1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Vacuum hose
[x] Cancel search: Vacuum hosePage 2533 of 2627

STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE EQUIPMENT
WARNING: EYE PROTECTION MUST BE WORN
WHEN SERVICING AN AIR CONDITIONING REFRIG-
ERANT SYSTEM. TURN OFF (ROTATE CLOCKWISE)
ALL VALVES ON THE EQUIPMENT BEING USED
BEFORE CONNECTING TO, OR DISCONNECTING
FROM THE REFRIGERANT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO
OBSERVE THESE WARNINGS MAY RESULT IN PER-
SONAL INJURY.
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
WARNING) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION).
When servicing the air conditioning system, a
R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging sta-
tion that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be used
(Fig. 2). Contact an automotive service equipment
supplier for refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
equipment. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for proper care
and use of this equipment.
A manifold gauge set may be needed with some
recovery/recycling/charging equipment (Fig. 3). The
service hoses on the gauge set being used should
have manual (turn wheel), or automatic back-flow
valves at the service port connector ends. This will
prevent refrigerant from being released into the
atmosphere.
MANIFOLD GAUGE SET CONNECTIONS
CAUTION: Do not use an R-12 manifold gauge set
on an R-134a system. The refrigerants are not com-
patible and system damage will result.
LOW PRESSURE GAUGE HOSE The low pressure
hose (Blue with Black stripe) attaches to the low side
service port. This service port is located on the suc-
tion line between the accumulator outlet port and the
A/C compressor.
HIGH PRESSURE GAUGE HOSE The high pres-
sure hose (Red with Black stripe) attaches to the
high side service port. This service port is located on
the discharge line near the A/C compressor. On this
model, an A/C pressure transducer is installed onto
the high pressure service port. A/C high side pres-
sures can be read using a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to
Body Diagnostic Procedures.
RECOVERY/RECYCLING/EVACUATION/CHARG-
ING HOSE The center manifold hose (Yellow, or
White, with Black stripe) is used to recover, evacu-
ate, and charge the refrigerant system. When the low
or high pressure valves on the manifold gauge set
are opened, the refrigerant in the system will escape
through this hose.
Fig. 2 Refrigerant Recovery/Recycling Station -
Typical
1 - R-134a REFRIGERANT STATION
Fig. 3 MANIFOLD GAUGE SET - TYPICAL
1 - HIGH PRESSURE GAUGE
2 - VALVE
3 - VACUUM/REFRIGERANT HOSE (YELLOW W/ BLACK STRIPE)
4 - HIGH PRESSURE HOSE (RED W/ BLACK STRIPE)
5 - LOW PRESSURE HOSE (BLUE W/ BLACK STRIPE)
6 - VALVE
7 - LOW PRESSURE GAUGE
24 - 46 PLUMBINGDR
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 2571 of 2627

EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION - EVAP SYSTEM............10
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EVAP SYSTEM...............11
CCV HOSE
DESCRIPTION - 8.0L V-10................12
OPERATION - 8.0L V-10..................12
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................12
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION...............13
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................14
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16ORVR
DESCRIPTION.........................17
OPERATION...........................17
P C V VA LV E
DESCRIPTION.........................17
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE -
3.7L V-6/ 4.7L V-8......................20
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................22
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................22
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
NATURAL VAC LEAK DETECTION ASSY
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................25
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION - EVAP SYSTEM
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through vent hoses or tubes into the two charcoal
filled evaporative canisters. The canisters tempo-
rarily hold the vapors. The Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum to draw
vapors into the combustion chambers during certain
operating conditions.
All gasoline powered engines use a duty cycle
purge system. The PCM controls vapor flow by oper-
ating the duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid. Refer to
Duty Cycle EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid for addi-
tional information.When equipped with certain emissions packages, a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) will be used as part of
the evaporative system. This pump is used as a part
of OBD II requirements. Refer to Leak Detection
Pump for additional information. Other emissions
packages will use a Natural Vacuum Leak Detection
(NVLD) system in place of the LDP. Refer to NVLD
for additional information.
NOTE: The hoses used in this system are specially
manufactured. If replacement becomes necessary, it
is important to use only fuel resistant hose.
Certain EVAP system components can be found in
(Fig. 1).
25 - 10 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
Page 2573 of 2627

CCV HOSE
DESCRIPTION - 8.0L V-10
The 8.0L V-10 engine is equipped with a Crankcase
Ventilation (CCV) system. The CCV system performs
the same function as a conventional PCV system, but
does not use a vacuum controlled valve (PCV valve).
A molded vacuum tube connects manifold vacuum
to the top of the right cylinder head (valve) cover.
The vacuum tube connects to a fixed orifice fitting
(Fig. 2) of a calibrated size 2.6 mm (0.10 inches).
OPERATION - 8.0L V-10
A molded vacuum tube connects manifold vacuum
to the top of the right cylinder head (valve) cover.
The vacuum tube connects to a fixed orifice fitting
(Fig. 2) of a calibrated size 2.6 mm (0.10 inches). The
fitting meters the amount of crankcase vapors drawn
out of the engine.The fixed orifice fitting is grey
in color.A similar fitting (but does not contain a
fixed orifice) is used on the left cylinder head (valve)
cover. This fitting is black in color. Do not inter-
change these two fittings.
When the engine is operating, fresh air enters the
engine and mixes with crankcase vapors. Manifold
vacuum draws the vapor/air mixture through the
fixed orifice and into the intake manifold. The vapors
are then consumed during engine combustion.
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid is
located in the engine compartment. It is attached to
the side of the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) operates
the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM ener-
gizes and de-energizes the solenoid 5 or 10 times per
second, depending upon operating conditions. The
PCM varies the vapor flow rate by changing solenoid
pulse width. Pulse width is the amount of time the
solenoid energizes. The PCM adjusts solenoid pulse
width based on engine operating condition.
REMOVAL
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid is
located in the engine compartment. It is attached to
the side of the Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig.
3).
(1) Disconnect electrical wiring connector at sole-
noid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum harness at solenoid (Fig. 3).
(3) Remove solenoid from mounting bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install solenoid assembly to mounting bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum harness.
(3) Connect electrical connector.
Fig. 2 FIXED ORIFICE FITTING - 8.0L V-10 ENGINE -
TYPICAL
1 - VACUUM TUBE
2 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
3 - COIL PACKS
4 - ORIFICE FITTING HOSE CONNECTIONS
25 - 12 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
Page 2577 of 2627

PUMPING ACTION
Action : During portions of this test, the PCM uses
the reed switch to monitor diaphragm movement.
The solenoid is only turned on by the PCM after the
reed switch changes from open to closed, indicating
that the diaphragm has moved down. At other times
during the test, the PCM will rapidly cycle the LDP
solenoid on and off to quickly pressurize the system.
During rapid cycling, the diaphragm will not move
enough to change the reed switch state. In the state
of rapid cycling, the PCM will use a fixed time inter-
val to cycle the solenoid. If the system does not pass
the EVAP Leak Detection Test, the following DTCs
may be set:
²P0442 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR 0.0409LEAK
DETECTED
²P0455 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR LARGE LEAK
DETECTED
²P0456 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR 0.0209LEAK
DETECTED
²P1486 - EVAP LEAK MON PINCHED HOSE
FOUND
²P1494 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP SW OR
MECH FAULT
²P1495 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP SOLENOID
CIRCUIT
REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) and LDP filter
are attached to the front of the EVAP canister
mounting bracket (Fig. 9). This is located near the
front of the fuel tank. The LDP and LDP filter are
replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Carefully remove hose at LDP filter.
(3) Remove LDP filter mounting bolt and remove
from vehicle.
(4) Carefully remove vapor/vacuum lines at LDP.
(5) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP.
(6) Remove LDP mounting bolt and remove LDP
from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
The LDP and LDP filter are attached to the front
of the EVAP canister mounting bracket. The LDP
and LDP filter are replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Install LDP to mounting bracket. Refer to
Torque Specifications.
(2) Install LDP filter to mounting bracket. Refer to
Torque Specifications.
(3) Carefully install vapor/vacuum lines to LDP,
and install hose to LDP filter.The vapor/vacuum
lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Fig. 8 DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Closed)
3 - Vent Valve (Closed)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Open)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Closed)
Fig. 9 LDP AND LDP FILTER LOCATION
1 - LDP
2 - LDP MOUNTING BOLT
3 - ELEC. CONNEC.
4 - FILTER MOUNTING BOLT
5 - LDP FILTER
6 - CONNECTING HOSE
7 - EVAP CANISTER MOUNTING BRACKET
8 - EVAP CANISTERS (2)
25 - 16 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2578 of 2627

Check the vapor/vacuum lines at the LDP, LDP
filter and EVAP canister purge solenoid for
damage or leaks. If a leak is present, a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
(4) Connect electrical connector to LDP.
ORVR
DESCRIPTION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system consists of a unique fuel tank, flow manage-
ment valve, fluid control valve, one-way check valve
and vapor canister.
OPERATION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system is used to remove excess fuel tank vapors.
This is done while the vehicle is being refueled.
Fuel flowing into the fuel filler tube (approx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect drawing air into the
fuel fill tube. During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the EVAP canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are
no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the
refueling vapors are captured by the EVAP canister,
the vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapor flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no, or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fuel fill tube, it
opens the normally closed check valve and enters the
fuel tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank
through the control valve and on to the vapor canis-
ter. Vapor is absorbed in the EVAP canister until
vapor flow in the lines stops. This stoppage occurs
following fuel shut-off, or by having the fuel level in
the tank rise high enough to close the control valve.
This control valve contains a float that rises to seal
the large diameter vent path to the EVAP canister.
At this point in the refueling process, fuel tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing liq-
uid fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel
then rises up the fuel filler tube to shut off the dis-
pensing nozzle.
PCV VALVE
DESCRIPTION
3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
The 3.7L V-6 and 4.7L V-8 engines are equipped
with a closed crankcase ventilation system and a
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve.
This system consists of:
²a PCV valve mounted to the oil filler housing
(Fig. 10). The PCV valve is sealed to the oil filler
housing with an o-ring.
²the air cleaner housing
²two interconnected breathers threaded into the
rear of each cylinder head (Fig. 11).
²tubes and hoses to connect the system compo-
nents.
Fig. 10 PCV VALVE - 3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
DREVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 17
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2580 of 2627

OPERATION
The PCV system operates by engine intake mani-
fold vacuum (Fig. 15). Filtered air is routed into the
crankcase through the air cleaner hose. The metered
air, along with crankcase vapors, are drawn through
the PCV valve and into a passage in the intake man-
ifold. The PCV system manages crankcase pressure
and meters blow by gases to the intake system,
reducing engine sludge formation.The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
This plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
When the engine is not operating or during an
engine pop-back, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat (Fig. 16). This will prevent vapors
from flowing through the valve.
During periods of high manifold vacuum, such as
idle or cruising speeds, vacuum is sufficient to com-
pletely compress spring. It will then pull the plunger
to the top of the valve (Fig. 17). In this position there
is minimal vapor flow through the valve.
During periods of moderate manifold vacuum, the
plunger is only pulled part way back from inlet. This
results in maximum vapor flow through the valve
(Fig. 18).
Fig. 14 PCV VALVE/HOSE - 5.9L V-8
1 - P C V VA LV E
2 - PCV VALVE HOSE CONNECTIONS
Fig. 15 TYPICAL CLOSED CRANKCASE
VENTILATION SYSTEM
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - AIR CLEANER
3 - AIR INTAKE
4 - P C V VA LV E
5 - COMBUSTION CHAMBER
6 - BLOW-BY GASES
7 - CRANKCASE BREATHER/FILTER
Fig. 16 ENGINE OFF OR ENGINE BACKFIRE - NO
VAPOR FLOW
Fig. 17 HIGH INTAKE MANIFOLD VACUUM -
MINIMAL VAPOR FLOW
Fig. 18 MODERATE INTAKE MANIFOLD VACUUM -
MAXIMUM VAPOR FLOW
DREVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 19
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 2581 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE - 3.7L
V-6/ 4.7L V-8
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 19) by discon-
necting rubber connecting hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward until locating tabs have been
freed at cam lock (Fig. 19). After tabs have cleared,
pull valve straight out from filler tube.To prevent
damage to PCV valve locating tabs, valve must
be pointed downward for removal. Do not force
valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 19). Also, PCV valve should rattle when
shaken.
(4) Reconnect PCV valve to its connecting line/
hose.
(5) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(6) If valve is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through valve. Also, a strong vac-
uum should be felt with a finger placed at valve
inlet.
(7) If vacuum is not felt at valve inlet, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at rear of manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out the
fitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
(8)Do not attempt to clean the old PCV valve.
(9) Return PCV valve back to oil filler tube by
placing valve locating tabs (Fig. 19) into cam lock.
Press PCV valve in and rotate valve upward. A slight
click will be felt when tabs have engaged cam lock.
Valve should be pointed towards rear of vehicle.
(10) Connect PCV line/hose and connecting rubber
hose to PCV valve.
(11) Disconnect rubber hose from fresh air fitting
at air cleaner resonator box. Start engine and bring
to idle speed. Hold a piece of stiff paper (such as a
parts tag) loosely over the opening of the discon-
nected rubber hose.
(12) The paper should be drawn against the hose
opening with noticeable force. This will be after
allowing approximately one minute for crankcase
pressure to reduce.
(13) If vacuum is not present, disconnect each PCV
system hose at top of each crankcase breather (Fig.
20). Check for obstructions or restrictions.
(14) If vacuum is still not present, remove each
PCV system crankcase breather (Fig. 20) from each
cylinder head. Check for obstructions or restrictions.
If plugged, replace breather. Tighten breather to 12
N´m (106 in. lbs.) torque. Do not attempt to clean
breather.(15) If vacuum is still not present, disconnect each
PCV system hose at each fitting, and at each check
valve (Fig. 21). Check for obstructions or restrictions.
Fig. 19 PCV VALVE - 3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 20 CRANKCASE BREATHERS (2) - 3.7L V-6 /
4.7L V-8
1 - CRANKCASE BREATHERS (2)
2 - REAR OF ENGINE
25 - 20 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 2583 of 2627
5.7L V-8
(1) Clean out intake manifold opening.
(2) Check condition of 2 o-rings on PCV valve.
(3) Apply engine oil to 2 o-rings.
(4) Place PCV valve into intake manifold and
rotate 90 degrees clockwise for installation.
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION
A vacuum schematic for emission related items can
be found on the vehicles VECI label. Refer to Vehicle
Emission Control Information (VECI) Label for label
location.
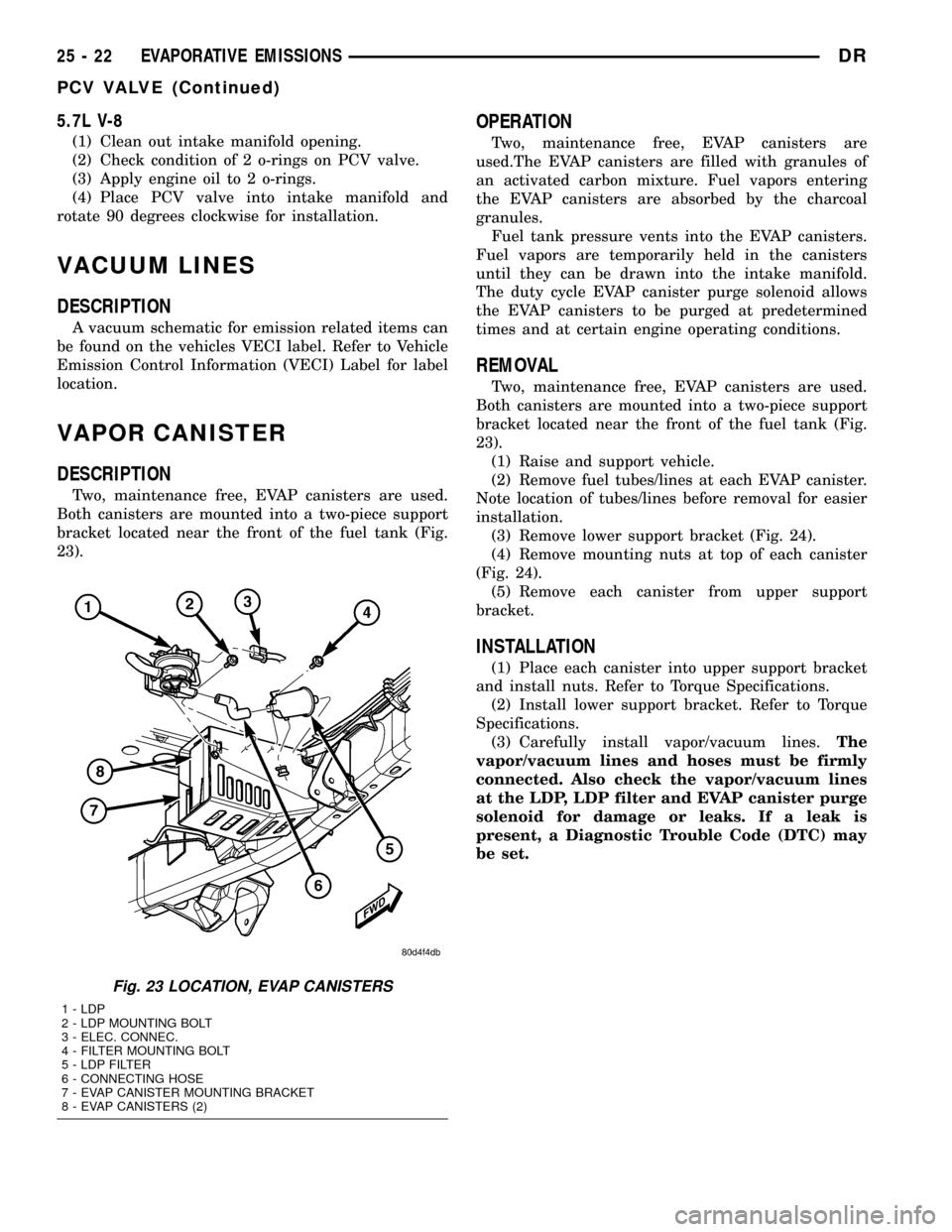
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are used.
Both canisters are mounted into a two-piece support
bracket located near the front of the fuel tank (Fig.
23).
OPERATION
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are
used.The EVAP canisters are filled with granules of
an activated carbon mixture. Fuel vapors entering
the EVAP canisters are absorbed by the charcoal
granules.
Fuel tank pressure vents into the EVAP canisters.
Fuel vapors are temporarily held in the canisters
until they can be drawn into the intake manifold.
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid allows
the EVAP canisters to be purged at predetermined
times and at certain engine operating conditions.
REMOVAL
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are used.
Both canisters are mounted into a two-piece support
bracket located near the front of the fuel tank (Fig.
23).
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove fuel tubes/lines at each EVAP canister.
Note location of tubes/lines before removal for easier
installation.
(3) Remove lower support bracket (Fig. 24).
(4) Remove mounting nuts at top of each canister
(Fig. 24).
(5) Remove each canister from upper support
bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place each canister into upper support bracket
and install nuts. Refer to Torque Specifications.
(2) Install lower support bracket. Refer to Torque
Specifications.
(3) Carefully install vapor/vacuum lines.The
vapor/vacuum lines and hoses must be firmly
connected. Also check the vapor/vacuum lines
at the LDP, LDP filter and EVAP canister purge
solenoid for damage or leaks. If a leak is
present, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) may
be set.
Fig. 23 LOCATION, EVAP CANISTERS
1 - LDP
2 - LDP MOUNTING BOLT
3 - ELEC. CONNEC.
4 - FILTER MOUNTING BOLT
5 - LDP FILTER
6 - CONNECTING HOSE
7 - EVAP CANISTER MOUNTING BRACKET
8 - EVAP CANISTERS (2)
25 - 22 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
PCV VALVE (Continued)