
within 1.5 seconds.
Refer to the Owner Handbook: Navigation, CARiN III & Traffic Master, Publication Part No. LRL 0586ENG for full
details of how to operate the road navigation, off-road navigation and Trafficmaster functions.
M86 6074
Sensor Check
Wheel Sensors
GPS Satellites
GPS Status
GYRO
Direction of Travel
< Return0
0
08
Position known
0285
Forward
Page 1484 of 1529
INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-1
INS TRUMENTS DESCRIPTION AND OPERAT ION
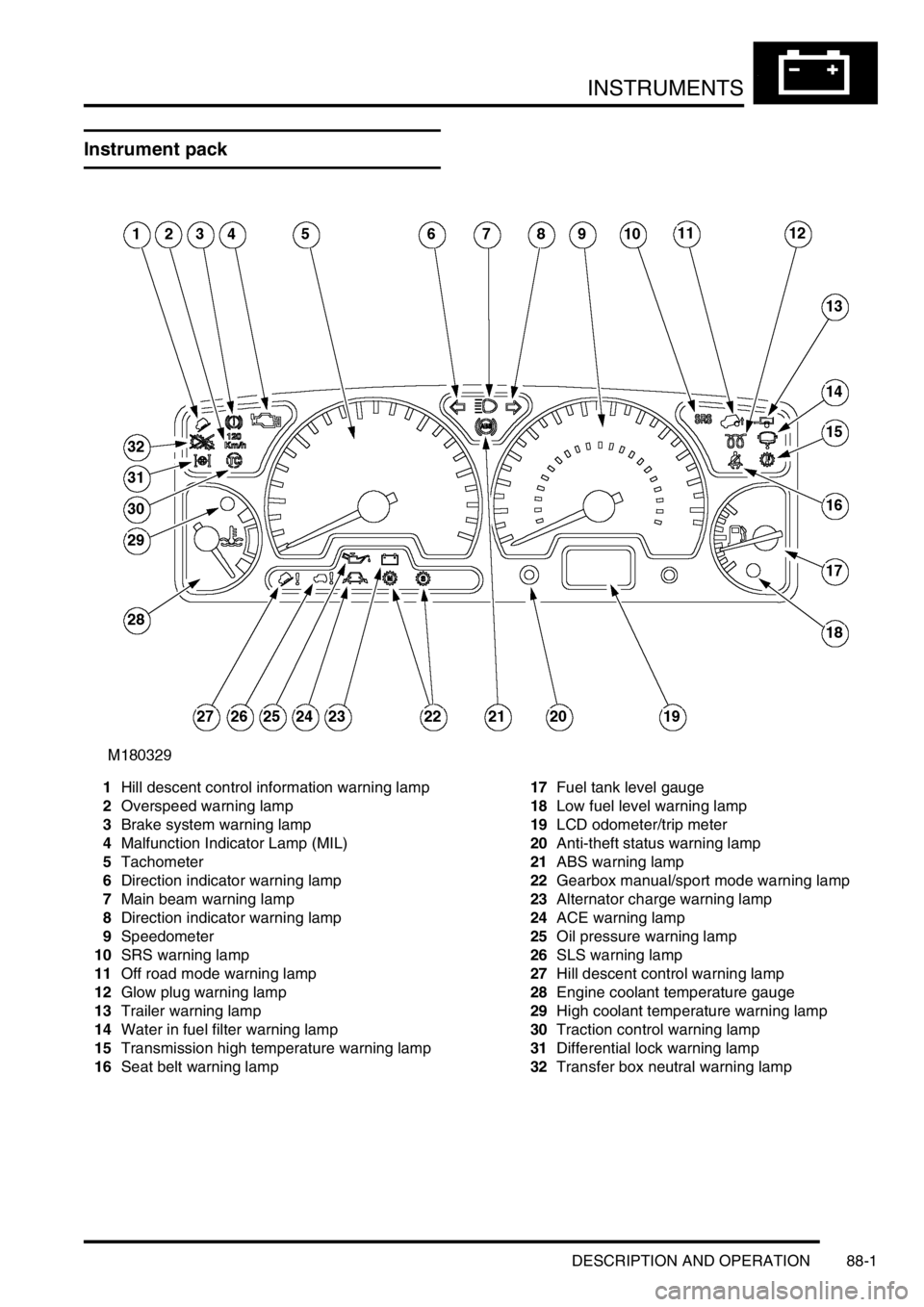
Instrument pack
1Hill descent control information warning lamp
2Overspeed warning lamp
3Brake system warning lamp
4Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
5Tachometer
6Direction indicator warning lamp
7Main beam warning lamp
8Direction indicator warning lamp
9Speedometer
10SRS warning lamp
11Off road mode warning lamp
12Glow plug warning lamp
13Trailer warning lamp
14Water in fuel filter warning lamp
15Transmission high temperature warning lamp
16Seat belt warning lamp17Fuel tank level gauge
18Low fuel level warning lamp
19LCD odometer/trip meter
20Anti-theft status warning lamp
21ABS warning lamp
22Gearbox manual/sport mode warning lamp
23Alternator charge warning lamp
24ACE warning lamp
25Oil pressure warning lamp
26SLS warning lamp
27Hill descent control warning lamp
28Engine coolant temperature gauge
29High coolant temperature warning lamp
30Traction control warning lamp
31Differential lock warning lamp
32Transfer box neutral warning lamp
Page 1489 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
88-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The third warning lamp pack is located in the top right-hand side of the instrument pack and contains the following
warning lamps:
lSRS warning lamp.
lSLS off road mode warning lamp.
lTrailer warning lamp.
lGlow plug warning lamp.
lWater in fuel filter warning lamp.
lSeat belt warning lamp.
lTransmission high temperature warning lamp.
The fourth warning lamp pack is located underneath the tachometer of the instrument pack contains the following
warning lamps:
lOil pressure warning lamp.
lAlternator charge warning lamp.
lHDC fault warning lamp.
lSelf Levelling Suspension (SLS) warning lamp.
lActive Cornering Enhancement (ACE) warning lamp.
lGearbox manual/sport mode warning lamps.
The serial communication link is used to allow information to travel to and from the instrument pack, and it provides
the ability to configure the instrument pack to a specific market. It also allows the instrument pack to be controlled by
TestBook for diagnostics.
There are five market specific variants of the instrument pack:
lUnited Kingdom (UK).
lNorth American Specification (NAS).
lCanada.
lAustralia.
lRest Of the World (ROW), Gulf and Japan.
The main difference between the five markets is that the speedometer will indicate road speed in mph as major figures
and km/h as minor figures, km/h as major figures and mph as minor figures or km/h only.
When TestBook is used to diagnose the instrument pack it demands each of the dials and warning lamps to operate
in-turn so a visual check of their operation can be made.
CAUTION: The instrument pack must not be stored on its face side at any time. This is because the dials have
damping fluid within them to ensure smooth operation of the dials' indicator needles. This fluid will leak out.
Speedometer
The speedometer informs the driver of the current vehicle road speed. It has a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) to show
odometer, trip meter and, on automatic gearbox models, the selected gear. The speedometer will not show speeds
of less than 1.5 mph (2.5 km/h).
There are three different market configurations:
lNAS and UK = mph as major figures km/h as minor figures.
lCanada = km/h as major figures mph as minor figures.
lROW and Australia = km/h only.
The Self Levelling and Anti-Lock Brake System (SLABS) ECU provides the signal input for the road speed. The signal
is at 8000 pulses per mile (1.6 kilometres).
Page 1510 of 1529
INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-27
Trailer warning lamp
The trailer warning lamp within the instrument pack utilises a green LED and a clear legend. When a trailer is fitted to
the vehicle, and the direction indicators are operated, the BCU detects additional current draw and illuminates the
LED, providing the driver with a visible warning.
When the ignition is switched on the BCU illuminates the LED to provide a self-check, providing there is no fault it will
remain illuminated for 3 seconds or until the ignition is switched off. This self-check is every time the ignition is
switched on, not only if a trailer is connected.
The power input for the LED is supplied by the instrument pack via fuse 13. The BCU provides the earth path to
illuminate the warning lamp.