1998 OPEL FRONTERA air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 1156 of 6000

6E–39 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
The data displayed on the other Tech 2 will appear the
same, with some exceptions. Some Tech 2s will only be
able to display certain vehicle parameters as values that
are a coded representation of the true or actual value. For
more information on this system of coding, refer to
Decimal/Binary/Hexadecimal Conversions. On this
vehicle Tech 2 displays the actual values for vehicle
parameters. It will not be necessary to perform any
conversions from coded values to actual values.
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
On-Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which is
a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive. When
a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
The diagnostic test has been completed since the last
ignition cycle.
The diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not
currently active.
W h e n a d i a g n o s t i c t e s t r e p o r t s a fail result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
The diagnostic test has been completed since the last
ignition cycle.
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is currently
active.
The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
Remember, a fuel trim DTC may be triggered by a list of
vehicle faults. Make use of all information available (other
DTCs stored, rich or lean condition, etc.) when
diagnosing a fuel trim fault.
Comprehensive Component Monitor
Diagnostic Operation
Input Components:
Input components are monitored for circuit continuity and
out-of-range values. This includes rationality checking.
Rationality checking refers to indicating a fault when the
signal from a sensor does not seem reasonable, i.e.
Throttle Position (TP) sensor that indicates high throttle
position at low engine loads or MAP voltage. Input
components may include, but are not limited to the
following sensors:
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
Knock Sensor (KS)
Throttle Position (TP) sensor
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensorIn addition to the circuit continuity and rationality check,
the ECT sensor is monitored for its ability to achieve a
steady state temperature to enable closed loop fuel
control.
Output Components:
Output components are diagnosed for proper response to
control module commands. Components where
functional monitoring is not feasible will be monitored for
circuit continuity and out-of-range values if applicable.
Output components to be monitored include, but are not
limited to, the following circuits:
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
Electronic Transmission controls
A/C relays
Cooling fan relay
VSS output
MIL control
Cruise control inhibit
Refer to PCM and Sensors in General Descriptions.
Passive and Active Diagnostic Tests
A passive test is a diagnostic test which simply monitors a
vehicle system or component. Conversely, an active test,
actually takes some sort of action when performing
diagnostic functions, often in response to a failed passive
test. For example, the EGR diagnostic active test will
force the EGR valve open during closed throttle decel
and/or force the EGR valve closed during a steady state.
Either action should result in a change in manifold
pressure.
Intrusive Diagnostic Tests
This is any on-board test run by the Diagnostic
Management System which may have an effect on
vehicle performance or emission levels.
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means that engine at temperature must
reach a minimum of 70
C (160F) and rise at least 22C
(40
F) over the course of a trip.
Freeze Frame
Freeze Frame is an element of the Diagnostic
Management System which stores various vehicle
information at the moment an emissions-related fault is
stored in memory and when the MIL is commanded on.
These data can help to identify the cause of a fault. Refer
to
Storing And Erasing Freeze Fame Data for more
detailed information.
Failure Records
Failure Records data is an enhancement of the OBD
Freeze Frame feature. Failure Records store the same
vehicle information as does Freeze Frame, but it will store
that information for any fault which is stored in on-board
memory, while Freeze Frame stores information only for
emission-related faults that command the MIL on.
Page 1158 of 6000

6E–41 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
If the MIL was set by either a fuel trim or misfire-related
DTC, additional requirements must be met. In addition to
the requirements stated in the previous paragraph, these
requirements are as follows:
The diagnostic tests that are passed must occur with
375 RPM of the RPM data stored at the time the last
test failed.
Plus or minus ten (10) percent of the engine load that
was stored at the time the last failed.
Similar engine temperature conditions (warmed up or
warming up ) as those stored at the time the last test
failed.
Meeting these requirements ensures that the fault which
turned on the MIL has been corrected.
The MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) is on the instrument
panel and has the following function:
It informs the driver that a fault affects vehicle emission
levels has occurred and that the vehicle should be
taken for service as soon as possible.
As a bulb and system check, the MIL will come “ON”
with the key “ON” and the engine not running. When
the engine is started, the MIL will turn “OFF.”
When the MIL remains “ON” while the engine is
running, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, a Powertrain
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD ll) System Check must be
performed. The procedures for these checks are given
in On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check. These
checks will expose faults which may not be detected if
other diagnostics are performed first.
DTC Types
Each DTC is directly related to a diagnostic test. The
Diagnostic Management System sets DTC based on the
failure of the tests during a trip or trips. Certain tests must
fail two (2) consecutive trips before the DTC is set. The
following are the four (4) types of DTCs and the
characteristics of those codes:
Ty p e A
Emissions related
Requests illumination of the MIL of the first trip with a
fail
Stores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
Stores a Freeze Frame (if empty)
Stores a Fail Record
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
Ty p e B
Emissions related
“Armed” after one (1) trip with a fail
“Disarmed” after one (1) trip with a pass
Requests illumination of the MIL on the second
consecutive trip
with a fail
Stores a History DTC on the second consecutive trip
with a fail (The DTC will be armed after the first fail)
Stores a Freeze Frame on the second consecutive
trip with a fail (if empty)
Stores a Fail Record when the first test fails (not
dependent on
consecutive trip fails)
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
Type C (if the vehicle is so equipped)
Non-Emissions related
Requests illumination of the Service Lamp or the
service message on the Drive Information Center
(DIC) on the
first trip with a fail
Stores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
Does not store a Freeze Frame
Stores Fail Record when test fails
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
Type D (Ty p e D non-emissions related are not utilized
on certain vehicle applications).
Non-Emissions related
Dose not request illumination of any lamp
Stores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
Does not store a Freeze Frame
Stores Fail Record when test fails
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
IMPORTANT:Only four Fail Records can be stored.
Each Fail Record is for a different DTC. It is possible that
there will not be Fail Records for every DTC if multiple
DTCs are set.
Storing and Erasing Freeze Frame Data and Failure
Records
The data captured is called Freeze Frame data. The
Freeze Frame data is very similar to a single record of
operating conditions. Whenever the MIL is illuminated,
the corresponding record of operating conditions is
recorded to the Freeze Frame buffer.
Data from these faults take precedence over data
associated with any other fault. The Freeze Frame data
will not be erased unless the associated history DTC is
cleared.
Each time a diagnostic test reports a failure, the current
engine operating conditions are recorded in the
Failure
Records
buffer. A subsequent failure will update the
recorded operating conditions. The following operating
conditions for the diagnostic test which failed
typically
include the following parameters:
Air Fuel Ratio
Air Flow Rate
Fuel Trim
Engine Speed
Engine Load
Engine Coolant Temperature
Vehicle Speed
TP Angle
MAP/BARO
Injector Base Pulse Width
Loop Status
Page 1159 of 6000

6E–42
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp
In the case of an “intermittent” fault, the MIL (“Check
Engine” lamp) may illuminate and then (after three trips)
go “OFF”. However, the corresponding diagnostic trouble
code will be stored in the memory. When unexpected
diagnostic trouble codes appear, check for an intermittent
malfunction.
A diagnostic trouble code may reset. Consult the
“Diagnostic Aids” associated with the diagnostic trouble
code. A physical inspection of the applicable sub-system
most often will resolve the problem.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communication with the control module
is the Data Link Connector (DLC). The DLC is used to
connect to Tech 2. Some common uses of Tech 2 are
listed below:
Identifying stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Clearing DTCs.
Performing output control tests.
Reading serial data.
TS24064
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more comprehensive
for vehicles with OBD system diagnostic. Following a
repair, the technician should perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records and/or Freeze
Frame data for the DTC which has been diagnosed
(Freeze Frame data will only be stored for an A or B
type diagnostic and only if the MIL has been
requested).
2. Clear DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail
Records and/or Freeze Frame data.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps are very important in verifying
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using
A Tech 2
The procedure for reading diagnostic trouble code(s) is to
used a diagnostic Tech 2. When reading DTC(s), follow
instructions supplied by Tech 2 manufacturer.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
IMPORTANT:Do not clear DTCs unless directed to do
so by the service information provided for each diagnostic
procedure. When DTCs are cleared, the Freeze Frame
and Failure Record data which may help diagnose an
intermittent fault will also be erased from memory.
If the fault that caused the DTC to be stored into memory
has been corrected, the Diagnostic Executive will begin to
count the “warm-up” cycles with no further faults
detected, the DTC will automatically be cleared from the
PCM memory.
To clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), use the
diagnostic Tech 2 “clear DTCs”. When clearing DTCs
follow instructions supplied by the tool manufacturer.
When Tech 2 is not available, DTCs can also be cleared
by disconnecting
one of the following sources for at least
thirty (30) seconds.
NOTE: To prevent system damage, the ignition key must
be “OFF” when disconnecting or reconnecting battery
power.
The power source to the control module. Examples:
fuse, pigtail at battery PCM connectors etc.
The negative battery cable. (Disconnecting the
negative battery cable will result in the loss of other
on-board memory data, such as preset radio tuning).
Page 1167 of 6000

6E–50
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Primary System-Based Diagnostic
Primary System-Based Diagnostic
There are primary system-based diagnostics which
evaluate system operation and its effect on vehicle
emissions. The primary system-based diagnostics are
listed below with a brief description of the diagnostic
function:
Oxygen Sensor Diagnosis
The fuel control heated oxygen sensors (Bank 1 HO2S 1
and Bank 2 HO2S 1) are diagnosed for the following
conditions:
Inactive signal (output steady at bias voltage – approx.
450 mV)
Signal fixed high
Signal fixed low
If the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector or terminal
are damaged, the entire oxygen sensor assembly must
be replaced. DO NOT attempt to repair the wiring,
connector or terminals. In order for the sensor to function
properly, it must have clean reference air provided to it.
This clean air reference is obtained by way of the oxygen
sensor wire(s). Any attempt to repair the wires, connector
or terminals could result in the obstruction of the
reference air and degrade oxygen sensor performance.
Refer to
On-Vehicle Service, Heated Oxygen Sensors.
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensor
The main function of the fuel control heated oxygen
sensors is to provide the control module with exhaust
stream oxygen content information to allow proper fueling
and maintain emissions within mandated levels. After it
reaches operating temperature, the sensor will generate
a voltage, inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen
present in the exhaust gases. The control module uses
the signal voltage from the fuel control heated oxygen
sensors while in closed loop to adjust fuel injector pulse
width. While in closed loop, the PCM can adjust fuel
delivery to maintain an air/fuel ratio which allows the best
combination of emission control and driveability.
HO2S Heater
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the amount
of time required for closed loop fuel control to begin
operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The
oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of
time required for fuel control sensors (Bank 1 HO2S 1 and
Bank2 HO2S 1) to become active. Oxygen sensor
heaters are required to maintain a sufficiently high
temperature which allows accurate exhaust oxygen
content readings further away from the engine.
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation
This system monitors the averages of short-term and
long-term fuel trim values. If these fuel trim values stay at
their limits for a calibrated period of time, a malfunction is
indicated. The fuel trim diagnostic compares the
averages of short-term fuel trim values and long-term fuel
trim values to rich and lean thresholds. If either value is
within the thresholds, a pass is recorded. If both values
are outside their thresholds, a rich or lean DTC will be
recorded.
The fuel trim system diagnostic also conducts an intrusive
test. This test determines if a rich condition is being
caused by excessive fuel vapor from the EVAP canister.
In order to meet OBD requirements, the control module
uses weighted fuel trim cells to determine the need to set
a fuel trim DTC. A fuel trim DTC can only be set if fuel trim
counts in the weighted fuel trim cells exceed
specifications. This means that the vehicle could have a
fuel trim problem which is causing a problem under
certain conditions (i.e., engine idle high due to a small
vacuum leak or rough idle due to a large vacuum leak)
while it operates fine at other times. No fuel trim DTC
would set (although an engine idle speed DTC or HO2S
DTC may set). Use a Tech 2 to observe fuel trim counts
while the problem is occurring.
A fuel trim DTC may be triggered by a number of vehicle
faults. Make use of all information available (other DTCs
stored, rich or lean condition, etc.) when diagnosing a fuel
trim fault.
Fuel Trim Cell Diagnostic Weights
N o f u e l t r i m D T C w i l l s e t r e g a r d l e s s o f t h e f u e l t r i m c o u n t s
in cell 0 unless the fuel trim counts in the weighted cells
are also outside specifications. This means that the
vehicle could have a fuel trim problem which is causing a
problem under certain conditions (i.e. engine idle high due
to a small vacuum leak or rough due to a large vacuum
leak) while it operates fine at other times. No fuel trim
DTC would set (although an engine idle speed DTC or
HO2S DTC may set). Use a Tech 2 to observe fuel trim
counts while the problem is occurring.
Page 1171 of 6000
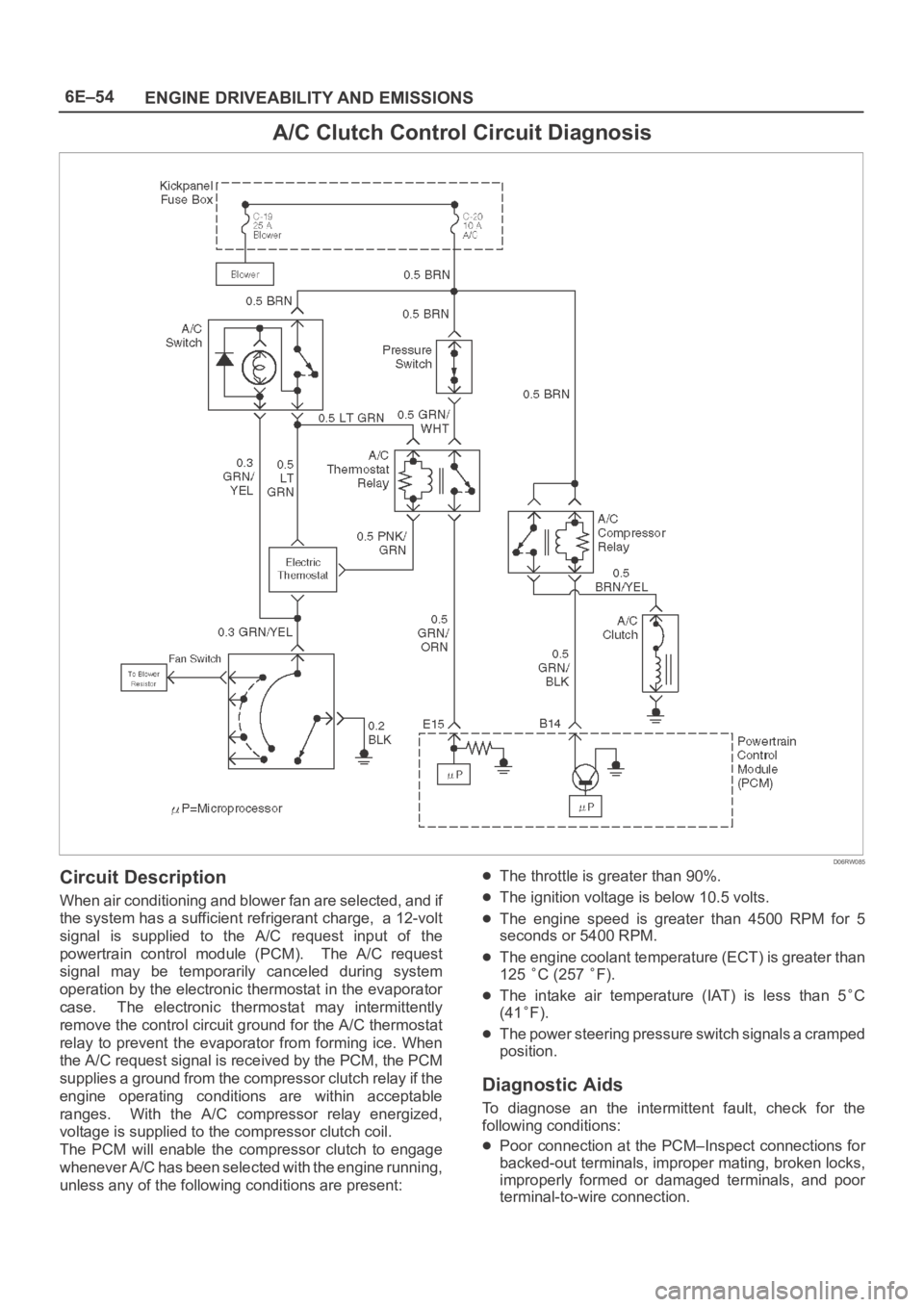
6E–54
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis
D06RW085
Circuit Description
When air conditioning and blower fan are selected, and if
the system has a sufficient refrigerant charge, a 12-volt
signal is supplied to the A/C request input of the
powertrain control module (PCM). The A/C request
signal may be temporarily canceled during system
operation by the electronic thermostat in the evaporator
case. The electronic thermostat may intermittently
remove the control circuit ground for the A/C thermostat
relay to prevent the evaporator from forming ice. When
the A/C request signal is received by the PCM, the PCM
supplies a ground from the compressor clutch relay if the
engine operating conditions are within acceptable
ranges. With the A/C compressor relay energized,
voltage is supplied to the compressor clutch coil.
The PCM will enable the compressor clutch to engage
whenever A/C has been selected with the engine running,
unless any of the following conditions are present:
The throttle is greater than 90%.
The ignition voltage is below 10.5 volts.
The engine speed is greater than 4500 RPM for 5
seconds or 5400 RPM.
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is greater than
125
C (257 F).
The intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 5C
(41
F).
The power steering pressure switch signals a cramped
position.
Diagnostic Aids
To diagnose an the intermittent fault, check for the
following conditions:
Poor connection at the PCM–Inspect connections for
backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.
Page 1172 of 6000
6E–55 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Damaged harness–Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to OK, observe the
A/C clutch while moving connectors and wiring
harnesses related to the A/C. A sudden clutch
malfunction will indicate the source of the intermittent
fault.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
This chart should be used for diagnosing the electrical
p o r t i o n o f t h e A / C c o m p r e s s o r c l u t c h c i r c u i t . A Te c h 2 w i l l
be used in diagnosing the system. The Tech 2 has the
ability to read the A/C request input to the PCM. The Tech
2 can display when the PCM has commanded the A/C
clutch “ON.” The Tech 2 should have the ability to
override the A/C request signal and energize the A/C
compressor relay.
Test Description
IMPORTANT:Do not engage the A/C compressor
clutch with the engine running if an A/C mode is not
selected at the A/C control switch.
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
Diagnostic Chart:3. This a test determine is the problem is with the
refrigerant system. If the switch is open, A/C
pressure gauges will be used to determine if the
pressure switch is faulty or if the system is partially
discharged or empty.
4. Although the normal complaint will be the A/C clutch
failing to engage, it is possible for a short circuit to
cause the clutch to run when A/C has not been
selected. This step is a test for that condition.
7. There is an extremely low probability that both relays
will fail at the same time, so the substitution process
is one way to check the A/C Thermostat relay. Use
a known good relay to do a substitution check.
9. The blower system furnishes a ground for the A/C
control circuit, and it also shares a power source
through the Heater and A/C Relay. The blower
must be “ON” in order to test the A/C system.
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any other DTCs stored?
—
Go to the
other DTC
chart(s) first
Go to Step 3
31. Disconnect the electrical connector at the pressure
switch located on the receiver/drier.
2. Use an ohmmeter to check continuity across the
pressure switch.
Is the pressure switch open?
—
Go to Air
Conditioning
to diagnose
the cause of
the open
pressure
switch
Go to Step 4
4IMPORTANT:Before continuing with the diagnosis, the
following conditions must be met:
The intake air temperature must be greater than
15
C. (60F).
The engine coolant temperature must be less
than 119
C (246F).
1. A/C “OFF.”
2. Start the engine and idle for 1 minute.
3. Observe the A/C compressor.
Is the A/C compressor clutch engaged even though
A/C has not been requested?
—Go to Step 45Go to Step 5
51. Idle the engine.
2. A/C “ON”.
3. Blower “ON”.
4. Observe the A/C compressor.
Is the A/C compressor magnetic clutch engaged?
—
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 6
Page 1177 of 6000

6E–60
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Electronic Ignition System Diagnosis
If the engine cranks but will not run or immediately stalls,
the Engine Cranks But Will Not Start chart must be used
to determine if the failure is the ignition system or the fuel
system. If DTC P0341, or P0336 is set, the appropriate
diagnostic trouble code chart must be used for diagnosis.
If a misfire is being experienced with no DTC set, refer to
the
Symptoms section for diagnosis.
Fuel Metering System Check
Some failures of the fuel metering system will result in an
“Engine Cranks But Will Not Run” symptom. If this
condition exists, refer to the
Cranks But Will Not Run
chart. This chart will determine if the problem is caused
by the ignition system, the PCM, or the fuel pump
electrical circuit.
Refer to
Fuel System Electrical Test for the fuel system
wiring schematic.
If there is a fuel delivery problem, refer to
Fuel System
Diagnosis
, which diagnoses the fuel injectors, the fuel
pressure regulator, and the fuel pump. If a malfunction
occurs in the fuel metering system, it usually results in
either a rich HO2S signal or a lean HO2S signal. This
condition is indicated by the HO2S voltage, which causes
the PCM to change the fuel calculation (fuel injector pulse
width) based on the HO2S reading. Changes made to the
fuel calculation will be indicated by a change in the long
term fuel trim values which can be monitored with a Tech
2. Ideal long term fuel trim values are around 0%; for a
lean HO2S signal, the PCM will add fuel, resulting in a fuel
trim value above 0%. Some variations in fuel trim values
are normal because all engines are not exactly the same.
If the fuel trim values are greater than +23%, refer to
DTC
P0131, DTC P0151, DTC P0171, and DTC 1171
f o r i t e m s
which can cause a lean HO2S signal.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The Tech 2 displays the IAC pintle position in counts. A
count of “0” indicates the PCM is commanding the IAC
pintle to be driven all the way into a fully-seated position.
This is usually caused by a large vacuum leak.
The higher the number of counts, the more air is being
commanded to bypass the throttle blade. Refer to IAC
System Check in order to diagnose the IAC system.
Refer to
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling in
Symptoms for other possible causes of idle problems.
Fuel System Pressure Test
A fuel system pressure test is part of several of the
diagnostic charts and symptom checks. To perform this
test, refer to
Fuel Systems Diagnosis.
Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure and
Fuel Injector Balance Test Procedure
T32003
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Relieve the fuel pressure by connecting the
5-8840-0378-0 Fuel Pressure Gauge to the fuel
pressure connection on the fuel rail.
CAUTION: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury, wrap a shop towel around the fuel
pressure connection. The towel will absorb any fuel
leakage that occurs during the connection of the fuel
pressure gauge. Place the towel in an approved
container when the connection of the fuel pressure
gauge is complete.
Place the fuel pressure gauge bleed hose in an
approved gasoline container.
With the ignition switch “OFF,” open the valve on the
fuel pressure gauge.
3. Record the lowest voltage displayed by the DVM
after the first second of the test. (During the first
second, voltage displayed by the DVM may be
inaccurate due to the initial current surge.)
Injector Specifications:
Resistance Ohms
Voltage Specification at
10
C-35C (50F-95F)
11.8 – 12.65.7 – 6.6
The voltage displayed by the DVM should be within
the specified range.
The voltage displayed by the DVM may increase
throughout the test as the fuel injector windings
warm and the resistance of the fuel injector windings
changes.
Page 1182 of 6000

6E–65 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Knock Sensor Diagnosis
The Tech 2 has two data displays available for diagnosing
the knock sensor (KS) system. The two displays are
described as follows:
“Knock Retard” indicates the number of degrees that
the spark timing is being retarded due to a knock
condition.
“KS Noise Channel” indicates the current voltage level
being monitored on the noise channel.
DTCs P0325 and P0327 are designed to diagnose the KS
module, the knock sensor, and the related wiring. The
problems encountered with the KS system should set a
DTC. However, if no DTC was set but the KS system is
suspect because of a detonation complaint, refer to
Detonation/Spark Knock in Symptoms.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Diagnosis
To read and clear diagnostic trouble codes, use a Tech 2.
IMPORTANT:Use of a Tech 2 is recommended to clear
diagnostic trouble codes from the PCM memory.
Diagnostic trouble codes can also be cleared by turning
the ignition “OFF” and disconnecting the battery power
from the PCM for 30 seconds. Turning off the ignition and
disconnecting the battery power from the PCM will cause
all diagnostic information in the PCM memory to be
cleared. Therefore, all the diagnostic tests will have to be
re-run.
Since the PCM can have a failure which may affect only
one circuit, following the diagnostic procedures in this
section will determine which circuit has a problem and
where it is.
If a diagnostic chart indicates that the PCM connections
or the PCM is the cause of a problem, and the PCM is
replaced, but this does not correct the problem, one of the
following may be the reason:
There is a problem with the PCM terminal connections.
The terminals may have to be removed from the
connector in order to check them properly.
The problem is intermittent. This means that the
problem is not present at the time the system is being
checked. In this case, refer to the
Symptoms p o r t i o n o f
the manual and make a careful physical inspection of
all component and wiring associated with the affected
system.
There is a shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness.
S o l e n o i d s a n d r e l a y s a r e t u r n e d “ O N ” a n d “ O F F ” b y t h e
PCM using internal electronic switches called drivers.
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness will not
damage the PCM but will cause the solenoid or relay to
be inoperative.
Multiple PCM Information Sensor
DTCS Set
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors various
sensors to determine the engine operating conditions.
The PCM controls fuel delivery, spark advance,
transmission operation, and emission control device
operation based on the sensor inputs.The PCM provides a sensor ground to all of the sensors.
The PCM applies 5 volts through a pull-up resistor, and
determines the status of the following sensors by
monitoring the voltage present between the 5-volt supply
and the resistor:
The engine coolant temperature (ETC) sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
The transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
The PCM provides the following sensors with a 5-volt
reference and a sensor ground signal:
The exhaust gas recirculating (EGR) pintle position
sensor
The throttle position (TP) sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
The PCM monitors the separate feedback signals from
these sensors in order to determine their operating
status.
Diagnostic Aids
IMPORTANT:Be sure to inspect PCM and engine
grounds for being secure and clean.
A short to voltage in one of the sensor input circuits may
cause one or more of the following DTCs to be set:
P0108
P0113
P0118
P0123
P0560
P0712
P0406
IMPORTANT:If a sensor input circuit has been shorted
to voltage, ensure that the sensor is not damaged. A
damaged sensor will continue to indicate a high or low
voltage after the affected circuit has been repaired. If the
sensor has been damaged, replace it.
An open in the sensor ground circuit between the PCM
and the splice will cause one or more of the following
DTCs to be set:
P0108
P0113
P0118
P0123
P0712
P0406
A short to ground in the 5-volt reference A or B circuit will
cause one or more of the following DTCs to be set:
P0107
P0122
In the 5-volt reference circuit A, between the PCM and the
splice, will cause one or more of the following DTCs to be
set:
P0122
In the 5-volt reference circuit B, between the PCM and the
splice, will cause one or more of the following DTCs to be
set:
P0107
Check for the following conditions: