1998 OPEL FRONTERA engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 2231 of 6000
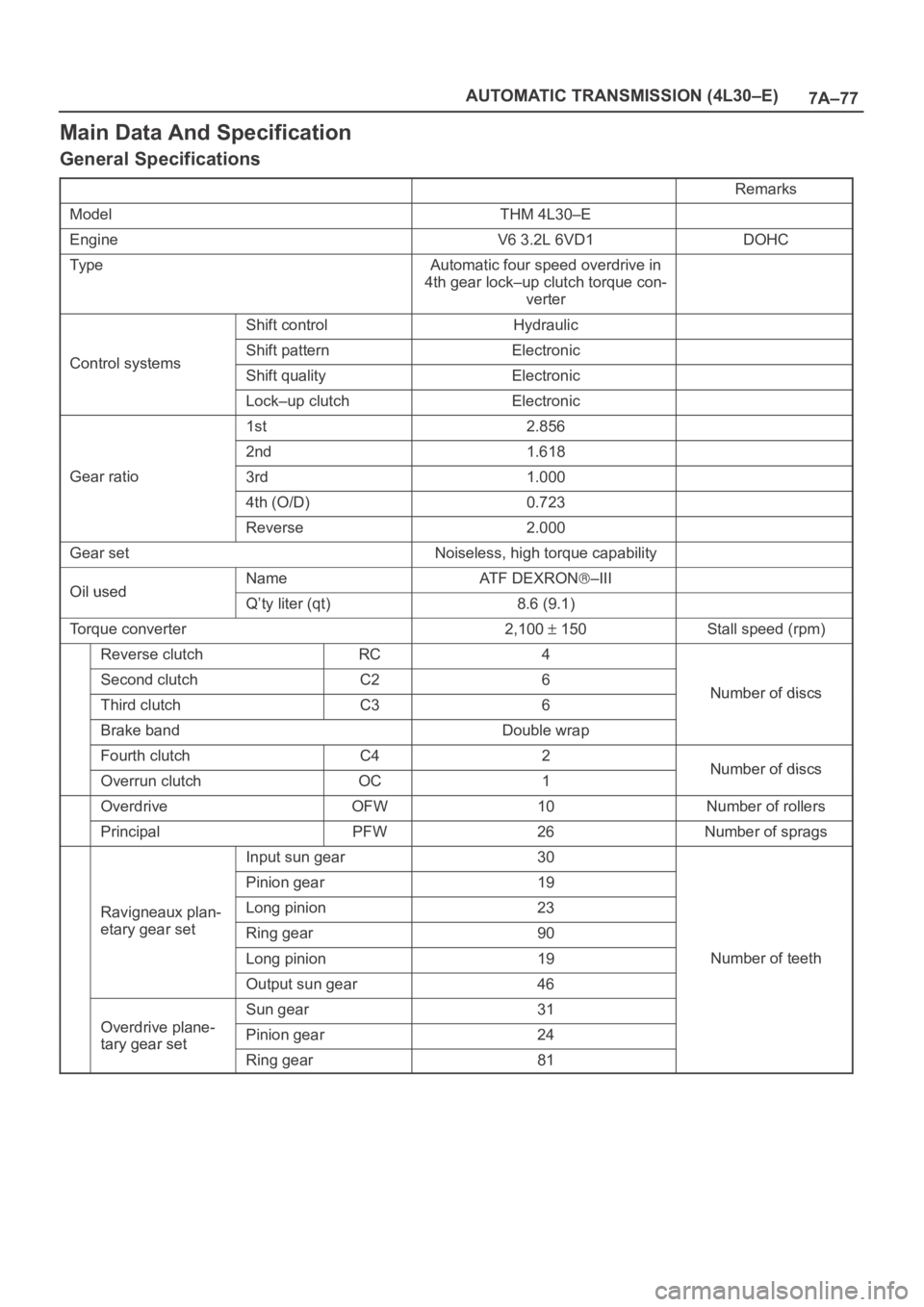
7A–77 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Main Data And Specification
General Specifications
Remarks
ModelTHM 4L30–E
EngineV6 3.2L 6VD1DOHC
Ty p eAutomatic four speed overdrive in
4th gear lock–up clutch torque con-
verter
Shift controlHydraulic
Control systemsShift patternElectronicControl systemsShift qualityElectronic
Lock–up clutchElectronic
1st2.856
2nd1.618
Gear ratio3rd1.000
4th (O/D)0.723
Reverse2.000
Gear setNoiseless, high torque capability
Oil usedNameAT F D E X R O N–IIIOil usedQ’ty liter (qt)8.6 (9.1)
Torque converter2,100 150Stall speed (rpm)
Reverse clutchRC4
Second clutchC26Number of discsThird clutchC36Number of discs
Brake bandDouble wrap
Fourth clutchC42Number of discsOverrun clutchOC1Number of discs
OverdriveOFW10Number of rollers
PrincipalPFW26Number of sprags
Input sun gear30
Pinion gear19
Ravigneaux plan-Long pinion23g
etary gear setRing gear90
Long pinion19Number of teeth
Output sun gear46
Odi l
Sun gear31
Overdrive plane-
tary gear setPinion gear24tary gear set
Ring gear81
Page 2251 of 6000

7A1–6
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Shift Control
The transmission gear is shifted according to the shift
pattern selected by the driver. In shifting gears, the gear
ratio is controlled by the ON/ OFF signal using the shift
solenoid A and the shift solenoid B.
Band Apply Control
The band apply is controlled when in the 3–2 downshift
(engine overrun prevention) and the garage shift (shock
control).
The band apply solenoid is controlled by the signal from
the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to regulate the flow of
the oil.
Torque Converter Clutch Control
The clutch ON/OFF is controlled by moving the converter
clutch valve through shifting Torque Converter Clutch
(TCC) solenoid using the ON/OFF signal.
Line Pressure Control
The throttle signal allows the current signal to be sent to
the force motor. After receiving the current signal, the
force motor activates the pressure regulator valve to
regulate the line pressure.
On–Board Diagnostic System
Several malfunction displays can be stored in the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) memory, and read out
of it afterward.The serial data lines, which are required for the testing of
the final assembly and the coupling to other electronic
modules, can be regulated by this function.
Fail Safe Mechanism
If there is a problem in the transmission system, the PCM
will go into a “backup” mode.
The vehicle can still be driven, but the driver must use the
select lever to shift gears.
Torque Management Control
The transmission control side sends the absolute spark
advance signal to the engine control side while the
transmission is being shifted. This controls the engine
spark timing in compliance with the vehicle running
condition to reduce the shocks caused by the change of
speed.
ATF Warning Control
The oil temperature sensor detects the ATF oil
temperature to control the oil temperature warning, TCC,
and the winter mode.
ABS Control (If equipped)
When the select lever is at “L” or “R” range, a signal is sent
to the ABS controller as one of the ABS control
conditions.
Page 2255 of 6000

7A1–10
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Functions of Input / Output Components
ComponentsFunction
Speed sensor
(fixed to transmission
(T/M))Senses rotation of output shaft and feeds the data to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
Throttle position sensor
(TPS)
(fixed to engine)Senses the extent of throttle valve opening and the speed of the throttle valve
lever motion to open the valve. Feeds the data to PCM.
I
N
Brake Switch (SW)
(fixed to brake pedal)Senses whether the driver has pressed the brake pedal or not and feeds the
information to PCM.
N-
P
U
Kickdown SW
(fixed to accelerator pedal)Senses whether the driver has pushed the accelerator pedal fully or not, and
feeds the information to PCM.
U
TMode SW (fixed to T/M)Senses the select lever position, and feeds the information to PCM.
S
I
Power drive SW
(fixed to front console)Senses whether the driver has selected the power mode, and feeds the informa-
tion to PCM.
I
G-T/M oil temp. sensorSenses the T/M oil temperature and feeds the data to PCM
N
A
L
Engine coolant tempera-
ture sensorSenses the engine coolant temperature, and feeds the data to PCM.
LEngine speed signalFeeds the signals monitoring engine speed to PCM from crank angle sensor.
Air conditioning informationSenses whether the air conditioner has been switched on or not, and feeds the
information to PCM.
Winter switch (fixed to front
console)Senses whether the driver has selected the winter mode, and feeds the informa-
tion to PCM.
Cruise controller * (Over-
drive OFF signal)Downshift takes place when Overdrive OFF signal is received from auto cruise
control unit.
S
Shift solenoid A, BSelects shift point and gear position suited to the vehicle running condition on
the basis of PCM output.
O
S
O-
L
Band apply solenoidControls oil flow suited to the vehicle running condition on the basis of PCM out-
put.
O
U
T-
P
E-
N
O
Torque Converter
Clutch solenoidControls clutch engagement/disengagement suited to the vehicle running condi-
tion on the basis of PCM output.
P
U
T
O
I
DForce motor
(Pressure regulator
valve)Adjusts the oil pump delivery pressure to line pressure suited to the vehicle run-
ning condition on the basis of PCM output.
S
I
Power drive mode lampInforms the driver whether the vehicle is in power mode or not.
I
G-Winter drive mode lampInforms the driver whether the vehicle is in winter mode or not.G
N
A
L
T/M monitor lamp
(“CHECK TRANS”)Informs the driver of failure in the system.
LATF warning lampLights when ATF oil temperature rises.
ABS signal *When the select lever is at “Reverse” or “L” range, sends a signal to the ABS
controller as one of the ABS control conditions.
* If equipped
Page 2256 of 6000
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–11
Diagnosis
Electronic Diagnosis
How To Diagnose The Problem
1. To avoid incorrect diagnostics, this book needs to be
followed accurately. Unless stated, do not jump
directly to a section that could contain the solution.
Some important information may be missed.
2. The sections in CAPITALS and bold are the main
sections that can be found in the contents.
3. The GOTO “SECTION” means to continue to check
going to the “section”.
4. The GOTHROUGH “SECTION” means to go
through the “section” and then to go back to the place
the GOTHROUGH was written.
5. BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUITS:
You should understand the basic theory of electricity.
This includes the meaning of voltage, amps, ohms,
and what happens in a circuit with an open or shorted
wire. You should also be able to read and understand
wiring diagrams.
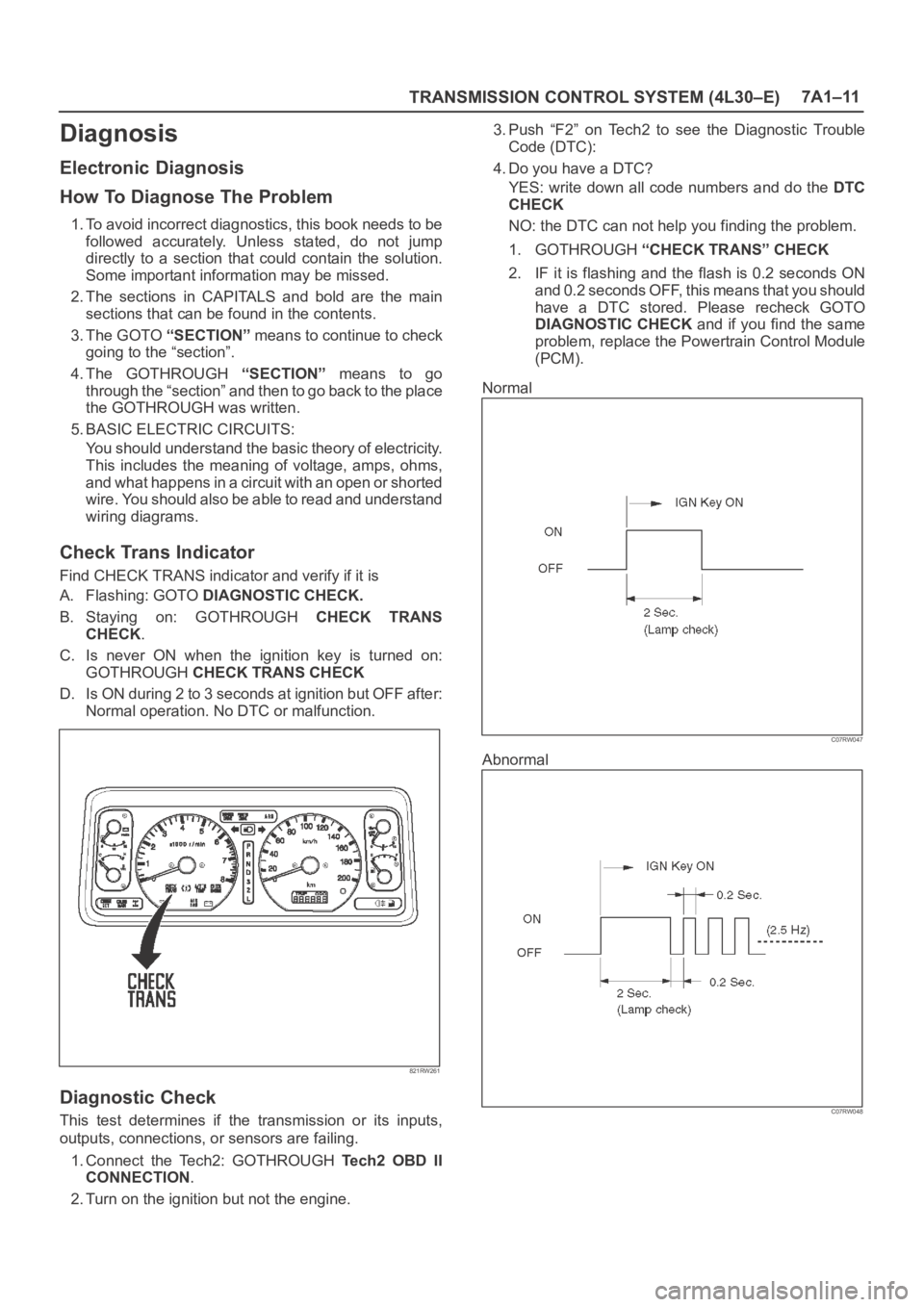
Check Trans Indicator
Find CHECK TRANS indicator and verify if it is
A. Flashing: GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK.
B. Staying on: GOTHROUGH CHECK TRANS
CHECK.
C. Is never ON when the ignition key is turned on:
GOTHROUGH CHECK TRANS CHECK
D. Is ON during 2 to 3 seconds at ignition but OFF after:
Normal operation. No DTC or malfunction.
821RW261
Diagnostic Check
This test determines if the transmission or its inputs,
outputs, connections, or sensors are failing.
1. Connect the Tech2: GOTHROUGH Te c h 2 O B D I I
CONNECTION.
2. Turn on the ignition but not the engine.3. Push “F2” on Tech2 to see the Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC):
4. Do you have a DTC?
YES: write down all code numbers and do the DTC
CHECK
NO: the DTC can not help you finding the problem.
1. GOTHROUGH “CHECK TRANS” CHECK
2. IF it is flashing and the flash is 0.2 seconds ON
and 0.2 seconds OFF, this means that you should
have a DTC stored. Please recheck GOTO
DIAGNOSTIC CHECK and if you find the same
problem, replace the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
Normal
C07RW047
Abnormal
C07RW048
Page 2257 of 6000
7A1–12
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
“Check Trans” Check
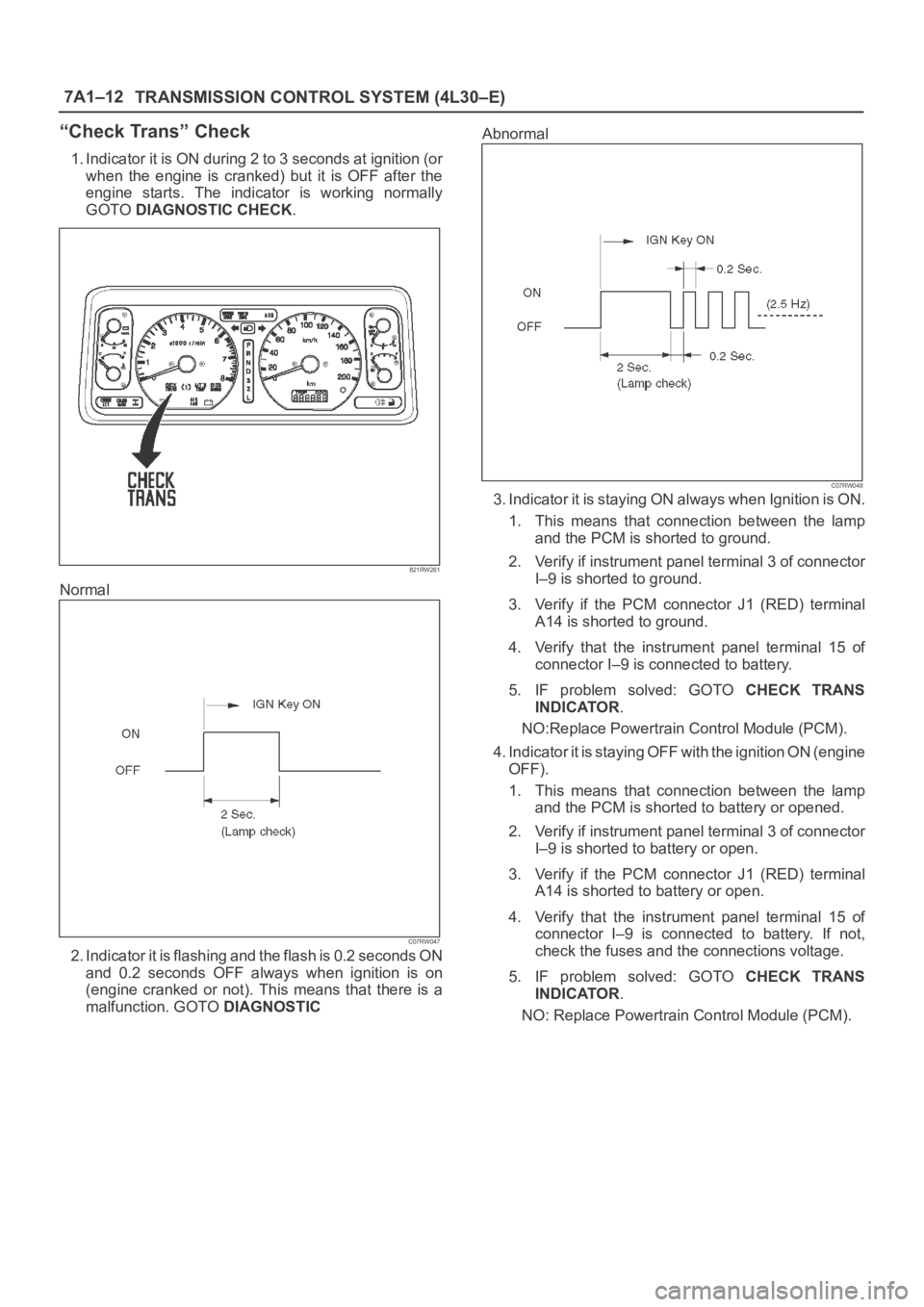
1. Indicator it is ON during 2 to 3 seconds at ignition (or
when the engine is cranked) but it is OFF after the
engine starts. The indicator is working normally
GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK.
821RW261
Normal
C07RW047
2. Indicator it is flashing and the flash is 0.2 seconds ON
and 0.2 seconds OFF always when ignition is on
(engine cranked or not). This means that there is a
malfunction. GOTO DIAGNOSTICAbnormal
C07RW048
3. Indicator it is staying ON always when Ignition is ON.
1. This means that connection between the lamp
and the PCM is shorted to ground.
2. Verify if instrument panel terminal 3 of connector
I–9 is shorted to ground.
3. Verify if the PCM connector J1 (RED) terminal
A14 is shorted to ground.
4. Verify that the instrument panel terminal 15 of
connector I–9 is connected to battery.
5. IF problem solved: GOTO CHECK TRANS
INDICATOR.
NO:Replace Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
4. Indicator it is staying OFF with the ignition ON (engine
OFF).
1. This means that connection between the lamp
and the PCM is shorted to battery or opened.
2. Verify if instrument panel terminal 3 of connector
I–9 is shorted to battery or open.
3. Verify if the PCM connector J1 (RED) terminal
A14 is shorted to battery or open.
4. Verify that the instrument panel terminal 15 of
connector I–9 is connected to battery. If not,
check the fuses and the connections voltage.
5. IF problem solved: GOTO CHECK TRANS
INDICATOR.
NO: Replace Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
Page 2263 of 6000

7A1–18
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
OBD II Diagnostic Management System
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Location
C07RW005
Class 2 Serial Data Bus
OBD II technology requires a much more sophisticated
PCM than does OBD I technology. The OBD II PCM
diagnostic management system not only monitors
systems and components that can impact emissions, but
they also run active tests on these systems and
components. The decision making functions of OBD II
PCMs have also greatly increased. To accommodate this
expansion in diagnostic complexity, Isuzu engineers have
designed the Class 2 serial data bus, which meets SAE
J1850 recommended practice for serial data.
“Serial Data” refers to information which is transferred in a
linear fashion – over a single line, one bit at a time. A “Data
Bus” is an electronic pathway through which serial data
travels.TROOPER previously used a 5 volt data bus called
UART, which is an acronym for “Universal Asynchronous
Receive and Transmit”. When neither the vehicle’s
control module nor the diagnostic tool, such as a Tech2,
are “talking,” the voltage level of the bus at rest is 5 volts.
The two computers talk to each other at a rate of 8,192
bits per second, by toggling or switching the voltage on
the data bus from 5 volts to ground.
Class 2 data, which is used on OBD II vehicles, is quite
different. Data is transferred at a rate of 10.4 kilobits per
second, and the voltage is toggled between zero and 7
volts.
Page 2265 of 6000
7A1–20
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
821RW263
810RT022
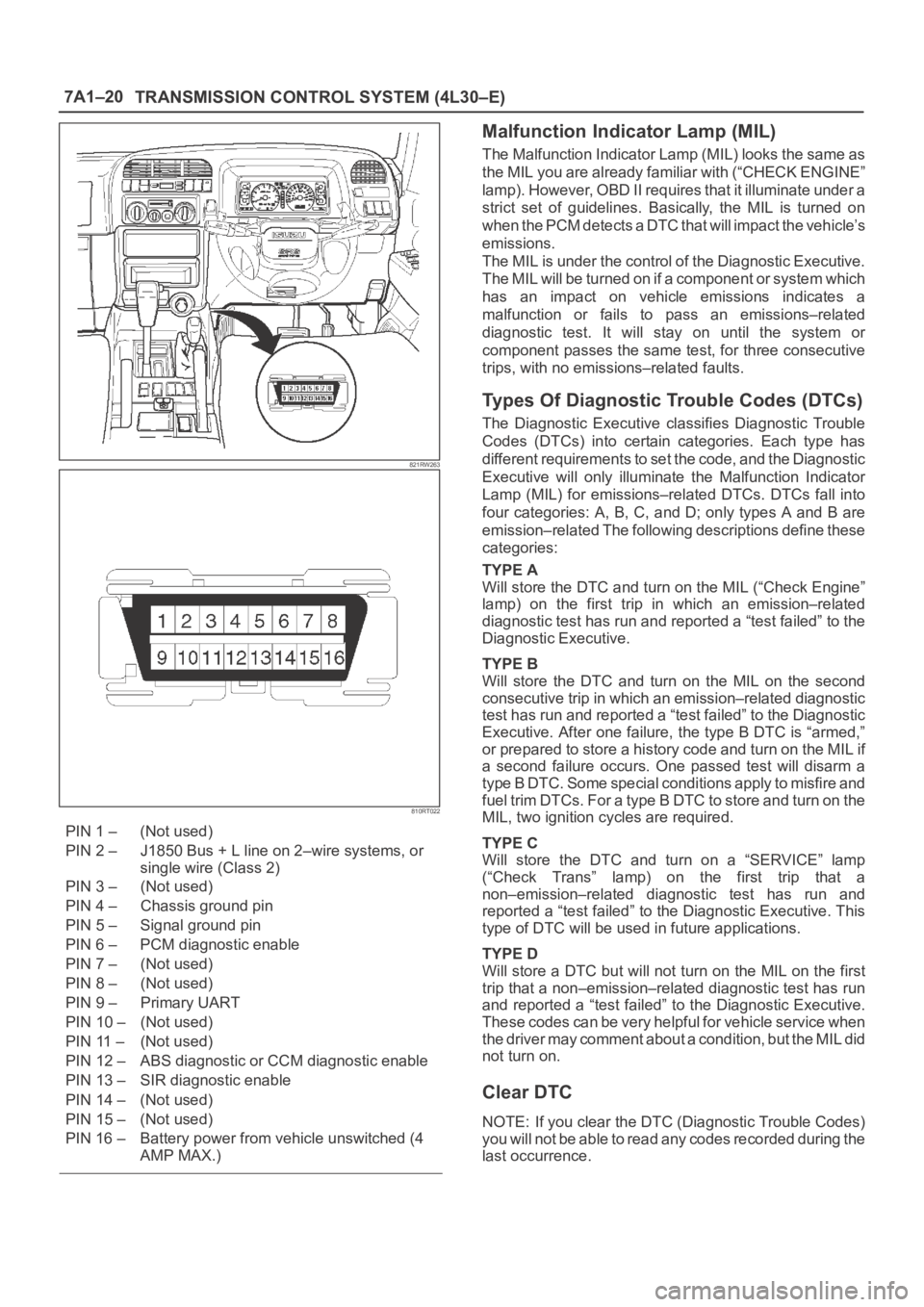
PIN 1 – (Not used)
PIN 2 – J1850 Bus + L line on 2–wire systems, or
single wire (Class 2)
PIN 3 – (Not used)
PIN 4 – Chassis ground pin
PIN 5 – Signal ground pin
PIN 6 – PCM diagnostic enable
PIN 7 – (Not used)
PIN 8 – (Not used)
PIN 9 – Primary UART
PIN 10 – (Not used)
PIN 11 – (Not used)
PIN 12 – ABS diagnostic or CCM diagnostic enable
PIN 13 – SIR diagnostic enable
PIN 14 – (Not used)
PIN 15 – (Not used)
PIN 16 – Battery power from vehicle unswitched (4
AMP MAX.)
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same as
the MIL you are already familiar with (“CHECK ENGINE”
lamp). However, OBD II requires that it illuminate under a
strict set of guidelines. Basically, the MIL is turned on
when the PCM detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle’s
emissions.
The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic Executive.
The MIL will be turned on if a component or system which
has an impact on vehicle emissions indicates a
malfunction or fails to pass an emissions–related
diagnostic test. It will stay on until the system or
component passes the same test, for three consecutive
trips, with no emissions–related faults.
Types Of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The Diagnostic Executive classifies Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs) into certain categories. Each type has
different requirements to set the code, and the Diagnostic
Executive will only illuminate the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) for emissions–related DTCs. DTCs fall into
four categories: A, B, C, and D; only types A and B are
emission–related The following descriptions define these
categories:
TYPE A
Will store the DTC and turn on the MIL (“Check Engine”
lamp) on the first trip in which an emission–related
diagnostic test has run and reported a “test failed” to the
Diagnostic Executive.
TYPE B
Will store the DTC and turn on the MIL on the second
consecutive trip in which an emission–related diagnostic
test has run and reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic
Executive. After one failure, the type B DTC is “armed,”
or prepared to store a history code and turn on the MIL if
a second failure occurs. One passed test will disarm a
type B DTC. Some special conditions apply to misfire and
fuel trim DTCs. For a type B DTC to store and turn on the
MIL, two ignition cycles are required.
TYPE C
Will store the DTC and turn on a “SERVICE” lamp
(“Check Trans” lamp) on the first trip that a
non–emission–related diagnostic test has run and
reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic Executive. This
type of DTC will be used in future applications.
TYPE D
Will store a DTC but will not turn on the MIL on the first
trip that a non–emission–related diagnostic test has run
and reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic Executive.
These codes can be very helpful for vehicle service when
the driver may comment about a condition, but the MIL did
not turn on.
Clear DTC
NOTE: If you clear the DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Codes)
you will not be able to read any codes recorded during the
last occurrence.
Page 2267 of 6000

7A1–22
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
connection or loose wiring. Terminals and grounds should
always be the prime suspect. Intermittents rarely occur
inside sophisticated electronic components such as the
PCM.
Use the DTC information to understand which wires and
sensors are involved.
When an intermittent problem is encountered, check
suspect circuits for:
1. Poor terminal to wire connection.
2. Terminals not fully seated in the connector body
(backed out).
3. Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
4. Loose, dirty, or corroded ground connections:
HINT: Any time you have an intermittent in more than
one circuit, check whether the circuits share a
common ground connection.
5. Pinched or damaged wires.
6. Electro–Magnetic Interference (EMI):
HINT: Check that all wires are properly routed away
from spark plug wires, distributor wires, coil, and
generator. Also check for improperly installed
electrical options, such as lights, 2–way radios, etc.Use the F3 SNAPSHOT mode of the Tech2 to help isolate
the cause of an intermittent fault. The snapshot mode will
record information before and after the problem occurs.
Set the snapshot to “trigger” on the suspect DTC. If you
notice the reported symptom during the test drive, trigger
the snapshot manually.
After the snapshot has been triggered, command the
Tech2 to play back the flow of data recorded from each of
the various sensors. Signs of an intermittent fault in a
sensor circuit are sudden unexplainable jump in data
values out of the normal range.
Transmission And PCM Identification
The chart below contains a list of all important information
concerning rear axle ratio, Powertrain Control Module
(PCM), and transmission identification.
VEHICLE
Rr axlePCMTRANSMISSION
Ty p eEngine
Rr axle
RatioISUZU Parts No.Calibration
CodeIsuzu Part No.Model Code
Isuzu /
Trooper3.2L V64.555
8–16254–949–0
8–16254–749–0
8–16253–989–0
G208–96018–272–3FP (4X4)