1998 OPEL FRONTERA engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 2231 of 6000
7A–77 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
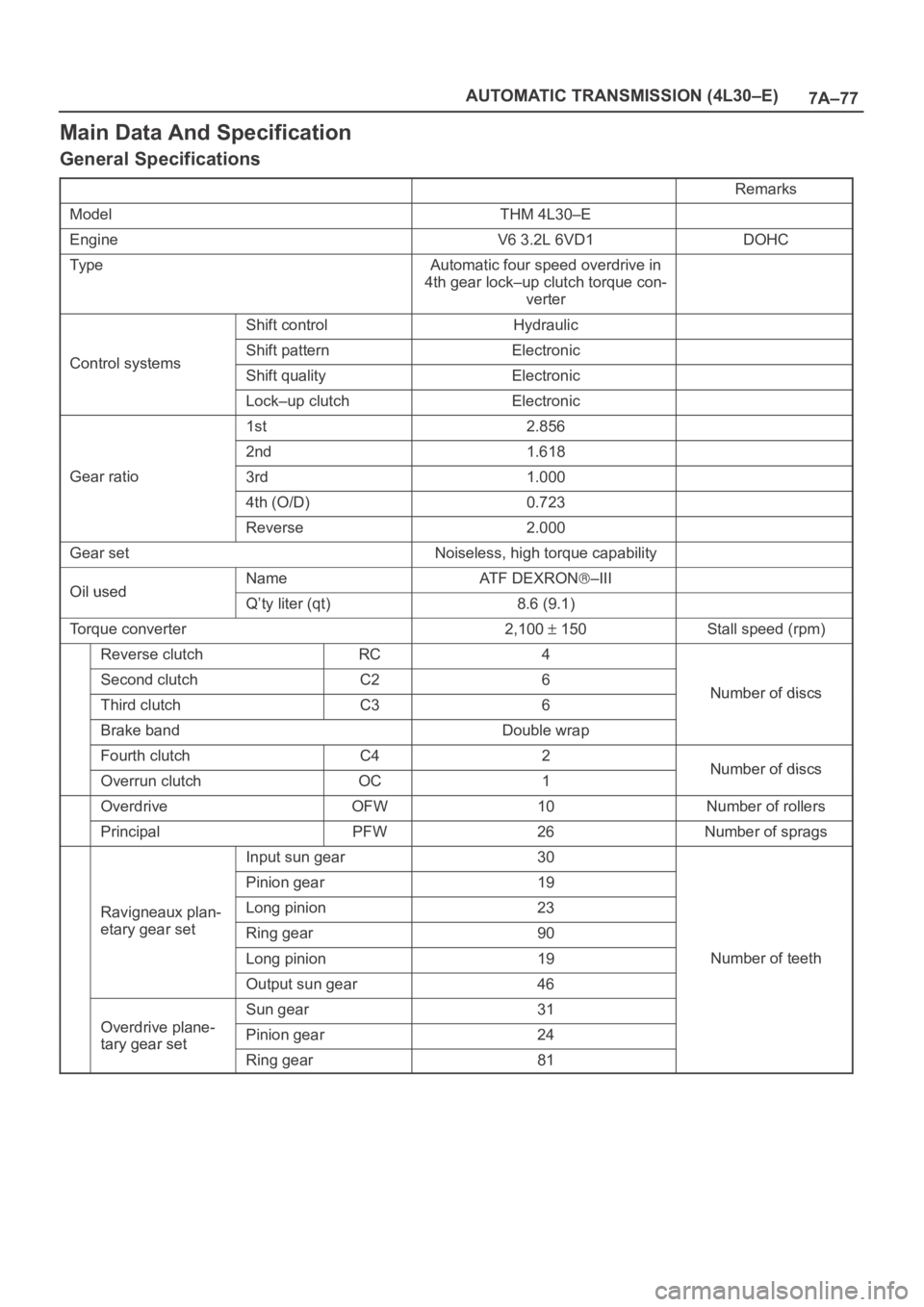
Main Data And Specification
General Specifications
Remarks
ModelTHM 4L30–E
EngineV6 3.2L 6VD1DOHC
Ty p eAutomatic four speed overdrive in
4th gear lock–up clutch torque con-
verter
Shift controlHydraulic
Control systemsShift patternElectronicControl systemsShift qualityElectronic
Lock–up clutchElectronic
1st2.856
2nd1.618
Gear ratio3rd1.000
4th (O/D)0.723
Reverse2.000
Gear setNoiseless, high torque capability
Oil usedNameAT F D E X R O N–IIIOil usedQ’ty liter (qt)8.6 (9.1)
Torque converter2,100 150Stall speed (rpm)
Reverse clutchRC4
Second clutchC26Number of discsThird clutchC36Number of discs
Brake bandDouble wrap
Fourth clutchC42Number of discsOverrun clutchOC1Number of discs
OverdriveOFW10Number of rollers
PrincipalPFW26Number of sprags
Input sun gear30
Pinion gear19
Ravigneaux plan-Long pinion23g
etary gear setRing gear90
Long pinion19Number of teeth
Output sun gear46
Odi l
Sun gear31
Overdrive plane-
tary gear setPinion gear24tary gear set
Ring gear81
Page 2251 of 6000

7A1–6
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Shift Control
The transmission gear is shifted according to the shift
pattern selected by the driver. In shifting gears, the gear
ratio is controlled by the ON/ OFF signal using the shift
solenoid A and the shift solenoid B.
Band Apply Control
The band apply is controlled when in the 3–2 downshift
(engine overrun prevention) and the garage shift (shock
control).
The band apply solenoid is controlled by the signal from
the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to regulate the flow of
the oil.
Torque Converter Clutch Control
The clutch ON/OFF is controlled by moving the converter
clutch valve through shifting Torque Converter Clutch
(TCC) solenoid using the ON/OFF signal.
Line Pressure Control
The throttle signal allows the current signal to be sent to
the force motor. After receiving the current signal, the
force motor activates the pressure regulator valve to
regulate the line pressure.
On–Board Diagnostic System
Several malfunction displays can be stored in the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) memory, and read out
of it afterward.The serial data lines, which are required for the testing of
the final assembly and the coupling to other electronic
modules, can be regulated by this function.
Fail Safe Mechanism
If there is a problem in the transmission system, the PCM
will go into a “backup” mode.
The vehicle can still be driven, but the driver must use the
select lever to shift gears.
Torque Management Control
The transmission control side sends the absolute spark
advance signal to the engine control side while the
transmission is being shifted. This controls the engine
spark timing in compliance with the vehicle running
condition to reduce the shocks caused by the change of
speed.
ATF Warning Control
The oil temperature sensor detects the ATF oil
temperature to control the oil temperature warning, TCC,
and the winter mode.
ABS Control (If equipped)
When the select lever is at “L” or “R” range, a signal is sent
to the ABS controller as one of the ABS control
conditions.
Page 2255 of 6000

7A1–10
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Functions of Input / Output Components
ComponentsFunction
Speed sensor
(fixed to transmission
(T/M))Senses rotation of output shaft and feeds the data to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
Throttle position sensor
(TPS)
(fixed to engine)Senses the extent of throttle valve opening and the speed of the throttle valve
lever motion to open the valve. Feeds the data to PCM.
I
N
Brake Switch (SW)
(fixed to brake pedal)Senses whether the driver has pressed the brake pedal or not and feeds the
information to PCM.
N-
P
U
Kickdown SW
(fixed to accelerator pedal)Senses whether the driver has pushed the accelerator pedal fully or not, and
feeds the information to PCM.
U
TMode SW (fixed to T/M)Senses the select lever position, and feeds the information to PCM.
S
I
Power drive SW
(fixed to front console)Senses whether the driver has selected the power mode, and feeds the informa-
tion to PCM.
I
G-T/M oil temp. sensorSenses the T/M oil temperature and feeds the data to PCM
N
A
L
Engine coolant tempera-
ture sensorSenses the engine coolant temperature, and feeds the data to PCM.
LEngine speed signalFeeds the signals monitoring engine speed to PCM from crank angle sensor.
Air conditioning informationSenses whether the air conditioner has been switched on or not, and feeds the
information to PCM.
Winter switch (fixed to front
console)Senses whether the driver has selected the winter mode, and feeds the informa-
tion to PCM.
Cruise controller * (Over-
drive OFF signal)Downshift takes place when Overdrive OFF signal is received from auto cruise
control unit.
S
Shift solenoid A, BSelects shift point and gear position suited to the vehicle running condition on
the basis of PCM output.
O
S
O-
L
Band apply solenoidControls oil flow suited to the vehicle running condition on the basis of PCM out-
put.
O
U
T-
P
E-
N
O
Torque Converter
Clutch solenoidControls clutch engagement/disengagement suited to the vehicle running condi-
tion on the basis of PCM output.
P
U
T
O
I
DForce motor
(Pressure regulator
valve)Adjusts the oil pump delivery pressure to line pressure suited to the vehicle run-
ning condition on the basis of PCM output.
S
I
Power drive mode lampInforms the driver whether the vehicle is in power mode or not.
I
G-Winter drive mode lampInforms the driver whether the vehicle is in winter mode or not.G
N
A
L
T/M monitor lamp
(“CHECK TRANS”)Informs the driver of failure in the system.
LATF warning lampLights when ATF oil temperature rises.
ABS signal *When the select lever is at “Reverse” or “L” range, sends a signal to the ABS
controller as one of the ABS control conditions.
* If equipped
Page 2267 of 6000

7A1–22
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
connection or loose wiring. Terminals and grounds should
always be the prime suspect. Intermittents rarely occur
inside sophisticated electronic components such as the
PCM.
Use the DTC information to understand which wires and
sensors are involved.
When an intermittent problem is encountered, check
suspect circuits for:
1. Poor terminal to wire connection.
2. Terminals not fully seated in the connector body
(backed out).
3. Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
4. Loose, dirty, or corroded ground connections:
HINT: Any time you have an intermittent in more than
one circuit, check whether the circuits share a
common ground connection.
5. Pinched or damaged wires.
6. Electro–Magnetic Interference (EMI):
HINT: Check that all wires are properly routed away
from spark plug wires, distributor wires, coil, and
generator. Also check for improperly installed
electrical options, such as lights, 2–way radios, etc.Use the F3 SNAPSHOT mode of the Tech2 to help isolate
the cause of an intermittent fault. The snapshot mode will
record information before and after the problem occurs.
Set the snapshot to “trigger” on the suspect DTC. If you
notice the reported symptom during the test drive, trigger
the snapshot manually.
After the snapshot has been triggered, command the
Tech2 to play back the flow of data recorded from each of
the various sensors. Signs of an intermittent fault in a
sensor circuit are sudden unexplainable jump in data
values out of the normal range.
Transmission And PCM Identification
The chart below contains a list of all important information
concerning rear axle ratio, Powertrain Control Module
(PCM), and transmission identification.
VEHICLE
Rr axlePCMTRANSMISSION
Ty p eEngine
Rr axle
RatioISUZU Parts No.Calibration
CodeIsuzu Part No.Model Code
Isuzu /
Trooper3.2L V64.555
8–16254–949–0
8–16254–749–0
8–16253–989–0
G208–96018–272–3FP (4X4)
Page 2282 of 6000
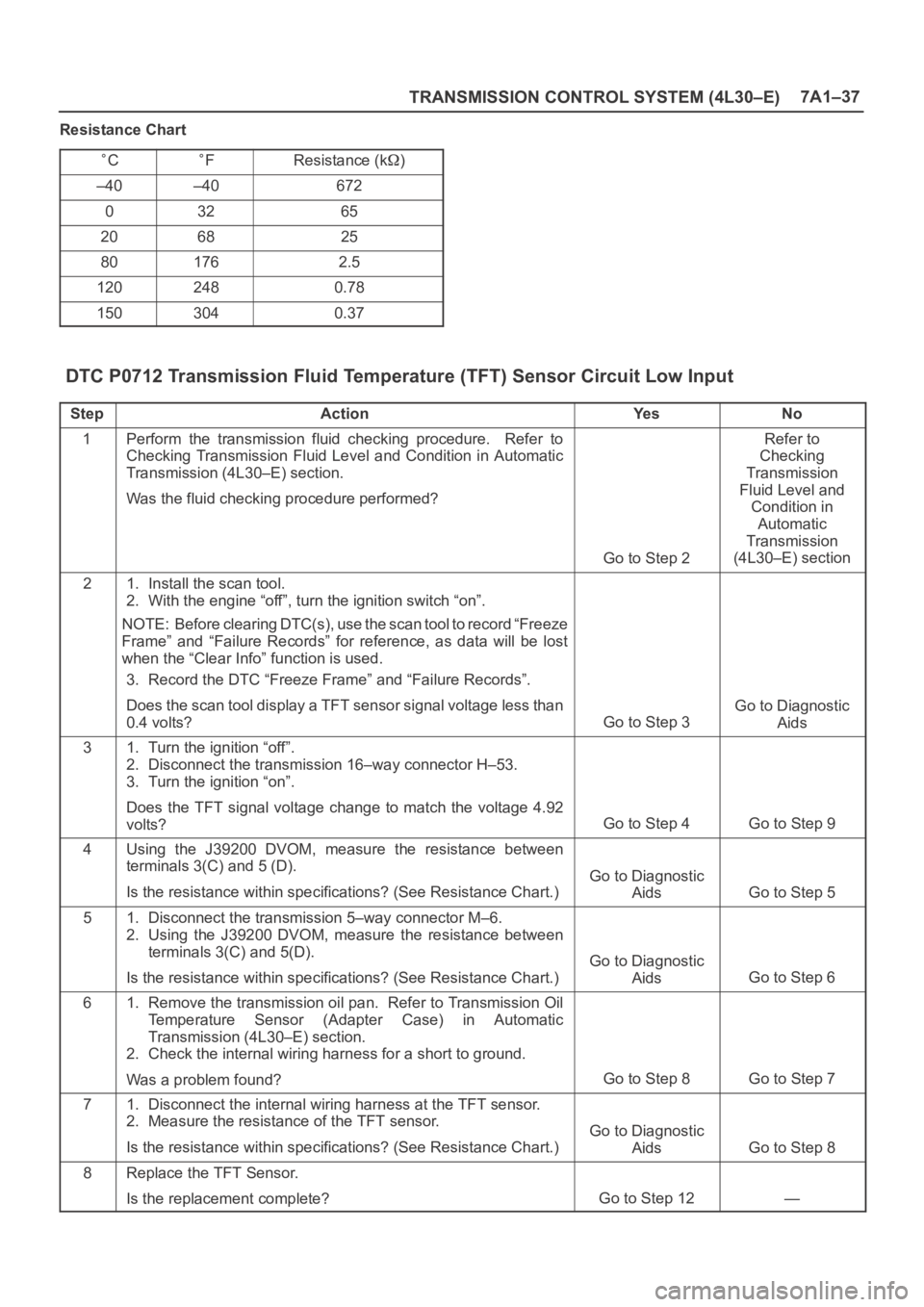
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–37
Resistance Chart
CFResistance (k)
–40–40672
03265
206825
801762.5
1202480.78
1503040.37
DTC P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit Low Input
StepActionYe sNo
1Perform the transmission fluid checking procedure. Refer to
Checking Transmission Fluid Level and Condition in Automatic
Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was the fluid checking procedure performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
Checking
Transmission
Fluid Level and
Condition in
Automatic
Transmission
(4L30–E) section
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Freeze
Frame” and “Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost
when the “Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Freeze Frame” and “Failure Records”.
Does the scan tool display a TFT sensor signal voltage less than
0.4 volts?
Go to Step 3
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
31. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
3. Turn the ignition “on”.
Does the TFT signal voltage change to match the voltage 4.92
volts?
Go to Step 4Go to Step 9
4Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals 3(C) and 5 (D).
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 5
51. Disconnect the transmission 5–way connector M–6.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals 3(C) and 5(D).
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 6
61. Remove the transmission oil pan. Refer to Transmission Oil
Temperature Sensor (Adapter Case) in Automatic
Transmission (4L30–E) section.
2. Check the internal wiring harness for a short to ground.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 8Go to Step 7
71. Disconnect the internal wiring harness at the TFT sensor.
2. Measure the resistance of the TFT sensor.
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 8
8Replace the TFT Sensor.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 12—
Page 2285 of 6000
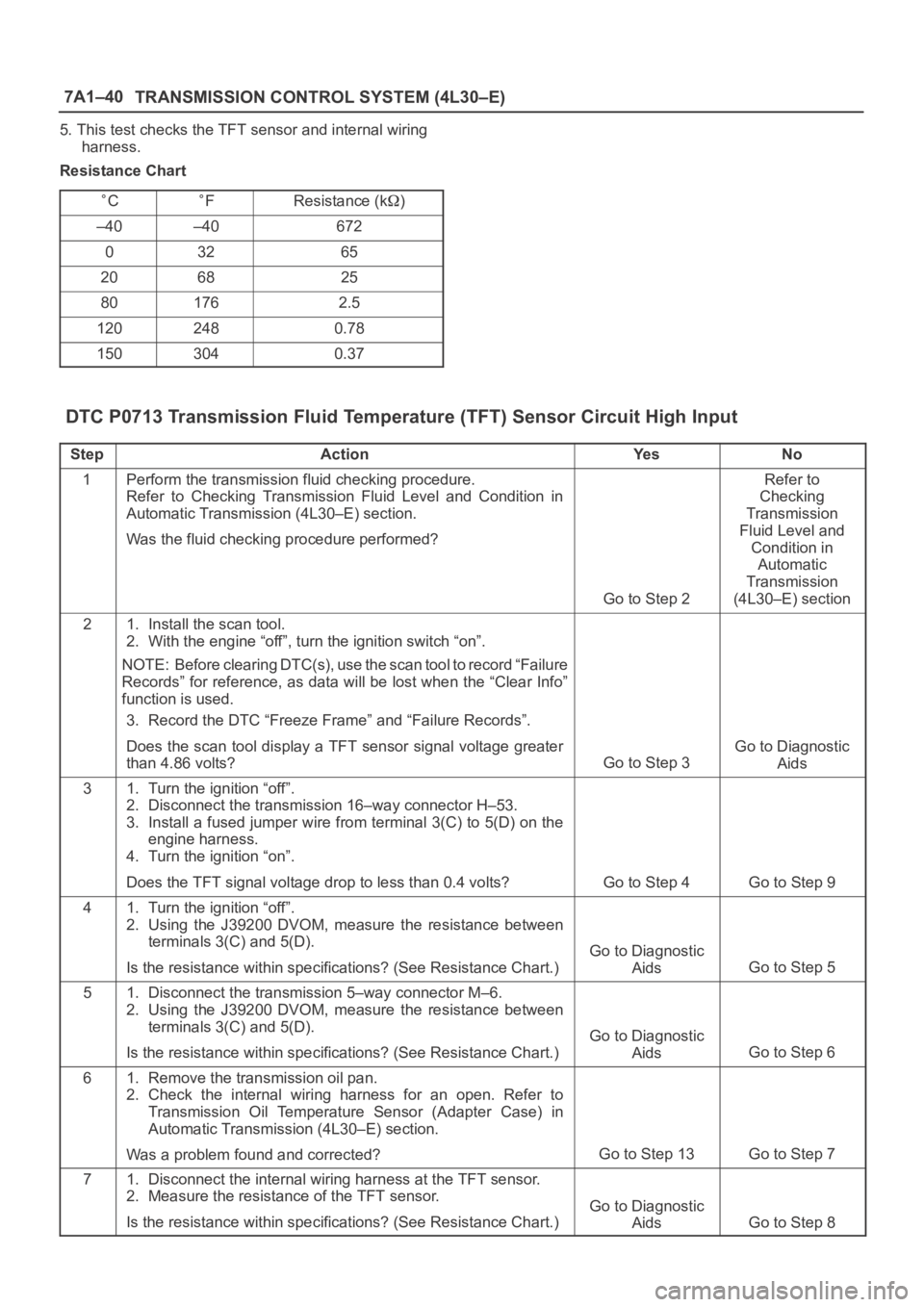
7A1–40
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
5. This test checks the TFT sensor and internal wiring
harness.
Resistance Chart
CFResistance (k)
–40–40672
03265
206825
801762.5
1202480.78
1503040.37
DTC P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit High Input
StepActionYe sNo
1Perform the transmission fluid checking procedure.
Refer to Checking Transmission Fluid Level and Condition in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was the fluid checking procedure performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
Checking
Transmission
Fluid Level and
Condition in
Automatic
Transmission
(4L30–E) section
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Freeze Frame” and “Failure Records”.
Does the scan tool display a TFT sensor signal voltage greater
than 4.86 volts?
Go to Step 3
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
31. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
3. Install a fused jumper wire from terminal 3(C) to 5(D) on the
engine harness.
4. Turn the ignition “on”.
Does the TFT signal voltage drop to less than 0.4 volts?
Go to Step 4Go to Step 9
41. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals 3(C) and 5(D).
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 5
51. Disconnect the transmission 5–way connector M–6.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals 3(C) and 5(D).
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 6
61. Remove the transmission oil pan.
2. Check the internal wiring harness for an open. Refer to
Transmission Oil Temperature Sensor (Adapter Case) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was a problem found and corrected?
Go to Step 13Go to Step 7
71. Disconnect the internal wiring harness at the TFT sensor.
2. Measure the resistance of the TFT sensor.
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 8
Page 2300 of 6000
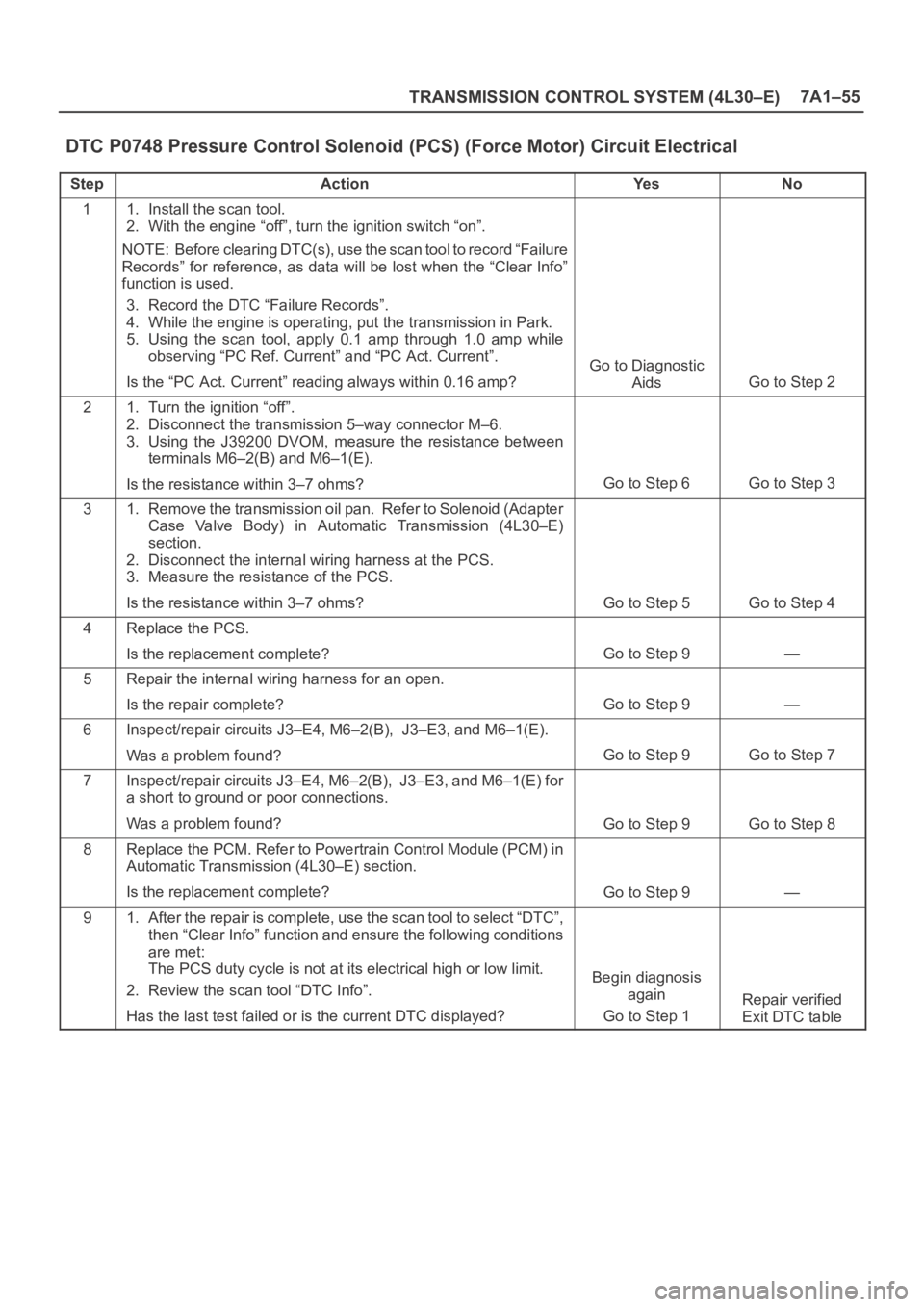
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–55
DTC P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (Force Motor) Circuit Electrical
StepActionYe sNo
11. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”.
4. While the engine is operating, put the transmission in Park.
5. Using the scan tool, apply 0.1 amp through 1.0 amp while
observing “PC Ref. Current” and “PC Act. Current”.
Is the “PC Act. Current” reading always within 0.16 amp?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 2
21. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 5–way connector M–6.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals M6–2(B) and M6–1(E).
Is the resistance within 3–7 ohms?
Go to Step 6Go to Step 3
31. Remove the transmission oil pan. Refer to Solenoid (Adapter
Case Valve Body) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E)
section.
2. Disconnect the internal wiring harness at the PCS.
3. Measure the resistance of the PCS.
Is the resistance within 3–7 ohms?
Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
4Replace the PCS.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 9—
5Repair the internal wiring harness for an open.
Is the repair complete?
Go to Step 9—
6Inspect/repair circuits J3–E4, M6–2(B), J3–E3, and M6–1(E).
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 9Go to Step 7
7Inspect/repair circuits J3–E4, M6–2(B), J3–E3, and M6–1(E) for
a short to ground or poor connections.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 9Go to Step 8
8Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 9—
91. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select “DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
The PCS duty cycle is not at its electrical high or low limit.
2. Review the scan tool “DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified
Exit DTC table
Page 2312 of 6000
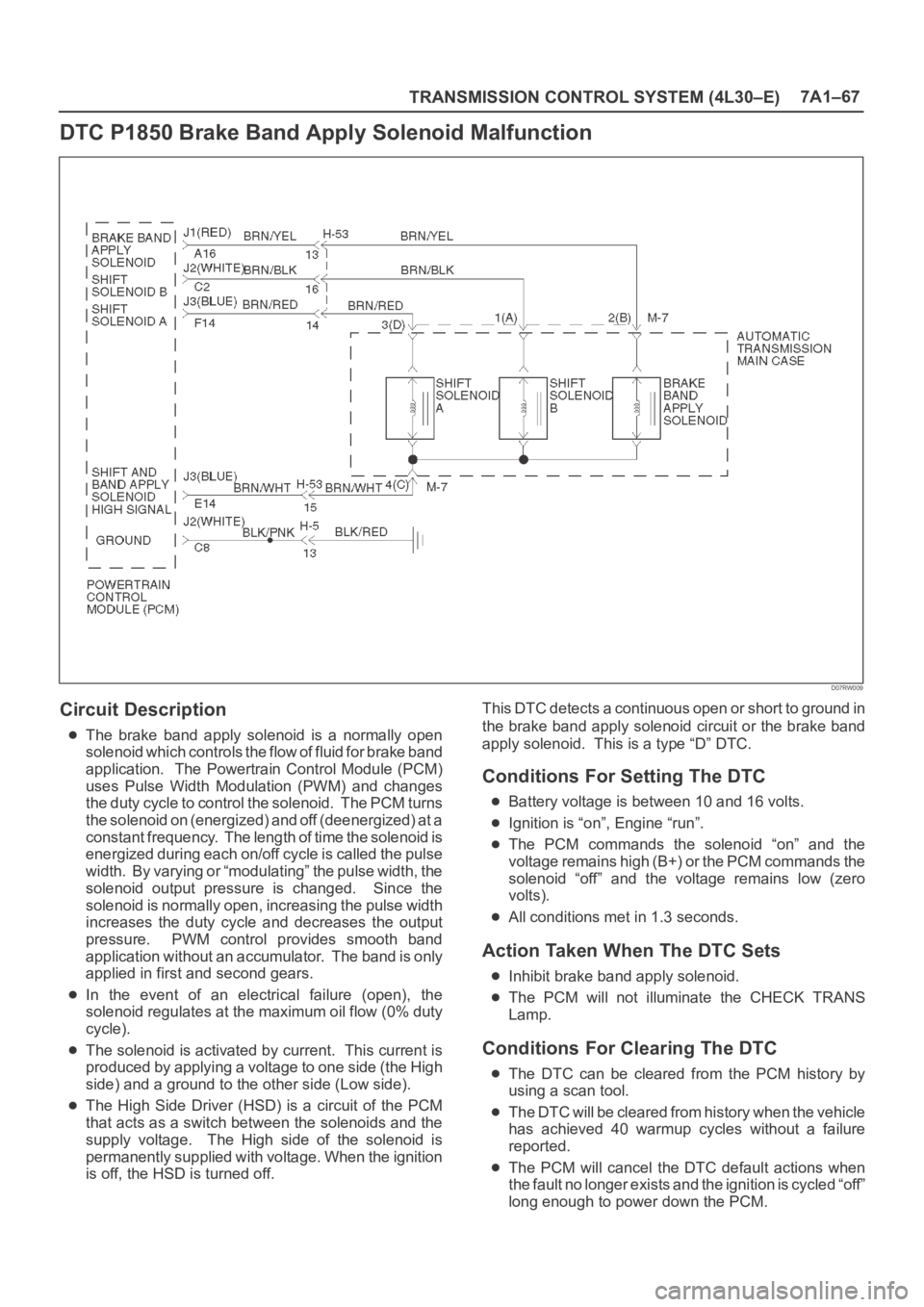
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–67
DTC P1850 Brake Band Apply Solenoid Malfunction
D07RW009
Circuit Description
The brake band apply solenoid is a normally open
solenoid which controls the flow of fluid for brake band
application. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
uses Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and changes
the duty cycle to control the solenoid. The PCM turns
the solenoid on (energized) and off (deenergized) at a
constant frequency. The length of time the solenoid is
energized during each on/off cycle is called the pulse
width. By varying or “modulating” the pulse width, the
solenoid output pressure is changed. Since the
solenoid is normally open, increasing the pulse width
increases the duty cycle and decreases the output
pressure. PWM control provides smooth band
application without an accumulator. The band is only
applied in first and second gears.
In the event of an electrical failure (open), the
solenoid regulates at the maximum oil flow (0% duty
cycle).
The solenoid is activated by current. This current is
produced by applying a voltage to one side (the High
side) and a ground to the other side (Low side).
The High Side Driver (HSD) is a circuit of the PCM
that acts as a switch between the solenoids and the
supply voltage. The High side of the solenoid is
permanently supplied with voltage. When the ignition
is off, the HSD is turned off.This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground in
the brake band apply solenoid circuit or the brake band
apply solenoid. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
Ignition is “on”, Engine “run”.
The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains high (B+) or the PCM commands the
solenoid “off” and the voltage remains low (zero
volts).
All conditions met in 1.3 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Inhibit brake band apply solenoid.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.