1998 HONDA CIVIC main fi
[x] Cancel search: main fiPage 866 of 2189

Transmission
17.
Cooler Flushing (cont'dl
Make sure the transmission is in the E position.
Fill the transmission with ATF, and run the enginefor 30 seconds or until approximately 0.95 f (1.0 USqt.,0.8 lmp qt.) is discharged.
Remove the drain hose, and reconnect the coolerreturn hose to the transmission (see page l4-192).
Refill the transmission with ATF to the oroDer level(see page 14-118).
18.
19.
b
14-18A
TOOL MAINTENANCE
1. Empty and rinse after each use. Fill the can with waterand pressurize the can. Flush the discharge line toensure that the unit is clean.
2. lf discharge liquid does not foam, the orifice may beblocked.
3. To clean, disconnect the plumbing from the tank atthe large coupling nut.
ORIFICE
GRT{G
Remove the in-line filter from the discharge side andclean if necessary.
The fluid orifice is tocated behind the filter.Clean it with the pick stored in the bottom of thetank handle, or blow it clean with air. Securelvreassemble all Darts.
FILLER CAP
Page 873 of 2189

Description
The Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is an electronically controlled automatic transmission with drive and driv
en Oullevs, and a steel belt. The CVT provides non stage speeds forward and one reverse. The entire unit is positioned in
line with the engine.
Transmission
Around the outside of the flywheel is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being staned.
The transmission has four parallel shafts: the input shaft, the drive pulley shaft. the driven pulley shaft, and the secondary
gear shaft. The input shaft is in line with the engine crankshaft. The drive pulley shaft and the driven pulley shaft consist of
movable and fixed face pulleys. Both pulleys are linked by the steel belt.
The input shaft includes the sun gear. The drive pulley shaft includes the forward clutch which mounts the carrier assem-
bly on the forward clutch drum. The carrier assembly includes the pinion gears which mesh with the sun gear and the ring
gear. The ring gear has a hub-mounted reverse brake disc.
The driven pulley shaft includes the start clutch and the secondary drive gear which is integral with the park gear' The sec-
ondary gear shaft is positioned between the secondary drive gear and the final driven gear. The secondary gear shaft
includes the secondary driven gear which serves to change the rotation direction. because the drive pulley shaft and the
driven oullev shaft rotate the same direction. When certain combinations of planetary gears in the transmission are
engaged by the clutches and the reverse brake, power is transmitted from the drive pulley shaft to the driven pulley shaft
to provide E, E, E, and El.
Electronic Control'96 - 98 Models:
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, three linear solenoids, and a
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions'
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the kick panel on the driver's side.'99 - 00 Models:
The electronic control svstem consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, three linear solenoids and an
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions. A Grade Logic Control System to control shift-
ing in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope.
The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the Pressure Low (PL) reguiator valve body, the shift valve
body, the start clutch control valve body, and the secondary valve body. They are positioned on the lower part of the
transmission housing.
The main valve body contains the Pressure High (PH) control valve, the lubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
The secondary valve body contains the PH regulator valve, the clutch reducing valve, the start clutch valve accumulator,
and the shift inhibitor valve. The PL regulator valve body contains the PL regulator valve and the PH-PL control valve
which is ioined to the PH,PL control linear solenoid. The inhibitor solenoid valve is bolted on the PL regulator valve body.
The shift valve body contains the shift valve and the shift control valve. which is joined to the shift control linear solenoid.
The start clutch control valve body contains the start clutch control valve, which is joined to the start clutch control linear
solenoid. The linear solenoids and the inhibitor solenoid are controlled by the TCM or PCM. The manual valve body which
contains the manual valve and the reverse inhibitor valve, is bolted on the intermediate housing.
The ATF pump assembly is located on the transmission housing, and is linked with the input shaft by the sprockets and
the sprocket chain. The pulleys and the clutch receive fluid from their respective feed pipes, and the reverse brake receives
fluid from internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which linear solenoid the TCM or PCM will activate.
Activating the shift control linear solenoid changes the shift control valve pressure, causing the shift valve to move. This
pressurizes the drive pulley pressure to the drive pulley and the driven pulley pressure to the driven pulley and changes
their effective pulley ratio. Activating the start clutch control linear solenoid moves the start clutch control valve. The start
clutch control valve uncovers the port, providing pressure to the start clutch to engage it(cont'd)
14-195
,!
Page 886 of 2189
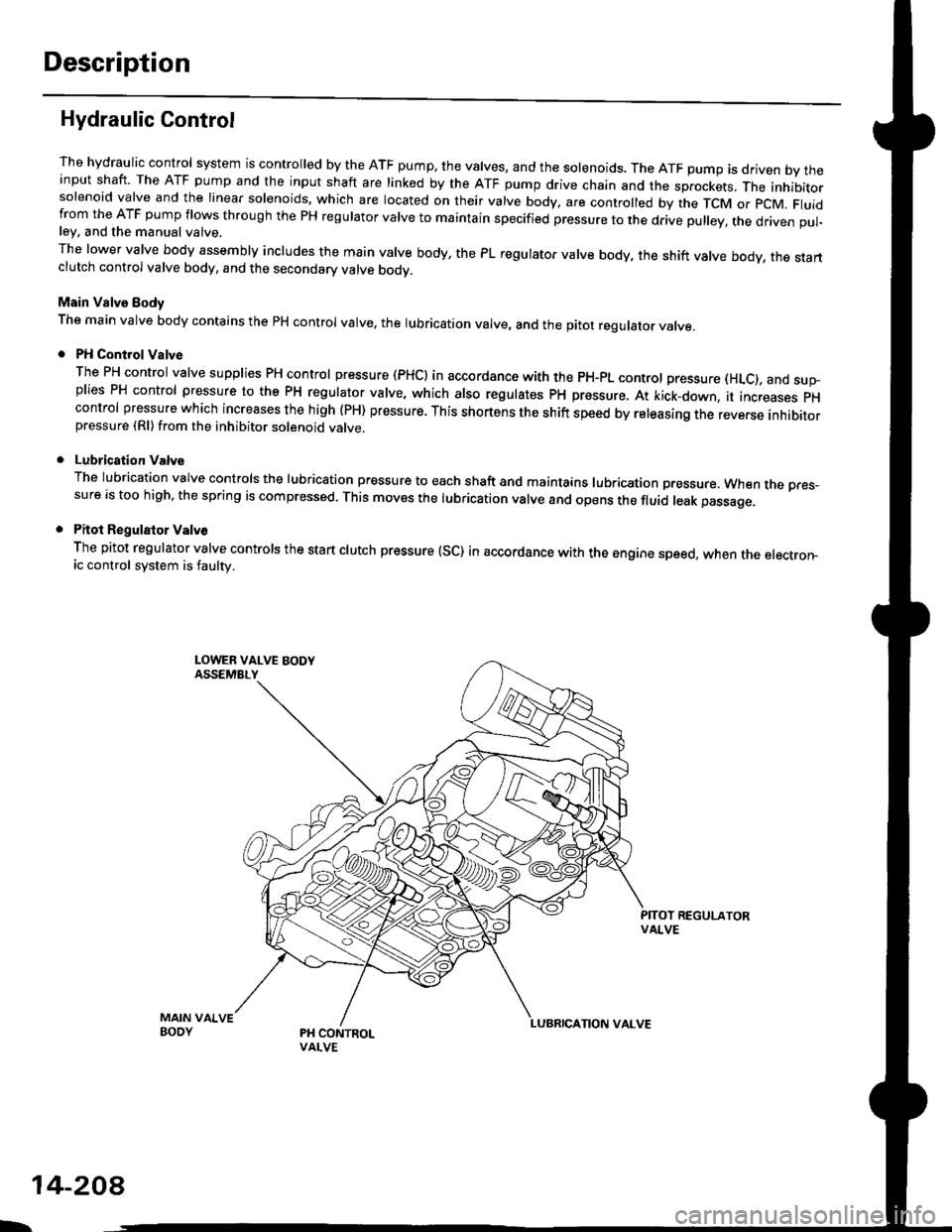
Description
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump. the valves, and the solenoids. The ATF pump is driven by theinput shaft. The ATF pump and the input shaft are linked by the ATF pump drive chain and the sprockets, The inhibitorsolenoid valve and the linear solenoids. which are located on their valve body, are controlled by the TCM or pcM. Fluidfrom the ATF pump flows through the PH regulator valve to maintain specified pressure to the drive pulley, the driven pul-ley, and the manual valve,
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the PL regulator valve body, the shift valve body, the startclutch control valve body, and the secondary valve bodv.
Main Valve Eody
The main valve body contains the pH control valve, the rubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
PH Control Valve
The PH control valve supplies PH control pressure (PHCI in accordance with the pH-pL control pressure (HLc), and sup-plies PH control pressure to the PH regulator valve, which also regulatss PH pressure. At kick-down, it increases pHcontrol pressure which increases the high (PH) pressure. This shortens the shift speed by releasing the reverse inhibitorpressure (Rl)from the inhibitor solenoid valve.
Lubrication Valve
The lubrication valve controls the lubrication pressure to each shaft and maintains lubrication pressure. When rne pres-sure is too high, the spring is compressed. This moves the lubrication valve and opens the fluid leak passage.
Pitot Regulalor Valv6
The pitot regulator valve controls the start clutch pressure (SC) in accordance with the engine speed, when the electron-ic control system is faulw.
MAIN VAIVEBODY
L.
14-208
Page 887 of 2189

Secondary Valve Body
The secondary valve body contains the PH regulator valve. the clutch reducing valve' the start clutch valve accumulator'
and the shift inhibitor valve
PH Regulator Valve
The pi regulator valve maintains hydraulic pressure supplied from the ATF pump. and supplies PH pressure to the
hvdraulic control circuit and the lubrication circuit. PH pressure is regulated at the PH regulator valve by the PH control
pressure (PHC) from the PH control valve.
Cluteh Reducing Valvo
The clutch reducing valve receives PH pressure from the PH regulator valve and regulates the clutch reducing pressure
(cR). The clutch reducing valve supplies clutch pressure (cR) to the manual valve and the start clutch control valve' and
supplies signal pressure to the PH-PL pressure control valve. the shift control valve, and the inhibitor solenoid valve'
Start Clutch Valv€ Accumulator
The start clutch vatve accumutator stabilizes the hydraulic pressure that is supplied to the start clutch'
Shift Inhibitor Valve
The shift inhibitor valve switches the fluid passage to switch the start clutch control from electronic control to hydraulic
control when the electronic control system is faulty. lt also suppliss clutch reducing pressure (cR) to the pitot regulator
valve and the pitot lubrication pipe.
START CLUTCH VALVE
SECONDARY VALVEBODY
SHIFT INHIBITOE VALVE
(cont'd)
PH REGULATOR VAL
REDUCING VALVE
14-209
Page 893 of 2189

E position, at middle sPeed range
Asthespeedofthevehic|ereachestheprescribedVa|ue,theshiftcontro||inearsolenoidisactivatedbytheTcMorPcM'
Theshiftcontro||inearso|enorocontroIsttresniftcontroIVa|vetoactivateshiftVa|vepressure(SV)'c|utchreducingpres-
sure (CR) trom the clutch reduclng valve becomes shift valve pressure (SV) at the shift control valve Shift valve pressure
(SV)flowstothe|eft"noottr'"st'ittu"tue.theshiftVa|Vetotherightsideandpositioningitinthemidd|eofitstrave|.The
shift valve covers th" pon ao ",oo nLior".irr" tiHl a ,tr" pulleys, and uncovers the port leading low pressure (PL) to the
pu eys. The drive pu ey and tne oriJen priLy |."""iu" to* pressure (PL). At this time, the pulley ratio is in the middle'
Pressure remains to apply the forward clutch and the start clutch'
NOTE: When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit'
(cont'd)
14-215
Page 894 of 2189
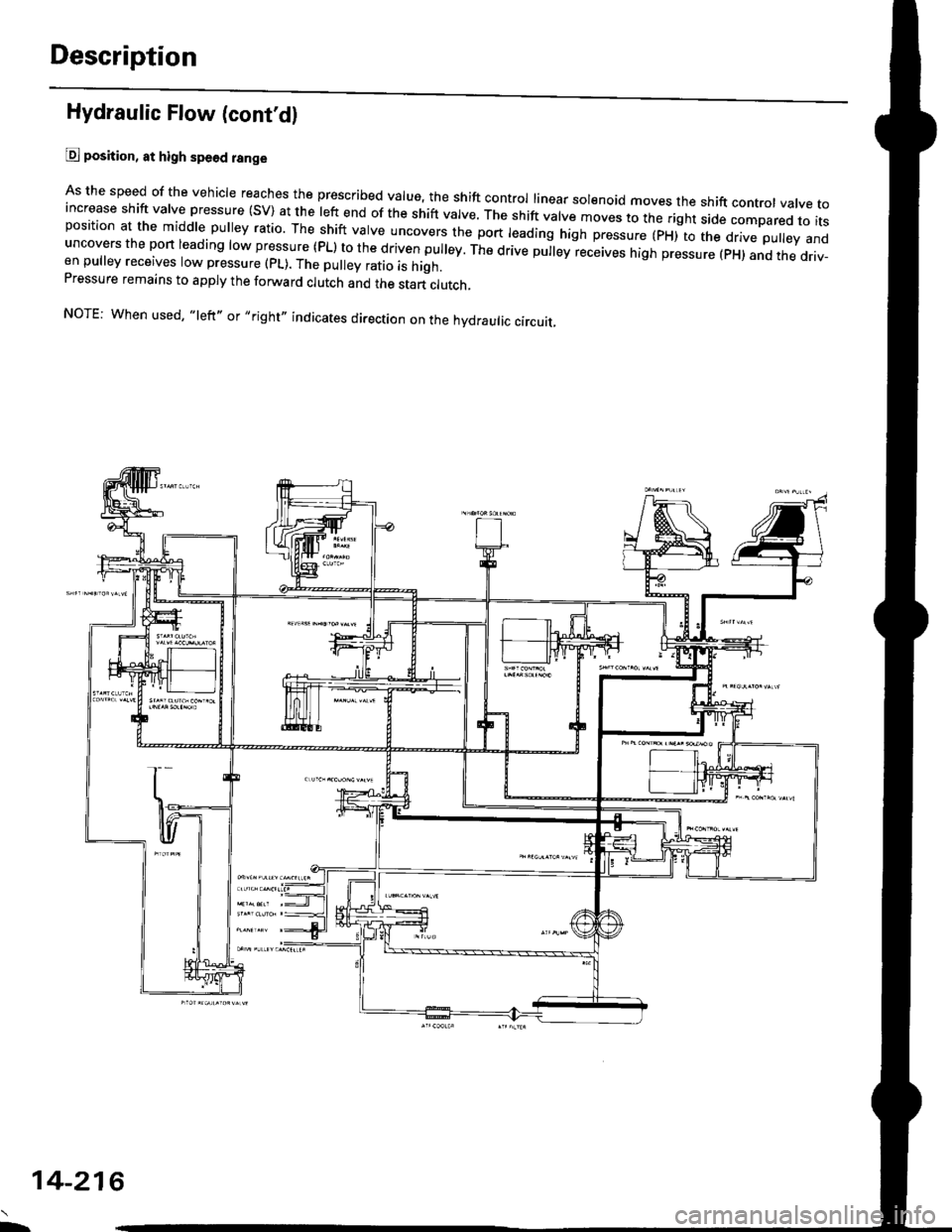
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'd)
@ position, at high spe6d range
As the speed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value, the shift control linear sol€noid moves the shift contror vatve toincrease shift valve pressure (SV) at the left end of the shift valve. ttre srrit vatve moves to the right side compared to itsposition at the middle pulley ratio. The shift valve uncovers the port leading high pressure (pxito ttre d.ve puley anduncovers the port leading low pressure (PL) to the driven pulley. The drive pu|ey receives high pressure (pH) and the driv-en pulley receives low pressure (pL). The pulley ratio is high.Pressure remains to apply the forward clutch and the start clutch,
NOTE: When used, "left,, or,,right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
L
14-216
Page 909 of 2189
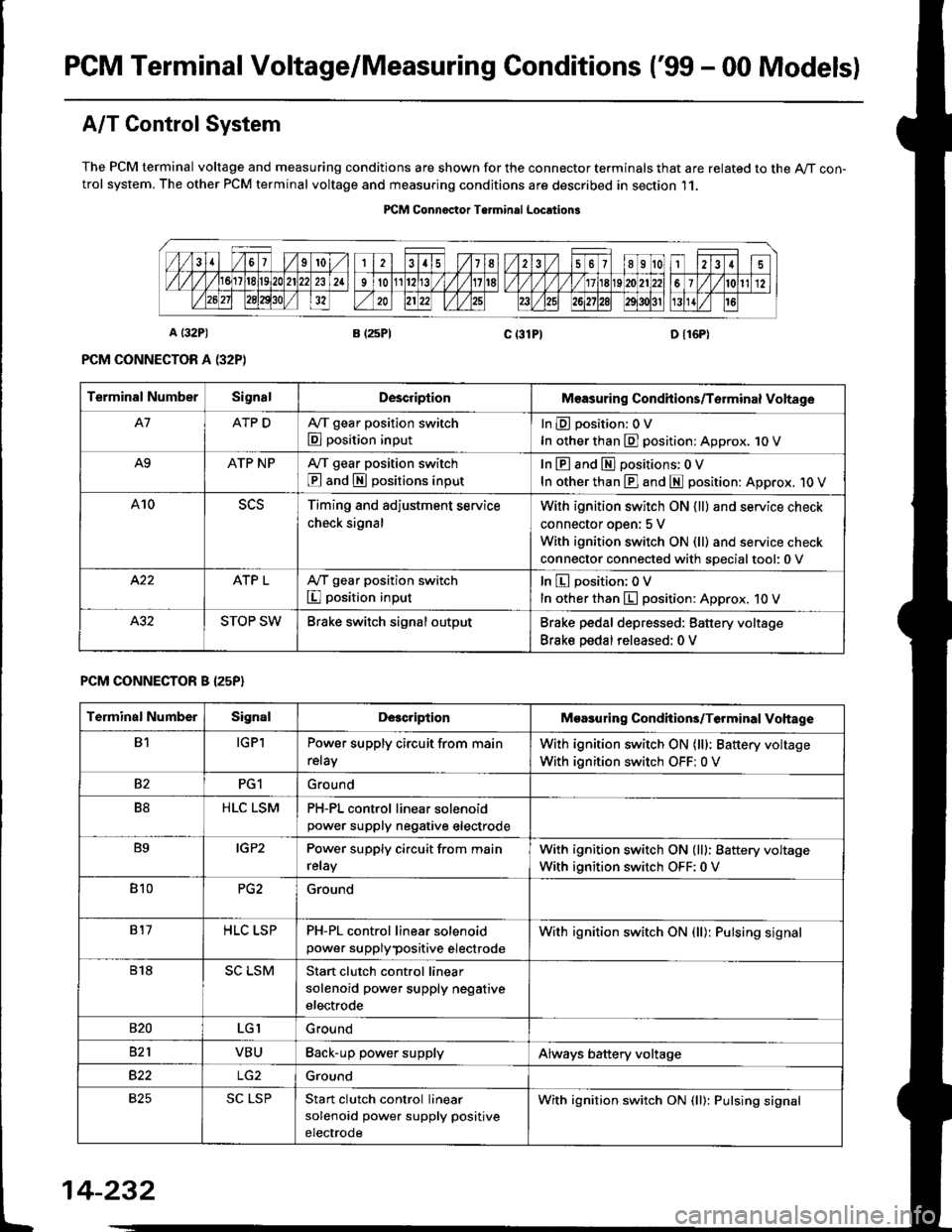
PGM Terminal Voltage/Measuring Conditions ('99 - 00 Modelsl
A/T Control System
The PCM terminal voltage and measuring conditions are shown for the connector terminals that are related to the A/T con-trol system. The other PCM terminal voltage and measuring conditions are described in section 11.
PICM Connoctor Terminrl Location3
Terminal NumberSignalDescriplionMeasuring Condhions/Torminal Voltage
A7ATP DA,/T gear position switch
E position input
InEposition:OV
In other than E] position: Approx. 1O V
A9ATP NPA/T gear position switch
@ and S positions input
In E and El positions: 0 V
In other than E] and E position: Approx. 1O V
A10Timing and adjustment service
check signal
With ignition switch ON {ll} and service check
connector oDen: 5 V
With ignition switch ON (ll) and service check
connector connected with soecialtool:0 v
ATP LA,/T gear position switch
I position input
In E position; OV
In other than E position: Approx. 10 V
STOP SWBrake switch signal outputBrake pedal depressed: Battery voltage
Brake pedal released: 0 V
PCM CONNECTOR B I25P}
Terminal NumberSignalDescriptionMoasuring Condhions/Terminal Vohage
B1IGPlPower supply circuit from main
relay
With ignition switch ON (lll: Battery voltage
With ignition switch OFF: 0 V
82PG1Ground
B8HLC LSMPH-PL control linear solenoidpower supply neqative electrode
B9IGP2Power supply circuit from main
relay
With ignition switch ON (lll: Battery voltage
With ignition switch OFF:0 V
810PG2Ground
817HLC LSPPH-PL control linear solenoid
power supplypositive electrode
With ignition switch ON {ll): Pulsing signal
818SC LSMStart clutch control linear
solenoid power supply negative
electrode
s20LGIGround
821VBUBack-up power supplyAlways battery voltage
B22Ground
825SC LSPStan clutch control linear
solenoid power supply positive
electrode
With ignition switch ON (ll): Pulsing signal
t
14-232
Page 965 of 2189
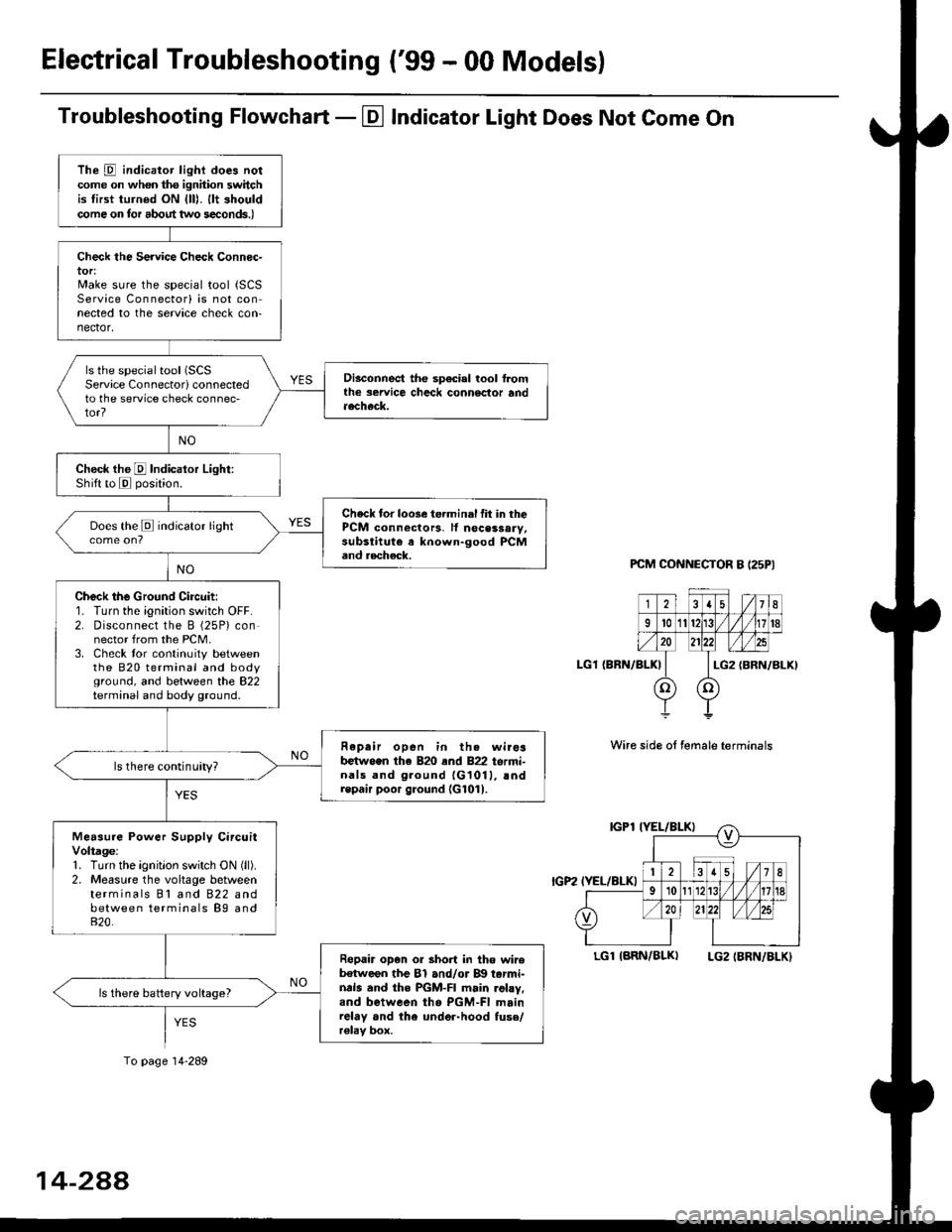
Electrical Troubleshooting ('99 - 00 Models)
Troubleshooting Flowchart - El Indicator Light Does Not Come On
PCM CONNECTOR B I25PI
LGl {BRN/BLK)
Wire side ot female terminals
LGlIARN/BLK) LG2IBRN/BLKI
The D indicator light does notcome on whon ths ignhion switchis tirst turned ON {lll. llt shouldcome on tor about two s€conds.)
Check the Service Check Connec-tor:Make sure the special tool {SCSService Connectorl is not connected to the service check con-nector,
ls the special tool (SCS
Service Connectorl connectedto the service check connec-tor?
Disconnect the sp€cial tool f]omthe seruice chcck connoclor andaecheck.
Check the E Indicalor Light:Shift to E posjtion.
Check tor loose te.minal fit in thePCM connectors, lf nocessary,substitute a known-good PCMand aecheck.
Does the E indicator light
Check the Ground Circuit:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the B (25P) connector from the PCM.3. Check tor continuity betweenthe 820 terminal and bodyground, and between the 822terminal and body ground.
Fepair open in th. wirosb€tw.en the 820 end 822 termi-nals and ground {G1011, !ndrepair poor ground {G1011.
ls there continuity?
Measure Power Supply CircuitVoltage:1. Turn the ignitlon switch ON (ll).
2. Measure the voltage betweenterminals Bl and 822 andbetween terminals B9 and820.
Ropair op€n or short in tho wireb€tween the Bl and/or B!| tarmi-nds and the PGM-FI main .ohy,and between tho PGM-FI mainrelay and the under-hood fuso/r€lav box.
ls there battery voltage?
To page 14-289
14-2AA