1998 DODGE RAM 1500 gear
[x] Cancel search: gearPage 2092 of 2627

(7) Mark all gears for location. The gears are
select fit and if the oil pump is to be reused, the
gears must be returned to their original locations.
(8) Remove the oil pump gears from the oil pump
case (Fig. 101).
Fig. 101 Oil Pump Housing and Gears
1 - SEPARATOR PLATE 5 - DOWEL (2)
2 - DRIVEN GEAR (2) 6 - DRIVE GEAR
3 - CHECK VALVE 7 - SCREW
4 - PUMP HOUSING
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 389
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2093 of 2627

(9) Remove the oil pump valve retainers and asso-
ciated valve and spring one at a time (Fig. 102) (Fig.
103). Mark the combination of components as a
group and tag them as to the location from which
they were removed.
CLEANING
Clean pump and support components with solvent
and dry them with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Check condition of the seal rings and thrust
washer on the reaction shaft support. The seal rings
do not need to be replaced unless cracked, broken, or
severely worn.
Inspect the pump and support components. Replace
the pump or support if the seal ring grooves or
machined surfaces are worn, scored, pitted, or dam-
aged. Replace the pump gears if pitted, worn
chipped, or damaged.
Inspect the pump reaction shaft support bushings.
Replace either bushing only if heavily worn, scored or
damaged. It is not necessary to replace the bushings
unless they are actually damaged.
Inspect the valves and plugs for scratches, burrs,
nicks, or scores. Minor surface scratches on steel
valves and plugs can be removed with crocus clothbutdo not round off the edges of the valve or
plug lands.Maintaining sharpness of these edges is
vitally important. The edges prevent foreign matter
from lodging between the valves and plugs and the
bore.
Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the oil
pump cover. Use a penlight to view the bore interi-
ors. Replace the oil pump if any bores are distorted
or scored. Inspect all of the valve springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Make sure
that all passages are thoroughly cleaned and are free
from dirt or debris. Make sure that all valves move
freely in their proper bore. Make sure that all gear
pockets and bushings are free from excessive wear
and scoring. Replace the oil pump if any excessive
wear or scoring is found.
(2) Coat the gears with MopartATF +4 and install
into their original locations.
(3) Lubricate the oil pump valves with Mopart
ATF +4 and install the valve, spring and retainer
Fig. 102 Oil Pump Valve Body
1 - T/C REGULATOR VALVE
2 - T/C LIMIT VALVE
3 - REGULATOR VALVE
4 - OIL PUMP VALVE BODY
Fig. 103 T/C Switch Valve
1 - RETAINER
2 - T/C SWITCH VALVE
3 - OIL PUMP VALVE BODY
21 - 390 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2094 of 2627

into the appropriate oil pump valve body bore (Fig.
102) (Fig. 103).
(4) Place the separator plate onto the oil pump
body (Fig. 101).
(5) Install the screws to hold the separator plate
onto the oil pump body (Fig. 101). Tighten the screws
to 4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(6) Position the oil pump cover onto the locating
dowels (Fig. 100).
(7) Seat the two oil pump halves together and
install all bolts finger tight.
(8) Torque all bolts down slowly starting in the
center and working outward. The correct torque is
4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(9) Verify that the oil pump gears rotate freely and
smoothly.
(10) Position the reaction shaft support into the oil
pump (Fig. 100).
(11) Install and torque the bolts to hold the reac-
tion shaft support to the oil pump (Fig. 100). The cor-
rect torque is 12 N´m (105 in.lbs.).
OIL PUMP FRONT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission from the vehicle.
(2) Remove the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
(3) Using a screw mounted in a slide hammer,
remove the oil pump front seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean seal bore of the oil pump of any residue
or particles from the original seal.
(2) Install new oil seal in the oil pump housing
using Seal Installer C-3860-A (Fig. 104).
OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Input and Output Speed Sensors are two-wire
magnetic pickup devices that generate AC signals as
rotation occurs. They are mounted in the left side of
the transmission case and are considered primary
inputs to the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil, an AC
voltage is generated and sent to the TCM. The TCM
interprets this information as input shaft rpm.
The Output Speed Sensor generates an AC signal
in a similar fashion, though its coil is excited by rota-
tion of the rear planetary carrier lugs. The TCM
interprets this information as output shaft rpm.
The TCM compares the input and output speed
signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The TCM also compares the input speed signal and
the engine speed signal to determine the following:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.
(3) Remove the wiring connector from the output
speed sensor (Fig. 105).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the output speed sen-
sor to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the output speed sensor from the
transmission case.
Fig. 104 Install Oil Pump Front Seal
1 - TOOL C-3860-A
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 391
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2098 of 2627
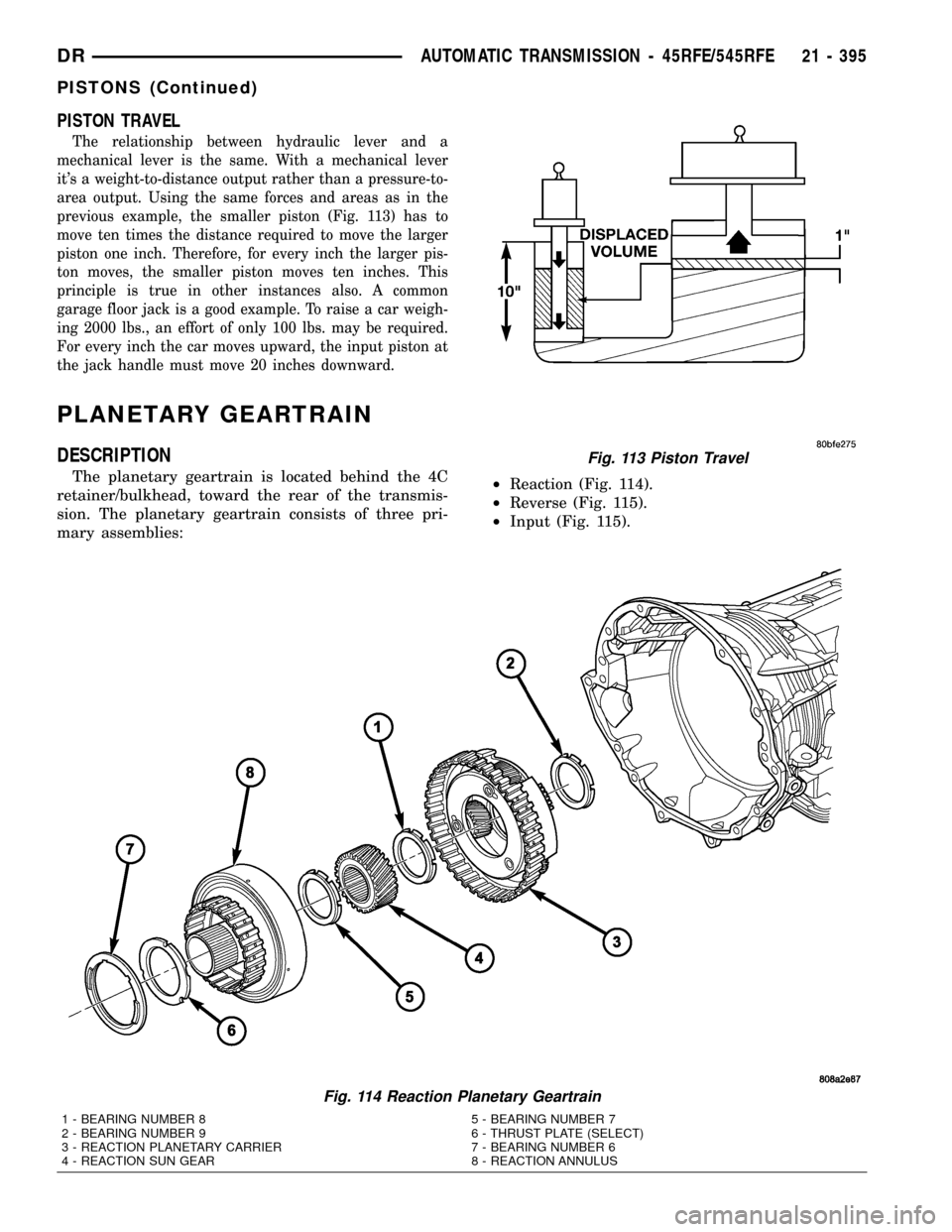
PISTON TRAVEL
The relationship between hydraulic lever and a
mechanical lever is the same. With a mechanical lever
it's a weight-to-distance output rather than a pressure-to-
area output. Using the same forces and areas as in the
previous example, the smaller piston (Fig. 113) has to
move ten times the distance required to move the larger
piston one inch. Therefore, for every inch the larger pis-
ton moves, the smaller piston moves ten inches. This
principle is true in other instances also. A common
garage floor jack is a good example. To raise a car weigh-
ing 2000 lbs., an effort of only 100 lbs. may be required.
For every inch the car moves upward, the input piston at
the jack handle must move 20 inches downward.
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION
The planetary geartrain is located behind the 4C
retainer/bulkhead, toward the rear of the transmis-
sion. The planetary geartrain consists of three pri-
mary assemblies:²Reaction (Fig. 114).
²Reverse (Fig. 115).
²Input (Fig. 115).
Fig. 113 Piston Travel
Fig. 114 Reaction Planetary Geartrain
1 - BEARING NUMBER 8 5 - BEARING NUMBER 7
2 - BEARING NUMBER 9 6 - THRUST PLATE (SELECT)
3 - REACTION PLANETARY CARRIER 7 - BEARING NUMBER 6
4 - REACTION SUN GEAR 8 - REACTION ANNULUS
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 395
PISTONS (Continued)
Page 2099 of 2627

OPERATION
REACTION PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
The reaction planetary carrier and reverse sun
gear of the reaction planetary geartrain are a single
component which is held by the 2C clutch when
required. The reaction annulus gear is a stand alone
component that can be driven by the reverse clutch
or held by the 4C clutch. The reaction sun gear is
driven by the overdrive clutch.
REVERSE PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
The reverse planetary geartrain is the middle of
the three planetary sets. The reverse planetary car-
rier can be driven by the overdrive clutch as
required. The reverse planetary carrier is also
splined to the input annulus gear, which can be held
by the low/reverse clutch. The reverse planetary
annulus, input planetary carrier, and output shaft
are all one piece.
INPUT PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
The input sun gear of the input planetary
geartrain is driven by the underdrive clutch.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the snap-ring holding the input annu-
lus into the input carrier (Fig. 116).
(2) Remove the input annulus from the input car-
rier (Fig. 116).
(3) Remove the number 9 bearing from the reverse
planetary carrier. Note that this planetary carrier
has four pinion gears.
(4) Remove the reverse planetary gear carrier (Fig.
116).
(5) Remove the number 10 bearing from the input
sun gear (Fig. 116).
(6) Remove the input sun gear from the input car-
rier (Fig. 116).
(7) Remove the number 11 bearing from the input
carrier (Fig. 116).
CLEANING
Clean the planetary components in solvent and dry
them with compressed air.
Fig. 115 Reverse/Input Planetary Geartrain
1 - SNAP-RING 5 - INPUT PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - BEARING NUMBER 10 6 - INPUT SUN GEAR
3 - BEARING NUMBER 11 7 - REVERSE PLANETARY CARRIER
4 - INPUT ANNULUS
21 - 396 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN (Continued)
Page 2100 of 2627

INSPECTION
Check sun gear and driving shell condition.
Replace the gear if damaged or if the bushings are
scored or worn. The bushings are not serviceable.
Replace the driving shell if worn, cracked or dam-
aged.
Replace planetary gear sets if gears, pinion pins, or
carrier are damaged in any way. Replace the annulus
gears and supports if either component is worn or
damaged.
Replace the output shaft if the machined surfaces
are scored, pitted, or damaged in any way. Also
replace the shaft if the splines are damaged, or
exhibits cracks at any location.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Replace any
components which show evidence of excessive wear
or scoring.(2) Install the number 11 bearing into the input
planetary carrier so that the inner race will be
toward the front of the transmission (Fig. 116).
(3) Install the input sun gear into the input carrier
(Fig. 116).
(4) Install the number 10 bearing onto the rear of
the reverse planetary carrier with the inner race
toward the carrier (Fig. 116).
(5) Install the number 9 bearing onto the front of
the reverse planetary carrier with the outer race
toward the carrier and the inner race facing upward
(Fig. 116).
(6) Install the reverse planetary gear carrier into
the input carrier (Fig. 116).
(7) Install the input annulus gear into the input
carrier (Fig. 116).
(8) Install the snap-ring to hold the input annulus
gear into the input carrier (Fig. 116).
Fig. 116 Reverse/Input Planetary Carrier Assembly
1 - SNAP-RING 5 - INPUT PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - BEARING NUMBER 10 6 - INPUT SUN GEAR
3 - BEARING NUMBER 11 7 - REVERSE PLANETARY CARRIER
4 - INPUT ANNULUS
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 397
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN (Continued)
Page 2101 of 2627

SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION
The gear shift mechanism provides six shift posi-
tions which are:
²Park (P)
²Reverse (R)
²Neutral (N)
²Drive (D)
²Manual second (2)
²Manual low (1)
OPERATION
MANUAL LOW (1) range provides first gear only.
Overrun braking is also provided in this range.
MANUAL SECOND (2) range provides first and sec-
ond gear only.
DRIVE range provides FIRST, SECOND, THIRD,
OVERDRIVE FOURTH, and OVERDRIVE FIFTH (if
applicable) gear ranges. The shift into OVERDRIVE
FOURTH and FIFTH (if applicable) gear ranges
occurs only after the transmission has completed the
shift into D THIRD gear range. No further movement
of the shift mechanism is required to complete the
3-4 or 4-5 (if applicable) shifts.
The FOURTH and FIFTH (if applicable) gear
upshifts occur automatically when the overdrive
selector switch is in the ON position. No upshift to
FOURTH or FIFTH (if applicable) gears will occur if
any of the following are true:
²The transmission fluid temperature is below 10É
C (50É F) or above 121É C (250É F).
²The shift to THIRD is not yet complete.
²Vehicle speed is too low for the 3-4 or 4-5 (if
applicable) shifts to occur.
Upshifts into FOURTH or FIFTH (if applicable)
will be delayed when the transmission fluid temper-
ature is below 4.5É C (40É F) or above 115.5É C (240É
F).
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) is located in the
valve body and controls the direction of the transmis-
sion fluid when the L/R-TCC solenoid is energized.
OPERATION
The Solenoid Switch Valve controls line pressure
from the LR-TCC solenoid. In 1st gear, the SSV will
be in the downshifted position, thus directing fluid to
the L/R clutch circuit. In 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th (if
applicable) gears, the solenoid switch valve will be in
the upshifted position and directs the fluid into the
torque converter clutch (TCC) circuit.When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
1. Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
2. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
21 - 398 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2105 of 2627

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 120) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 121).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 122) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmis-
sion and buffer the powertrain against torsional
vibrations, the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Sole-
noid to achieve a smooth application of the torque
converter clutch. This function, referred to as Elec-
tronically Modulated Converter Clutch (EMCC) can
occur at various times depending on the following
variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle²Engine speed
Fig. 120 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 121 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 122 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 402 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)