1999 LAND ROVER DEFENDER fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: fuel pressurePage 143 of 667

12ENGINE
18
REPAIR
35.Remove 2 bolts and remove acoustic cover from
rear of cylinder head.
36.FitLRT-12-138to suitable lifting chains and
connect to lifting eyes on engine.
37.Remove 2 nuts from RH and LH front engine
mountings.
38.Fit trolley jack to support gearbox.
39.With assistance raise chains and remove engine
from vehicle.Refit
40.With assistance, raise engine from bench and
position in vehicle.
41.With assistance, align engine to gearbox input
shaft.
42.Position 2 upper bolts securing gearbox housing
to engine and tighten to50 Nm (37 lbf.ft).
43.Lower engine onto mountings and tighten nuts to
85 Nm (63 lbf.ft).
44.RemoveLRT-12-138from engine.
45.Fit and tighten bolt securing engine closing panel
to gearbox.
46.Raise vehicle on ramp.
47.Fit bolts securing gearbox housing to engine and
tighten to50 Nm (37 lbf.ft).
48.Lower ramp.
49.Fit acoustic cover to rear of cylinder head and
tighten bolts.
50.Position coolant hose to engine oil cooler and
secure clip.
51.Position PAS pump and tighten bolts to25 Nm
(18 lbf.ft).
52.Position PAS pulley and tighten bolts to25 Nm
(18 lbf.ft).
53.Position A/C compressor and tighten bolts to25
Nm (18 lbf.ft).
54.Route engine harness beneath inlet manifold
and connect multiplugs to oil pressure switch,
A/C compressor, and ECT sensor.
55.Fit and tighten bolts securing engine harness to
camshaft carrier.
56.Connect multiplug to alternator.
57.Connect battery lead to alternator and tighten
nut.
58.Clean CKP sensor and mating face.
CAUTION: If originally fitted:- Fit spacer to
CKP sensor.
59.Using a new’O’ring, fit CKP sensor, tighten bolt
to10 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
60.Connect CKP sensor multiplug.
61.Connect multiplugs to EGR solenoid, inlet
manifold sensor, injector harness, fuel
temperature sensor and CKP sensor.
62.Connect glow plug leads.
63.Connect multiplug to condensor cooling fan.
64.Connect vacuum hose to EGR valve.
65.Connect EGR vacuum hose to vacuum pipe.
66.Position pipe to vacuum pump and secure pipe
to acoustic cover clips.
67.Position fuel cooler. Apply Loctite 242 to bolts
and tighten to18 Nm (13 lbf.ft).
68.Disconnect fuel hose from connector block and
connect to fuel cooler.
69.Connect fuel hoses to fuel cooler and connector
block on cylinder head.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 155 of 667

12ENGINE
30
REPAIR Refit
10.Clean oil cooler and mating faces.
11.Fit oil pressure switch and tighten to9Nm(7
lbf.ft).
12.Position oil cooler using a new gasket and
tighten bolts to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
13.Position oil filter adaptor, fit new gasket and
tighten bolts to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
14.Position oil filter element hand tight then a
further half turn.
15.Position coolant hose to oil cooler and secure
clip.
16.Position coolant pipe and tighten clutch housing
bolt to50 Nm (37 lbf.ft).
17.Connect oil pressure switch multiplug.
18.Fit centrifuge assembly.See this Section.
19.Refill cooling system.See COOLING SYSTEM,
Adjustment.
20.Top up engine oil.CENTRIFUGE ASSEMBLY
Service repair no - 12.60.90
Remove
1.Remove fixings and remove underbelly panel.
See CHASSIS AND BODY, Repair.
2.Remove 2 bolts securing centrifuge drain pipe to
engine sump and discard gasket.
3.Remove turbocharger.See FUEL SYSTEM,
Repair.
Models with air conditioning only
4.Remove auxiliary drive belt.See
ELECTRICAL, Repair.
5.Remove 4 bolts securing compressor and move
to one side.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 167 of 667
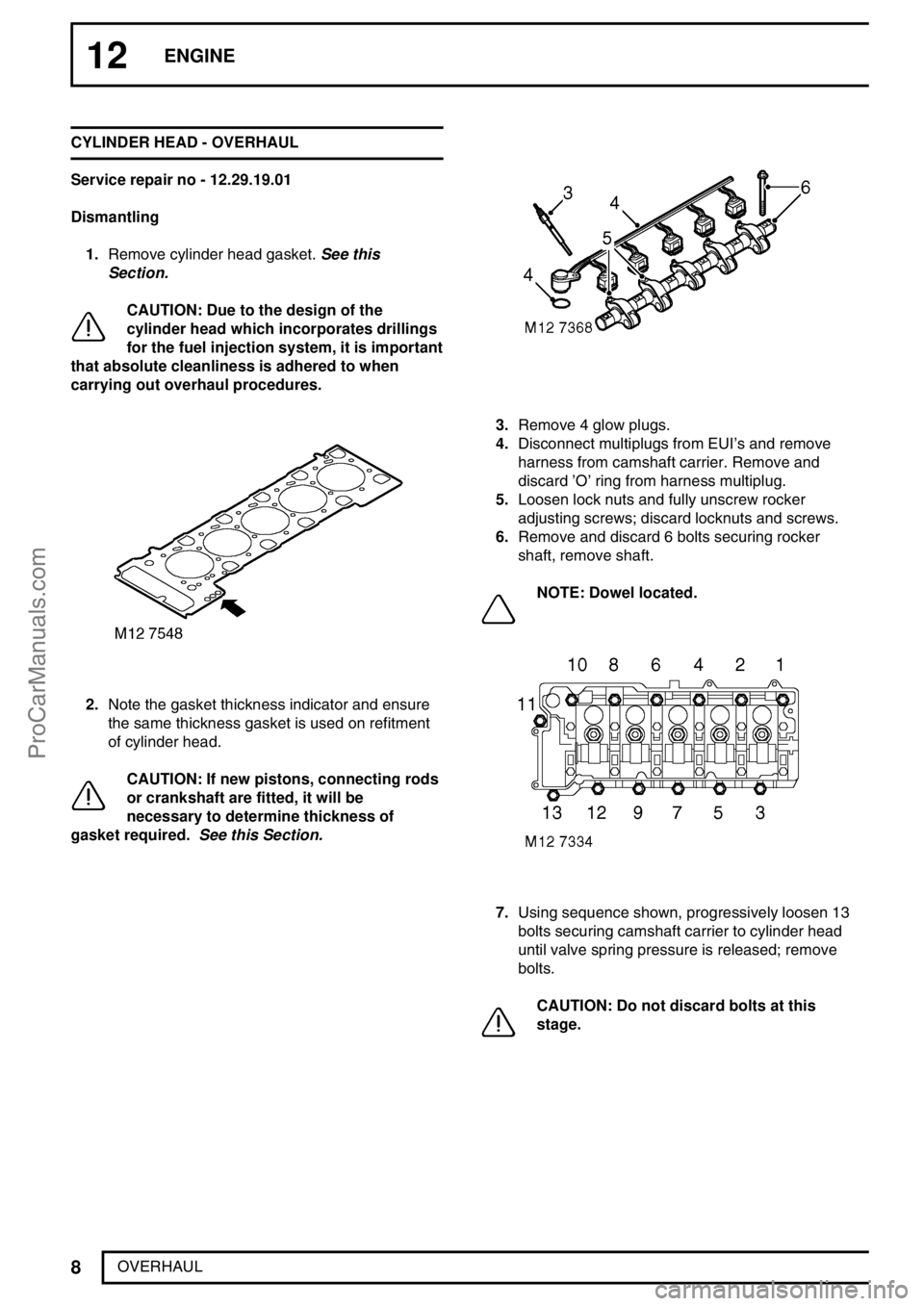
12ENGINE
8
OVERHAUL CYLINDER HEAD - OVERHAUL
Service repair no - 12.29.19.01
Dismantling
1.Remove cylinder head gasket.See this
Section.
CAUTION: Due to the design of the
cylinder head which incorporates drillings
for the fuel injection system, it is important
that absolute cleanliness is adhered to when
carrying out overhaul procedures.
2.Note the gasket thickness indicator and ensure
the same thickness gasket is used on refitment
of cylinder head.
CAUTION: If new pistons, connecting rods
or crankshaft are fitted, it will be
necessary to determine thickness of
gasket required.See this Section.
3.Remove 4 glow plugs.
4.Disconnect multiplugs from EUI’s and remove
harness from camshaft carrier. Remove and
discard’O’ring from harness multiplug.
5.Loosen lock nuts and fully unscrew rocker
adjusting screws; discard locknuts and screws.
6.Remove and discard 6 bolts securing rocker
shaft, remove shaft.
NOTE: Dowel located.
7.Using sequence shown, progressively loosen 13
bolts securing camshaft carrier to cylinder head
until valve spring pressure is released; remove
bolts.
CAUTION: Do not discard bolts at this
stage.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 208 of 667

EMISSION CONTROL
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL
All internal combustion engines generate oil vapour and smoke in the crankcase as a result of high crankcase
temperatures and piston ring and valve stem blow-by. A closed crankcase ventilation system is used to vent
crankcase gases back to the air induction system and so reduce the emission of hydrocarbons.
Gases from the crankcase are drawn into the inlet manifold to be burnt in the combustion chambers with the fresh
air/fuel mixture. The system provides effective emission control under all engine operating conditions.
Crankcase gases are drawn through the breather port in the top of the camshaft cover and routed through the
breather hose and breather valve on the flexible air intake duct to be drawn into the turbocharger intake for
delivery to the air inlet manifold via the intercooler.
An oil separator plate is included in the camshaft cover which removes the heavy particles of oil before the
crankcase gas leaves via the camshaft cover port. The rocker cover features circular chambers which promote
swirl in the oil mist emanating from the cylinder head and camshaft carrier. As the mist passes through the series
of chambers between the rocker cover and oil separator plate, oil particles are thrown against the separator walls
where they condense and fall back into the cylinder head via two air inlet holes located at each end of the rocker
cover.
The breather valve is a pressure depression limiting valve which progressively closes as engine speed increases,
thereby limiting the depression in the crankcase. The valve is of moulded plastic construction and has a port on
the underside which plugs into a port in the flexible air duct. A port on the side of the breather valve connects to
the camshaft cover port by means of a breather hose which is constructed from a heavy duty braided rubber hose
which is held in place by hose clips. A corrugated plastic sleeve is used to give further protection to the breather
hose. The breather valve is orientation sensitive, and’TOP’is marked on the upper surface to ensure it is
mounted correctly.
It is important that the system is air tight. Hose connections to ports should be checked and the condition of the
breather hose should be periodically inspected to ensure it is in good condition.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 222 of 667

18 - ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPONENT LOCATION 2...................................................................................
DESCRIPTION 5.....................................................................................................
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) 6.................................................................
SENSOR - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) 7....................................................................
SENSOR - AMBIENT AIR PRESSURE AND 8.......................................................
SENSOR - MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE 9................................................
SENSOR - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE 11.............................................
SENSOR - CRANKSHAFT SPEED AND 12...........................................................
SENSOR - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) 14............................................................
SENSOR - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) 15............................................................
ELECTRONIC UNIT INJECTOR (EUI) 18...............................................................
SENSOR - FUEL TEMPERATURE (FT) 20............................................................
RELAY - FUEL PUMP 21........................................................................................
RELAY - MAIN 21...................................................................................................
SWITCH - BRAKE PEDAL 22.................................................................................
SWITCH - CLUTCH PEDAL 22...............................................................................
MODULATOR - EXHAUST GAS REGULATOR (EGR) 23.....................................
WARNING LAMP - GLOW PLUG 23......................................................................
GLOW PLUGS 24...................................................................................................
TURBOCHARGER 26.............................................................................................
INTERCOOLER 27.................................................................................................
OPERATION 28......................................................................................................
REPAIR
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) 1.................................................................
SENSOR - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) 1....................................
SENSOR - CRANKSHAFT SPEED AND POSITION (CKP) 2................................
ProCarManuals.com
Page 226 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1.Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
2.Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
3.Glow plugs.
4.Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) / Inlet Air Temperature (IAT) sensor.
5.Fuel pump relay.
6.Engine Control Module (ECM).
7.Air Conditioning (A/C) and cooling fan relay.
8.Fuel Temperature (FT) sensor.
9.Crankshaft Speed and Position (CKP) sensor.
10.Electronic Unit Injectors (EUI).
11.Ambient Air Pressure (AAP) sensor.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 228 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
General
An engine control module (ECM) controls the five cylinder direct injection diesel engine, and works on the drive by
wire principal. This means there is no throttle cable, the ECM controls the drivers needs via a signal from the
Throttle Position (TP) sensor on the throttle pedal.
The ECM is a full authoritative diesel specific microprocessor that also incorporates features for air conditioning. In
addition, the ECM supplies output control for the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) and turbocharger boost
pressure. The ECM has a self diagnostic function, which is able to provide backup strategies for most sensor
failures.
The ECM processes information from the following input sources:
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
Ambient Air Pressure (AAP) sensor.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) / Inlet Air Temperature (IAT) sensor.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
Crankshaft Speed and Position (CKP) sensor.
Throttle Position (TP) sensor.
Fuel Temperature (FT) sensor.
Air conditioning request.
Air conditioning fan request.
Brake pedal switch.
Clutch pedal switch.
The input from the sensors constantly updates the ECM with the current operating condition of the engine. Once
the ECM has compared current information with stored information within its memory, it can make any adjustment
it requires to the operation of the engine via the following:
Air conditioning clutch relay.
Air conditioning cooling fan relay.
Electronic vacuum regulator solenoid.
Fuel pump relay.
Glow plug warning lamp.
Glow plugs.
Fuel injectors.
Main relay.
Turbocharger wastegate modulator.
Temperature gauge.
The ECM interfaces with the following:
Serial communication link.
Instrument pack.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 232 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION SENSOR - MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
(MAP) / INLET AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT)
The MAP/IAT sensors are combined in one unit located in the inlet manifold. It provides pressure and temperature
information about the air in the inlet manifold to the ECM. The ECM compares the voltage signal to stored values
and compensates fuel delivery as necessary. The ECM uses the signal from the MAP/IAT sensor for the following
functions:
To calculate the delivered fuel limits.
To calculate the air mass in the cylinder.
To calculate the air speed density.
To calculate the air temperature.
The MAP sensor works on the piezo crystal principal. Piezo crystals are pressure sensitive and will oscillate in
accordance to changes in air pressure. The MAP sensor produces a voltage between 0 and 5 volts proportional to
the pressure level of the air in the inlet manifold. A reading of 0 volts indicates a low pressure, a reading of 5 volts
a high pressure.
The IAT portion of the sensor works as a Negative Temperature Co-efficient (NTC) sensor. As air temperature
rises, the resistance in the sensor decreases. As temperature decreases the resistance in the sensor increases.
The ECM compares the voltage signal to stored values and compensates fuel delivery as necessary.
Inputs / Outputs
The MAP/IAT sensor (C0567-3) is provided a 5 volt supply by the ECM (C0158-8) on a pink/purple wire. The
MAP/IAT sensor provides the ECM with 2 outputs. The MAP sensor output (C0567-4) is connected to the ECM
(C0158-6) by a white/yellow wire. The IAT sensor output (C0567-2) is connected to the ECM (C0158-34) on a
green/black wire. The MAP/IAT sensor is earthed (C0567-1) via the ECM (C0158-17) on a pink/black wire.
ProCarManuals.com