1999 LAND ROVER DEFENDER ad blue
[x] Cancel search: ad bluePage 210 of 667

EMISSION CONTROL
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION EGR MODULATOR
1.Port to vacuum source (white band)
2.Port to EGR valve (blue band)3.Port to atmosphere via in-line filter (green band)
4.Harness connector
The EGR modulator is located on a plate fixed to the inner RH front wing. The modulator is attached to the plate
by two studs, each with two nuts which secure the assembly to a rubber mounting, which helps reduce noise. The
modulator must be mounted vertically with the two vacuum ports uppermost.
Modulator operation is controlled by a signal from the ECM which determines the required amount of EGR needed
in response to inputs relating to air flow, engine operation, and ambient conditions. The modulator has a two pin
connector at its base to connect it to the ECM via the engine harness.
The modulator features three ports:
The top port is identified by a white band and connects to a T-piece in the vacuum line via a small bore light
brown plastic hose. The two other ports on the T-piece connect to the vacuum line hoses of black vinyl tubing
between the vacuum pump and the brake servo assembly attached to the bulkhead. The vacuum pump end of
the tubing terminates in a rubber elbow, which gives a vacuum tight seal on the suction port of the vacuum
pump. The brake servo end of the tubing terminates with a non-return valve in a plastic housing which plugs
into the front face of the brake servo housing.
The middle port is identified by a blue band, and connects to the suction port on the EGR valve through a small
bore blue plastic hose.
The lower port is identified by a green band and connects to atmosphere through an in-line filter via a small
bore green plastic hose.
The blue and brown vacuum hoses are protected by corrugated plastic sheaths. The ends of the hoses are fitted
with rubber boots to ensure vacuum tight seals at the component ports.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 211 of 667

17EMISSION CONTROL
10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION INLET THROTTLE (ILT) MODULATOR
1.Port to vacuum source (white band)
2.Port to ILT valve (blue band)
3.Port to atmosphere via in-line filter (green band)
4.Harness connector (green)
The ILT modulator is located on a plate fixed to the inner wing on the RH side of the engine below the EGR
modulator. The modulator is attached to the plate by two through-studs, each with two nuts which secure the
modulator assembly to a rubber mounting which helps to reduce noise. The modulator must be mounted in the
vertical orientation with the two vacuum ports uppermost.
The modulator operation is controlled by a signal from the ECM which determines the required ratio of exhaust
gas to fresh inlet air needed in response to inputs relating to air flow and engine operating and ambient conditions.
The modulator has a green two-pin connector at its base to connect it to the ECM through the engine harness.
The ILT valve modulator features three ports:
The top port is identified by a white band and connects to a’T’-piece in the vacuum line via a small-bore brown
plastic hose where it is connected in parallel with the vacuum source line to the EGR valve modulator. The two
other ports on the’T’-piece connect vacuum line hoses of black vinyl tubing between the vacuum pump
attached to the alternator and the brake-servo assembly attached to the bulkhead.
The middle port is identified by a blue band and connects to the suction port on the ILT valve through a
small-bore blue plastic hose.
The lower port is identified by a green band and connects to atmosphere through an in-line filter via a green
plastic hose and a three-way connector positioned in-line between the modulators and the filter. The ILT
modulator hose is connected opposite to the two parallel ports at the three-way connector which connect the
vent lines to the EGR valve modulator and the in-line filter. The other port of the in-line filter vents directly to
atmosphere.
The blue and brown vacuum hoses are protected by corrugated plastic sheaths. The ends of the hoses are fitted
with rubber boots to ensure vacuum tight seals at the component ports.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 212 of 667

EMISSION CONTROL
11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION EGR VALVE
1.EGR valve vacuum port
2.EGR valve assembly
3.Gasket - EGR valve to inlet manifold
4.EGR pipe connection5.Exhaust gas intake
6.Intake air
7.EGR valve open (vacuum applied to EGR valve)
8.EGR valve closed (no vacuum applied to EGR
valve)
The EGR valve is a cast and machined assembly which locates on the front end of the inlet manifold assembly.
The machined faces of the EGR assembly and the inlet manifold are attached attached together using four bolts
passing through the four corners of a flange in the EGR assembly to tappings in the front face of the inlet manifold.
A gasket is used to seal the interface between the EGR valve and the front face of the inlet manifold. The gasket
should be changed every time the EGR valve assembly is removed from the air intake manifold.
The intake side of the EGR valve allows the passage of fresh intercooled air through to the inlet manifold via a
rubber hose which is attached to the front face of the EGR valve assembly by a metal band clamp. The bottom
port of the EGR valve is connected to the EGR pipe using a metal band clamp.
A vacuum port on top of the EGR valve connects the EGR solenoid through a blue, small bore suction hose.
When a vacuum is applied to the EGR valve suction port it causes a spindle with sealing disc (EGR valve) to be
raised, thereby opening the port at the EGR pipe to allow the recirculated exhaust gas to pass through into the
inlet manifold. When the vacuum is removed from the suction port the EGR valve returns to its rest position under
the influence of a spring to tightly close the exhaust gas port. Thus, controlled opening of the EGR valve
determines the mass of recirculated gas allowed to flow through to the inlet manifold.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 213 of 667
17EMISSION CONTROL
12
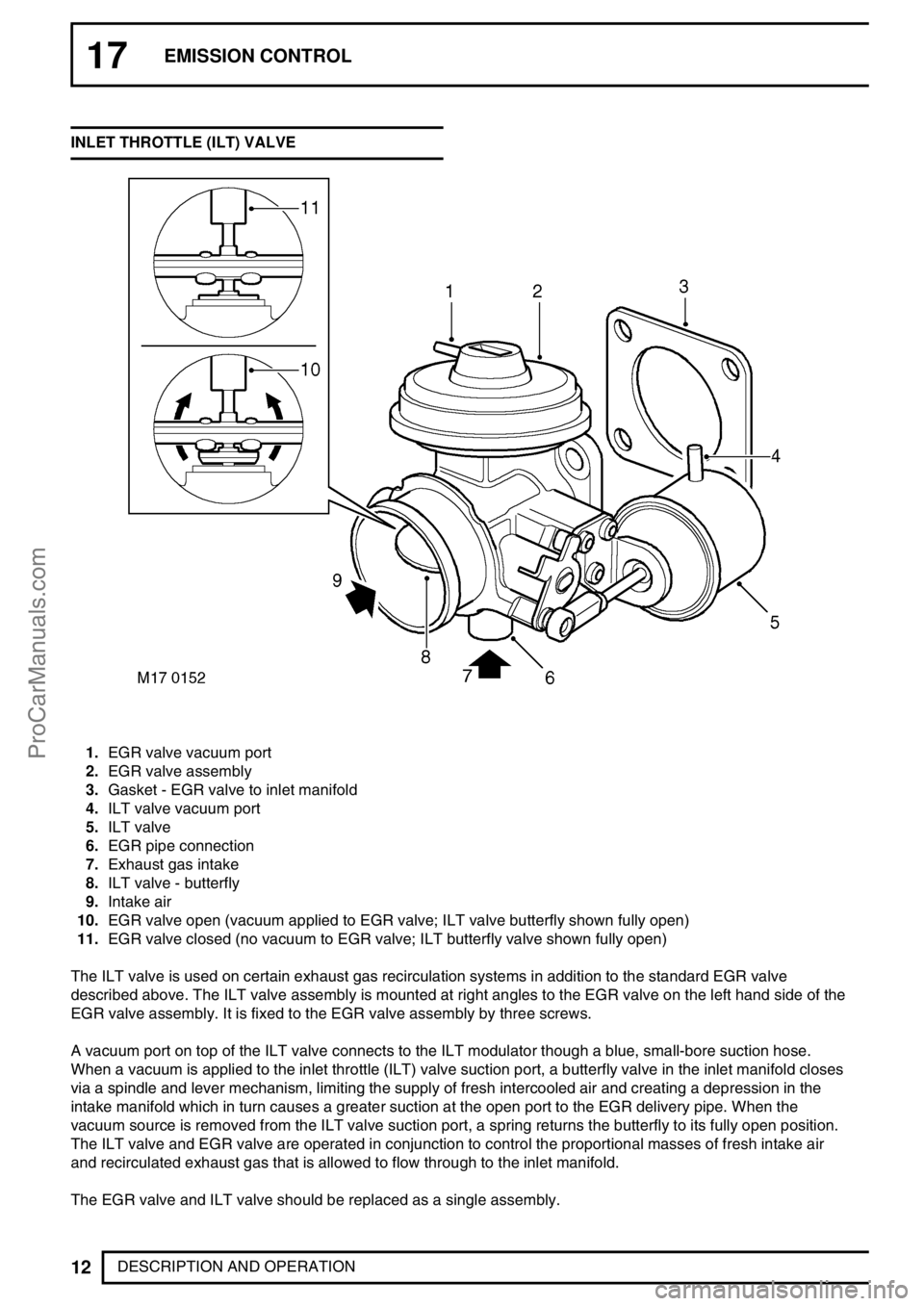
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION INLET THROTTLE (ILT) VALVE
1.EGR valve vacuum port
2.EGR valve assembly
3.Gasket - EGR valve to inlet manifold
4.ILT valve vacuum port
5.ILT valve
6.EGR pipe connection
7.Exhaust gas intake
8.ILT valve - butterfly
9.Intake air
10.EGR valve open (vacuum applied to EGR valve; ILT valve butterfly shown fully open)
11.EGR valve closed (no vacuum to EGR valve; ILT butterfly valve shown fully open)
The ILT valve is used on certain exhaust gas recirculation systems in addition to the standard EGR valve
described above. The ILT valve assembly is mounted at right angles to the EGR valve on the left hand side of the
EGR valve assembly. It is fixed to the EGR valve assembly by three screws.
A vacuum port on top of the ILT valve connects to the ILT modulator though a blue, small-bore suction hose.
When a vacuum is applied to the inlet throttle (ILT) valve suction port, a butterfly valve in the inlet manifold closes
via a spindle and lever mechanism, limiting the supply of fresh intercooled air and creating a depression in the
intake manifold which in turn causes a greater suction at the open port to the EGR delivery pipe. When the
vacuum source is removed from the ILT valve suction port, a spring returns the butterfly to its fully open position.
The ILT valve and EGR valve are operated in conjunction to control the proportional masses of fresh intake air
and recirculated exhaust gas that is allowed to flow through to the inlet manifold.
The EGR valve and ILT valve should be replaced as a single assembly.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 235 of 667

18ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
12
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION SENSOR - CRANKSHAFT SPEED AND
POSITION (CKP)
The CKP sensor is located in the transmission housing with its tip adjacent to the outer circumference of the
flywheel. The CKP sensor works on the variable reluctance principal, which sends a signal back to the ECM in the
form of an ac voltage.
The ECM uses the signal from the CKP sensor for the following functions.
To calculate engine speed.
To determine engine crank position.
To determine fuel injection timing.
The CKP sensor works as a Variable Reluctance Sensor (VRS). It uses an electromagnet and a target ring to
generate a signal. As the target ring passes the tip of the CKP sensor the magnetic field produced by the sensor is
cut and then re-instated. The ECM measures the signal as an ac voltage.
The outer circumference of the flywheel acts as the target ring for the sensor. The flywheel is divided into 36
segments, each of 10°. 31 segments have drilled holes and 5 segments are spaces. This equals 360°or one
engine revolution. The 5 spaces correspond to the TDC position of the 5 cylinders. This allows the ECM to control
fuel injection timing for each of the cylinders.
Inputs / Outputs
The two pins of the CKP sensor (C1068-1 & C1068-2) are both outputs. The ECM (C0158-13 & C0158-36)
processes the outputs of the sensor. To protect the integrity of the CKP sensor signal, an earth screen is used.
The ECM measures the outputs from the CKP sensor. The ECM (C0158-13) measures a positive signal on a
pink/black wire, and a negative signal (C0158-36) on a white/blue wire. The earth path for the sensor is via the
ECM (C0158-16).
ProCarManuals.com
Page 241 of 667

18ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
18
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ELECTRONIC UNIT INJECTOR (EUI)
The EUI’s are located in the top of the engine inside the camshaft cover. There is one EUI per cylinder. They inject
finely atomised fuel directly into the combustion chamber. Each EUI has its own electrical connection, which is
linked to a common harness also located under the camshaft cover. Each of the EUI’s has its own 5 letter grading
code. This code is used so that greater EUI precision is achieved.
Using an injection timing map within its memory and information from the CKP sensor the ECM is able to
determine precise crankshaft angle. When the ECM determines the crankshaft speed and position it closes the
spill valve within the EUI. Fuel pressure rises inside the EUI to a predetermined limit of 1500 bar (22,000 lbf.in
2)on
pre EU3 models, and 1750 bar (25,500 lbf.in2) on EU3 models . At this limit the pintle lifts off its seat allowing the
fuel to inject into the combustion chamber. The ECM de-energises the spill valve to control the quantity of fuel
delivered. This causes a rapid pressure drop within the EUI which allows the EUI return spring to re-seat the
pintle, ending fuel delivery.
The electrical circuit that drives the EUI works in two stages depending on battery voltage. If battery voltage is
between 9 and 16 volts the EUI’s will provide normal engine performance. If however battery voltage falls to
between 6 and 9 volts on pre EU3 models, EUI operation is restricted to a limit of 2100 rev/min. On EU3 models,
EUI operation is restricted to idle. If the vehicle is fitted with a new ECM, the EUI grades for that specific vehicle
must be downloaded to the new ECM using TestBook. In the event of the engine failing to rev above 3000 rev/min
it is probable that the EUI grading has not been completed.
Input / Output
Input to the EUI takes the form of both mechanical and electrical signals. The mechanical input to the EUI is diesel
fuel via the fuel pump operating at approximately 4 to 5 bar (58 to 72 lbf.in
2). Each of the EUI’s is operated
mechanically by an overhead camshaft to enable injection pressures of up to 1500 bar (22,000 lbf.in2) on pre EU3
models, and 1750 bar (25,500 lbf.in2) on EU3 models, to be achieved. The ECM controls the EUI’s to ensure that
fuel delivery is precise and as intended.
The EUI’s earth paths are as follows:
EUI 1 (C0522-1) via the ECM (C0158-25) on a yellow wire.
EUI 2 (C0523-1) via the ECM (C0158-26) on a yellow/brown wire.
EUI 3 (C0524-1) via the ECM (C0158-27) on a yellow/blue wire.
EUI 4 (C0525-1) via the ECM (C0158-24) on a yellow/red wire.
EUI 5 (C0526-1) via the ECM (C0158-1) on a yellow/purple wire.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 244 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
21
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION RELAY - FUEL PUMP
The fuel pump relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It switches on the fuel pump to draw fuel from
the tank to the electronic unit injectors (EUI).
Input / Output
The fuel pump relay is a 4 pin normally open relay. The fuel pump relay (C0730-4) is provided with a feed by the
main relay (C0063-78) via header 291 on a brown/orange wire. An earth path is provided for the fuel pump relay
(C0730-6) via the ECM (C658-5) on a blue/purple wire. This energises the fuel pump relay and allows a feed to be
provided to the fuel pump. When the ECM interrupts the earth, the relay is de-energised and the fuel pump stops
operating.
The fuel pump relay can fail in one or more of the following ways:
Relay open circuit.
Short circuit to vehicle supply.
Short circuit to vehicle earth.
Broken relay return spring.
In the event of a fuel pump relay failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
Engine will crank but not start.
If the engine is running, it will stop.
RELAY - MAIN
The main relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box and supplies battery voltage to the following:
The ECM.
The MAF sensor.
Fuel pump relay.
Input / Output
The main relay is a 4 pin normally open relay, which must be energised to provide a voltage to the ECM. The main
relay (C0063-86) is provided with an earth path via a transistor within the ECM (C0658-21) on a blue/red wire.
When the earth path is completed, the relay is energised and supplies the ECM (C0658-3, C0658-22 & C0658-27)
with a feed on brown/orange wires via header 291.
The main relay can fail in the following ways:
Relay open circuit.
Short circuit to vehicle supply.
Short circuit to vehicle earth.
Broken relay return spring.
In the event of a main relay failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
Engine will crank but not start.
If the engine is running, it will stop.
For the ECM start up to take place the ignition feed when the switch is in position’II’must be greater than 6.0
volts.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 246 of 667

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
23
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION MODULATOR - EXHAUST GAS REGULATOR (EGR)
The EGR modulator is located on the RH side inner front wing. It regulates the vacuum source to the EGR valve
allowing it to open or close. The ECM utilises the EGR modulator to control the amount of exhaust gas being
recirculated in order to reduce exhaust emissions and combustion noise. Optimum EGR is usually obtained when
the vehicle is operating at light throttle openings, and the vehicle is cruising at approximately 2000 to 3000
rev/min.
Input / Output
The EGR modulator (C0191-1) receives a feed from the main relay (C0063-87) on a brown/orange wire via header
294. The earth path for the modulator (C0191-2) is controlled by the ECM (C0158-3) on a blue wire. The length of
time the ECM supplies an earth is how long the exhaust gases are allowed to recirculate. The ECM decides how
long to supply the earth by looking at engine temperature and engine load.
The EGR modulator can fail in one or more of the following ways:
Solenoid open circuit.
Short circuit to vehicle supply.
Short circuit to earth.
In the event of an EGR modulator failure, the EGR system will become inoperative.
WARNING LAMP - GLOW PLUG
The glow plug warning lamp is located in the instrument pack. It illuminates to alert the driver that the glow plugs
are being heated prior to the engine being started. The length of time that the lamp illuminates and the glow plugs
are operating prior to cranking is the pre-heat period. The length of time of this period is determined by the ECT
sensor signal, controlled by the ECM.
ProCarManuals.com