1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Control module
[x] Cancel search: Control modulePage 1837 of 2627

IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan gas-
ket surface (Fig. 2). Refer to this information when
ordering replacement parts.
GEAR RATIOS
The 48RE gear ratios are:
1st.................................2.45:1
2nd................................1.45:1
3rd................................1.00:1
4th.................................0.69:1
Rev.................................2.20:1
OPERATION
The application of each driving or holding compo-
nent is controlled by the valve body based upon the
manual lever position, throttle pressure, and gover-
nor pressure. The governor pressure is a variable
pressure input to the valve body and is one of the
signals that a shift is necessary. First through fourth
gear are obtained by selectively applying and releas-
ing the different clutches and bands. Engine power is
thereby routed to the various planetary gear assem-
blies which combine with the overrunning clutch
assemblies to generate the different gear ratios. The
torque converter clutch is hydraulically applied and
is released when fluid is vented from the hydraulic
circuit by the torque converter control (TCC) solenoid
on the valve body. The torque converter clutch is con-
trolled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The
torque converter clutch engages in fourth gear, and
in third gear under various conditions, such as when
the O/D switch is OFF, when the vehicle is cruising
on a level surface after the vehicle has warmed up.
The torque converter clutch can also be engaged in
the MANUAL SECOND gear position if high trans-
mission temperatures are sensed by the PCM. The
torque converter clutch will disengage momentarily
when an increase in engine load is sensed by the
PCM, such as when the vehicle begins to go uphill or
the throttle pressure is increased. The torque con-
verter clutch feature increases fuel economy and
reduces the transmission fluid temperature.
Since the overdrive clutch is applied in fourth gear
only and the direct clutch is applied in all ranges
except fourth gear, the transmission operation for
park, neutral, and first through third gear will be
described first. Once these powerflows are described,
the third to fourth shift sequence will be described.
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER 10 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - INPUT SHAFT 11 - DIRECT CLUTCH
3 - OIL PUMP 12 - PLANETARY GEAR
4 - FRONT BAND 13 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
5 - FRONT CLUTCH 14 - OVERDRIVE OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
6 - REAR CLUTCH 15 - DIRECT CLUTCH SPRING
7 - PLANETARIES 16 - OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER
8 - REAR BAND 17 - OIL PAN
9 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH 18 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 2 Transmission Part Number And Serial
Number Location
1 - PART NUMBER
2 - BUILD DATE
3 - SERIAL NUMBER
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1842 of 2627
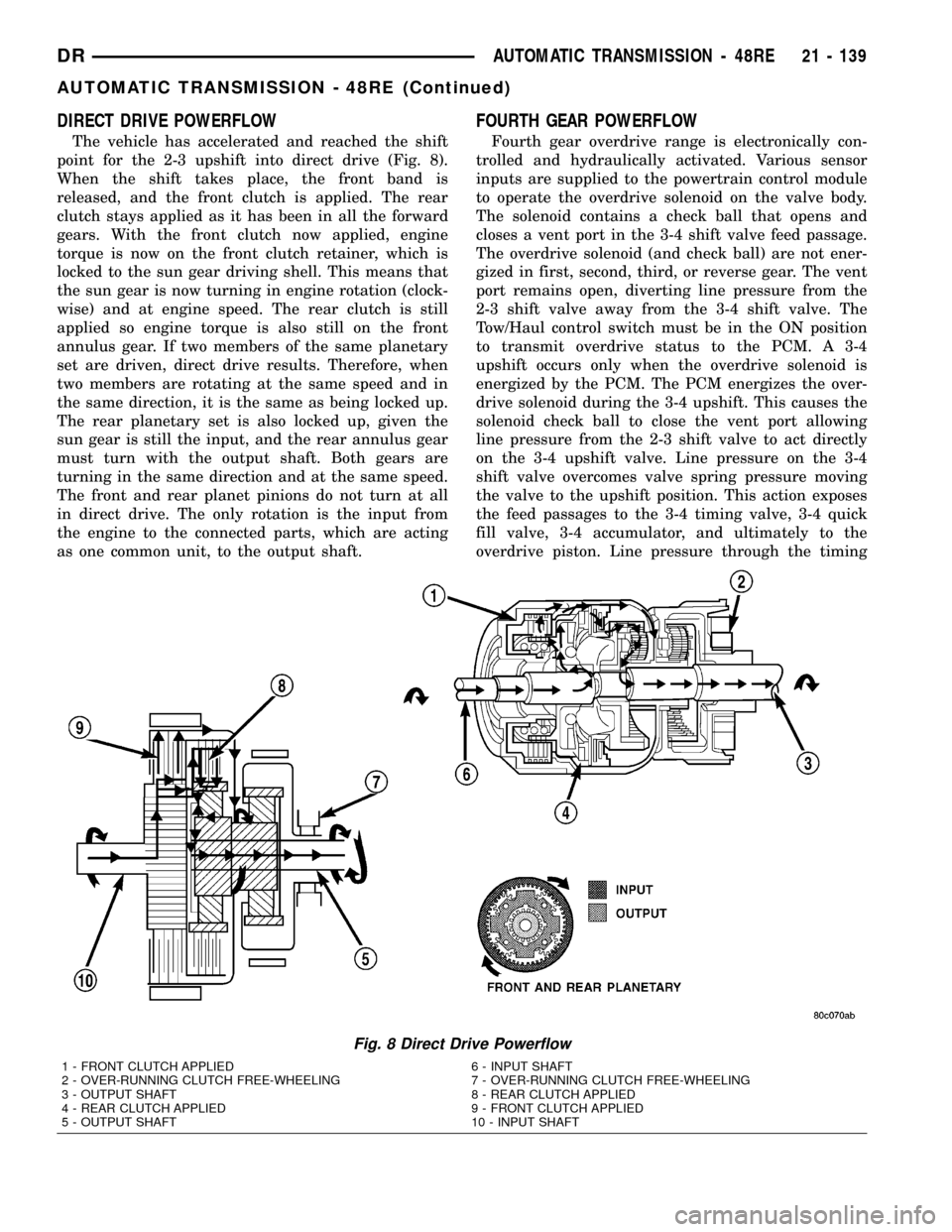
DIRECT DRIVE POWERFLOW
The vehicle has accelerated and reached the shift
point for the 2-3 upshift into direct drive (Fig. 8).
When the shift takes place, the front band is
released, and the front clutch is applied. The rear
clutch stays applied as it has been in all the forward
gears. With the front clutch now applied, engine
torque is now on the front clutch retainer, which is
locked to the sun gear driving shell. This means that
the sun gear is now turning in engine rotation (clock-
wise) and at engine speed. The rear clutch is still
applied so engine torque is also still on the front
annulus gear. If two members of the same planetary
set are driven, direct drive results. Therefore, when
two members are rotating at the same speed and in
the same direction, it is the same as being locked up.
The rear planetary set is also locked up, given the
sun gear is still the input, and the rear annulus gear
must turn with the output shaft. Both gears are
turning in the same direction and at the same speed.
The front and rear planet pinions do not turn at all
in direct drive. The only rotation is the input from
the engine to the connected parts, which are acting
as one common unit, to the output shaft.
FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
Tow/Haul control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
Fig. 8 Direct Drive Powerflow
1 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED 6 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING 7 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT 8 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED
4 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED 9 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED
5 - OUTPUT SHAFT 10 - INPUT SHAFT
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 139
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1846 of 2627

(3) Have helper start and run engine at 1600 rpm
for test.
(4)
Move transmission shift lever four detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is Reverse range.
(5) Move transmission throttle lever fully forward
then fully rearward and note reading at Gauge
C-3293-SP.
(6) Pressure should be 145 - 175 psi (1000-1207
kPa) with throttle lever forward and increase to 230 -
280 psi (1586-1931 kPa) as lever is gradually moved
rearward.
Test Five - Governor Pressure
This test checks governor operation by measuring
governor pressure response to changes in vehicle
speed. It is usually not necessary to check governor
operation unless shift speeds are incorrect or if the
transmission will not downshift. The test should be
performed on the road or on a hoist that will allow
the rear wheels to rotate freely.
(1) Move 100 psi Test Gauge C-3292 to governor
pressure port.
(2) Move transmission shift lever two detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is D range.
(3) Have helper start and run engine at curb idle
speed. Then firmly apply service brakes so wheels
will not rotate.
(4) Note governor pressure:
²
Governor pressure should be no more than 20.6
kPa (3 psi) at curb idle speed and wheels not rotating.
²If pressure exceeds 20.6 kPa (3 psi), a fault
exists in governor pressure control system.
(5) Release brakes, slowly increase engine speed,
and observe speedometer and pressure test gauge (do
not exceed 30 mph on speedometer). Governor pres-
sure should increase in proportion to vehicle speed.
Or approximately 6.89 kPa (1 psi) for every 1 mph.
(6) Governor pressure rise should be smooth and
drop back to no more than 20.6 kPa (3 psi), after
engine returns to curb idle and brakes are applied to
prevent wheels from rotating.
(7)
Compare results of pressure test with analysis
chart.
Test Six - Transmission In Overdrive Fourth Gear
This test checks line pressure at the overdrive
clutch in fourth gear range. Use 300 psi Test Gauge
C-3293-SP for this test. The test should be performed
on the road or on a chassis dyno.
(1)
Remove tachometer; it is not needed for this test.
(2) Move 300 psi Gauge to overdrive clutch pres-
sure test port. Then remove other gauge and reinstall
test port plug.
(3) Lower vehicle.
(4) Turn OD switch on.(5) Secure test gauge so it can be viewed from
drivers seat.
(6) Start engine and shift into D range.
(7) Increase vehicle speed gradually until 3-4 shift
occurs and note gauge pressure.
(8) Pressure should be 524-565 kPa (76-82 psi)
with closed throttle and increase to 690-896 kPa
(100-130 psi) at 1/2 to 3/4 throttle. Note that pres-
sure can increase to around 965 kPa (140 psi) at full
throttle.
(9) Return to shop or move vehicle off chassis
dyno.
PRESSURE TEST ANALYSIS CHART
TEST CONDITION INDICATION
Line pressure OK during
any one testPump and regulator
valve OK
Line pressure OK in R
but low in D, 2, 1Leakage in rear clutch
area (seal rings, clutch
seals)
Pressure low in D Fourth
Gear RangeOverdrive clutch piston
seal, or check ball
problem
Pressure OK in 1, 2 but
low in D3 and RLeakage in front clutch
area
Pressure OK in 2 but low
in R and 1Leakage in rear servo
Front servo pressure in 2 Leakage in servo; broken
servo ring or cracked
servo piston
Pressure low in all
positionsClogged filter, stuck
regulator valve, worn or
faulty pump, low oil level
Governor pressure too
high at idle speedGovernor pressure
solenoid valve system
fault. Refer to diagnostic
book.
Governor pressure low at
all mph figuresFaulty governor pressure
solenoid, transmission
control module, or
governor pressure
sensor
Lubrication pressure low
at all throttle positionsClogged fluid cooler or
lines, seal rings leaking,
worn pump bushings,
pump, clutch retainer, or
clogged filter.
Line pressure high Output shaft plugged,
sticky regulator valve
Line pressure low Sticky regulator valve,
clogged filter, worn pump
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 143
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1900 of 2627

BTSI FUNCTION CHECK
(1) Verify removal of ignition key allowed in PARK
position only.
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK, the ignition
key cylinder should rotate freely from off to lock.
When the shifter is in any other position, the ignition
key should not rotate from off to lock.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should be possible when
the ignition key cylinder is in the off position.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal force, and ignition key cylin-
der is in the run or start positions, unless the foot
brake pedal is depressed approximately 1/2 inch
(12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the accessory or
lock position.
(6) Shifting between any gear and NEUTRAL, or
PARK, may be done without depressing foot brake
with ignition switch in run or start positions.
(7) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL positions only. Engine
starts must not be possible in any position other than
PARK or NEUTRAL.
(8) With shifter lever in the:
²PARK position - Apply upward force on the shift
arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must be
possible.²PARK position - Apply downward force on the
shift arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must
be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Normal position. Engine
starts must be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Engine running and brakes
applied, apply upward force on the shift arm. Trans-
mission shall not be able to shift from neutral to
reverse.
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION
Governor pressure is controlled electronically. Com-
ponents used for governor pressure control include:
²Governor body
²Valve body transfer plate
²Governor pressure solenoid valve
²Governor pressure sensor
²Fluid temperature thermistor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Transmission speed sensor
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The solenoid valve is a duty-cycle solenoid which
regulates the governor pressure needed for upshifts
and downshifts. It is an electro-hydraulic device
located in the governor body on the valve body trans-
fer plate (Fig. 76).
Fig. 75 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
Fig. 76 Governor Pressure Solenoid Valve
1 - SOLENOID FILTER
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 197
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1901 of 2627

GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The governor pressure sensor measures output
pressure of the governor pressure solenoid valve (Fig.
77).
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate is designed to supply transmis-
sion line pressure to the governor pressure solenoid
valve and to return governor pressure.
The governor pressure solenoid valve is mounted in
the governor body. The body is bolted to the lower
side of the transfer plate (Fig. 77).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absenceof sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher
than normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
Fig. 77 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 198 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1902 of 2627

sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
heavily loaded vehicle or on steep grades. When
hunting occurs, it is very objectionable because shifts
are frequent and accompanied by large changes in
noise and acceleration.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive mem-
ory in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the
preprogrammed optimum speed. WOT operation is
determined from the throttle position sensor, which
is also a part of the emission control system. The ini-
tial setting for the WOT upshift is below the opti-
mum engine speed. As WOT shifts are repeated, the
PCM learns the time required to complete the shifts
by comparing the engine speed when the shifts occur
to the optimum speed. After each shift, the PCM
adjusts the shift point until the optimum speed is
reached. The PCM also considers vehicle loading,
grade and engine performance changes due to high
altitude in determining when to make WOT shifts. It
does this by measuring vehicle and engine accelera-
tion and then factoring in the shift time.
TRANSFER CASE LOW RANGE OPERATION
On four-wheel drive vehicles operating in low
range, the engine can accelerate to its peak more
rapidly than in Normal range, resulting in delayed
shifts and undesirable engine9flare.9The low range
governor pressure curve is also higher than normal
to initiate upshifts sooner. The PCM compares elec-
tronic vehicle speed signal used by the speedometer
to the transmission output shaft speed signal to
determine when the transfer case is in low range.REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Remove transmission fluid pan and filter.
(3) Disengage wire connectors from pressure sen-
sor and solenoid (Fig. 78).
(4) Remove screws holding pressure solenoid
retainer to governor body.
(5) Separate solenoid retainer from governor (Fig.
79).
Fig. 78 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 79 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 199
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1956 of 2627

SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The speed sensor (Fig. 221) is located in the over-
drive gear case. The sensor is positioned over the
park gear and monitors transmission output shaft
rotating speed.
OPERATION
Speed sensor signals are triggered by the park
gear lugs as they rotate past the sensor pickup face.
Input signals from the sensor are sent to the trans-
mission control module for processing. Signals from
this sensor are shared with the powertrain control
module.
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Transmission throttle valve cable (Fig. 222) adjust-
ment is extremely important to proper operation.
This adjustment positions the throttle valve, which
controls shift speed, quality, and part-throttle down-
shift sensitivity.
If cable setting is too loose, early shifts and slip-
page between shifts may occur. If the setting is too
tight, shifts may be delayed and part throttle down-
shifts may be very sensitive.
The transmission throttle valve is operated by a
cam on the throttle lever. The throttle lever is oper-
ated by an adjustable cable (Fig. 223). The cable is
attached to an arm mounted on the throttle lever
shaft. A retaining clip at the engine-end of the cable
is removed to provide for cable adjustment. The
retaining clip is then installed back onto the throttle
valve cable to lock in the adjustment.
Fig. 222 Throttle Valve Cable Attachment - At Engine
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - CABLE BRACKET
3 - THROTTLE BODY LEVER
4 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
5 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
Fig. 223 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
Fig. 221 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED SENSOR
2 - SEAL
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 253
Page 1963 of 2627

STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 234).
Under stall conditions the turbine is stationary and
the oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of
the stator blades and tries to rotate them in a coun-
terclockwise direction. When this happens the over-
running clutch of the stator locks and holds the
stator from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil
strikes the stator blades and is redirected into a
ªhelpingº direction before it enters the impeller. This
circulation of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to
stator, and stator to impeller, can produce a maxi-
mum torque multiplication of about 1.75:1. As the
turbine begins to match the speed of the impeller, the
fluid that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied or released when fluid is feed or vented from
the hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in FOURTH gear, and in THIRD gear under various
conditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, orwhen the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after
the vehicle has warmed up. The torque converter
clutch can also be engaged in the MANUAL SEC-
OND gear position if high transmission temperatures
are sensed by the PCM. The torque converter clutch
may disengage momentarily when an increase in
engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when the
vehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pressure is
increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
Fig. 234 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 260 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)