Page 523 of 1395
E Po3ition
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft.
The countershaft is locked by the park pawl interlocking the park gear,
E Position
Engine power transmitted from the torque converter drives the mainshaft. but hydraulic pressure is not applied to the
clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft. The countershaft 4th gear is engaged with the reverse selector hub
and the countershaft by the reverse selector, when the shift lever is shifted in E position from E or E position. The
countershaft reverse gear is engaged when shifted from E position.
NOTE; The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; oower flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identi-
cal to the 4WD exceDt for oarts related to the transfer assemblv.
PARK GEAR
SELECTOR
(cont'd)
COUNTERSHAFTREVEBSE GEAR
14-7
www.emanualpro.com
Page 524 of 1395
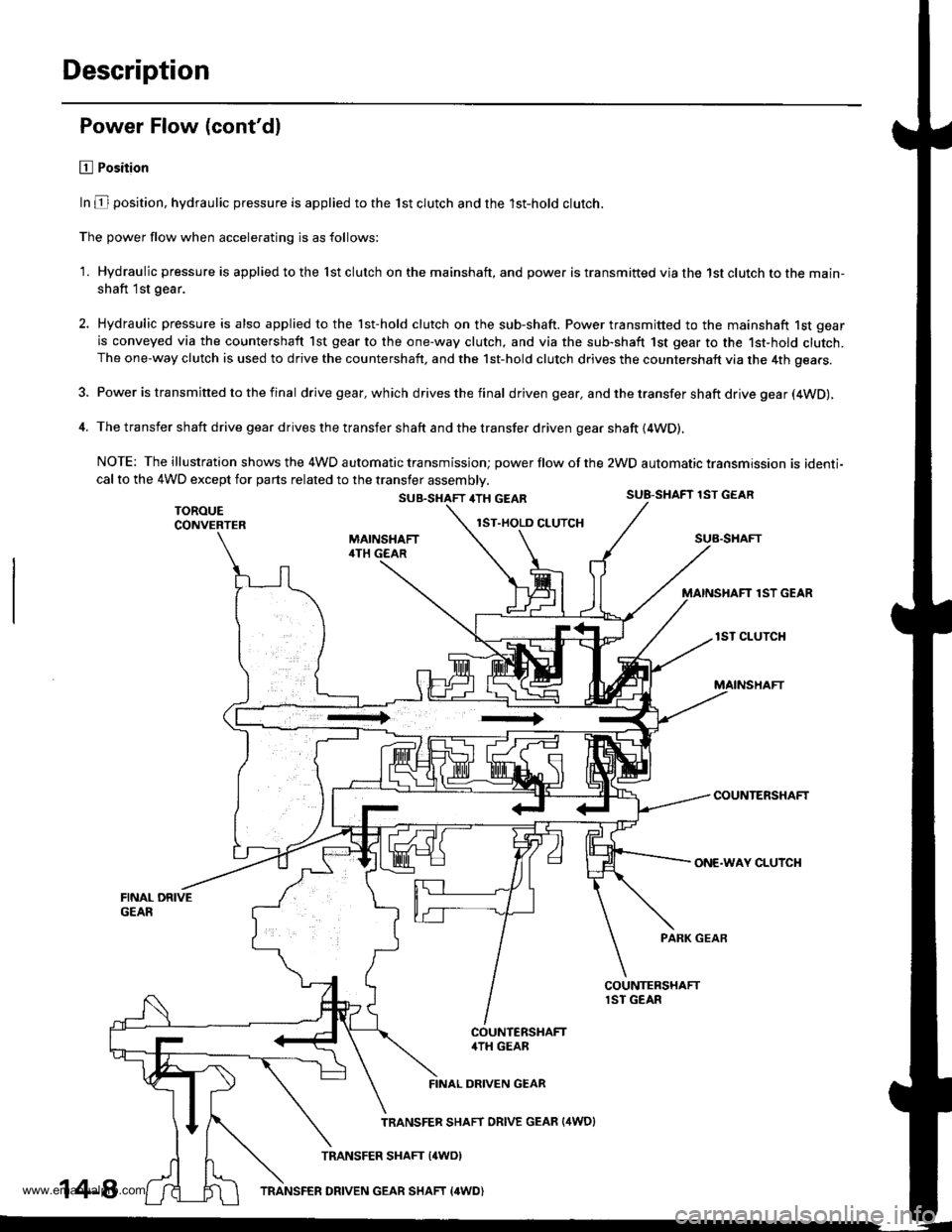
Description
Power Flow (cont'dl
E Position
In E position, hydraulic pressure is applied to the lst clutch and the lst-hold clutch.
The power flow when accelerating is as follows:
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the lst clutch on the mainshaft, and power is transmitted via the 1st clutch to the main-
shaft 1st gear.
Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the lst-hold clutch on the sub-shaft. Power transmitted to the mainshaft 1st gear
is conveyed via the countershaft 1st gear to the one-way clutch, and via the sub-shaft 1st gear to the 1st-hold clutch.The one-way clutch is used to drive the countershaft, and the 1st-hold clutch drives the countershaft via the 4th gears.
Power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which drives the final driven gear, and the transfer shaft drive gear (4WD),
The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE; The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmissjon; power flow ot the 2WD automatic transmission is identi-cal to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
SUB.SHAFT 4TH GEARSU8-SHAFT 1ST GEAR
4.
TOROUECONVERTERlST.HOLD CLUTCHSUB.SHAFT
1ST GEAR
lST CLUTCH
COUNTERSHAFT
ONE.WAY CLUTCH
FINAL DRIVEGEAR
PARK GEAB
COUNTERSHAFT4TH GEAR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
TRANSFER SHAFT ORIVE GEAR {4WD}
TRANSFER SHAFT {4WD}
14-8TRANSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT {4WD)
www.emanualpro.com
Page 525 of 1395
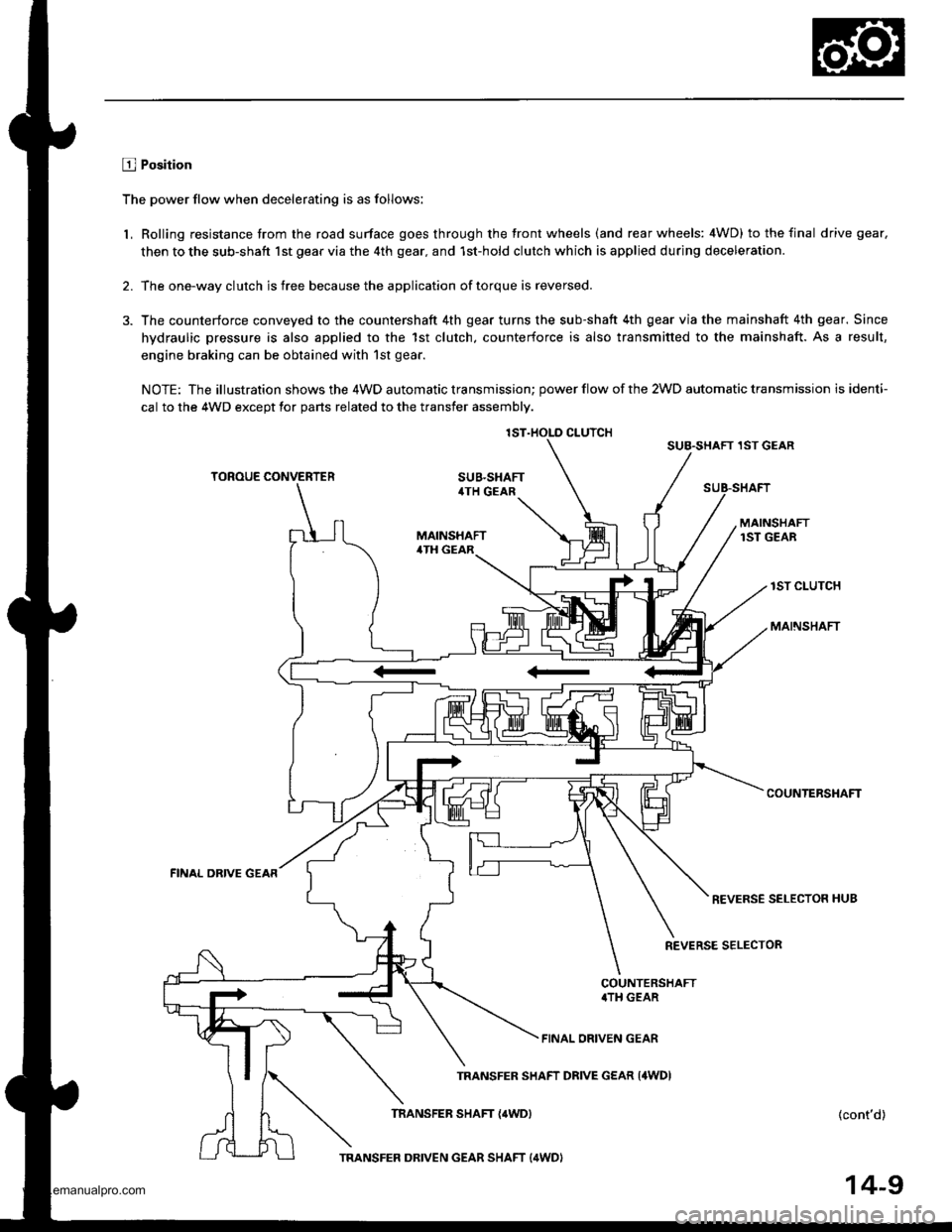
2.
L
E Position
The power flow when decelerating is as follows:
Rolling resistance trom the road surface goes through the tront wheels (and rear wheels: 4WD) to the final drive gear.
then to the sub-shaft lst gear via the 4th gear. and 1st-hold clutch which is applied during deceleration.
The one-way clutch is free because the application of torque is reversed.
The counterforce conveyed to the countershaft 4th gear turns the sub-shaft 4th gear via the mainshaft 4th gear. Since
hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch. counterforce is also transmitted to the mainshaft. As a result,
engine braking can be obtained with'lst gear.
NOTE: The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; power flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identi-
cal to the 4WD except tor parts related to the transfer assembly.
J.
SUB.SHAFT 1ST GEAR
TOROUE CONVERTER
FINAL DRIVE GEAR
SUB.SHAFT{TH GEAR
MAINSHAFTlST GEAR
lST CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
REVERSE SELECTOR HUB
REVERSE SELECTOR
COUNTERSHAFTIITH GEAR
FINAL ORIVEN GEAR
TRANSFER SHAFT DRIVE GEAR {4WDI
TRANSFEB SHAFT {{WD){cont'd}
lST.HOLD CLUTCH
TRANSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT {,lWDl
14-9
www.emanualpro.com
Page 526 of 1395
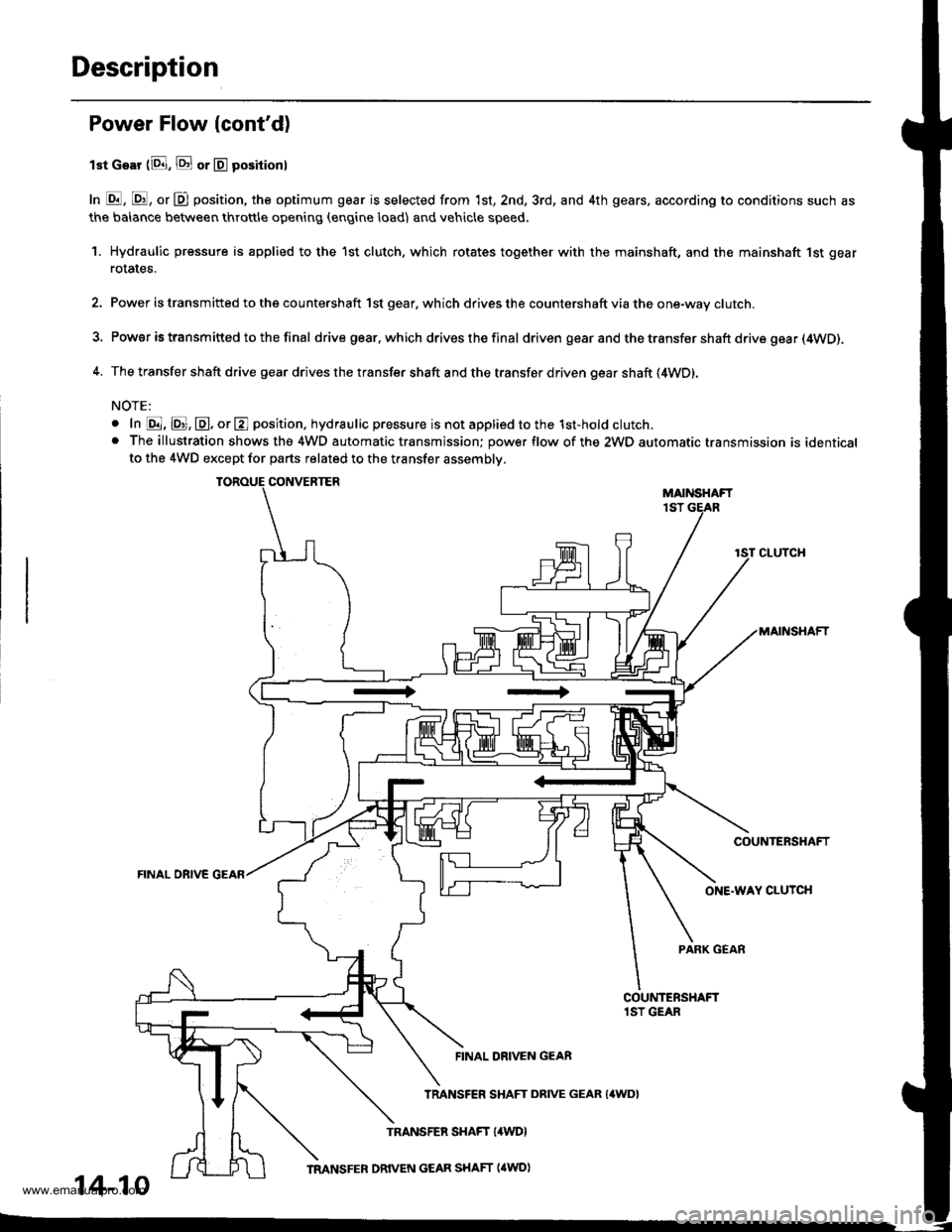
Description
Power Flow lcont'd)
lst Gear (8. E or E positionl
In E, E, or D position, the optimum gear is selected from 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th gears, according to conditions such as
the balance between throttle opening (engine load) and vehicle speed.
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 1st clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 1st gear
rotates.
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 1st gear. which drives the countershaft via the one-way clutch.
3. Power is transm itted to the final drive gear.which drives the final driven gear and the transfer shaft drive gea r (4WD).
4. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE:
o In @, @, @, or E position. hydraulic pressure is not applied to the 1st-hold clutch.. The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; power flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identicalto the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
CONVERTERMAIiISHAFT1ST
CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
FINAL OBIVE GEAR
ONE.WAY CLUTCH
PARK GEAR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
14-10
TRANSFER SHAFT DRIVE GEAR {4WD}
www.emanualpro.com
Page 527 of 1395
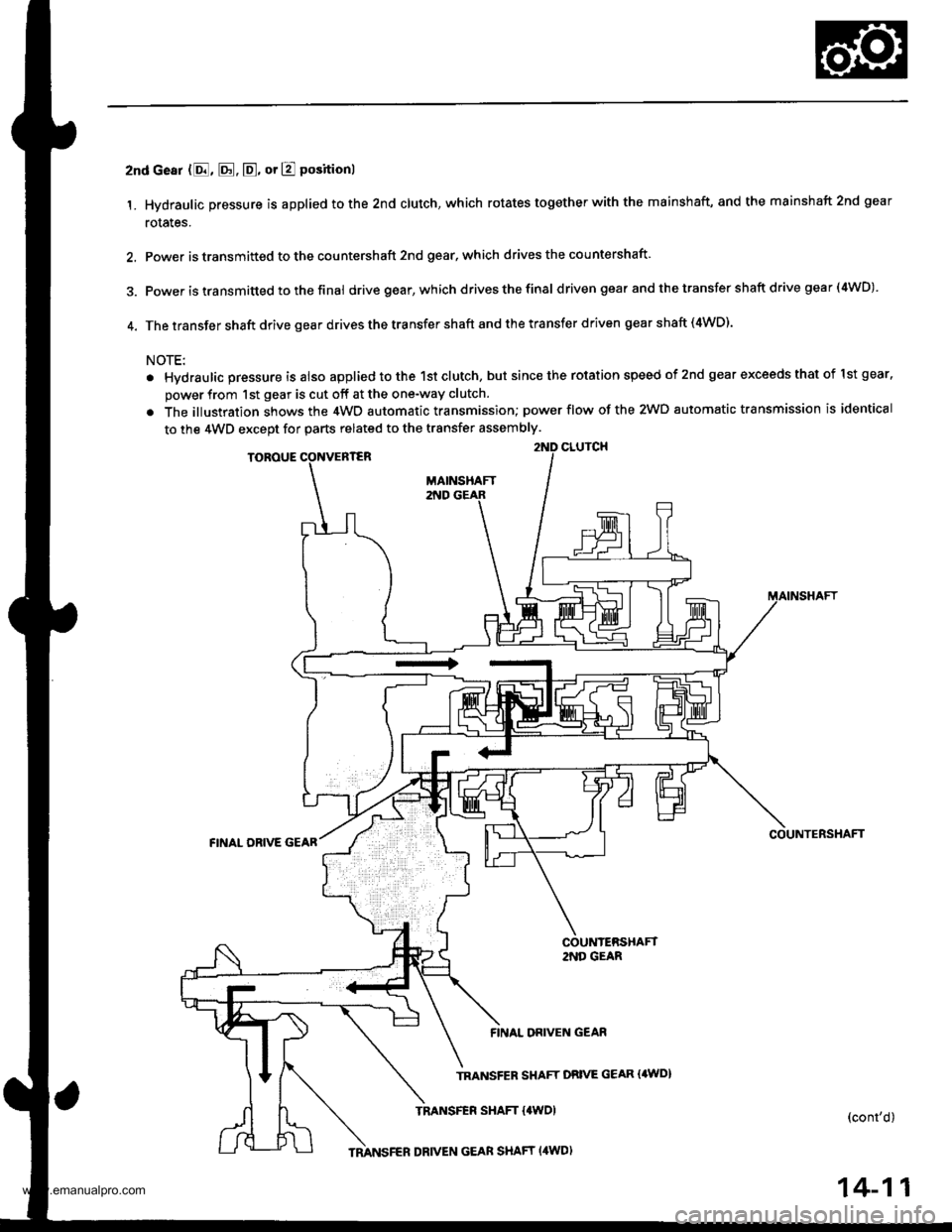
2nd cesr (8, E. E, or E positionl
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 2nd clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 2nd gear
rotales.
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 2nd gear, which drives the countershaft
3. power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which drivesthefinal d riven gear and the transfer shaft drive gea r (4WD)
4. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE:
. Hvdraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch, but since the rotation speed of 2nd gear exceeds that of lst gear.
power from 1st gear is cut off at the one-way clutch.
. The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; power flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
CLUICHTOROUE
COUNTERSHAFTFINAL ORIVE GEAR
2NO GEAR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAF
TRANSFER SHAFT DBIVE GEAR {4WD}
TRANSFER SHAFT {4WDI(cont'd)
TMNSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT (4WD)
14-11
www.emanualpro.com
Page 528 of 1395
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
3rd Gear {8. @, or @ position)
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 3rd clutch. Power from the mainshaft 3rd gear is transmitted to the countershaft
3rd gear.
2. Power is transm ifted to the final d rive gear, wh ich d rives the f inal driven gear and the transfer shaft drive gear (4WD).
3, The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transter shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE:
. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch, but since the rotation speed of 3rd gear exceeds that of 1st gear,
power from lst gear is cut off at the one-way clutch.
. The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; Dower flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
CONVERTEF
MAINSHAFT 3RD GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT3RO GEAR
3RD CLUTCH
DRIVEN GEAR
SHAFT DRIVE GEAR (4WO)
TRANSFER SHAFT (,lwDl
TRANSFER ORIVEN GEAN SHAFT (4WD)
14-12
www.emanualpro.com
Page 529 of 1395

4th Goar (E or D positionl
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 4th clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 4th gear
rotates,
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 4th gear, which drives the countershaft.
3. Power is transm ifted to the f inal d rive gear, which drives the fina I driven gear and the transfer shaft drive gear (4WD).
4. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft {4WD).
NOTE:
. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch, but since the rotation speed of 4th gear exceeds that of 1st gear,
power from 1st gear is cut off at the one-way clutch,
. The illustration shows the 4WO automatic transmission; power flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
ilTH GEAR
TOROUE CONVERTER
.TH CLUTCH
COU'{TERSHAFT
REVERSE SELECTOR HUB
REVERSE SELECTOR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
TRANSFEB SHAFT DRIVE GEAB I'WD)
TNANSFER SHAFT I4WDI{cont'd)
14-13
TMNSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT (4WDI
www.emanualpro.com
Page 530 of 1395
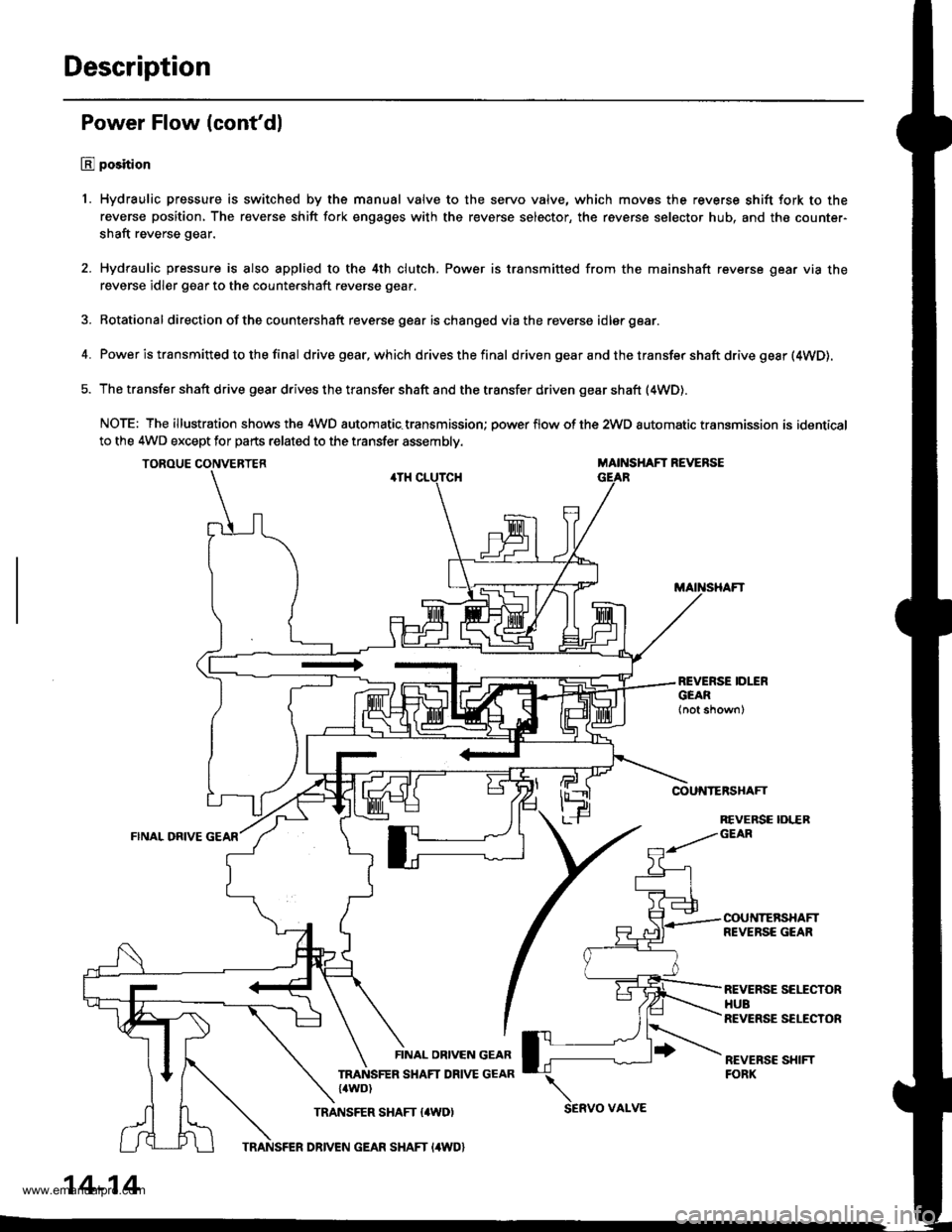
Description
Power Flow (cont'dl
E position
1. Hydraulic pressure is switched by the manual valve to the servo valve, which movss the reverse shift fork to the
reverse position, The reverse shift fork engages with the reverse selector, the reverse selector hub, and the counter-
shaft reverse gear.
2. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 4th clutch. Power is transmitted from the mainshaft reverse gear via the
reverse idler gear to the countershaft reverse gear.
3. Rotational direction ofthe countershaft reverse gear ischanged viathe reverse idlergear.
4. Power is transmitted to the final drivegear,which drivesthefinal d riven gear a nd the transfer shaft drive gesr (4WD).
5. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE: The illustration shows the 4WD automatic.transmission; power flow of the 2wD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
TOROUE CONVERTERMAINSHAFT REVERSE
COUNTERSHAFT
FINAL ORIVE
REVERSE IDLERGEAR
COUNTERSHAFTREVERSE GEAR
REVERSE SEITCTORHUBREVERSE SELECTOR
REVEBSC SHIFTFORK
FINAL OBIVEN GEAR
TRANSFER SHAFT DRIVE GEAR{4WD)
TRANSFER SHAFT {4WD)SERVO VAI-VE
14-14
TRANSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT I4WD}
www.emanualpro.com