Page 680 of 1463
M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2-31
Failure
codeItemChecking method Test
stepRequirementSpecified
valuePossible cause
1 liter of fuel
supply for
max. 35
seconds· ·· ·
· Fuel pump:
- Fuel supply
ratio· Ignition:ON
- Disconnect the fuel
return pipe and
connect the host to
beaker to collect
the supplied fuel Þ 1.0· Þ 2.0
· Fuel line
5 - 9 A
· ·· ·
· Fuel pump:
- Current
consumption· Ignition:ON
- Remove the fuel
relay from the fuse
and relay box in
luggage
compartment and
connect the
amperemeter
between No.1 and
No.3 in relay
box(fuel pump relay
removed position)
for measuring
current
consumption Þ 2.0· Fuel pump
533
Multi tester(DC current)
31
Page 681 of 1463
1F2-32 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
INJECTOR TEST
1 ECU
2 Test Coupling(No.1-60)
3 Test Coupling(No.61-120)
4 Measuring Beaker
5 Shop Made Cable
Preparation
0 3 Test Box
04 ECU Test Cable
Connection of the Equipment
1. Connect the test box to the ECU as shown in the figure.
2. Remove the 2-pin coupling from injector.
3. Remove the fuel distributor and injector with a unit. At this
time, do not remove the supply and return line.
4. Connect the shop made cable to the injector with a firing
order.
5. Collect the fuel from injector.
Tools Required
129 589 00 21 00 Test Box
210 589 08 63 00 ECU Test Cable
Page 682 of 1463
M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2-33
Figure 8. Shop Made Cable Figure 9. Fuel Injector Normal Spary Pattern
Failure
codeItemChecking method Test
stepRequirementSpecified
valuePossible cause
There should
be no leaks
and later
drops from
the injector· ·· ·
· Injector:
- Leakage
test· Ignition:ON
- Remove the fuel
distributor and fuel
injector with a unit. Þ 1.0· Þ 2.0
· Injector
The spray
pattern of the
injector most
show in the
figure 10
· Ignition:ON
- Connect the shop
made cable to the
injector.
- Collect the
spraying fuel with a
beaker
- Connect the shop
made cable to
No.11(+) and No.5
(-) terminal in test
box. Þ 2.0· Injector
533
· ·· ·
· Injector:
- Function
test and
spray
pattern
check
533
Page 686 of 1463
M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2-37
Pin No.Abbreviation Description
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60BRS
-
-
-
-
-
KLIKU
-
-
-
GND
SP1+5V
KP
TEV
ML
-
CAN L
CAN H
-
-
-
-
KPI
KLIMA
ETS
-
SP1S
SP2S
BLS
GND
SP2+2.5V
S+B
WA
S-B
KSK
-
AUS
DIAG
V-SIG
TN-SIG Brake switch
-
-
-
-
-
Air conditioning clutch relay
-
-
-
Pedal potentiometer 1 ground
Pedal potentiometer 1 supply
Fuel pump relay
Tank purge valve
Engine fan(High)
-
CAN-Low
CAN-High
-
-
-
-
-
Air conditioning
Electronic traction signal
-
Pedal potentiometer 1 signal
Pedal potentiometer 2 signal
Brake light switch
Pedal potentiometer 2 ground
Pedal potentiometer 2 supply
Cruise accelerate/Set
Cruise resume
Cruise decelerate/Set
Cruise safety contact switch
-
Cruise off switch
Diagnostics(K-Line)
Vehicle speed signal
Engine speed signal
Page 690 of 1463
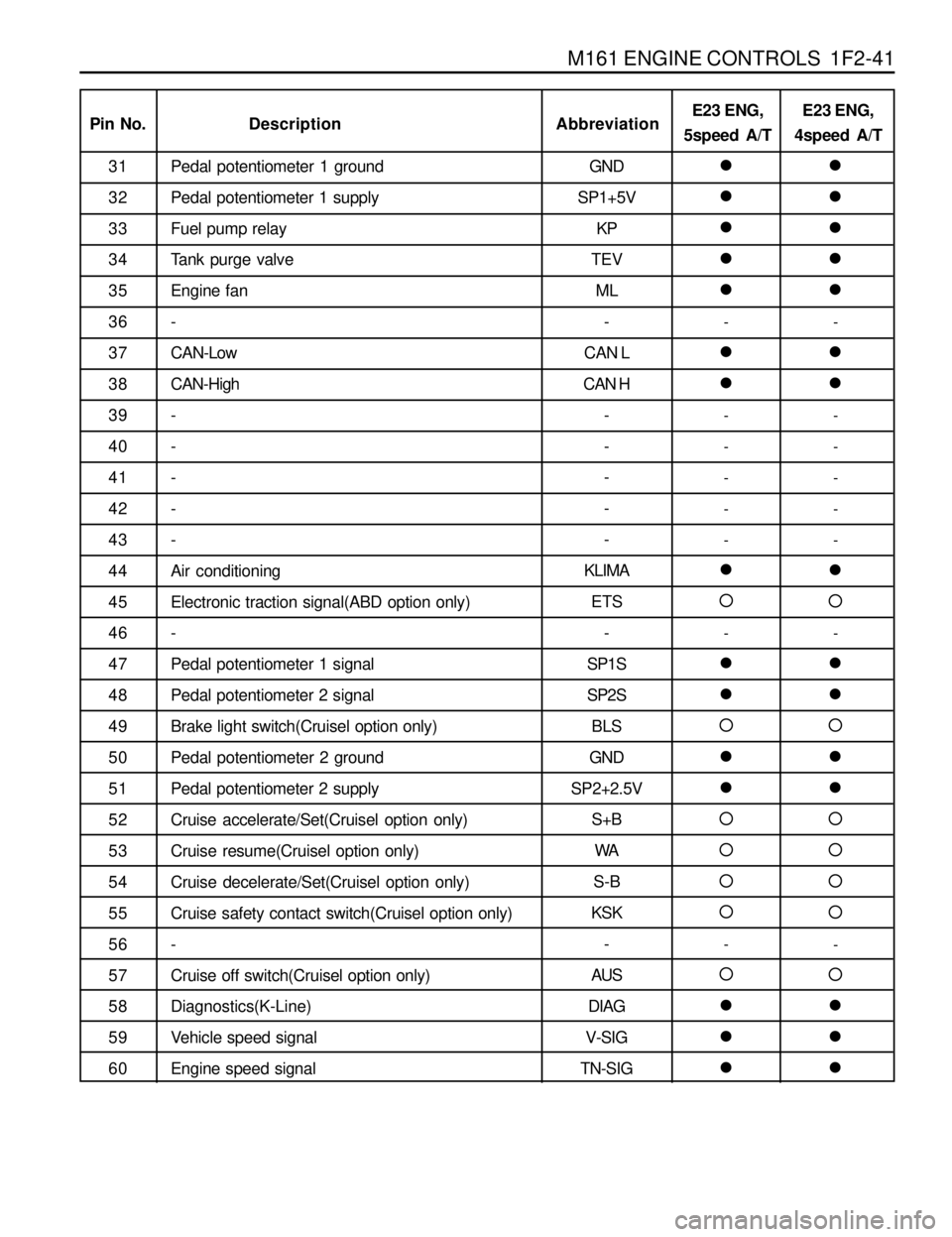
M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2-41
Pin No.Abbreviation Description
Pedal potentiometer 1 ground
Pedal potentiometer 1 supply
Fuel pump relay
Tank purge valve
Engine fan
-
CAN-Low
CAN-High
-
-
-
-
-
Air conditioning
Electronic traction signal(ABD option only)
-
Pedal potentiometer 1 signal
Pedal potentiometer 2 signal
Brake light switch(Cruisel option only)
Pedal potentiometer 2 ground
Pedal potentiometer 2 supply
Cruise accelerate/Set(Cruisel option only)
Cruise resume(Cruisel option only)
Cruise decelerate/Set(Cruisel option only)
Cruise safety contact switch(Cruisel option only)
-
Cruise off switch(Cruisel option only)
Diagnostics(K-Line)
Vehicle speed signal
Engine speed signal31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60GND
SP1+5V
KP
TEV
ML
-
CAN L
CAN H
-
-
-
-
-
KLIMA
ETS
-
SP1S
SP2S
BLS
GND
SP2+2.5V
S+B
WA
S-B
KSK
-
AUS
DIAG
V-SIG
TN-SIGl
l
l
l
l
-
l
l
-
-
-
-
-
l
¡
-
l
l
¡
l
l
¡
¡
¡
¡
-
¡
l
l
ll
l
l
l
l
-
l
l
-
-
-
-
-
l
¡
-
l
l
¡
l
l
¡
¡
¡
¡
-
¡
l
l
l
E23 ENG,
4speed A/T E23 ENG,
5speed A/T
Page 694 of 1463
M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2-45
1 Vacuum Hose
2 Circlip
3 Fuel Pressure Regulator
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 O-ring ..................................................... replace
5 O-ring ..................................................... replace
Page 695 of 1463
1F2-46 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
3. Disconnect the vacuum hose.
4. Disconnect the circlip and remove the fuel pressure
regulator.
5. Apply the oil to O-ring lightly and then replace it.
6. Installation should follow the removal procedure in the
reverse order.
7. Check for fuel pressure and internal leaks by operating the
engine. 2. Discharge the pressure in fuel supply system by pressing
the service valve.
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Remove the fuel pressure test connector.
Page 696 of 1463

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2-47
A . Valves Closed
B. Valves Opened
The pressure difference between the fuel pressure and the
intake manifold is about 3.8 bars during the full load.
The spring chamber(9) is connected to the intake manifold
with the vacuum hose at the intake pipe connection(7). The
negative pressure generated in the intake manifold activates
the diaphragm, and thus the fuel pressure gets reduced to the
rate of the operating extent of the diaphragm by the intake
manifold's negative pressure.
Consequently, the fuel pressure in the fuel distributor changes
by the intake manifold's negative pressure, and the injector's
fuel pressure gets reduced independently to the throttle valve's
position. Thus, the fuel injection volume can only be determined
according to the injector's injecting duration.
2. Fuel return line
3. Valve
5. Diaphragm
6. Compression Spring
8. Fuel chamber
9. Spring Chamber
1. Fuel pressure Regulator
2. Intake Manifold
3. Fuel return(to fuel tank)
4. Fuel supply(form fuel pump)
5. Fuel pressure(approx. 3.8 bars)
6. Intake Manifold Negative Pressure(0 bar)
Function of the Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel pressure in the
fuel line with the pressure of 3.2 bars to 3.8 bars according to
the intake manifold pressure. This operating pressure cannot
be changed, and the fuel injection volume will be only
determined by the injection time. Over supplied fuel returns to
the fuel tank through the return line.
There is no negative pressure applied to the spring chamber(9)
during the full load, and it is separated from the fuel chamber(8)
by the diaphragm(5).
When the fuel pressure goes up, the diaphragm forces the
compression spring(6) in the direction of compression . At this
moment, the valve(3) sticks to the diaphragm by the fuel
pressure, and the fuel return line(2) opens. The fuel over
supplied returns to the fuel tank through the return line.