Page 4728 of 6000
6E–71 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
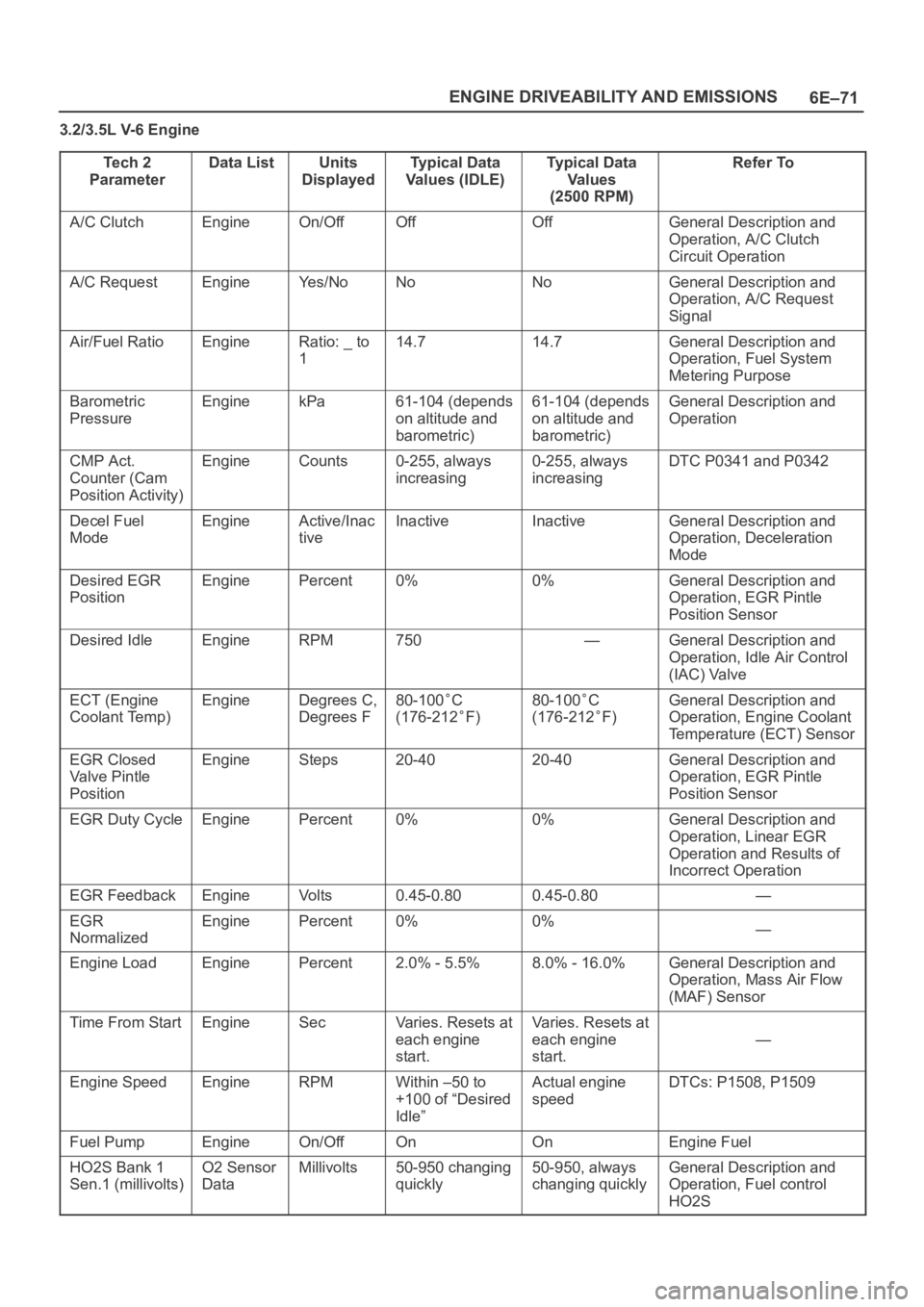
3.2/3.5L V-6 Engine
Te c h 2
Parameter
Data ListUnits
DisplayedTypical Data
Values (IDLE)Typical Data
Va l u e s
(2500 RPM)Refer To
A/C ClutchEngineOn/OffOffOffGeneral Description and
Operation, A/C Clutch
Circuit Operation
A/C RequestEngineYe s / N oNoNoGeneral Description and
Operation, A/C Request
Signal
Air/Fuel RatioEngineRatio: _ to
114.714.7General Description and
Operation, Fuel System
Metering Purpose
Barometric
PressureEnginekPa61-104 (depends
on altitude and
barometric)61-104 (depends
on altitude and
barometric)General Description and
Operation
CMP Act.
Counter (Cam
Position Activity)EngineCounts0-255, always
increasing0-255, always
increasingDTC P0341 and P0342
Decel Fuel
ModeEngineActive/Inac
tiveInactiveInactiveGeneral Description and
Operation, Deceleration
Mode
Desired EGR
PositionEnginePercent0%0%General Description and
Operation, EGR Pintle
Position Sensor
Desired IdleEngineRPM750—General Description and
Operation, Idle Air Control
(IAC) Valve
ECT (Engine
Coolant Temp)EngineDegrees C,
Degrees F80-100C
(176-212
F)
80-100C
(176-212
F)
General Description and
Operation, Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) Sensor
EGR Closed
Valve Pintle
PositionEngineSteps20-4020-40General Description and
Operation, EGR Pintle
Position Sensor
EGR Duty CycleEnginePercent0%0%General Description and
Operation, Linear EGR
Operation and Results of
Incorrect Operation
EGR FeedbackEngineVo l t s0.45-0.800.45-0.80—
EGR
NormalizedEnginePercent0%0%—
Engine LoadEnginePercent2.0% - 5.5%8.0% - 16.0%General Description and
Operation, Mass Air Flow
(MAF) Sensor
Time From StartEngineSecVaries. Resets at
each engine
start.Varies. Resets at
each engine
start.
—
Engine SpeedEngineRPMWithin –50 to
+100 of “Desired
Idle”Actual engine
speedDTCs: P1508, P1509
Fuel PumpEngineOn/OffOnOnEngine Fuel
HO2S Bank 1
Sen.1 (millivolts)O2 Sensor
DataMillivolts50-950 changing
quickly50-950, always
changing quicklyGeneral Description and
Operation, Fuel control
HO2S
Page 5001 of 6000

6E–344
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
0006
Run Mode
The run mode has the following two conditions:
Open loop
Closed loop
When the engine is first started the system is in “open
loop” operation. In “open loop,” the PCM ignores the
signal from the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S). It
calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the TP,
ECT, and MAF sensors.
The system remains in “open loop” until the following
conditions are met:
The HO2S has a varying voltage output showing that
it is hot enough to operate properly (this depends on
temperature).
The ECT has reached a specified temperature.
A specific amount of time has elapsed since starting
the engine.
Engine speed has been greater than a specified RPM
since start-up.
The specific values for the above conditions vary with
different engines and are stored in the programmable
read only memory (PROM). When these conditions are
met, the system enters “closed loop” operation. In
“closed loop,” the PCM calculates the air/fuel ratio
(injector on-time) based on the signal from the HO2S.
This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7:1.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is first turned “ON,” the PCM energizes
the fuel pump relay for two seconds to allow the fuel pump
to build up pressure. The PCM then checks the engine
coolant temperature (ECT) sensor and the throttle
position (TP) sensor to determine the proper air/fuel ratio
for starting.
The PCM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by adjusting how long the fuel injectors are
energized by pulsing the injectors for very short times.
Throttle Body Unit
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the amount
of air delivered to the engine. The TP sensor and IAC
valve are also mounted on the throttle body. Vacuum
ports located behind the throttle plate provide the vacuum
signals needed by various components.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in the
throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to prevent
icing.
0019
General Description (Electronic
Ignition System)
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
As the camshaft sprocket turns, a magnet in the sprocket
activates the Hall-effect switch in the CMP sensor. When
the Hall-effect switch is activated, it grounds the signal
line to the PCM, pulling the camshaft position sensor
signal circuit’s applied voltage low. This is a CMP signal.
The CMP signals is created as piston #1 is approximately
25
after top dead counter on the power stroke. If the
correct CMP signal is not received by the PCM, DTC
P0341 will be set.
Page 5382 of 6000

ENGINE FUEL 6C – 1
ENGINE FUEL
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–1
On-Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–8
Fuel Filter Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–8
Fuel Filter Cartridge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–8
Injector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–10High Pressure Oil Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–14
Fuel Tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–20
Fuel Gauge Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–21
Fuel Filler Cap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6C–21
To realize the compatibility between low exhaust
emission and high engine output, an HEUI
(Hydraulically actuated Electronically controlled Unit
Injector) system, has been introduced. This system is
comprised of a hydraulic system, fuel system, and
electronic control system, using a high-pressure oil
pump in place of the conventional fuel injection pump.
The oil pressurized by means of this pump and by
signals from the ECM (Electronic Control Module)
actuates the fuel injector provided for each cylinder.
Inside of the fuel injector, fuel pressure is increased due
to the high-pressure oil. The ECM detects the driving
state of the vehicle, forms, signals sent by engine and
other part sensors, which determines the optimum fuel
injection amount and timing, thus controlling the fuel
injectors. Thus high engine output, good fuel economy,
and low exhaust emission are realized.When working on the fuel system, there are several
things to keep in mind:
1) Any time the fuel system is being worked on,
disconnect the negative battery cable except for
those tests where battery voltage is required.
2)Always keep a dry chemical (Class B) fire
extinguisher near the work area.
3) Replace all pipes with the same pipe and fittings
that were removed.
Clean and inspect “O” rings. Replace where
required.
4) Always relieve the line pressure before servicing
any fuel system components.
5) Do not attempt repairs on the fuel system until you
have read the instructions and checked the pictures
relating to that repair.
6) After maintenance work, push priming pump and
send enough fuel to the fuel system before starting
the engine.
NOTE: In comparison with the conventional engine,
the capacity of fuel passage in the 4JX1 engine is
larger. It takes the priming pump more time to fill the
engine with fuel.
Page 5464 of 6000
6E–35 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Guid to the System
Fuel Injection system is an HEUI (Hydraulically
Actuated, Electronically Controlled, Unit, Injector)
type. In this type of injector system, the oil
pressurized by means of High Pressure Oil Pump
(16) is fed through Rail Pressure Control Valve (10)
and Oil Rail (7) to Injector (29) from which fuel is
injected under this oil pressure.
For diagnosis, therefore, the Rail Pressure as well as
the Electric Circuit must be inspected.
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
A Group
060RW135