1998 DODGE RAM 1500 weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 1944 of 2627

PISTON TRAVEL
The relationship between hydraulic lever and a
mechanical lever is the same. With a mechanical
lever it's a weight-to-distance output rather than a
pressure-to-area output. Using the same forces and
areas as in the previous example, the smaller piston
(Fig. 191) has to move ten times the distance
required to move the larger piston one inch. There-
fore, for every inch the larger piston moves, the
smaller piston moves ten inches. This principle is
true in other instances also. A common garage floor
jack is a good example. To raise a car weighing 2000
lbs., an effort of only 100 lbs. may be required. For
every inch the car moves upward, the input piston at
the jack handle must move 20 inches downward.
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/
OUTPUT SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The planetary gearsets (Fig. 192) are designated as
the front, rear, and overdrive planetary gear assem-
blies and located in such order. A simple planetary
gearset consists of three main members:²The sun gear which is at the center of the sys-
tem.
²The planet carrier with planet pinion gears
which are free to rotate on their own shafts and are
in mesh with the sun gear.
²The annulus gear, which rotates around and is
in mesh with the planet pinion gears.
NOTE: The number of pinion gears does not affect
the gear ratio, only the duty rating.
OPERATION
With any given planetary gearset, several condi-
tions must be met for power to be able to flow:
²One member must be held.
²Another member must be driven or used as an
input.
²The third member may be used as an output for
power flow.
²For direct drive to occur, two gear members in
the front planetary gearset must be driven.
NOTE: Gear ratios are dependent on the number of
teeth on the annulus and sun gears.
Fig. 191 Piston Travel
Fig. 192 Planetary Gearset
1 - ANNULUS GEAR
2 - SUN GEAR
3 - PLANET CARRIER
4 - PLANET PINIONS (4)
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 241
PISTONS (Continued)
Page 2098 of 2627
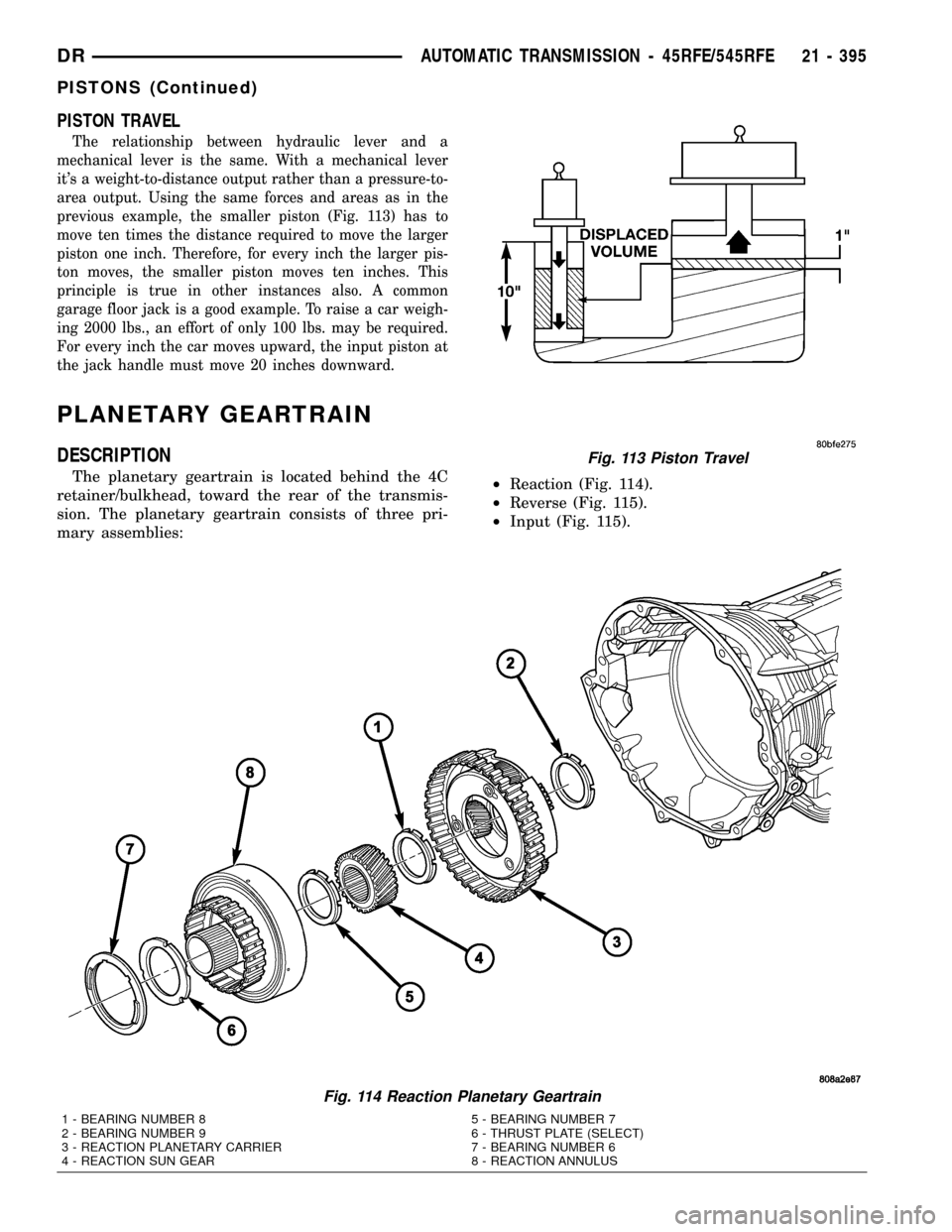
PISTON TRAVEL
The relationship between hydraulic lever and a
mechanical lever is the same. With a mechanical lever
it's a weight-to-distance output rather than a pressure-to-
area output. Using the same forces and areas as in the
previous example, the smaller piston (Fig. 113) has to
move ten times the distance required to move the larger
piston one inch. Therefore, for every inch the larger pis-
ton moves, the smaller piston moves ten inches. This
principle is true in other instances also. A common
garage floor jack is a good example. To raise a car weigh-
ing 2000 lbs., an effort of only 100 lbs. may be required.
For every inch the car moves upward, the input piston at
the jack handle must move 20 inches downward.
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION
The planetary geartrain is located behind the 4C
retainer/bulkhead, toward the rear of the transmis-
sion. The planetary geartrain consists of three pri-
mary assemblies:²Reaction (Fig. 114).
²Reverse (Fig. 115).
²Input (Fig. 115).
Fig. 113 Piston Travel
Fig. 114 Reaction Planetary Geartrain
1 - BEARING NUMBER 8 5 - BEARING NUMBER 7
2 - BEARING NUMBER 9 6 - THRUST PLATE (SELECT)
3 - REACTION PLANETARY CARRIER 7 - BEARING NUMBER 6
4 - REACTION SUN GEAR 8 - REACTION ANNULUS
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 395
PISTONS (Continued)
Page 2283 of 2627

(3) Break down the tire and remount it 180
degrees on the rim (Fig. 7).
(4) Measure the total indicator runout again. Mark
the tire to indicate the high spot.
(5) If runout is still excessive, the following proce-
dures must be done.
²If the high spot is within 101.6 mm (4.0 in.) of
the first spot and is still excessive, replace the tire.
²If the high spot is within 101.6 mm (4.0 in.) of
the first spot on the wheel, the wheel may be out of
specifications. Refer to Wheel and Tire Runout.
²If the high spot is NOT within 101.6 mm (4.0
in.) of either high spot, draw an arrow on the tread
from second high spot to first. Break down the tire
and remount it 90 degrees on rim in that direction
(Fig. 8). This procedure will normally reduce the
runout to an acceptable amount, if not replace the
rim.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND WHEEL
BALANCE
It is recommended that a two plane service
dynamic balancer be used when a tire and wheel
assembly require balancing. Refer to balancer opera-
tion instructions for proper cone mounting proce-
dures. Typically use front cone mounting method for
steel wheels. For aluminum wheel use back cone
mounting method without cone spring.NOTE: Static should be used only when a two plane
balancer is not available.
NOTE: Cast aluminum and forged aluminum wheels
require coated balance weights and special align-
ment equipment.
Wheel balancing can be accomplished with either
on or off vehicle equipment. When using on-vehicle
balancing equipment, remove the opposite wheel/tire.
Off-vehicle balancing is recommended.
For static balancing, find the location of the heavy
spot causing the imbalance. Counter balance wheel
directly opposite the heavy spot. Determine weight
required to counter balance the area of imbalance.
Place half of this weight on theinnerrim flange and
the other half on theouterrim flange (Fig. 9).
For dynamic balancing, the balancing equipment is
designed to locate the amount of weight to be applied
to both the inner and outer rim flange (Fig. 10).
Fig. 7 Remount Tire 180 Degrees
1 - VALVE STEM
2 - REFERENCE MARK
Fig. 8 Remount Tire 90 Degrees In Direction of
Arrow
1 - 2ND HIGH SPOT ON TIRE
2 - 1ST HIGH SPOT ON TIRE
22 - 4 TIRES/WHEELSDR
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
Page 2284 of 2627

Fig. 9 Static Unbalance & Balance
1 - HEAVY SPOT
2 - CENTER LINE OF SPINDLE
3 - ADD BALANCE WEIGHTS HERE4 - CORRECTIVE WEIGHT LOCATION
5 - TIRE OR WHEEL TRAMP, OR WHEEL HOP
Fig. 10 Dynamic Unbalance & Balance
1 - CENTER LINE OF SPINDLE
2 - ADD BALANCE WEIGHTS HERE3 - CORRECTIVE WEIGHT LOCATION
4 - HEAVY SPOT WHEEL SHIMMY AND VIBRATION
DRTIRES/WHEELS 22 - 5
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
Page 2290 of 2627

WHEELS
DESCRIPTION
Original equipment wheels are designed for the
specified Maximum Vehicle Capacity.
All models use steel or aluminum drop center
wheels.
Aluminum wheels require special balance weights
and alignment equipment.
(1) On vehicles equipped with dual rear wheels,
The rim is an eight stud hole pattern wheel. The
wheels have a flat mounting surface (Fig. 18). The
slots in the wheel must be aligned to provide access
to the valve stem (Fig. 19).
OPERATION
The wheel (Fig. 20) has raised sections between
the rim flanges and the rim well. Initial inflation of
the tire forces the bead over these raised sections. In
case of tire failure, the raised sections hold the tire
in position on the wheel until the vehicle can be
brought to a safe stop.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WHEEL INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive run out
²Dents or cracks
²Damaged wheel lug nut holes
²Air Leaks from any area or surface of the rim
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by hammer-
ing, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they should be equivalent in
load carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset,
pilot hole and bolt circle of the wheel should be the
same as the original wheel.
WARNING: FAILURE TO USE EQUIVALENT
REPLACEMENT WHEELS MAY ADVERSELY
AFFECT THE SAFETY AND HANDLING OF THE
VEHICLE. USED WHEELS ARE NOT RECOM-
MENDED. THE SERVICE HISTORY OF THE WHEEL
MAY HAVE INCLUDED SEVERE TREATMENT OR
VERY HIGH MILEAGE. THE RIM COULD FAIL WITH-
OUT WARNING.
Fig. 18 FLAT FACE WHEEL
1 - FLAT FACE
2 - VALVE STEM
Fig. 19 DUAL REAR WHEELS
1 - WINDOW OPENINGS (5)
2 - INBOARD VALVE STEM
3 - OUTBOARD VALVE STEM
Fig. 20 Safety Rim
1 - FLANGE
2 - RIDGE
3 - WELL
DRTIRES/WHEELS 22 - 11
Page 2529 of 2627

REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION.........................68
OPERATION...........................69
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
OIL LEVEL...........................69
SERVICE PORT VALVE CORE
DESCRIPTION.........................70
REMOVAL - SERVICE PORT VALVE CORES . . 70
INSTALLATION.........................70
SUCTION LINE
DESCRIPTION.........................70REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE.........70
REMOVAL - 3.7L/4.7L AND 5.7L HEMI
ENGINE.............................71
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE.....72
INSTALLATION - 3.7L/4.7L AND 5.7L HEMI
ENGINE.............................73
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT LINE
The refrigerant lines and hoses are used to carry
the refrigerant between the various air conditioning
system components. A barrier hose design with a
nylon tube, which is sandwiched between rubber lay-
ers, is used for the R-134a air conditioning system on
this vehicle. This nylon tube helps to further contain
the R-134a refrigerant, which has a smaller molecu-
lar structure than R-12 refrigerant. The ends of the
refrigerant hoses are made from lightweight alumi-
num or steel, and commonly use braze-less fittings.
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from an exhaust manifold.
OPERATION- REFRIGERANT LINES
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
The refrigerant lines and hoses are coupled with
other components of the HVAC system with either
O-rings or dual plane seals.
The refrigerant lines and hoses cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, they must be replaced.
WARNING
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
WARNING: THE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM IS
DESIGNED TO DEVELOP INTERNAL PRESSURES
OF 97 TO 123 KILOPASCALS (14 TO 18 POUNDS
PER SQUARE INCH). DO NOT REMOVE OR
LOOSEN THE COOLANT PRESSURE CAP, CYLIN-
DER BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS, RADIATOR DRAIN,
RADIATOR HOSES, HEATER HOSES, OR HOSE
CLAMPS WHILE THE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM IS
HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE. FAILURE TO
OBSERVE THIS WARNING CAN RESULT IN SERI-
OUS BURNS FROM THE HEATED ENGINE COOL-
ANT. ALLOW THE VEHICLE TO COOL FOR A
MINIMUM OF 15 MINUTES BEFORE OPENING THE
COOLING SYSTEM FOR SERVICE.
24 - 42 PLUMBINGDR
Page 2552 of 2627

(1) Drain the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM DRAIN).
(2) Remove the heater hose retaining brackets as
required (depending on engine application).
(3) Using spring tension clamp pliers, compress
and slide the clamps off of each end of the hose being
removed (Fig. 25).
CAUTION: DO NOT apply excessive pressure on
heater tubes or connections when removing heater
hoses. Excessive pressure may damage or deform
the tubes/heater core, causing an engine coolant
leak.
(4) Disconnect each hose end by carefully twisting
the hose back and forth on the tube, while gently
pulling it away from the end of the tube.
(5) If necessary, carefully cut the hose end and
peel the hose off of the tube.
NOTE: Replacement of the heater return hose will
be required if the hose ends are cut for removal.
(6) Remove the heater return hose from the engine
compartment.
(7) Separate the heater hoses from each other as
required (depending on engine application).INSTALLATION
(1) If separated, reconnect the heater hoses to each
other as required (depending on engine application).
(2) Position the heater return hose into the engine
compartment.
(3) Using spring tension clamp pliers, compress
and slide each clamp away from the end of the hose
being installed.
(4) Install each hose by carefully twisting the hose
back and forth while gently pushing it onto the tube
end.
(5) Using spring tension clamp pliers, compress
and slide the clamps onto each end of the hose being
installed.
(6) Install the heater hose retaining brackets as
required (depending on engine application).
(7) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
LIQUID LINE
DESCRIPTION
The liquid line is the refrigerant line that carries
refrigerant from the A/C condenser to the evaporator.
The liquid line for this model consist of two separate
lines that connect to each other. The liquid lines are
made from light-weight aluminum or steel, and use
braze-less fittings.
The front half of the liquid line contains the fixed
orifice tube. The liquid lines are only serviced as an
assembly, except for the rubber O-ring seals used on
the end fittings. The liquid lines cannot be adjusted
or repaired and, if found to be leaking or damaged,
they must be replaced.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
WARNING) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) If equipped with the diesel engine, remove the
passenger side battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL).
(3) If equipped with the diesel engine, remove the
passenger side battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL).
(4) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
Fig. 25 Heater Hoses - Typical
1 - HEATER CORE TUBES
2 - HEATER INLET HOSE
3 - RETAINING BRACKET
4 - HOSE CONNECTOR
5 - SPRING CLAMP
6 - HEATER RETURN HOSE
DRPLUMBING 24 - 65
HEATER RETURN HOSE (Continued)