Page 694 of 2189

Description
Electronic Control System {cont'dl
Ascending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E position, the system oxtends the sngagement area of2nd gear and 3rd gear to prevent ths transmission from fr€quently shifting between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rdand 4th gears, so the vehicle can run smooth and have more power when needed. There are two ascending modes withdifferent 3rd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradient stored in the pCM.
NOTE:
. The PCM memory contains shift schedules between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rd and 4th gears that enable thePCM's fuzzy logic to automatically select the most suitable gear according to the magnitude of a gradient. Fuzzy logic is a form of artificial intelligence that lets computers respond to changing conditions much like a humanmind would,
Dssconding Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hilt in E position, the shift-up speed from 3rd to 4th gearwhen th€ throftle is closed becomes faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear driving area.This, in combination with engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle isdescending. There are two descending modes with different downshift (4 - 3) schedules according to the magnitude of agradient stored in the PCM. When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating on a gradual hill, or when you areapplying the brakes on a steep hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear. When you accel6rate, the transmission willthen return to 4th gear.
ASCENDING MODEDESCENDING MODE
4TH SHIFTING
L.
F
CHARACTERISIICSCONTROL AREA
ff.1"11", vehicr. 3pe€dff;Tlr., vohicre speed
GRADUAL ASCENOINGCONTROL AREA
Docel6ration Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner. and needs to first decelerate and then accelerate. the rcM sets the data for decelerationcontrol to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 26 mph(41 km/h), the rcM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlier than normal to cope with upcoming acceleration.
14-16
Page 1128 of 2189
Wheel Alignment
,f,
Caster
NOTE: For proper inspection/adjustment of the wheel
alignment check and adjust the following before check-
ing the alignment.
. Check that the suspension is not modified.
. Check the tire size and tire pressure.
. Check the runout of the wheels and tires.
. Check the suspension ball ioints. {Hold a wheel with
your hands and move it up and down and right and
left to check for wobbling.)
Inspection
NOTE: Use commercia lly-available computerized four
wheel alignment equipment to measure wheel align-
ment {caster. camber, toe, and turning angle). Follow
the equiDment manufacturer's instructions.
Check the caster angle.
Caster angle: 1',10' I 1'
lf out of specification, check for bent or damaged
suspensron components.
2.
1.
18-4
Camber
lnspection
NOTE: Use commercially-available computerized four
wheel alignment equipment to measure wheel align-
ment (caster, camber, toe, and turning angle). Follow
the equipment manufacturer's instructions.
1. Check the camber angle.
Camber angle:
Front: 0'00' j 1"
Rear:-1"11"
2. lf out ol specification, check for bent or damaged
suspensron components.
Page 1129 of 2189
?
Front Toe Inspection/Adiustment
NOTE: Use commercially-available computerized four
wheel alignment equipment to measure wheel align-
ment (caster, camber, toe, and turning angle). Follow
the equipment manufacturer's instructions.
1. Check the tire pressure.
Center steering wheel spokes.
Check the toe with the wheels pointed straight
a head.
Front toe: lN 1 1 2 mm llN l/16 r 1/16 inl
- lf adjustment is required, go on to step 4.
- lf no adjustment is required, remove alignment
equrpmenr.
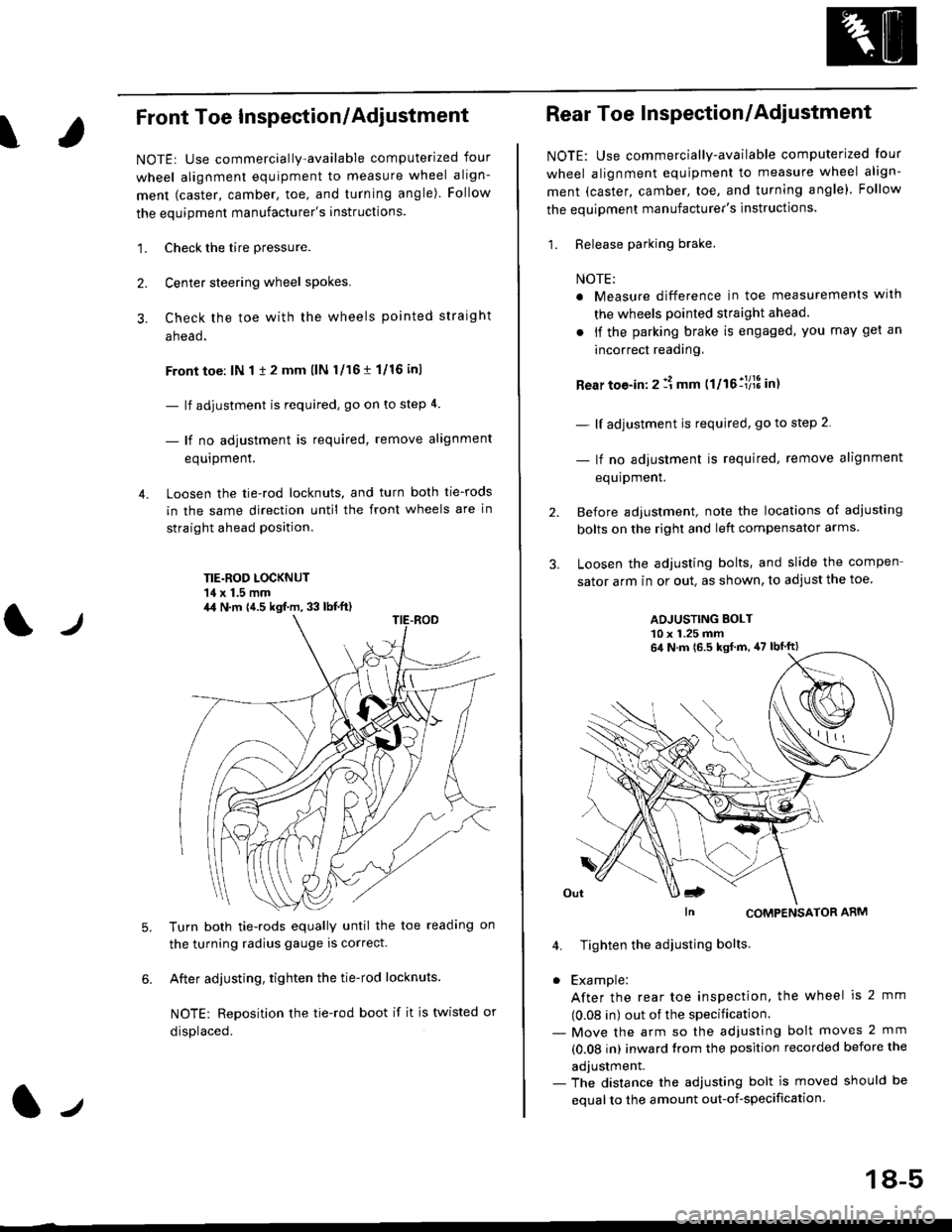
Loosen the tie-rod locknuts, and turn both tie-rods
in the same direction until the front wheels are in
straight ahead position.
TIE.ROD LOCKNUT'14 x 1.5 mm
4.
tJ
6.
Turn both tie-rods equally until the toe readang on
the turning radius gauge is correct.
After adjusting, tighten the tie-rod locknuts.
NOTE: Reposition the tie-rod boot if it is twisted or
displaced.
4,1 N.m {4.5 kgf.m, 33 lb{.ft)
2.
Rear Toe Inspection/Adiustment
NOTE: Use commercially-available computerjzed Iour
wheel alignment equjpment to measure wheel align-
ment (caster, camber, toe, and turning angle). Follow
the equipment manufacturer's instructions.
1. Release parking brake.
NOTE:
a Measure difference in toe measurements wlth
the wheels pointed straight ahead.
. if the parking brake is engaged, you may get an
incorrect readang,
Rear toe-in: 2 11 mm ttltollllS int
- lf adjustment is required, go to step 2.
- lf no adjustment is required, remove alignment
equipment.
Before adjustment, note the locations of adiusting
bolts on the right and left compensator arms
Loosen the adjusting bolts, and slide the compen
sator arm in or out. as shown, to adjust the toe
ADJUSTING BOLT10 x 1.25 mm
In CoMPENSAToR ARM
4. Tighten the adiusting bolts
. Example:
After the rear toe inspection, the wheel is 2 mm
(0.08 in) out of the specification.- Move the arm so the adjusfing bolt moves 2 mm
(0.08 in) inward trom the position recorded before the
adjustment.- The distance the adjusting bolt is moved should be
equal to the amount out-of-specification.
64 N.m 16.5 ksf m, 47 lbtft)
18-5
Page 1130 of 2189
Wheel Alignment
Turning Angle Inspection
NOTEr Use commercially-available computerized four
wheel alignment equipment to measure wheel align-
ment (caster, camber, toe, and turning angle). Follow
the equipment manufacturer's instructions.
'1. Turn the wheel right and left while applying the
brake, and measure the turning angle of both
wneets.
Turning angle:
lnward wheel: 39'50'
Outwald wheel (ref erencel: 33'10'
2.lf the turning angle
check for bent or
nents,
is not within the specifications,
da m aged suspension compo-
18-6