1998 SSANGYONG MUSSO manual transmission
[x] Cancel search: manual transmissionPage 998 of 1463
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-21
Downshift Type
RANGE ‘1’ (MANUAL ‘1’):
RANGE ‘2’ (MANUAL ‘2’):
RANGE ‘3’ (MANUAL ‘3’):
RANGE ‘D’ (DRIVE):
RANGE ‘N’ (NEUTRAL):
RANGE ‘R’ (REVERSE):
RANGE ‘P’ (PARK):Inhibited Above
First gear operation only with inhibited engagement as a function of vehicle
speed. Engine braking is applied with reduced throttle.
First and second gear operation with inhibited engagement of second gear, as
a function of vehicle speed. Engine braking is applied with reduced throttle.
First, second and third gear operation with an inhibited third gear engagement
at high vehicle speed. Refer to the vehicle owner’s manual.
Engine braking is applied with reduced throttle.
First, second, third and fourth gear operation. First to second (1-2), first to third
(1-3), second to third (2-3), second to fourth (2-4), third to fourth (3-4), fourth
to third (4-3), fourth to second (4-2), third to second (3-2), third to first (3-1)
and second to first (2-1), shifts are all available as a function of vehicle speed,
throttle position and the time rate of change of the throttle position (forced
downshift). Lockup clutch may be enabled in 3rd and 4th gears depending on
vehicle type. Refer to the owner’s manual.
Rear band applied only, with inhibited engagement as a function of vehicle
speed, engine speed and throttle position. The inhibitor switch allows the en-
gine to start.
Reverse gear operation, with inhibitor engagement as a function of vehicle
speed, engine speed and throttle position. The inhibitor switch enables reverse
lamp operation.
Rear band applied only, with inhibited engagement as a function of vehicle
speed, engine speed and throttle position. The transmission output shaft is
locked. The inhibitor switch allows the engine to start.
Table 2.1 - Gear Selections
DRIVING MODE SELECTOR
The driving mode selector consists of a mode selection switch and indicator light. The driving mode selector is
located on the centre console. See figure 2,1.
The schedules available to be selected vary with vehicle types. Typically the driver should have the option to select
between ‘NORMAL’ , ‘POWER’ or ‘WINTER’ modes.
When ‘NORMAL’ mode is selected upshifts will occur to maximise fuel economy and the indicator lights remain
extinguished. When ‘POWER’ mode is selected upshifts will occur to give maximum performance and the ‘POWER’
mode indicator light is switched on. When ‘WINTER’ mode is selected, starting at second gear is facilitated, the
‘WINTER’ mode indicator light is switched on and the ‘POWER’ mode indicator light is switched off.
Refer to the vehicle owner’s manual for specific modes for each vehicle type.
Page 1003 of 1463

5A-26 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Inhibitor
Switch Throttle Position Sensor
The throttle position sensor(TPS) is a resistance potentiometer
mounted on the throttle body of the engine.
It transmits a signal to the TCU proportional to the throttle plate
opening.
The potentiometer is connected to the TCU by three wires:
5 volts positive supply, earth and variable wiper voltage.
Throttle voltage adjustments are as follows:
lClosed throttle voltage is 0.2V to 1.0V.
lWide open throttle voltage is 3V -4.7V.
These measurements are taken between pins 29 and 27 of
the TCU.
Maintaining good shift feel through the transmission life span
is dependant on having an accurate measure of
the engine throttle position. To achieve this the TCU
continuously monitors the maximum and minimum throttle
potentiometer voltages and, if a change occurs, stores the new
voltage values.
However these limits will be lost and will require relearning
should a new TCU be installed, or the throttle calibration data
is cleared by the execution of a particular sequence, This last
instance depends on the installation, and reference should be
made to the Diagnostics Section of this manual. The relearning
will happen automaticallyNotice
Above figure of T.P.S. is for the diesel engine
which is installed on the injection pump.
Gear Position Sensor
The gear position sensor is incorporated in the inhibitor switch
mounted on the side of the transmission case.
(Refer to figure 3.5.) The gear position sensor is a multi-function
switch providing three functions:
lInhibit starting of the vehicle when the shift lever is in a
position other than Park or Neutral
lIlluminate the reversing lamps when Reverse is
selected indicate to the TCU which lever position has
been selected by way of a varying resistance (Refer to
table 3.3.)
Figure 3.5 - Inhibitor Switch
Page 1004 of 1463
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-27
Shift Lever Position
Manual 1
Manual 2
Manual 3
Drive
Netural
Reverse
ParkResistance (OHMS)
1k - 1.4k
1.8k - 2.2k
3k - 3.4k
4.5k - 4.9k
6.8k - 7.2k
10.8k - 11.2k
18.6k - 19k
Table 3.3 - Readings for Resistance/Shift Lever Positions
Diagnostics Inputs
The diagnostics control input or K-line is used to initiate the outputting of diagnostics data from the TCU to a diagnostic
test instrument. This input may also be used to clear the stored fault history data from the TCU’s
retentive memory. Connection to the diagnostics input of the TCU is via a connector included in the vehicle’s wiring
harness or computer interface. Refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s manual for the location of the self test
connectors.
Battery Voltage Monitoring Input
The battery voltage monitoring input connects to the positive side of the battery. The signal is taken from the
main supply to the TCU.
If operating conditions are such that the battery voltage at the TCU falls below 11.3V the transmission will adopt a ‘low
voltage’ mode of operating in which shifts into first gear are inhibited. All other shifts are allowed but may not occur
because of the reduced voltage. This condition normally occurs only when the battery is in poor condition.
When system voltage recovers, the TCU will resume normal operation after a 3 second delay period.
TCU Outputs
The outputs from the TCU are supplied to the components described below:
Solenoids
The TCU controls seven solenoids. Solenoids 1 to 6 (S1 to S6) are mounted in the valve body, while Solenoid 7 (S7)
is mounted in the pump cover. The normal state (OPEN/CLOSED) and the functions associated with the solenoids
are detailed in table 3.4. Table 3.5 details the S1 and S2 logic for static gear states. The logic during gear changes for
S1 to S4 and S7 is detailed in table 3.6.
Page 1008 of 1463

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-31
K-Line
The K-line is typically used for obtaining diagnostic information from the TCU. A computer with a special interface is
connected to the TCU and all current faults, stored faults, runtime parameters are then available. The stored fault
codes can also be cleared.
The K-line can be used for vehicle coding at the manufacturer’s plant or in the workshop. This allows for one TCU
design to be used over different vehicle models. The particular code is sent to the microprocessor via the K line and
this results in the software selecting the correct shift and VPS ramp parameters.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The hydraulic controls are located in the valve body, pump body and main case.
The valve body contains the following:
lManual valve,
lThree shift valves,
lSequence valve,
lsolenoid supply pressure regulator valve,
lline pressure control valve,
lclutch apply regulator valve,
lband apply regulator valve,
lS1 to S6, and
lReverse lockout valve.
lThe pump body contains the following:
lPrimary regulator valve for line pressure,
lconverter clutch regulator valve,
lconverter clutch control valve,
lS7,and
lC1 bias valve.
The main case contains the following:
lB1R exhaust valve
The hydraulic control system schematic is shown at figure 3.7.
All upshifts are accomplished by simultaneously switching on a shift valve(s), switching VPS pressure to the band
and/or clutch regulator valve, and then sending the VPS a ramped current. The shift is completed by switching the
regulators off and at the same time causing the VPS to reach maximum . pressure. All downshifts are accomplished
by switching VPS pressure to the band and/or clutch regulator valve and sending a ramped current to the VPS. The
shift is completed by simultaneously switching the regulators off, switching the shift valves and at the same time
causing the VPS to return to stand-by pressure.
The primary regulator valve is located in the pump cover and supplies four line pressures; high and low for forward
gears, and high and low for reverse. This pressure has no effect on shift quality and merely provides static clutch
capacity during steady state operation. Low pressure can be obtained by activating an On/off solenoid with high line
pressure being the default mode.
Torque converter lock-up is initiated by toggling the converter clutch control valve with an On/off solenoid. The actual
apply and release of the clutch is regulated by the VPS via the converter clutch regulator valve. As an additional
safety feature, the lock-up is hydraulically disabled in first and second gear by the bias valve which only supplies oil
to the lock-up solenoid when C1 is applied in third and fourth gears. This prevents the vehicle from being rendered
immobile in the unlikely event of S7 becoming stuck.
The solenoid supply valve provides reference pressure for all the solenoids.
Page 1011 of 1463
5A-34 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
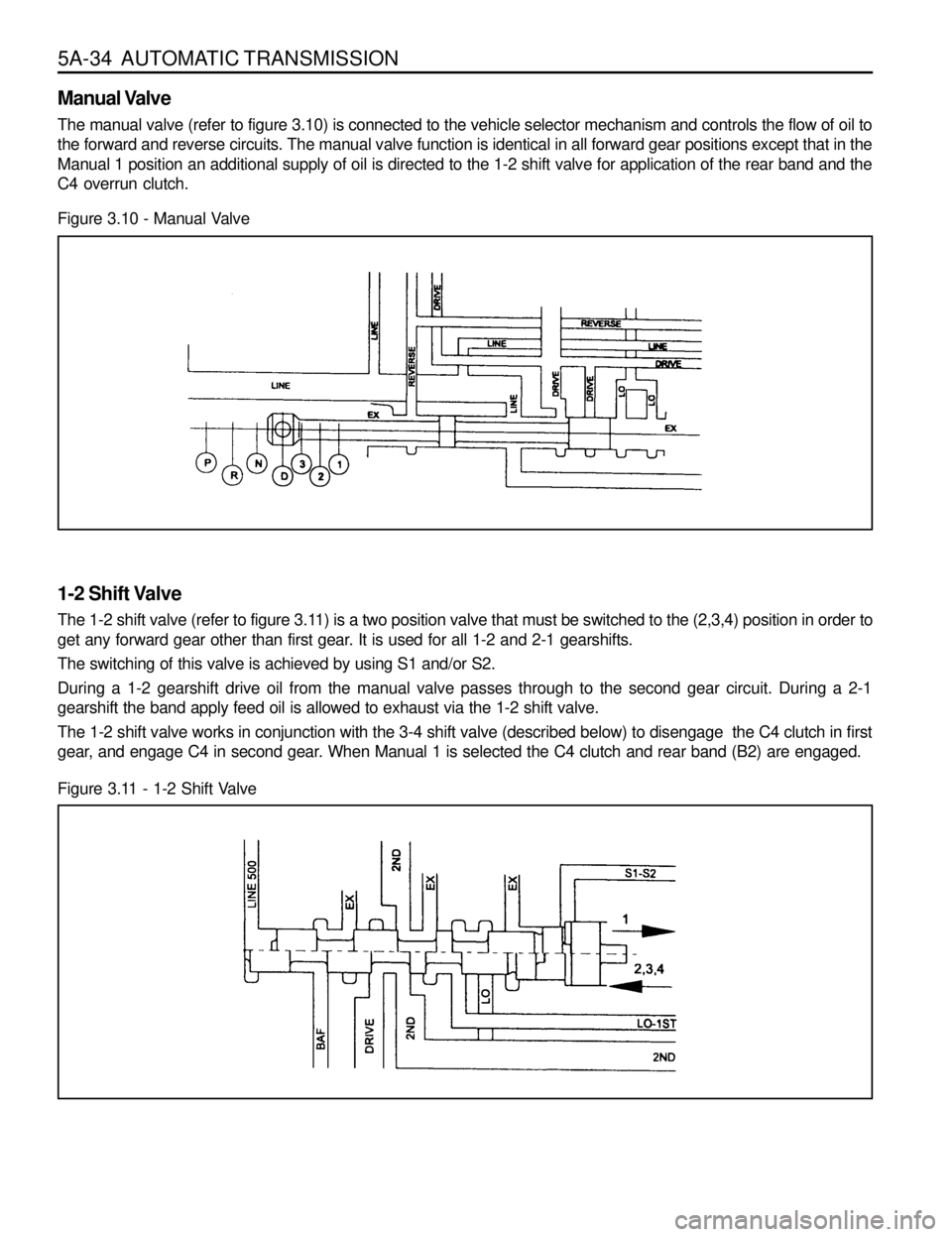
Figure 3.10 - Manual Valve
1-2 Shift Valve
The 1-2 shift valve (refer to figure 3.11) is a two position valve that must be switched to the (2,3,4) position in order to
get any forward gear other than first gear. It is used for all 1-2 and 2-1 gearshifts.
The switching of this valve is achieved by using S1 and/or S2.
During a 1-2 gearshift drive oil from the manual valve passes through to the second gear circuit. During a 2-1
gearshift the band apply feed oil is allowed to exhaust via the 1-2 shift valve.
The 1-2 shift valve works in conjunction with the 3-4 shift valve (described below) to disengage the C4 clutch in first
gear, and engage C4 in second gear. When Manual 1 is selected the C4 clutch and rear band (B2) are engaged.
Figure 3.11 - 1-2 Shift Valve
Manual Valve
The manual valve (refer to figure 3.10) is connected to the vehicle selector mechanism and controls the flow of oil to
the forward and reverse circuits. The manual valve function is identical in all forward gear positions except that in the
Manual 1 position an additional supply of oil is directed to the 1-2 shift valve for application of the rear band and the
C4 overrun clutch.
Page 1012 of 1463
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-35
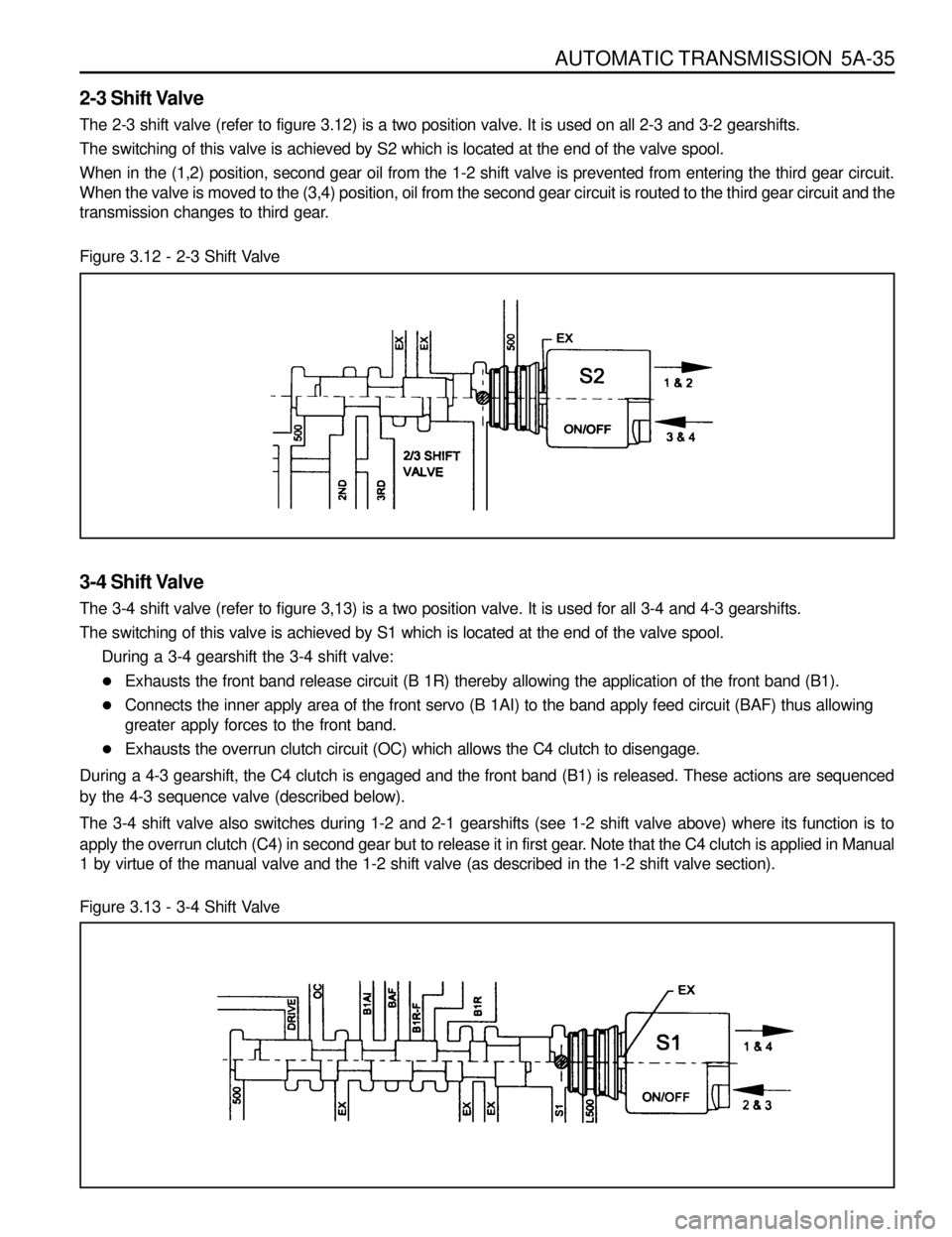
2-3 Shift Valve
The 2-3 shift valve (refer to figure 3.12) is a two position valve. It is used on all 2-3 and 3-2 gearshifts.
The switching of this valve is achieved by S2 which is located at the end of the valve spool.
When in the (1,2) position, second gear oil from the 1-2 shift valve is prevented from entering the third gear circuit.
When the valve is moved to the (3,4) position, oil from the second gear circuit is routed to the third gear circuit and the
transmission changes to third gear.
Figure 3.12 - 2-3 Shift Valve
3-4 Shift Valve
The 3-4 shift valve (refer to figure 3,13) is a two position valve. It is used for all 3-4 and 4-3 gearshifts.
The switching of this valve is achieved by S1 which is located at the end of the valve spool.
During a 3-4 gearshift the 3-4 shift valve:
lExhausts the front band release circuit (B 1R) thereby allowing the application of the front band (B1).
lConnects the inner apply area of the front servo (B 1AI) to the band apply feed circuit (BAF) thus allowing
greater apply forces to the front band.
lExhausts the overrun clutch circuit (OC) which allows the C4 clutch to disengage.
During a 4-3 gearshift, the C4 clutch is engaged and the front band (B1) is released. These actions are sequenced
by the 4-3 sequence valve (described below).
The 3-4 shift valve also switches during 1-2 and 2-1 gearshifts (see 1-2 shift valve above) where its function is to
apply the overrun clutch (C4) in second gear but to release it in first gear. Note that the C4 clutch is applied in Manual
1 by virtue of the manual valve and the 1-2 shift valve (as described in the 1-2 shift valve section).
Figure 3.13 - 3-4 Shift Valve
Page 1015 of 1463
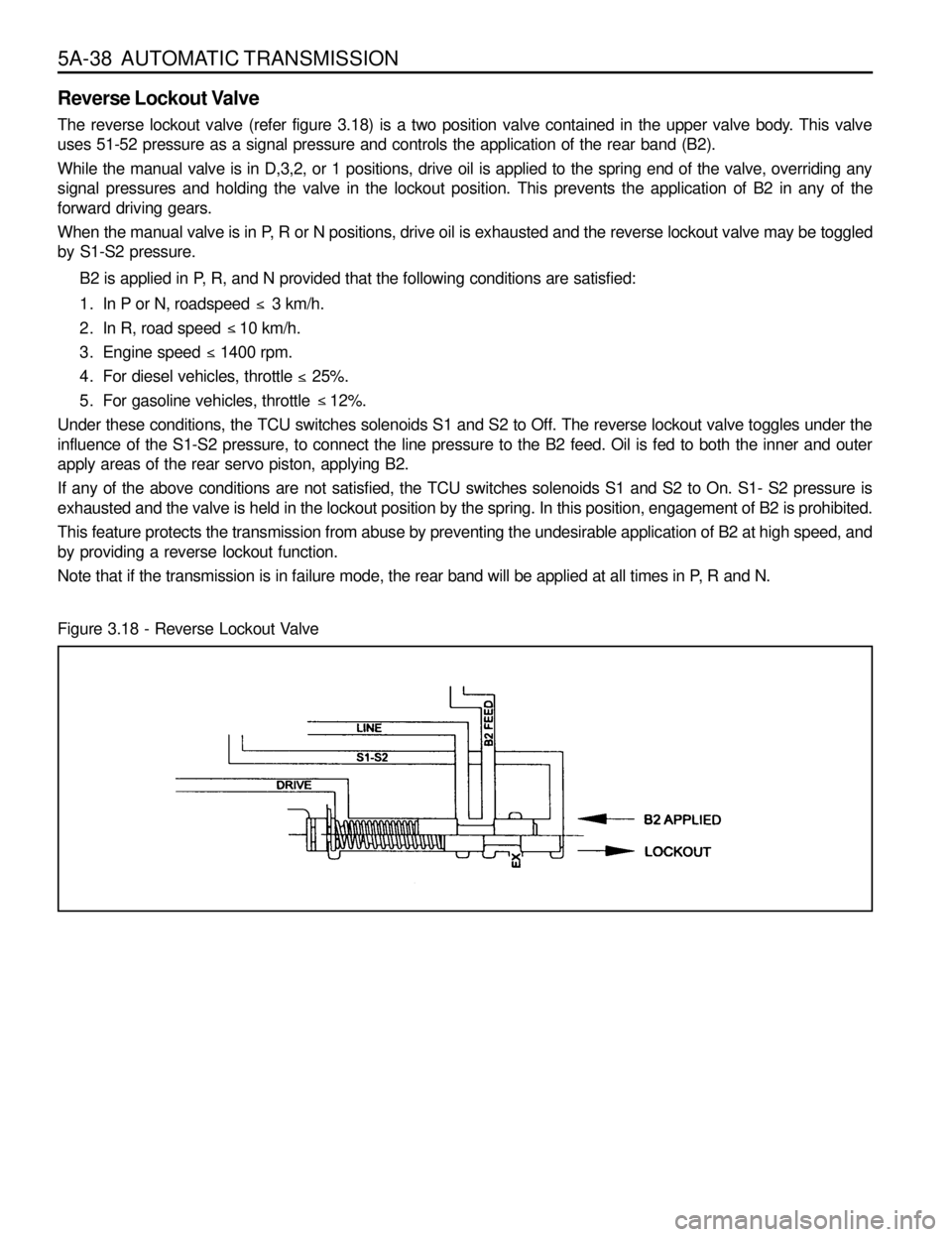
5A-38 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Reverse Lockout Valve
The reverse lockout valve (refer figure 3.18) is a two position valve contained in the upper valve body. This valve
uses 51-52 pressure as a signal pressure and controls the application of the rear band (B2).
While the manual valve is in D,3,2, or 1 positions, drive oil is applied to the spring end of the valve, overriding any
signal pressures and holding the valve in the lockout position. This prevents the application of B2 in any of the
forward driving gears.
When the manual valve is in P, R or N positions, drive oil is exhausted and the reverse lockout valve may be toggled
by S1-S2 pressure.
B2 is applied in P, R, and N provided that the following conditions are satisfied:
1. In P or N, roadspeed 3 km/h.
2. In R, road speed 10 km/h.
3. Engine speed 1400 rpm.
4. For diesel vehicles, throttle 25%.
5. For gasoline vehicles, throttle 12%.
Under these conditions, the TCU switches solenoids S1 and S2 to Off. The reverse lockout valve toggles under the
influence of the S1-S2 pressure, to connect the line pressure to the B2 feed. Oil is fed to both the inner and outer
apply areas of the rear servo piston, applying B2.
If any of the above conditions are not satisfied, the TCU switches solenoids S1 and S2 to On. S1- S2 pressure is
exhausted and the valve is held in the lockout position by the spring. In this position, engagement of B2 is prohibited.
This feature protects the transmission from abuse by preventing the undesirable application of B2 at high speed, and
by providing a reverse lockout function.
Note that if the transmission is in failure mode, the rear band will be applied at all times in P, R and N.
Figure 3.18 - Reverse Lockout Valve
<
<
<
<
<
Page 1019 of 1463
5A-42 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
POWER TRAIN SYSTEM
The Power Train System consists of:
lA torque converter with single face lock-up clutch
lFour multi-plate clutch assemblies
lTwo brake bands
lTwo one-way clutches
lPlanetary gearset
lParking mechanism
A conventional six pinion Ravigneaux compound planetary gearset is used with overdrive (fourth gear) being obtained
by driving the carrier.
The cross-sectional arrangement is very modular in nature. Four main sub-assemblies are installed within the case
to complete the build. These sub-assemblies are:
lGearset-sprag-centre support
lC1 -C2-C3-C4 clutch sub-assembly
lPump assembly
lValve body assembly
One, or a combination of selective washers are used between the input shaft flange and the number 4 bearing to
control the transmission end float. This arrangement allows for extensive subassembly testing and simplistic final
assembly during production.
A general description of the operation of the Power Train System is detailed below. Refer to table 4.1 and figure 4.1.
First gear is engaged by applying the C2 clutch and locking the 1-2 One Way Clutch (1-2 OWC). The 1-2 shift is
accomplished by applying the B1 band and overrunning the 1-2 OWC. The 2-3 shift is accomplished by applying the
C1 clutch and releasing the B1 band. The 3-4 shift is accomplished by re-applying the B1 band and overrunning the
3-4 OWC. Reverse gear is engaged by applying the C3 clutch and the B2 band.
The C4 clutch is applied in the Manual 1,2 and 3 ranges to provide engine braking. In addition, the C4 clutch is also
applied in the Drive range for second and third gears to eliminate objectionable freewheel coasting. The B2 band is
also applied in the Manual 1 range to accomplish the low-overrun shift.
Both the front and rear servos are dual area designs to allow accurate friction element matching without the need for
secondary regulator valves. All the friction elements have been designed to provide low shift energies and high static
capacities when used with the new low static co-efficient transmission fluids. Non-asbestos friction materials are used
throughout.
Gear
First
Second
Third
Fourth
Reverse
Manual 1Gear
Ratio
2.741
1.508
1.000
0.708
2.428
2.741C1
X
XC2
X
X
X
X
XC3
XC4
X
XB1
X
X
XB2
X
X1-2
OWC
X3-4
OWC
X
X
XLU
CLUTCH
X*
X ELEMENTS ENGAGED
* For Certain Vehicle Applications, Refer to the Owner's Manual. Table 4.1 - Engaged Elements vs Gear Ratios