1998 HONDA CIVIC Crankshaft position sensor
[x] Cancel search: Crankshaft position sensorPage 370 of 2189

DTC(MlL indicationlDetection ltemProbable CausePage
P1336(54iCrankshaft SpeedFluctuation SensorIntermittent Interruption
. CKF sensor11 183
P1337 (54)Crankshaft SpeedFluctuation SensorNo Signal
CKF sensorCKF sensor circuitECM,PCM
11-'183
P13s9 (8)Crankshaft Position/TopDead Center SensorDisconnected
' CKP/TDC sensor circuit11-187
P1361 (8)Top Dead CenterSensor IntermittentInterruptron
. tuL sensor
11-172
P1362 (8)Top Dead CenterSensor No SignalTDC sensorTDC sensor circuitECIV/PCM
11-172
P1381 {9)Cylinder Position SensorIntermittent Interruption
. CYP sensor11-172
P1382 (9)Cylinder Position SensorNo SignalCYP sensorCYP sensor circuitECM/PCM
11-112
P1456*5(90)
Evaporative Emission ControlSystem Leak Detected {FuelTankArea)
FuelfillcapVacuum connectionFu€ltankFuel tank pressure sensorEVAP bypass solenoid valveEVAP two way valveEVAP control canister vent shut valveEVAP control canisterEVAP purge control solenoid valve
11-283
P1457*6 (90)
Evaporative Emission ControlSystem Leak Detected (EVAP
Control Canister Area)
Vacuum connectionEVAP control canisterFuel tank pressure sensorEVAP bypass solenoid valveEVAP two way valveEVAP control canister vent shut valveFuel TankEVAP purge control solenoid valve
11-283
L
*6: '96 D16Y8 engine (coupe),'97 Dl6Y7 engine (coupe: KL model, sedan: KL (LXl model),'97 D16Y8 engine (coupe: all models,
sedan: KL model),'98-all models,'99-all models,'00-all models.
(cont'd)
1 1-1 01
I ta
Page 435 of 2189
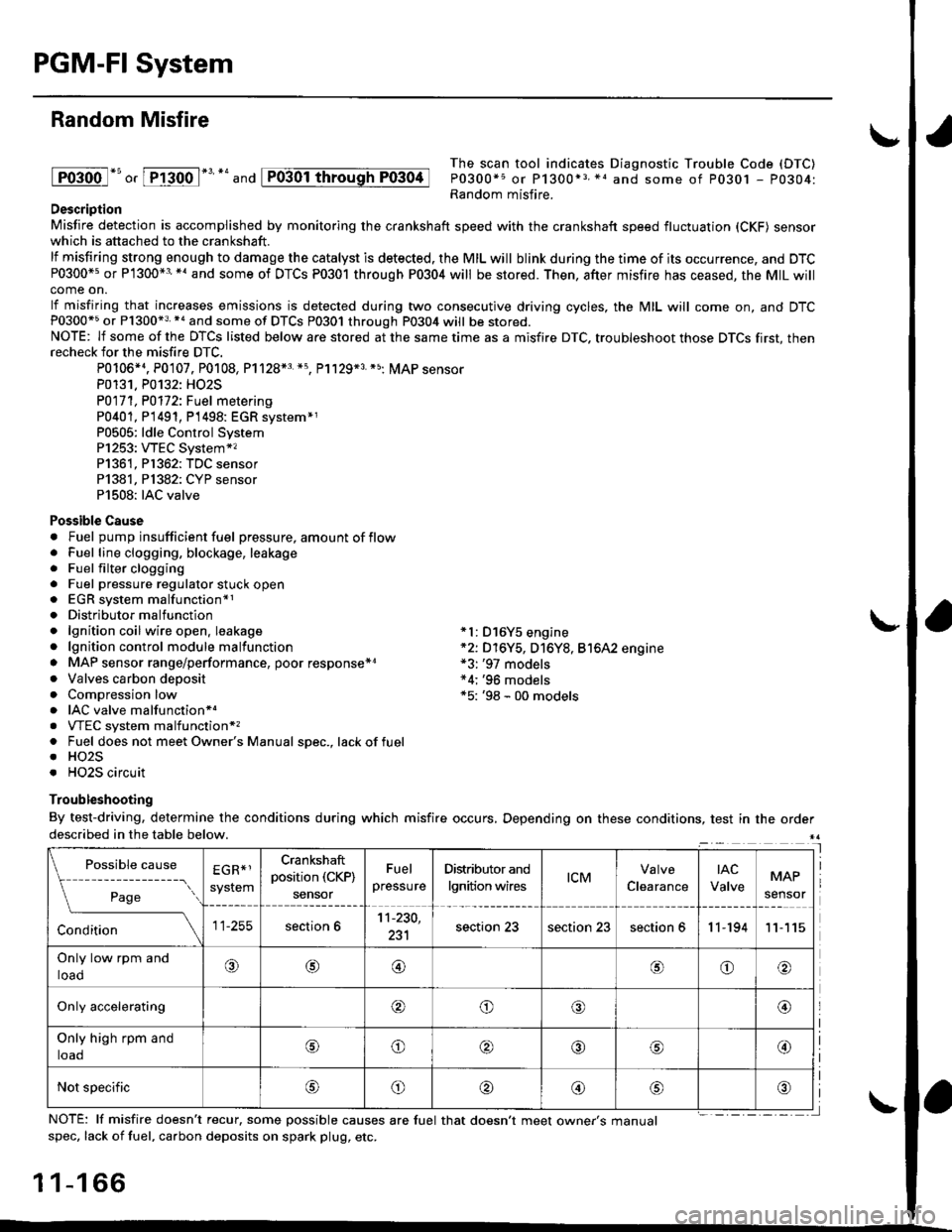
PGM-FI System
Random Misfire
lFoioo l*u o, [FTioo l*' *' and
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
P0300*5 or P1300*3 *1 and some of P0301 - P0304:Random misfire.Description
Misfire detection is accomplished by monitoring the crankshaft speed with the crankshaft speed fluctuation (CKF) sensorwhich is attached to the crankshaft.
lf misfiring strong enough to damage the catalyst is detected. the MIL will blink during the time of its occurrence, and DTCP0300*5 or P1300*3'*' and some of DTCs P0301 through P0304 will be stored. Then, after misfire has ceased, the MIL willcome on.
lf misfiring that increases emissions is detected during two consecutive driving cycles, the MIL will come on, and DTCP0300*5 or P1300*3 *a and some of DTCS P0301 through P0304 will be stored.NOTE: lf some of the DTCS listed below are stored at the same time as a misfire DTC. troubleshoot those DTCS first, thenrecheck for the misfire DTC.
P0106*4. P0107. P0108, P1128*3 *5, Pl129*3 *5; MAP sensorP0131. P0132: HO2S
P0171, P0112i Fuel metering
P0401, P 1491, P1498: EGR svstem*1P0505: ldle Control SystemP1253: VTEC System*,P1361, P1362: TDC sensorP1381, Pl382: CYP sensorP1508: IAC valve
Possible Cause. Fuel pump insufficient fuel pressure, amount of flow. Fuel line clogging, blockage, leakage. Fuel filter clogging. Fuel pressure regulator stuck open. EGR system malfunction*1. Distributormalfunction. lgnition coil wire open. leakage *l: D16Y5 engine. lgnition control module malfunction *2: D16Y5, D16Y8, Bt6A2 engine. MAP sensor range/performance, poor response*r *3: '97 models. Valves carbon deposit *4;'96 models. Compression low *5: '98 - 00 models. IAC valve malfunctionr.. VTEC system malfunction*,. Fuel does not meet Owner's Manual spec., lackoffuel. HO2S. HO2S circuit
Troubleshooting
By test-driving, determine the conditions during which misfire occurs, Depending on these conditions, test in the orderdescribed in the table below.
Possible
- --^ ---
rage
causeEGR*1
system
Crankshaft
position (CKP)
sensor
Fuel
pressure
Distributor and
lgnition wirestcMClearance
tAc
ValveMAP
sensor
section 611-230,
231section 23section 23section 611-19411
Only low rpm and
loado@@oo
Only accelerating@o@@
Only high rpm and
toaooo@
Not specificoo@
NOTE: lf misfire doesn't recur, some possible causes are fuel that doesn't meet owne/s manualspec, lack of fuel, carbon deposits on spark plug, etc.
1 1-1 66
I
P0304
Page 441 of 2189

PGM-FI System
tFos3sl
tFffi6l
tPr361 I
fPfi62l
fFr38il
tF13s2-l
Crankshaft Position/Top Dead Genter/Gylinder Position (CKP/TDC/CYP) Sensor
('96 - 98 Models, '!n - 00 D16Y5 engine with M/Tl
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0335: A malfunction in the Crankshaft position (CKp)
sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336: A range/performance problem in the CrankshaftPosition (CKP) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1361: Intermittent interruotion in the Too Dead Center(TDC) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC) P1362: No signal in the Top Dead Center (TDC} sensorcircuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1381: Intermittent interruption in the Cvlinder Position{CYP) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC) Pl382: No signal in the Cylinder Position (CYP} sensorcircuit.
Description
The CKP Sensor determines timing for fuel injection and ignition of each cylinder and also detects engine speed. The TDCSensor determines ignition timing at start-up (cranking) and when crank angle is abnormal. The Cyp Sensor detects theposition of No. 1 cylinder for sequential fuel injection to each cylinder. The CKP/TDC/CYP Sensor is built into the distribu-ror.
NOTE: lf DTC P1359 is stored atthesametime as DTC P0335. P0336, P1361, Pl362, P1381 and/or P1382, troubteshoor DTCP1359 first, then recheck for those DTCS. Ot6y5 6ngine: Dt6y7, ot6y8 enqin6s:
SENSORBOTOR
TDCSENSORCKPSENSORSENSORROTORSENSORROTORSENSORROTORROTORROTOR
DISTRIBUTOR 1OPcoNNECTOR tC120tTDC P
- The MIL hrs been reported on.- DTC P0335, P0336, P1361,P1362, P1381 and/or Pl382 6restored,
Problem verification:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Proce-dure.2. Stan the engine.
Intermittent hilu.e, system b OKat this time. Check tor poor con-n€ctions or 10036 wiros at C120{distributor} and ECM/PCM.
ls DTC P0335, P0336, P1361, P1362,P1381 and/or P'l382 indicated?
Check for an open in the CKP/TDC/CYP sensor:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the distributor 10P
3. Measure resistance betweenthe terminals of the indicatedsensor (*see table).
Replace the distributor ignitionhousing (soe section 23).ls there 350 - 700 0?
CYP M {BLK}
SENSORDTCSENSORIERMINATECMfCMTERMINATCOLOR
CKPP033s
m336
2c2BLU
6c12
TDCP1361
P1362
3GRN
7cl3RED
CYPP!381
P't382
c4YEL
8c148LK11-172
Page 443 of 2189

PGM-FI System
l-Fos3sl
tFos36l
tF1361 l
Fr362-1
tF13sil
Crankshaft Position/Top Dead Center/Cylinder Position (CKP/TDC/CYPI Sensor
f99 - 00 Models except D16Y5 engine with M/T)
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0335: A malfunction in the Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336: A range/performance problem in the Crankshaft
Position (CKP) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1361: Intermittent interruption in the Top Dead Center
{TDC) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC) P1362: No signal in the Top Dead Center (TDC) sensor
circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1381: Intermittent interruption in the Cylinder Position(CYP) sensor circuit.
lTiaSt The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1382; No signal in the Cylinder Position (CYP) sensor: circuil.
DoscriDtion
The CKP Sensor determines timing for fuel injection and ignition of each cylinder and also detects engine speed. The TDC
Sensor determines ignition timing at start-up (cranking) and when crank angle is abnormal. The CYP Sensor detects the
position of No. 1 cylinder for sequential fuel injection to each cylinder. The CKP/TDC/CYP Sensor is built into the distribu-
tor.
NOTE; lf DTC P1359 is stored at the same time as DTC P0335, P0336, P1361. P1362, P1381 and/or P1382, troubleshoot DTC
P1359 first, then recheck for those DTCS. D16Y5 engino:
SENSORROTOR
TDGSENSORCKPSENSOBTDCSENSOBCKPSENSOBCYPs€NsonBOTORROTORBOTONROTOR ROTOR
D16Y7, D16Y8 ongine:
(To page 11-175)
1-174
- The MIL has been reportod on.- DTC P0335, P0336. P1361,P1362, P1381 rnd/or P1382.restored.
Problem verific{tion:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Proce-dure.2. Start the engine.
Intormittcnt failure, systom b OKat thb time. Check to. poor con-nections or loose wires at C120(dktributorl and ECM/PCM.
ls DTC P0335, P0336, P1361, P1362,P1381 and/or Pl382 indicated?
Check tor an open in the CKP/TDC/CYP 3enior:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the distributor 10Pconnector,3. Measure resistance betweenthe terminals of the indicatedsensor (*see table).
Replrce the distributor ignitionhou3ing (!ee section 231.ls there 350 700 0?
SENSORDTCSENSORTEBMINAIECM/PCMTERI\,4INAICOLOR
CKPP0335
P0336
2c88LU
6c9
TDCP1361
P1362
3c20GRN
7c21BED
CYPP1381
P1342
c29YEL
Ic30BLK
Page 456 of 2189

l,a
Crankshaft Position/Top Dead Center/Cylinder Position (CKP/TDC/CYPI Sensor
Thescantoo|indicatesDiagnosticTroub|ecode(DTc)P1359:Aprob|eminthecrankshaftPosjtion/TopDead
Center/Cvlinder Position (CKP/TDC/CYP) sensor circuit'
- The MIL has been reported on- DTC P1359 is stored
Problem veritication:1. Do the ECM Reset Procedure
2. Stan the engine lftheengine
won't start, crank it for at least
10 seconds-
lntermittent failure, sYstem is OK
Check for poor connecllon3 or
loose wires at C120 {distributor}and ECM,/PCM.
ls DTC P1359 indicated?
Check for poor connections or
loose wires between the distribu
tor and the ECM/PCM
Substitute a known'good ECM/
PCM, and rccheck. lt 3ymPtom/
indication goes awtY, rePlace
the original ECM/PCM.
r ta
11-1A7
Page 681 of 2189

Description
The automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides
4 soeeds forward and 1 reverse.
Torque Convertel, Geats, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear
which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly seryes as a
flywheel while transmiuing power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in Iine with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, gears tor 2nd, 4th, reverse and lst (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch, and
gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse. 1st and park. The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the counter-
shaft. When certain combinations of gears in transmission are engaged by clutches. power is transmitted from the main-
shaft to the countershaft to provide E, ld, E, and E positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Powertrain Control Module {PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenojd valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comtonable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main vatve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body and the
lock-up valve body through the respective separator plates, They are bolted on the torque converter housang
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve, the CPB {Clutch Pressure
Back-up) valve, the modulator valve. the servo control valve, the relief valve, and ATF pump gears The secondary valve
body contains the 2-3 shift valve. the 3-4 shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch
pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve,
the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the
reverse shift fork, and the accumulators. The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing
valve. The linear solenoid and the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid from regulator
passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective teed pipes
or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will activate
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a line
to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear, The shift control solenoid valves A and B are con-
trolled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
In ,Dt1 position, in 3rd and 4th. and in E position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the timing of
the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and
B, and linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 873 of 2189

Description
The Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is an electronically controlled automatic transmission with drive and driv
en Oullevs, and a steel belt. The CVT provides non stage speeds forward and one reverse. The entire unit is positioned in
line with the engine.
Transmission
Around the outside of the flywheel is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being staned.
The transmission has four parallel shafts: the input shaft, the drive pulley shaft. the driven pulley shaft, and the secondary
gear shaft. The input shaft is in line with the engine crankshaft. The drive pulley shaft and the driven pulley shaft consist of
movable and fixed face pulleys. Both pulleys are linked by the steel belt.
The input shaft includes the sun gear. The drive pulley shaft includes the forward clutch which mounts the carrier assem-
bly on the forward clutch drum. The carrier assembly includes the pinion gears which mesh with the sun gear and the ring
gear. The ring gear has a hub-mounted reverse brake disc.
The driven pulley shaft includes the start clutch and the secondary drive gear which is integral with the park gear' The sec-
ondary gear shaft is positioned between the secondary drive gear and the final driven gear. The secondary gear shaft
includes the secondary driven gear which serves to change the rotation direction. because the drive pulley shaft and the
driven oullev shaft rotate the same direction. When certain combinations of planetary gears in the transmission are
engaged by the clutches and the reverse brake, power is transmitted from the drive pulley shaft to the driven pulley shaft
to provide E, E, E, and El.
Electronic Control'96 - 98 Models:
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, three linear solenoids, and a
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions'
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the kick panel on the driver's side.'99 - 00 Models:
The electronic control svstem consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, three linear solenoids and an
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions. A Grade Logic Control System to control shift-
ing in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope.
The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the Pressure Low (PL) reguiator valve body, the shift valve
body, the start clutch control valve body, and the secondary valve body. They are positioned on the lower part of the
transmission housing.
The main valve body contains the Pressure High (PH) control valve, the lubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
The secondary valve body contains the PH regulator valve, the clutch reducing valve, the start clutch valve accumulator,
and the shift inhibitor valve. The PL regulator valve body contains the PL regulator valve and the PH-PL control valve
which is ioined to the PH,PL control linear solenoid. The inhibitor solenoid valve is bolted on the PL regulator valve body.
The shift valve body contains the shift valve and the shift control valve. which is joined to the shift control linear solenoid.
The start clutch control valve body contains the start clutch control valve, which is joined to the start clutch control linear
solenoid. The linear solenoids and the inhibitor solenoid are controlled by the TCM or PCM. The manual valve body which
contains the manual valve and the reverse inhibitor valve, is bolted on the intermediate housing.
The ATF pump assembly is located on the transmission housing, and is linked with the input shaft by the sprockets and
the sprocket chain. The pulleys and the clutch receive fluid from their respective feed pipes, and the reverse brake receives
fluid from internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which linear solenoid the TCM or PCM will activate.
Activating the shift control linear solenoid changes the shift control valve pressure, causing the shift valve to move. This
pressurizes the drive pulley pressure to the drive pulley and the driven pulley pressure to the driven pulley and changes
their effective pulley ratio. Activating the start clutch control linear solenoid moves the start clutch control valve. The start
clutch control valve uncovers the port, providing pressure to the start clutch to engage it(cont'd)
14-195
,!
Page 1486 of 2189
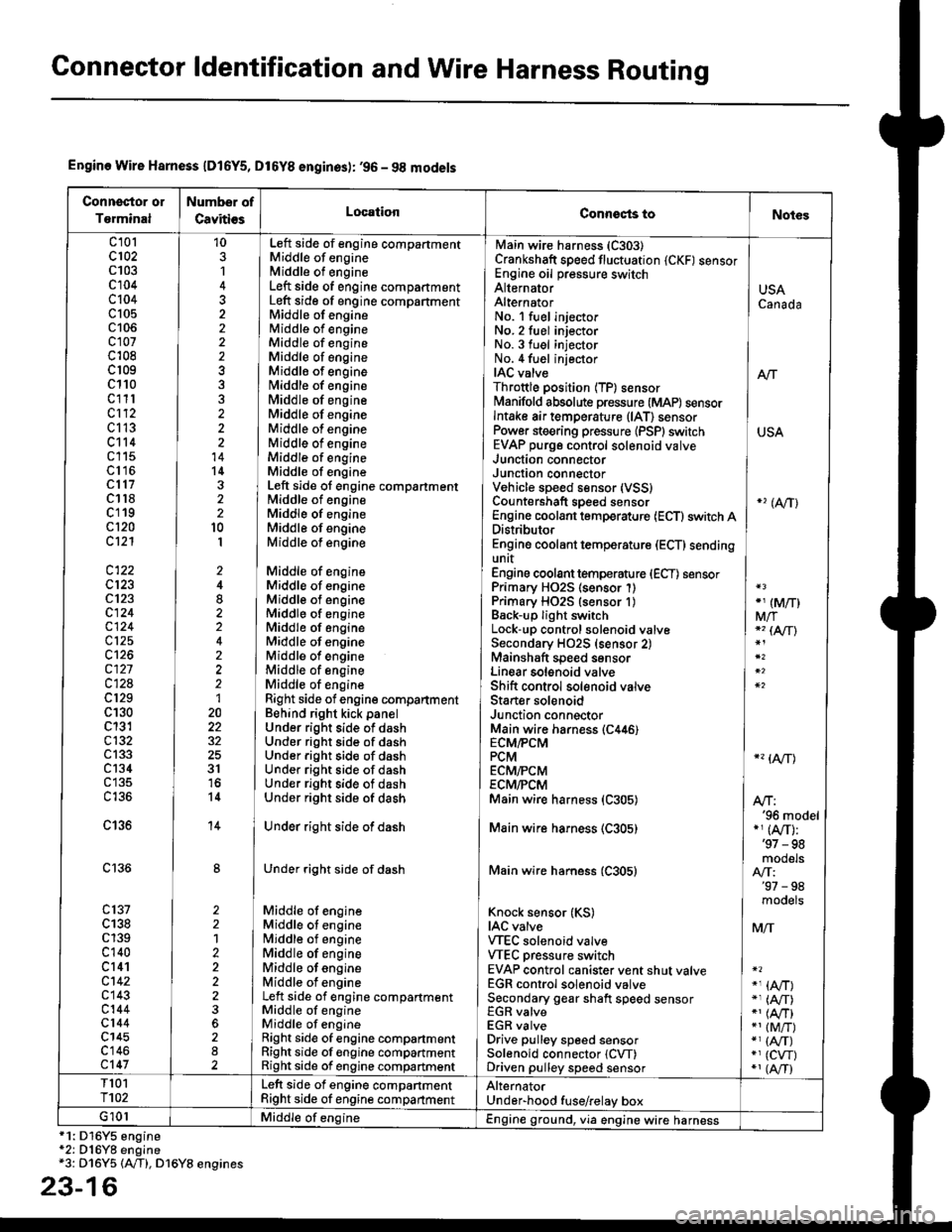
Connector ldentification and Wire Harness Routing
Engine Wire Harness lD16Y5, D16Y8 enginss): '96 - 98 models
Connector or
Torminal
Numbsr of
CavitissLocationConnects toNot€s
c 101c102c103c104c104c105c106c107c108c 109c110c111c112c113c114c115c116cl17c118c119c120cl21
c122c123cl23c124
c125
c127c12Ac129c130c131c132c 133c134c135
c136
c138c139c140c 141c142c 143c144cl44c145c'146cl47
10
1
22
14l4322l0I
2
2
2
2120
3l
14
14
1222
2
2
22
Left side of engine compartmentMiddle of engineMiddle of engineLeft side of engine companmentLeft side of engine compartmentMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of enginefvliddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineLeft side of engine compartmentMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engine
Middle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of engineRight side of engine companmentBehind right kick panelUnder right side of dashUnder riOht side of dashUnder right side of dashUnder right side of dashUnder right side of dashUnder right side of dash
Under right side of dash
Under right side of dash
Middle of engineMiddle ot enginel iddle of engineMiddle of engineMiddle of ongineMiddle of engineLeft side of engine compartmentMiddle of engineMiddle of engineRight side of engine compartmentRight side of engine compartmentRight side of engine compartment
USACanada
Afi
USA
-' (A/r)
Main wire harness (C303)Crankshaft speed fluctuation (CKF) sensorEngine oil pressure switchAlternatorAlternatorNo. 'l fuel injectorNo. 2 fuel injectorNo.3 fuel injectorNo. 4 fuel injectorIAC valveThrottle position (TP) sensorl\4anifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensorIntake air temperature (lAT) sensorPower steering pressure {PSPI switchEVAP purge control solenoid valveJunction connectorJunction conn€ctorVehicle speed sensor {VSS}Countershaft speed sensorEngine coolant temp€rature (ECT) switch ADistributorEngine coolant temperature (ECT) sendingunrtEngine coolant temperature (ECT) sensorPrimary HO2S (sensor'l)Primary HO2S (sensor 1)Back-up light switchLock-up control solenoid valveSecondary HO2S (sensor 2)Mainshaft speed sensorLinear solgnoid valveShift control solsnoid valveStarter solenoidJunction connectorMain wire harnesE (C446)ECM/PCMPCMECMiPCMECM/PCMMain wire harness (C305)
Main wire harness (C305)
Main wire harness (C305)
Knock sensor (KS)IAC valveVTEC solenoid valveVTEC pressure switchEVAP control canister vent shut valveEGR control solenoid valveSecondary gear shaft speed sensorEGR valveEGR valveDrive pulley speed sensorSolenoid connector {CVT)Driven pulley speed sensor
*, (M/T)M/T*" INT\
*, tAtf)
NT:'96 model*,(A,/T):'97 - 98mooets
moqets
M/T
-1 (l,/T)*, (A,/T)-,(4,/T)*1 {M/T)*, (A,/T)*1 (CW)*, (A,T)
T101r102Left side of engine companmentRight side of engine companmentAlternatorUnder-hood fuse/relay boxG 101Middle of engineEngine ground, via engine wire harness
2
*1: Dl6Y5 engine*2: D16Y8 engine*3: D16Y5 (Ay'T), D16Y8 engines
3-16