1998 OPEL FRONTERA ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 1134 of 6000

6E–17 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinouts
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red Connector – Row “A”
TS23344
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
A15 Volt Reference “A”RED5.0 V5.0 VAppropriate Sensor
A2Knock SensorYEL0.0 V DC
2mV AC0.0 V DC
18mV AC
(at idle)General Description and
Operation, Knock Sensor
A3Not Used————
A4Battery FeedWHTB+B+Chassis Electrical
A5Idle Air Control (IAC) “A”
HighBLUB+/0.8 VB+/0.8 VGeneral Description and
Operation, IAC
A6IAC “A” LowBLU/WHTB+/0.8 VB+/0.8 VGeneral Description and
Operation, IAC
A7IAC “B” LowBLU/BLKB+/0.8 VB+/0.8 VGeneral Description and
Operation, IAC
A8IAC “B” HighBLU/REDB+/0.8 VB+/0.8 VGeneral Description and
Operation, IAC
A9Automatic Transmission
Fluid (ATF) LampORN/BLUB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
A10Winter LampPNK/GRNB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
A11Power LampGRY/WHTB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
A12Antilock Brake System
(ABS)GRYB+B+Antilock Brake System
A13Malfunction Indicator
(Check Engine or MIL)
LampBLU0.0 VB+Chassis Electrical
A14“Check Transmission”
Lamp Driver (AT)ORN/BLKB+B+Chassis Electrical
Up Shift Lamp Driver (MT)ORN/BLU
Page 1144 of 6000
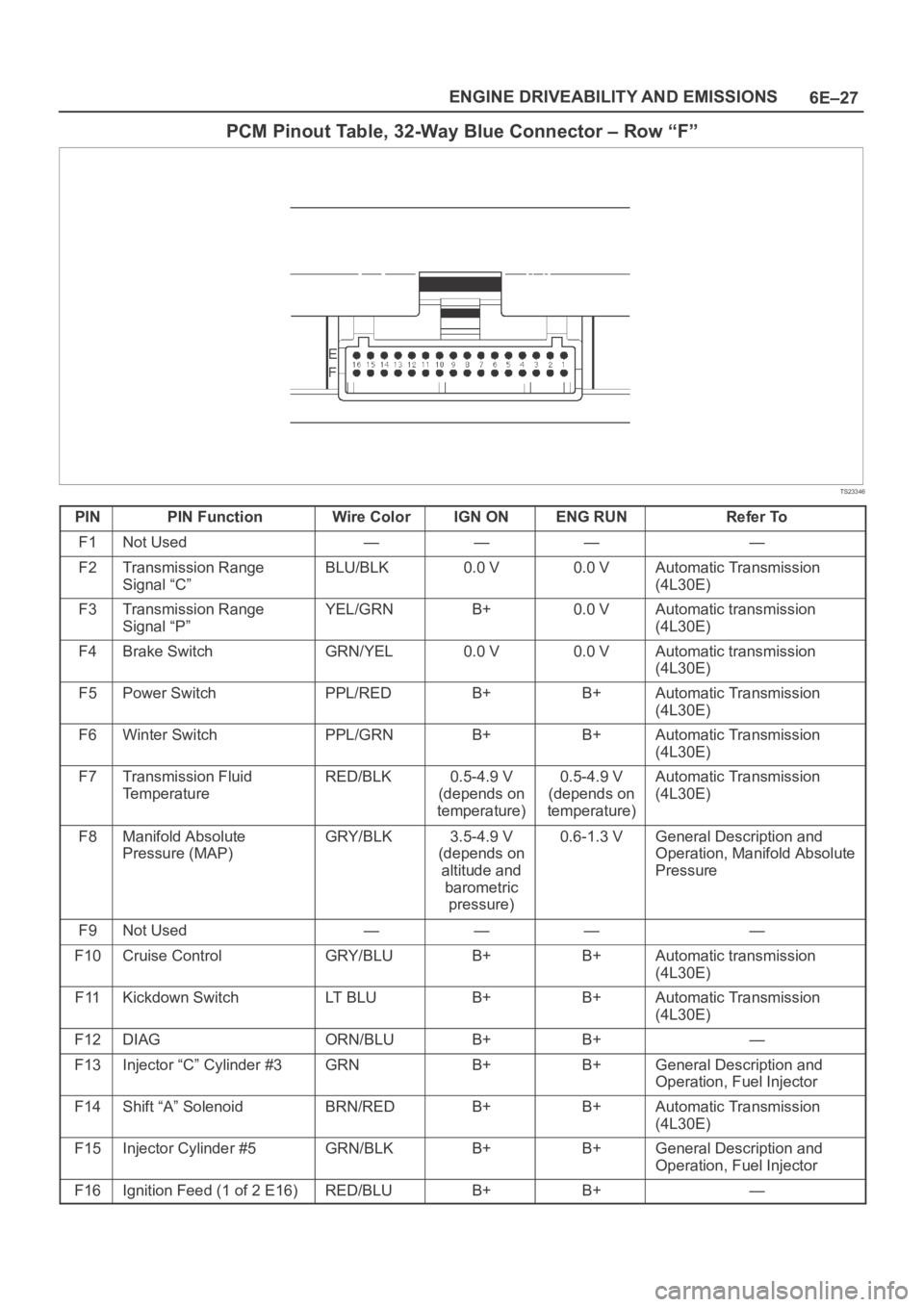
6E–27 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Blue Connector – Row “F”
TS23346
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
F1Not Used————
F2Transmission Range
Signal “C”BLU/BLK0.0 V0.0 VAutomatic Transmission
(4L30E)
F3Transmission Range
Signal “P”YEL/GRNB+0.0 VAutomatic transmission
(4L30E)
F4Brake SwitchGRN/YEL0.0 V0.0 VAutomatic transmission
(4L30E)
F5Power SwitchPPL/REDB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
F6Winter SwitchPPL/GRNB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
F7Transmission Fluid
TemperatureRED/BLK0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
F8Manifold Absolute
Pressure (MAP)GRY/BLK3.5-4.9 V
(depends on
altitude and
barometric
pressure)0.6-1.3 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Manifold Absolute
Pressure
F9Not Used————
F10Cruise ControlGRY/BLUB+B+Automatic transmission
(4L30E)
F11Kickdown SwitchLT B L UB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
F12DIAGORN/BLUB+B+—
F13Injector “C” Cylinder #3GRNB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
F14Shift “A” SolenoidBRN/REDB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
F15Injector Cylinder #5GRN/BLKB+B+General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
F16Ignition Feed (1 of 2 E16)RED/BLUB+B+—
Page 1146 of 6000
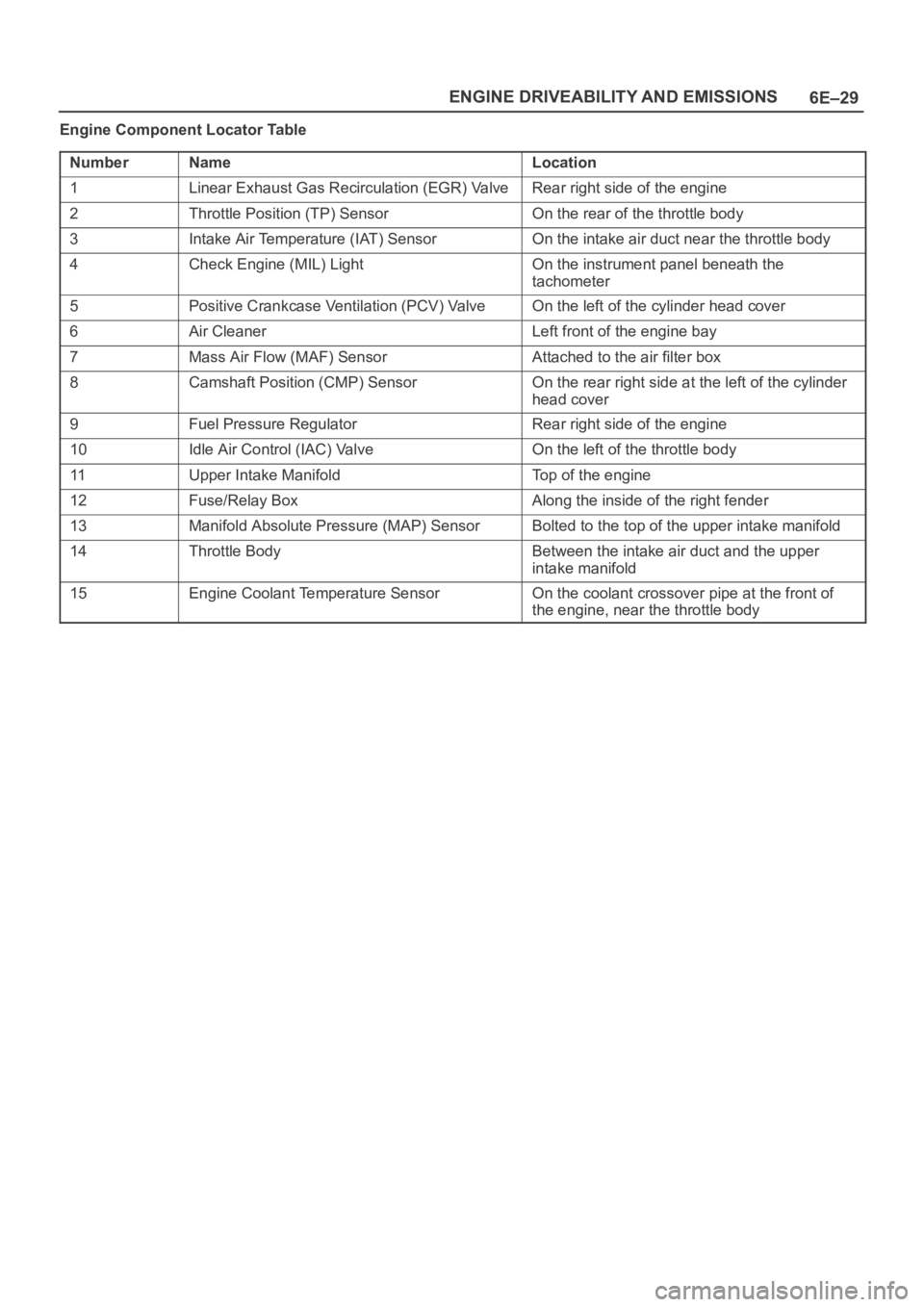
6E–29 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Engine Component Locator Table
Number
NameLocation
1Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ValveRear right side of the engine
2Throttle Position (TP) SensorOn the rear of the throttle body
3Intake Air Temperature (IAT) SensorOn the intake air duct near the throttle body
4Check Engine (MIL) LightOn the instrument panel beneath the
tachometer
5Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) ValveOn the left of the cylinder head cover
6Air CleanerLeft front of the engine bay
7Mass Air Flow (MAF) SensorAttached to the air filter box
8Camshaft Position (CMP) SensorOn the rear right side at the left of the cylinder
head cover
9Fuel Pressure RegulatorRear right side of the engine
10Idle Air Control (IAC) ValveOn the left of the throttle body
11Upper Intake ManifoldTop of the engine
12Fuse/Relay BoxAlong the inside of the right fender
13Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorBolted to the top of the upper intake manifold
14Throttle BodyBetween the intake air duct and the upper
intake manifold
15Engine Coolant Temperature SensorOn the coolant crossover pipe at the front of
the engine, near the throttle body
Page 1148 of 6000
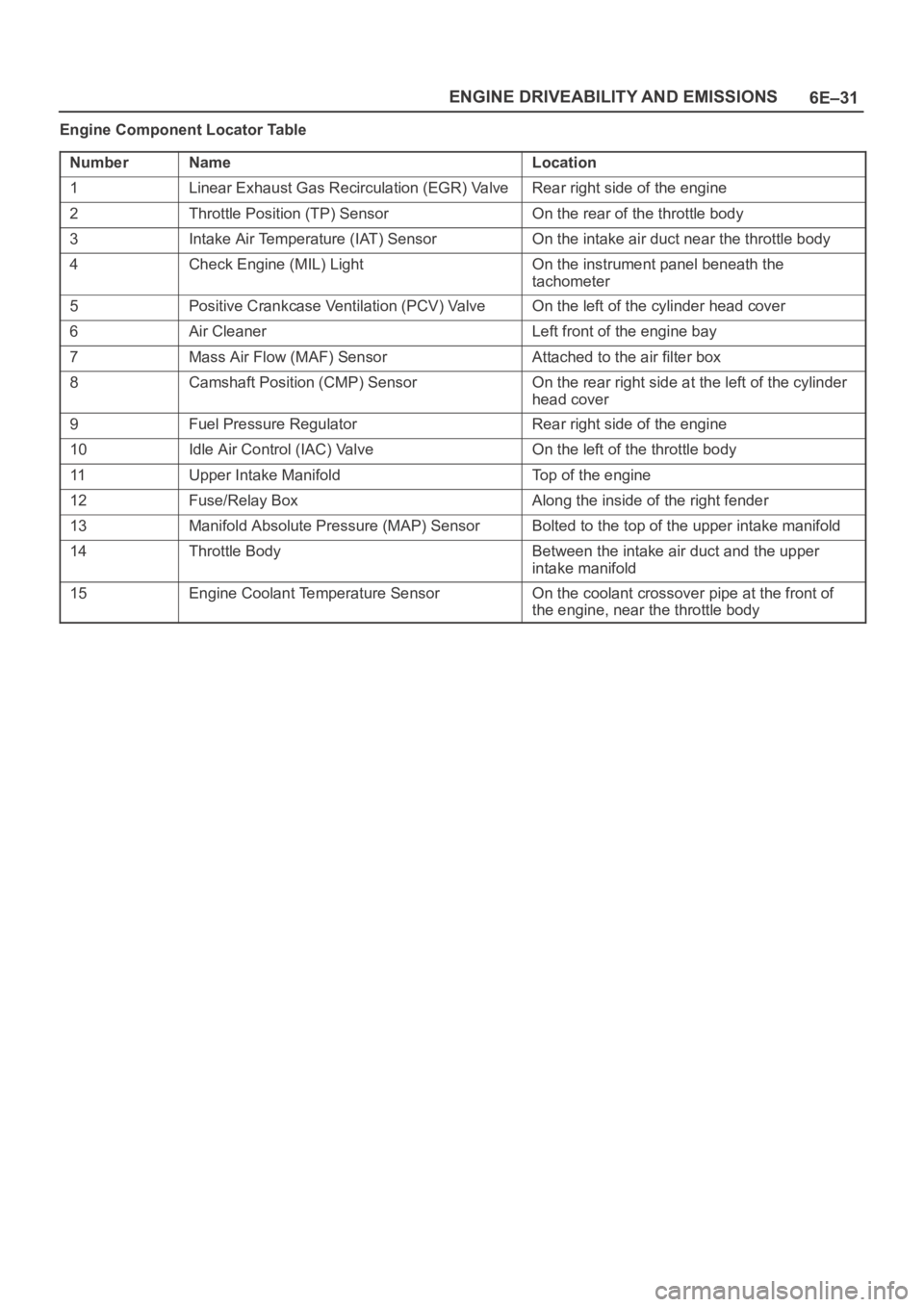
6E–31 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Engine Component Locator Table
Number
NameLocation
1Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ValveRear right side of the engine
2Throttle Position (TP) SensorOn the rear of the throttle body
3Intake Air Temperature (IAT) SensorOn the intake air duct near the throttle body
4Check Engine (MIL) LightOn the instrument panel beneath the
tachometer
5Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) ValveOn the left of the cylinder head cover
6Air CleanerLeft front of the engine bay
7Mass Air Flow (MAF) SensorAttached to the air filter box
8Camshaft Position (CMP) SensorOn the rear right side at the left of the cylinder
head cover
9Fuel Pressure RegulatorRear right side of the engine
10Idle Air Control (IAC) ValveOn the left of the throttle body
11Upper Intake ManifoldTop of the engine
12Fuse/Relay BoxAlong the inside of the right fender
13Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorBolted to the top of the upper intake manifold
14Throttle BodyBetween the intake air duct and the upper
intake manifold
15Engine Coolant Temperature SensorOn the coolant crossover pipe at the front of
the engine, near the throttle body
Page 1156 of 6000

6E–39 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
The data displayed on the other Tech 2 will appear the
same, with some exceptions. Some Tech 2s will only be
able to display certain vehicle parameters as values that
are a coded representation of the true or actual value. For
more information on this system of coding, refer to
Decimal/Binary/Hexadecimal Conversions. On this
vehicle Tech 2 displays the actual values for vehicle
parameters. It will not be necessary to perform any
conversions from coded values to actual values.
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
On-Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which is
a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive. When
a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
The diagnostic test has been completed since the last
ignition cycle.
The diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not
currently active.
W h e n a d i a g n o s t i c t e s t r e p o r t s a fail result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
The diagnostic test has been completed since the last
ignition cycle.
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is currently
active.
The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
Remember, a fuel trim DTC may be triggered by a list of
vehicle faults. Make use of all information available (other
DTCs stored, rich or lean condition, etc.) when
diagnosing a fuel trim fault.
Comprehensive Component Monitor
Diagnostic Operation
Input Components:
Input components are monitored for circuit continuity and
out-of-range values. This includes rationality checking.
Rationality checking refers to indicating a fault when the
signal from a sensor does not seem reasonable, i.e.
Throttle Position (TP) sensor that indicates high throttle
position at low engine loads or MAP voltage. Input
components may include, but are not limited to the
following sensors:
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
Knock Sensor (KS)
Throttle Position (TP) sensor
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensorIn addition to the circuit continuity and rationality check,
the ECT sensor is monitored for its ability to achieve a
steady state temperature to enable closed loop fuel
control.
Output Components:
Output components are diagnosed for proper response to
control module commands. Components where
functional monitoring is not feasible will be monitored for
circuit continuity and out-of-range values if applicable.
Output components to be monitored include, but are not
limited to, the following circuits:
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
Electronic Transmission controls
A/C relays
Cooling fan relay
VSS output
MIL control
Cruise control inhibit
Refer to PCM and Sensors in General Descriptions.
Passive and Active Diagnostic Tests
A passive test is a diagnostic test which simply monitors a
vehicle system or component. Conversely, an active test,
actually takes some sort of action when performing
diagnostic functions, often in response to a failed passive
test. For example, the EGR diagnostic active test will
force the EGR valve open during closed throttle decel
and/or force the EGR valve closed during a steady state.
Either action should result in a change in manifold
pressure.
Intrusive Diagnostic Tests
This is any on-board test run by the Diagnostic
Management System which may have an effect on
vehicle performance or emission levels.
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means that engine at temperature must
reach a minimum of 70
C (160F) and rise at least 22C
(40
F) over the course of a trip.
Freeze Frame
Freeze Frame is an element of the Diagnostic
Management System which stores various vehicle
information at the moment an emissions-related fault is
stored in memory and when the MIL is commanded on.
These data can help to identify the cause of a fault. Refer
to
Storing And Erasing Freeze Fame Data for more
detailed information.
Failure Records
Failure Records data is an enhancement of the OBD
Freeze Frame feature. Failure Records store the same
vehicle information as does Freeze Frame, but it will store
that information for any fault which is stored in on-board
memory, while Freeze Frame stores information only for
emission-related faults that command the MIL on.
Page 1177 of 6000

6E–60
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Electronic Ignition System Diagnosis
If the engine cranks but will not run or immediately stalls,
the Engine Cranks But Will Not Start chart must be used
to determine if the failure is the ignition system or the fuel
system. If DTC P0341, or P0336 is set, the appropriate
diagnostic trouble code chart must be used for diagnosis.
If a misfire is being experienced with no DTC set, refer to
the
Symptoms section for diagnosis.
Fuel Metering System Check
Some failures of the fuel metering system will result in an
“Engine Cranks But Will Not Run” symptom. If this
condition exists, refer to the
Cranks But Will Not Run
chart. This chart will determine if the problem is caused
by the ignition system, the PCM, or the fuel pump
electrical circuit.
Refer to
Fuel System Electrical Test for the fuel system
wiring schematic.
If there is a fuel delivery problem, refer to
Fuel System
Diagnosis
, which diagnoses the fuel injectors, the fuel
pressure regulator, and the fuel pump. If a malfunction
occurs in the fuel metering system, it usually results in
either a rich HO2S signal or a lean HO2S signal. This
condition is indicated by the HO2S voltage, which causes
the PCM to change the fuel calculation (fuel injector pulse
width) based on the HO2S reading. Changes made to the
fuel calculation will be indicated by a change in the long
term fuel trim values which can be monitored with a Tech
2. Ideal long term fuel trim values are around 0%; for a
lean HO2S signal, the PCM will add fuel, resulting in a fuel
trim value above 0%. Some variations in fuel trim values
are normal because all engines are not exactly the same.
If the fuel trim values are greater than +23%, refer to
DTC
P0131, DTC P0151, DTC P0171, and DTC 1171
f o r i t e m s
which can cause a lean HO2S signal.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The Tech 2 displays the IAC pintle position in counts. A
count of “0” indicates the PCM is commanding the IAC
pintle to be driven all the way into a fully-seated position.
This is usually caused by a large vacuum leak.
The higher the number of counts, the more air is being
commanded to bypass the throttle blade. Refer to IAC
System Check in order to diagnose the IAC system.
Refer to
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling in
Symptoms for other possible causes of idle problems.
Fuel System Pressure Test
A fuel system pressure test is part of several of the
diagnostic charts and symptom checks. To perform this
test, refer to
Fuel Systems Diagnosis.
Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure and
Fuel Injector Balance Test Procedure
T32003
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Relieve the fuel pressure by connecting the
5-8840-0378-0 Fuel Pressure Gauge to the fuel
pressure connection on the fuel rail.
CAUTION: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury, wrap a shop towel around the fuel
pressure connection. The towel will absorb any fuel
leakage that occurs during the connection of the fuel
pressure gauge. Place the towel in an approved
container when the connection of the fuel pressure
gauge is complete.
Place the fuel pressure gauge bleed hose in an
approved gasoline container.
With the ignition switch “OFF,” open the valve on the
fuel pressure gauge.
3. Record the lowest voltage displayed by the DVM
after the first second of the test. (During the first
second, voltage displayed by the DVM may be
inaccurate due to the initial current surge.)
Injector Specifications:
Resistance Ohms
Voltage Specification at
10
C-35C (50F-95F)
11.8 – 12.65.7 – 6.6
The voltage displayed by the DVM should be within
the specified range.
The voltage displayed by the DVM may increase
throughout the test as the fuel injector windings
warm and the resistance of the fuel injector windings
changes.
Page 1180 of 6000
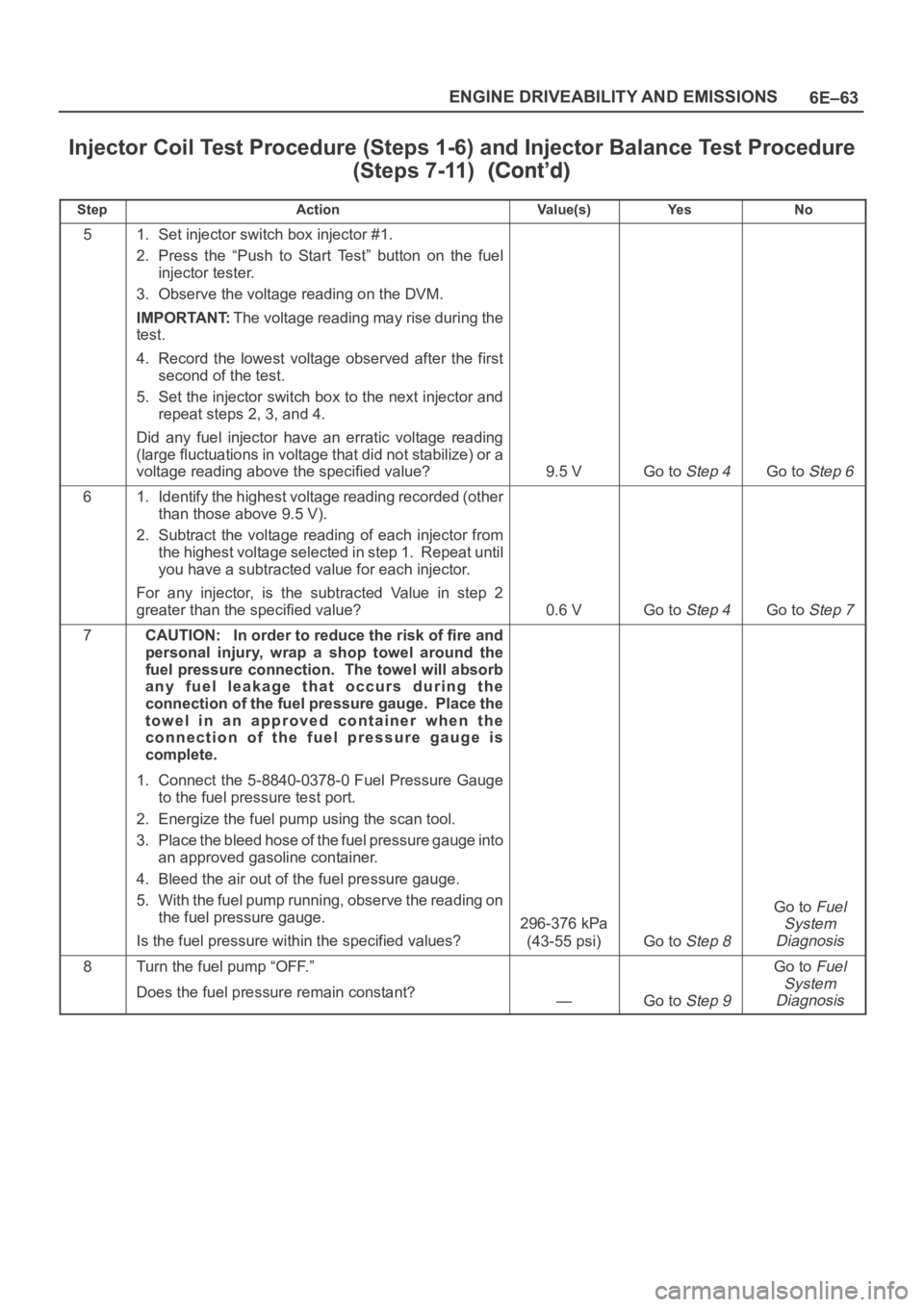
6E–63 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Injector Coil Test Procedure (Steps 1-6) and Injector Balance Test Procedure
(Steps 7-11)
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
51. Set injector switch box injector #1.
2. Press the “Push to Start Test” button on the fuel
injector tester.
3. Observe the voltage reading on the DVM.
IMPORTANT:The voltage reading may rise during the
test.
4. Record the lowest voltage observed after the first
second of the test.
5. Set the injector switch box to the next injector and
repeat steps 2, 3, and 4.
Did any fuel injector have an erratic voltage reading
(large fluctuations in voltage that did not stabilize) or a
voltage reading above the specified value?
9.5 VGo to Step 4Go to Step 6
61. Identify the highest voltage reading recorded (other
than those above 9.5 V).
2. Subtract the voltage reading of each injector from
the highest voltage selected in step 1. Repeat until
you have a subtracted value for each injector.
For any injector, is the subtracted Value in step 2
greater than the specified value?
0.6 VGo to Step 4Go to Step 7
7CAUTION: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury, wrap a shop towel around the
fuel pressure connection. The towel will absorb
any fuel leakage that occurs during the
connection of the fuel pressure gauge. Place the
towel in an approved container when the
connection of the fuel pressure gauge is
complete.
1. Connect the 5-8840-0378-0 Fuel Pressure Gauge
to the fuel pressure test port.
2. Energize the fuel pump using the scan tool.
3. Place the bleed hose of the fuel pressure gauge into
an approved gasoline container.
4. Bleed the air out of the fuel pressure gauge.
5. With the fuel pump running, observe the reading on
the fuel pressure gauge.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified values?
296-376 kPa
(43-55 psi)
Go to Step 8
Go to Fuel
System
Diagnosis
8Turn the fuel pump “OFF.”
Does the fuel pressure remain constant?
—Go to Step 9
Go to Fuel
System
Diagnosis
Page 1182 of 6000

6E–65 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Knock Sensor Diagnosis
The Tech 2 has two data displays available for diagnosing
the knock sensor (KS) system. The two displays are
described as follows:
“Knock Retard” indicates the number of degrees that
the spark timing is being retarded due to a knock
condition.
“KS Noise Channel” indicates the current voltage level
being monitored on the noise channel.
DTCs P0325 and P0327 are designed to diagnose the KS
module, the knock sensor, and the related wiring. The
problems encountered with the KS system should set a
DTC. However, if no DTC was set but the KS system is
suspect because of a detonation complaint, refer to
Detonation/Spark Knock in Symptoms.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Diagnosis
To read and clear diagnostic trouble codes, use a Tech 2.
IMPORTANT:Use of a Tech 2 is recommended to clear
diagnostic trouble codes from the PCM memory.
Diagnostic trouble codes can also be cleared by turning
the ignition “OFF” and disconnecting the battery power
from the PCM for 30 seconds. Turning off the ignition and
disconnecting the battery power from the PCM will cause
all diagnostic information in the PCM memory to be
cleared. Therefore, all the diagnostic tests will have to be
re-run.
Since the PCM can have a failure which may affect only
one circuit, following the diagnostic procedures in this
section will determine which circuit has a problem and
where it is.
If a diagnostic chart indicates that the PCM connections
or the PCM is the cause of a problem, and the PCM is
replaced, but this does not correct the problem, one of the
following may be the reason:
There is a problem with the PCM terminal connections.
The terminals may have to be removed from the
connector in order to check them properly.
The problem is intermittent. This means that the
problem is not present at the time the system is being
checked. In this case, refer to the
Symptoms p o r t i o n o f
the manual and make a careful physical inspection of
all component and wiring associated with the affected
system.
There is a shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness.
S o l e n o i d s a n d r e l a y s a r e t u r n e d “ O N ” a n d “ O F F ” b y t h e
PCM using internal electronic switches called drivers.
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness will not
damage the PCM but will cause the solenoid or relay to
be inoperative.
Multiple PCM Information Sensor
DTCS Set
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors various
sensors to determine the engine operating conditions.
The PCM controls fuel delivery, spark advance,
transmission operation, and emission control device
operation based on the sensor inputs.The PCM provides a sensor ground to all of the sensors.
The PCM applies 5 volts through a pull-up resistor, and
determines the status of the following sensors by
monitoring the voltage present between the 5-volt supply
and the resistor:
The engine coolant temperature (ETC) sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
The transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
The PCM provides the following sensors with a 5-volt
reference and a sensor ground signal:
The exhaust gas recirculating (EGR) pintle position
sensor
The throttle position (TP) sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
The PCM monitors the separate feedback signals from
these sensors in order to determine their operating
status.
Diagnostic Aids
IMPORTANT:Be sure to inspect PCM and engine
grounds for being secure and clean.
A short to voltage in one of the sensor input circuits may
cause one or more of the following DTCs to be set:
P0108
P0113
P0118
P0123
P0560
P0712
P0406
IMPORTANT:If a sensor input circuit has been shorted
to voltage, ensure that the sensor is not damaged. A
damaged sensor will continue to indicate a high or low
voltage after the affected circuit has been repaired. If the
sensor has been damaged, replace it.
An open in the sensor ground circuit between the PCM
and the splice will cause one or more of the following
DTCs to be set:
P0108
P0113
P0118
P0123
P0712
P0406
A short to ground in the 5-volt reference A or B circuit will
cause one or more of the following DTCs to be set:
P0107
P0122
In the 5-volt reference circuit A, between the PCM and the
splice, will cause one or more of the following DTCs to be
set:
P0122
In the 5-volt reference circuit B, between the PCM and the
splice, will cause one or more of the following DTCs to be
set:
P0107
Check for the following conditions: