1998 OPEL FRONTERA mileage
[x] Cancel search: mileagePage 1366 of 6000

6E–249 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1404 EGR Closed Stuck
D06RW106
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the EGR
valve pintle position input to ensure that the valve
responds properly to commands from the PCM, and to
detect a fault if current pintle zero position is different from
the learned zero position. If the PCM detects a pintle
position signal indicates more than 30 % different
between current zero position and the learned zero
position and more than 5 seconds, and this condition
meet 3 times during trip, then the PCM will set DTC
P1404.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Ignition voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
Intake Air temp is more than 3C.
Desire EGR position is 0.
Difference EGR pintle position between current and
the learned zero is more than 30 % last more than 5
seconds, and meet three time to the above condition
during a trip. Then it trigger the PCM lights on.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after consecutive 2nd trip in which the fault is
detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in Failure
Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1404 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Excessive carbon deposit on EGR valve shaft or/and
foreign material may cause no return to EGR valve
fully seated. Those carbon deposit may occur by
unusual port operation. Remove foreign material
or/and excessive carbon deposit on EGR valve shaft
may make return to EGR valve fully seated.
Poor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
wiring harness for damage. Same as P1406
description
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Page 1369 of 6000
6E–252
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
passage and on the IAC pintle, and excessive deposits
in the throttle bore and on the throttle plate.
Large vacuum leak – Check for a condition that causes
a large vacuum leak, such as an incorrectly installed or
faulty PCV valve or a disconnected brake booster
hose.Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
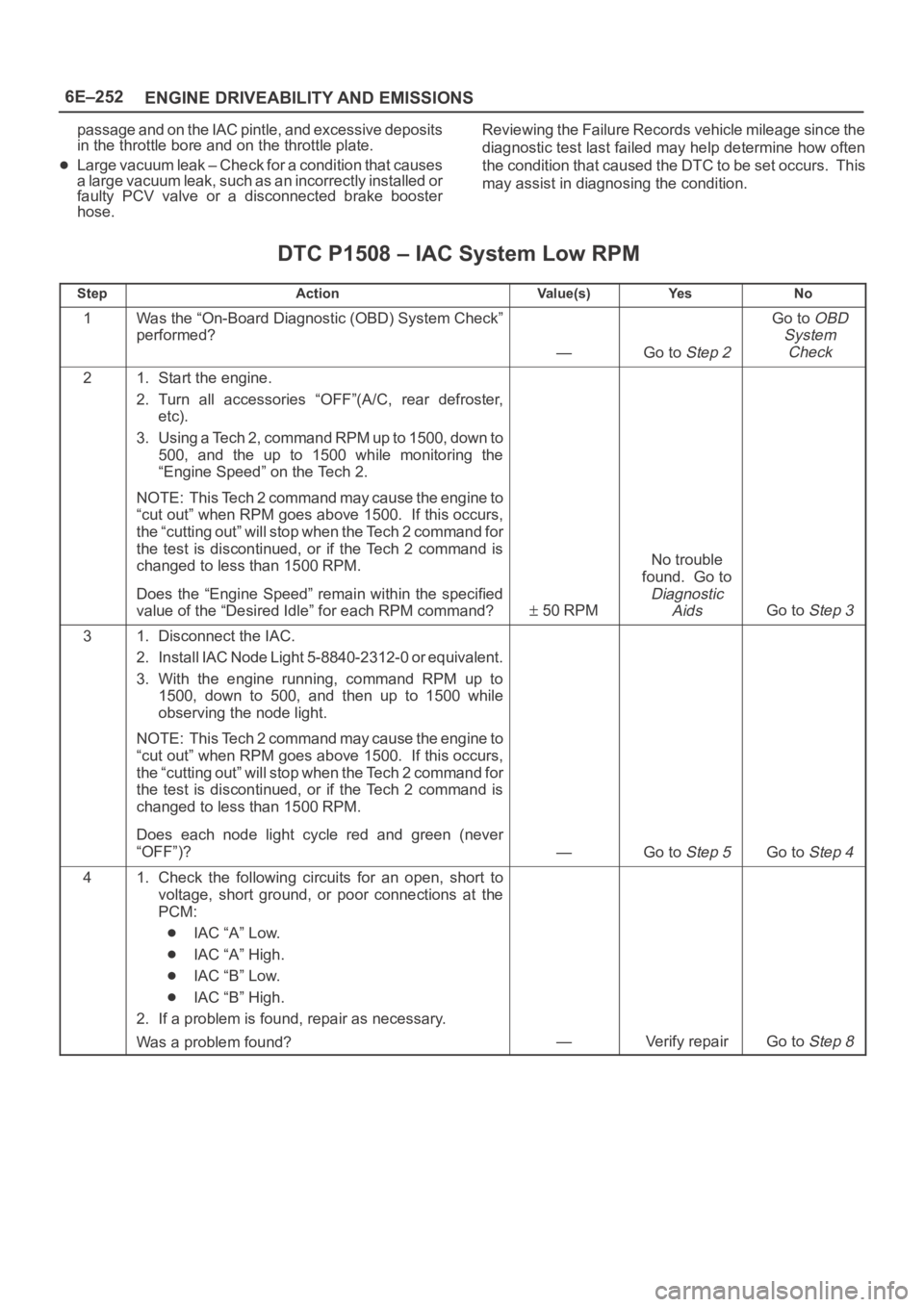
DTC P1508 – IAC System Low RPM
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Start the engine.
2. Turn all accessories “OFF”(A/C, rear defroster,
etc).
3. Using a Tech 2, command RPM up to 1500, down to
500, and the up to 1500 while monitoring the
“Engine Speed” on the Tech 2.
NOTE: This Tech 2 command may cause the engine to
“cut out” when RPM goes above 1500. If this occurs,
the “cutting out” will stop when the Tech 2 command for
the test is discontinued, or if the Tech 2 command is
changed to less than 1500 RPM.
Does the “Engine Speed” remain within the specified
value of the “Desired Idle” for each RPM command?
50 RPM
No trouble
found. Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 3
31. Disconnect the IAC.
2. Install IAC Node Light 5-8840-2312-0 or equivalent.
3. With the engine running, command RPM up to
1500, down to 500, and then up to 1500 while
observing the node light.
NOTE: This Tech 2 command may cause the engine to
“cut out” when RPM goes above 1500. If this occurs,
the “cutting out” will stop when the Tech 2 command for
the test is discontinued, or if the Tech 2 command is
changed to less than 1500 RPM.
Does each node light cycle red and green (never
“OFF”)?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
41. Check the following circuits for an open, short to
voltage, short ground, or poor connections at the
PCM:
IAC “A” Low.
IAC “A” High.
IAC “B” Low.
IAC “B” High.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
Page 1372 of 6000
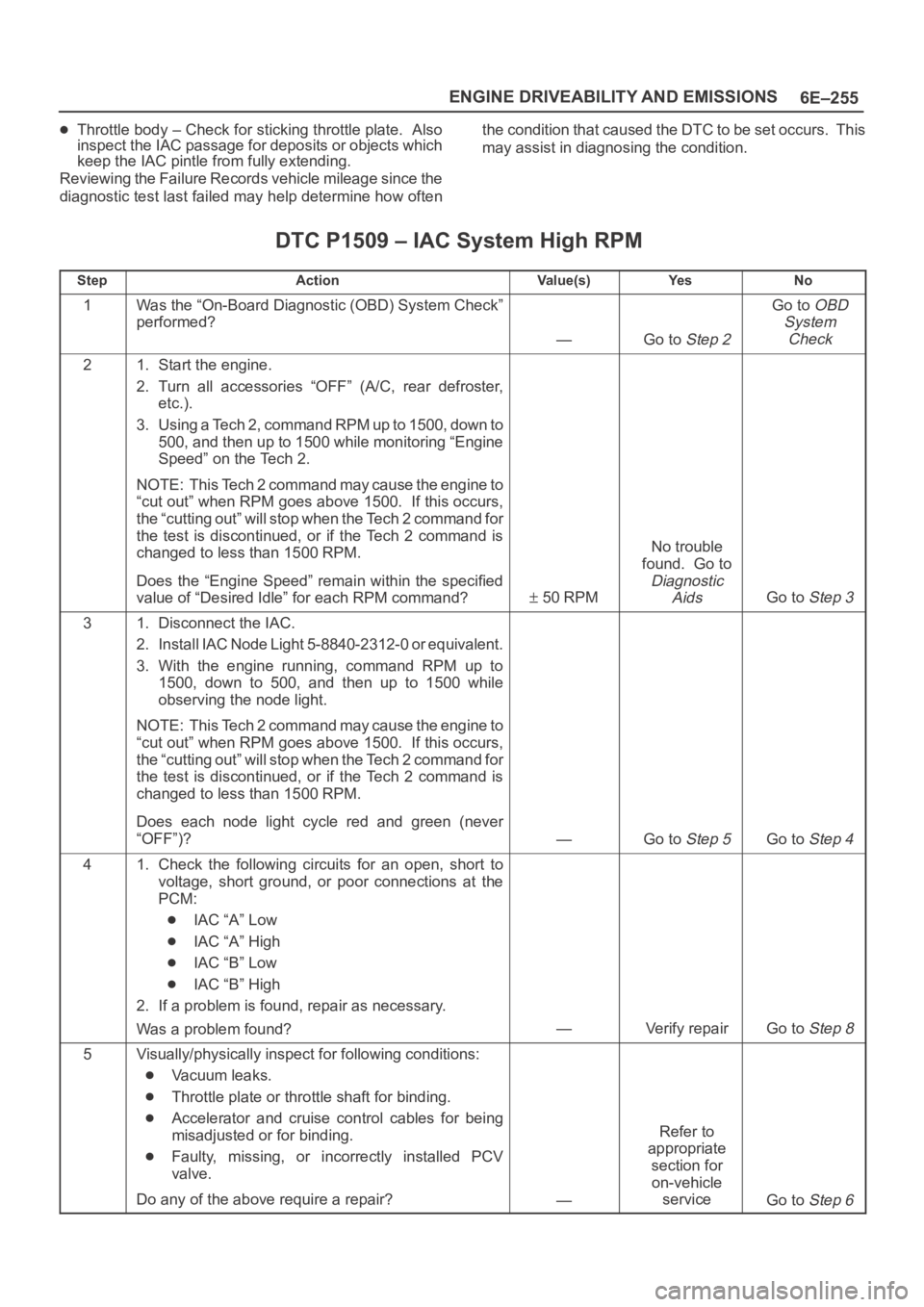
6E–255 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Throttle body – Check for sticking throttle plate. Also
inspect the IAC passage for deposits or objects which
keep the IAC pintle from fully extending.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how oftenthe condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P1509 – IAC System High RPM
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Start the engine.
2. Turn all accessories “OFF” (A/C, rear defroster,
etc.).
3. Using a Tech 2, command RPM up to 1500, down to
500, and then up to 1500 while monitoring “Engine
Speed” on the Tech 2.
NOTE: This Tech 2 command may cause the engine to
“cut out” when RPM goes above 1500. If this occurs,
the “cutting out” will stop when the Tech 2 command for
the test is discontinued, or if the Tech 2 command is
changed to less than 1500 RPM.
Does the “Engine Speed” remain within the specified
value of “Desired Idle” for each RPM command?
50 RPM
No trouble
found. Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 3
31. Disconnect the IAC.
2. Install IAC Node Light 5-8840-2312-0 or equivalent.
3. With the engine running, command RPM up to
1500, down to 500, and then up to 1500 while
observing the node light.
NOTE: This Tech 2 command may cause the engine to
“cut out” when RPM goes above 1500. If this occurs,
the “cutting out” will stop when the Tech 2 command for
the test is discontinued, or if the Tech 2 command is
changed to less than 1500 RPM.
Does each node light cycle red and green (never
“OFF”)?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
41. Check the following circuits for an open, short to
voltage, short ground, or poor connections at the
PCM:
IAC “A” Low
IAC “A” High
IAC “B” Low
IAC “B” High
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
5Visually/physically inspect for following conditions:
Vacuum leaks.
Throttle plate or throttle shaft for binding.
Accelerator and cruise control cables for being
misadjusted or for binding.
Faulty, missing, or incorrectly installed PCV
valve.
Do any of the above require a repair?
—
Refer to
appropriate
section for
on-vehicle
service
Go to Step 6
Page 1376 of 6000

6E–259 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1640 Driver-1-Input High Voltage
Circuit Description
Output driver modules (ODMs) are used by the
powertrain control module (PCM) to turn “ON” many of
the current-driven devices that are needed to control
various engine and transmission functions. Each ODM is
capable of controlling up to 7 separate outputs by
applying ground to the device which the PCM is
commanding “ON.”
Unlike the Quad Driver Modules (QDMs) used in prior
model years, ODMs have the capability of diagnosing
each output circuit individually. DTC P1640 set indicates
an improper voltage level has been detected on an ODM
output.
Since A/C is an option, No A/C will cause the air
conditioning clutch relay output to always fault. If a fault is
seen on the air conditioning clutch relay output, it will not
be logged as a fault until the A/C request input interrupts a
high voltage, indicating that A/C has been installed.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Ignition “ON.”
Engine running.
No DTC 1618.
Ignition voltage is above 13.2 volts for 4 seconds.
Output voltage does not equal ignition voltage when
output is “OFF” or output voltage is not less than 1 volt
when output is “ON.”
Above conditions occur for at least 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records only. This
information will not be stored as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1640 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the PCM, turn the ignition “ON” and observe a
voltmeter connected to the suspect driver circuit at the
PCM harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses relates to the MIL. A change in
voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Poor connection at component – Examine for
damaged connectors, unplugged connector, or
damaged terminals at the following locations:
Instrument cluster harness, canister purge solenoid,
A/C clutch relay. An open ignition feed circuit at any of
these components will cause DTC P1640 to be set.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
The following PCM pins are controlled by output driver
modules (ODMs):
A13 – “Check Engine Lamp”
A14 – SVS (”Check Trans”)
B14 – A/C Clutch
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
6. The Tech 2 Driver Module Status indicates the PCM
pin that is affected.
11. The Tech 2 may indicate “short circuit” even when
the problem is an open circuit. The cause of an
open circuit may be in the component itself-lamp,
purge, solenoid, or A/C compressor relay.
13.A short to ground on the ignition side of the
component will blow the fuse. Since the fuse was
checked in Step 4, a short to ground would be
between the affected component and the PCM.
Page 1949 of 6000
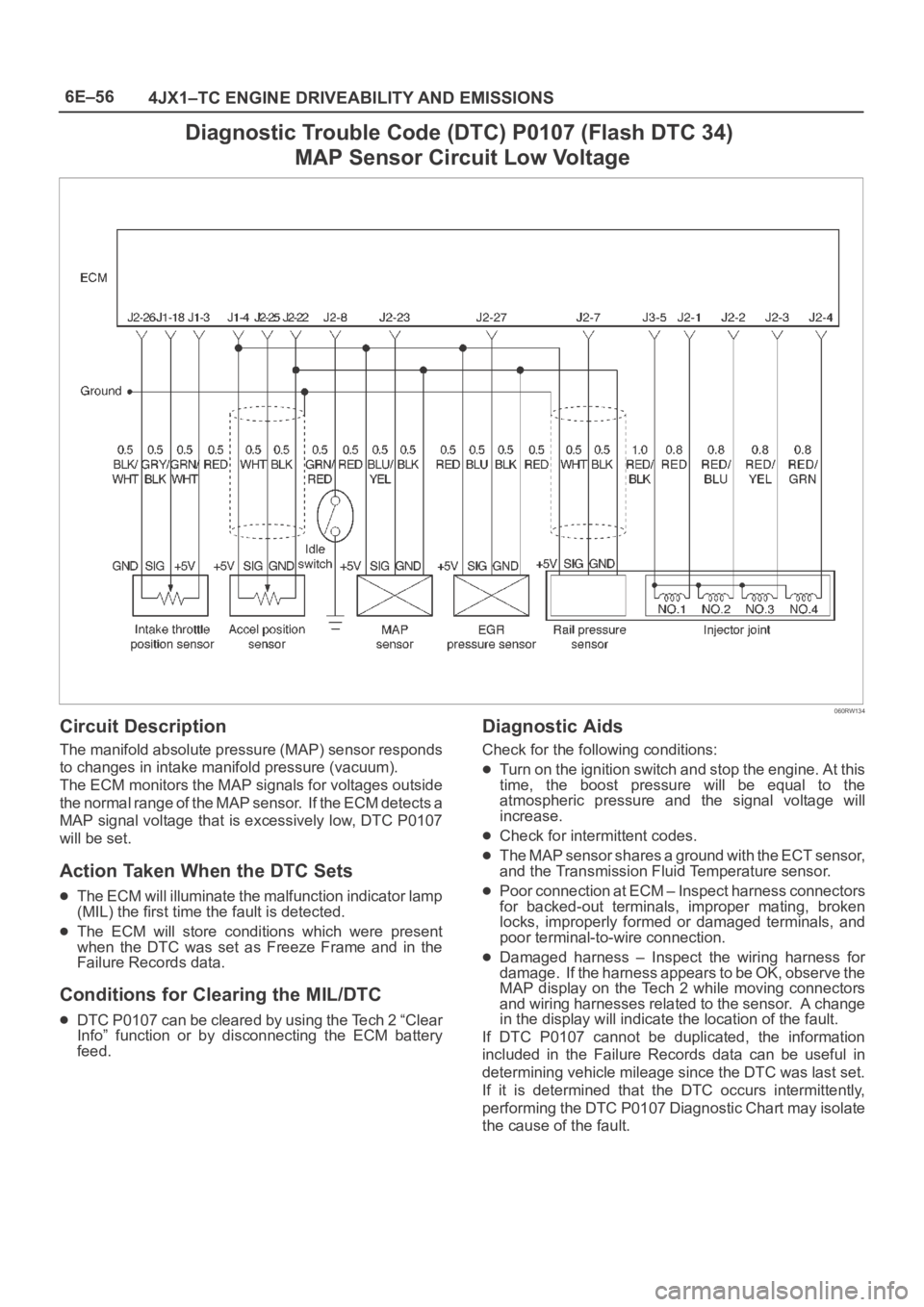
6E–56
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107 (Flash DTC 34)
MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum).
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is excessively low, DTC P0107
will be set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0107 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Turn on the ignition switch and stop the engine. At this
time, the boost pressure will be equal to the
atmospheric pressure and the signal voltage will
increase.
Check for intermittent codes.
The MAP sensor shares a ground with the ECT sensor,
and the Transmission Fluid Temperature sensor.
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0107 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P0107 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 1951 of 6000
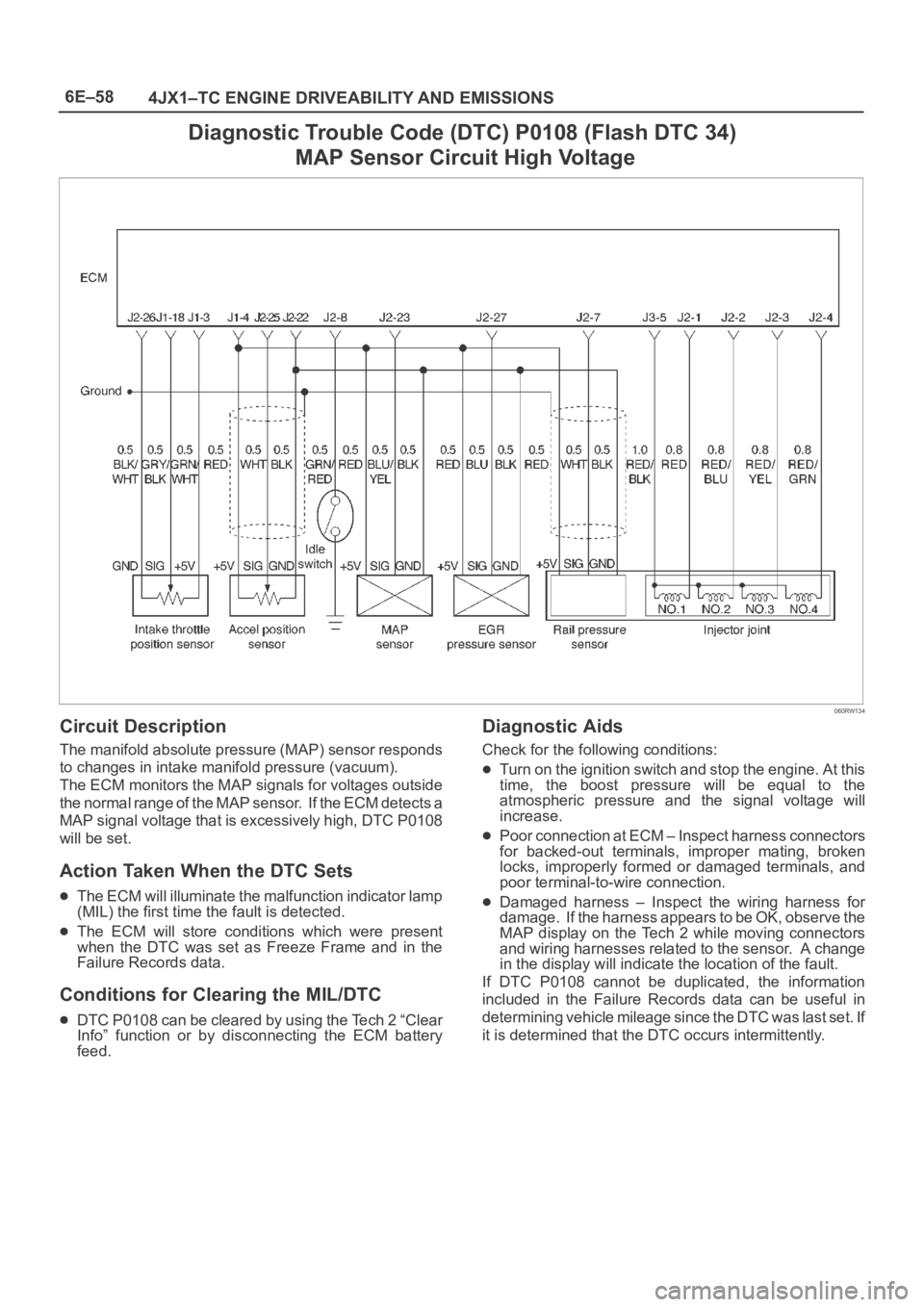
6E–58
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108 (Flash DTC 34)
MAP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum).
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is excessively high, DTC P0108
will be set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0108 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Turn on the ignition switch and stop the engine. At this
time, the boost pressure will be equal to the
atmospheric pressure and the signal voltage will
increase.
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0108 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set. If
it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently.
Page 1953 of 6000

6E–60
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0112 (Flash DTC 23)
IAT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
060RW129
Circuit Description
The Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which measures the temperature of the air entering the
engine. The Engine Control Module ECM applies 5 volts
through a pull-up resistor to the IAT sensor. When the
intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the
ECM will monitor a high signal voltage on the IAT signal
circuit. If the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance is
lower, causing the ECM to monitor a lower voltage. DTC
P0112 will set when the ECM detects an excessively low
signal voltage on the Intake air temperature sensor signal
circuit.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0112 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
IAT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the IAT sensor. A change
in the IAT display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0112 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Page 1955 of 6000

6E–62
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0113 (Flash DTC 23)
IAT Sensor Circuit High Voltage
060RW129
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which measures the temperature of the air entering the
engine. The Engine Control Module ECM applies 5 volts
through a pull-up resistor to the IAT sensor. When the
intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the
ECM will monitor a high signal voltage on the IAT signal
circuit. If the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance is
lower causing the ECM to monitor a lower voltage. DTC
P0113 will set when the ECM detects an excessively high
signal voltage on the intake air temperature sensor signal
circuit.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0113 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
IAT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the IAT sensor. A change
in the IAT display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0113 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.