1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Body
[x] Cancel search: BodyPage 1671 of 2627

TILT LEVER KNOB RELEASE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the tilt lever handle.
(2) Remove the steering column opening cover
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN OPENING COVER - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the lower shroud.
NOTE: Use special care not to pry on the clock-
spring electrical connector when removing or
installing the mounting screw located next to the
clockspring.
(4) Remove the two mounting screws from the tilt
lever knob release bracket (Fig. 22).
(5) Disconnect the electrical harness plastic
mounting tab from the the bracket (Fig. 22).
(6) Unsnap the cable from the bracket (Fig. 23).
(7) Remove the end of the cable from the tilt lever
knob release bracket (Fig. 24).
INSTALLATION
(1) Route the cable into the tilt lever release knob
bracket (Fig. 24).
(2) Snap the cable end into the bracket (Fig. 23).
NOTE: Use special care not to pry on the clock-
spring electrical connector when removing or
installing the mounting screw located next to the
clockspring.
NOTE: New screws should be used when installing
the tilt lever release knob bracket to the column.(3) Install the tilt lever release knob bracket to the
column and install the two new mounting screws
(Fig. 22) Tighten the two new screws to 4.5 N´m (40
in. lbs.).
(4) Install the electrical harness plastic mounting
tab to the bracket (Fig. 22).
(5) Install the lower shroud.
(6) Install the steering column opening cover
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTALLA-
TION).
(7) Install the tilt lever handle.
Fig. 22 TILT LEVER KNOB RELEASE BRACKET
1 - TILT LEVER RELEASE KNOB BRACKET
2 - ELECTRICAL HARNESS TAB
3 - MOUNTING SCREWS (2)
Fig. 23 CABLE UNSNAPPED
1 - TILT LEVER RLEASE KNOB BRACKET
2 - TILT LEVER CABLE REMOVAL/INSTALL
Fig. 24 END OF CABLE TO THE TILT LEVER
RELEASE KNOB
1 - TILT LEVER RELEASE KNOB BRACKET
2 - END OF CABLE REMOVAL/INSTALL
19 - 16 COLUMNDR
Page 1696 of 2627

(8) Fill the system with fluid and perform Steering
Pump Initial Operation, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/
PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(9) Start the engine and run it for fifteen minutes
then stop the engine.
(10) Remove the return line/lines from the pump
and plug the pump port/ports.
(11) Pour fresh fluid into the reservoir and check
the draining fluid for contamination. If the fluid is
still contaminated, then flush the system again.
(12) Install the return line/lines and perform
Steering Pump Initial Operation, (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GAS
(1) Drain and siphon the power steering fluid from
the reservoir.
(2) Remove the serpentine belt.
CAUTION: Do not remove the fitting on the pump
that the high pressure hose screws into. The fitting
may come loose unless it is backed up using
another wrench. If the fitting does come loose, it
must be retightened before continuing. (57 - 67Nm,
40 - 50 lbft) If this fitting comes out of the pump
body, the internal spring and valve parts will fall out
of the pump and they cannot be reinstalled prop-
erly. If this occurs the pump needs to be replaced
with a new pump.
(3) Disconnect the return hose. (Fig. 2)
(4) Disconnect the pressure hose. (Fig. 2)
(5) Access to remove the three bolts securing the
pump to the cylinder head can be gained thru the
pulley holes. (Fig. 2)
REMOVAL - DIESEL
(1) Drain and siphon the power steering fluid from
the reservoir.
(2) Remove the serpentine belt.
CAUTION: Do not remove the fitting on the pump
that the high pressure hose screws into. The fitting
may come loose unless it is backed up using
another wrench. If the fitting does come loose, it
must be retightened before continuing. (57 - 67Nm,
40 - 50 lbft) If this fitting comes out of the pump
body, the internal spring and valve parts will fall out
of the pump and they cannot be reinstalled prop-
erly. If this occurs the pump needs to be replaced
with a new pump.
(3) Disconnect the return hose.
(4) Disconnect the pressure hose.(5) Access to remove the three bolts securing the
pump to the cylinder head can be gained thru the
pulley holes.
(6) Loosen the pump bracket to the block.
(7) Remove the 6 intake plenum bolts (Fig. 3).
(8) loosen the inner cooler tube clamp at the
intake plenum and remove the intake plenum.
(9) Loosen the inner cooler tube clamp at the radi-
ator support side and remove the tube from the vehi-
cle.
(10) Remove the power steering pump from the top
of the engine compartment where the intake plenum
was (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 POWER STEERING PUMP
1 - POWER STEERING PULLEY
2 - POWER STEERING RESERVOIR
3 - RETURN HOSE
4 - HIGH PRESSURE HOSE
Fig. 3 POWER STEERING PUMP ACCESS
1 - INTAKE PLENUM MOUNTING
2 - POWER STEERING PUMP
DRPUMP 19 - 41
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1702 of 2627

PULLEY
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Do not reuse the old power steering
pump pulley it is not intended for reuse. A new pul-
ley must be installed if removed.
(1) Remove the power steering pump assembly,
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the pulley from the pump using (OTCt
7185) power steering pulley removal tool or equiva-
lent (Fig. 10).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do not reuse the old power steering
pump pulley it is not intended for reuse. A new pul-
ley must be installed if removed.
(1) Replace the pulley if it's bent, cracked, or loose.
(2) Install the pulley on the pump using (OTCt
7771) power steering pulley installation tool or equiv-
alent (Fig. 11) making sure it is flush with the end of
the shaft. Ensure the tool and pulley remain aligned
with the pump shaft.
(3) Install the power steering pump assembly,
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(4) Run engine until warm (5 min.) and note any
belt chirp. If chirp exists, move pulley outward
approximately 0.5 mm (0.020 in.). If noise increases,
press on 1.0 mm (0.040 in.).Be careful that pulley
does not contact mounting bolts.
RESERVOIR
REMOVAL
(1) Drain and siphon the power steering fluid from
the reservoir.
(2) Remove the serpentine belt.
(3) Remove the power steering pump (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the reservoir mounting bolts.
(5) Remove the reservoir.
(6) Remove the rear bracket to the pump mounting
bolts.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the reservoir bracket to the pump hous-
ing.Do not reuse the o-rings (install new
o-rings).Tighten bolts to 7 N´m (62 in. lbs.).
NOTE: Ensure the reservoir is fully seated onto the
pump.
(2) Install the reservoir to the bracket/pump body.
(3) Install the reservoir mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 13 N´m (120 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the power steering pump (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the serpentine drive belt, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(6) Fill the power steering pump, (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 10 PULLEY REMOVAL
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP
2 - PULLEY
3 - POWER STEERING PULLEY REMOVAL TOOL
Fig. 11 PULLEY INSTALLATION
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP
2 - PULLEY
3 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY INSTALLATION TOOL
DRPUMP 19 - 47
Page 1834 of 2627

OUTPUT SHAFT FRONT BEARING
REMOVAL............................216
INSTALLATION........................216
OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING
REMOVAL............................216
INSTALLATION........................217
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION........................217
OPERATION..........................217
OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL............................218
DISASSEMBLY........................218
CLEANING...........................225
INSPECTION.........................225
ASSEMBLY...........................226
INSTALLATION........................235
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE
PISTON RETAINER
DESCRIPTION........................236
OPERATION..........................236
DISASSEMBLY........................236
CLEANING...........................236
INSPECTION.........................237
ASSEMBLY...........................237
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION........................239
OPERATION..........................239
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT
DESCRIPTION........................241
OPERATION..........................241
DISASSEMBLY........................242
INSPECTION.........................243
ASSEMBLY...........................244
REAR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION........................247
OPERATION..........................248
DISASSEMBLY........................248
CLEANING...........................248
INSPECTION.........................248
ASSEMBLY...........................249
REAR SERVO
DESCRIPTION........................251
OPERATION..........................251
DISASSEMBLY........................251
CLEANING...........................251
ASSEMBLY...........................251
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................252OPERATION..........................252
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION........................252
OPERATION..........................252
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................253
OPERATION..........................253
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION........................253
ADJUSTMENTS - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE . 254
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................255
OPERATION..........................259
REMOVAL............................260
INSTALLATION........................260
TORQUE CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................261
OPERATION..........................261
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE........261
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................261
OPERATION..........................262
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERDRIVE
ELECTRICAL CONTROLS..............262
REMOVAL............................262
INSTALLATION........................262
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................263
OPERATION..........................263
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSMISSION
RANGE SENSOR (TRS)................264
REMOVAL............................265
INSTALLATION........................266
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................267
OPERATION..........................267
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................267
OPERATION..........................272
REMOVAL............................286
DISASSEMBLY........................287
CLEANING...........................298
INSPECTION.........................298
ASSEMBLY...........................299
INSTALLATION........................309
ADJUSTMENTS - VALVE BODY...........310
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 131
Page 1835 of 2627

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
48RE
DESCRIPTION
The 48RE (Fig. 1) is a four speed fully automatic
transmissions with an electronic governor. The 48RE
is equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.
The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and thelow/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
21 - 132 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
Page 1837 of 2627

IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan gas-
ket surface (Fig. 2). Refer to this information when
ordering replacement parts.
GEAR RATIOS
The 48RE gear ratios are:
1st.................................2.45:1
2nd................................1.45:1
3rd................................1.00:1
4th.................................0.69:1
Rev.................................2.20:1
OPERATION
The application of each driving or holding compo-
nent is controlled by the valve body based upon the
manual lever position, throttle pressure, and gover-
nor pressure. The governor pressure is a variable
pressure input to the valve body and is one of the
signals that a shift is necessary. First through fourth
gear are obtained by selectively applying and releas-
ing the different clutches and bands. Engine power is
thereby routed to the various planetary gear assem-
blies which combine with the overrunning clutch
assemblies to generate the different gear ratios. The
torque converter clutch is hydraulically applied and
is released when fluid is vented from the hydraulic
circuit by the torque converter control (TCC) solenoid
on the valve body. The torque converter clutch is con-
trolled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The
torque converter clutch engages in fourth gear, and
in third gear under various conditions, such as when
the O/D switch is OFF, when the vehicle is cruising
on a level surface after the vehicle has warmed up.
The torque converter clutch can also be engaged in
the MANUAL SECOND gear position if high trans-
mission temperatures are sensed by the PCM. The
torque converter clutch will disengage momentarily
when an increase in engine load is sensed by the
PCM, such as when the vehicle begins to go uphill or
the throttle pressure is increased. The torque con-
verter clutch feature increases fuel economy and
reduces the transmission fluid temperature.
Since the overdrive clutch is applied in fourth gear
only and the direct clutch is applied in all ranges
except fourth gear, the transmission operation for
park, neutral, and first through third gear will be
described first. Once these powerflows are described,
the third to fourth shift sequence will be described.
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER 10 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - INPUT SHAFT 11 - DIRECT CLUTCH
3 - OIL PUMP 12 - PLANETARY GEAR
4 - FRONT BAND 13 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
5 - FRONT CLUTCH 14 - OVERDRIVE OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
6 - REAR CLUTCH 15 - DIRECT CLUTCH SPRING
7 - PLANETARIES 16 - OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER
8 - REAR BAND 17 - OIL PAN
9 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH 18 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 2 Transmission Part Number And Serial
Number Location
1 - PART NUMBER
2 - BUILD DATE
3 - SERIAL NUMBER
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1842 of 2627
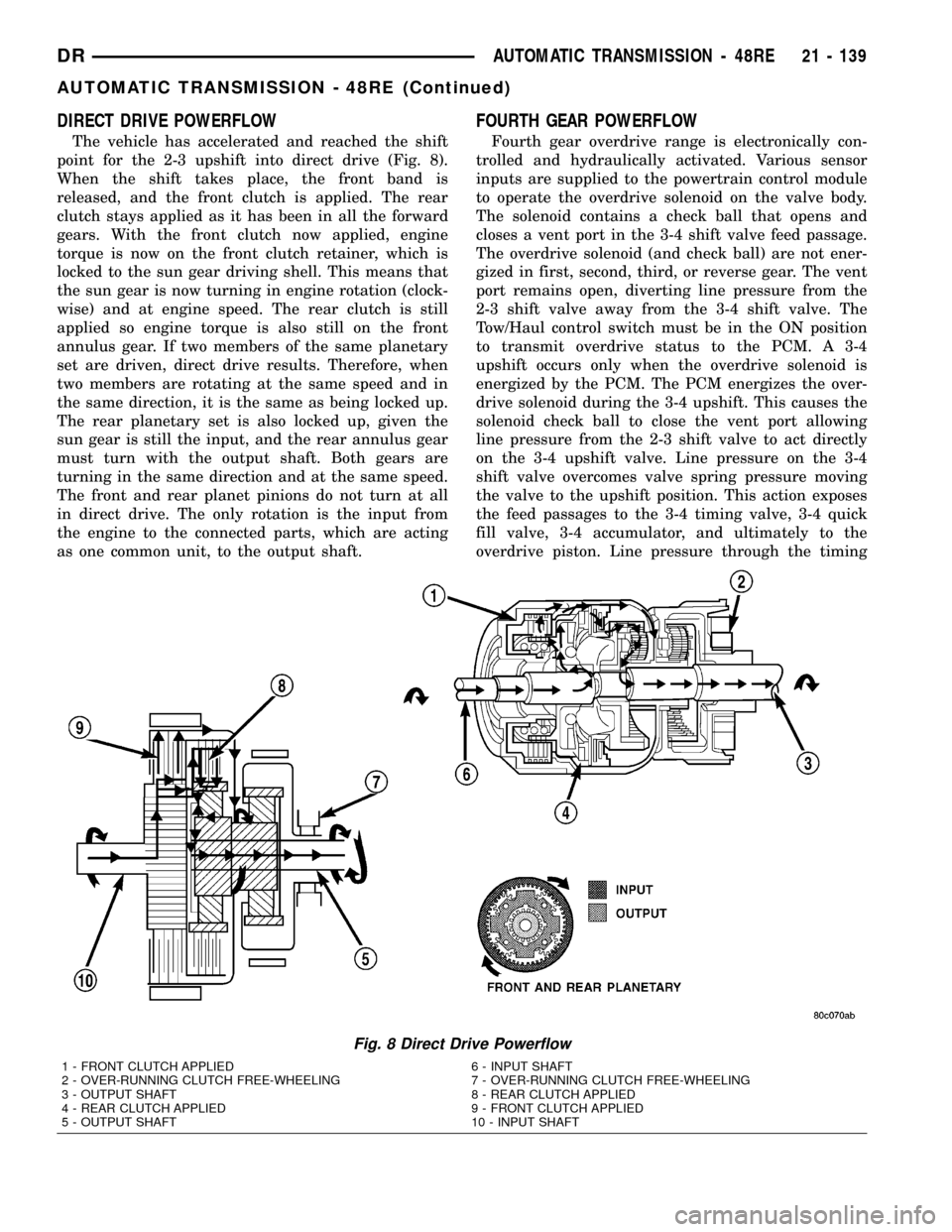
DIRECT DRIVE POWERFLOW
The vehicle has accelerated and reached the shift
point for the 2-3 upshift into direct drive (Fig. 8).
When the shift takes place, the front band is
released, and the front clutch is applied. The rear
clutch stays applied as it has been in all the forward
gears. With the front clutch now applied, engine
torque is now on the front clutch retainer, which is
locked to the sun gear driving shell. This means that
the sun gear is now turning in engine rotation (clock-
wise) and at engine speed. The rear clutch is still
applied so engine torque is also still on the front
annulus gear. If two members of the same planetary
set are driven, direct drive results. Therefore, when
two members are rotating at the same speed and in
the same direction, it is the same as being locked up.
The rear planetary set is also locked up, given the
sun gear is still the input, and the rear annulus gear
must turn with the output shaft. Both gears are
turning in the same direction and at the same speed.
The front and rear planet pinions do not turn at all
in direct drive. The only rotation is the input from
the engine to the connected parts, which are acting
as one common unit, to the output shaft.
FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
Tow/Haul control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
Fig. 8 Direct Drive Powerflow
1 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED 6 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING 7 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT 8 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED
4 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED 9 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED
5 - OUTPUT SHAFT 10 - INPUT SHAFT
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 139
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1845 of 2627

The rear servo and governor pressure ports are at
the right rear of the transmission case. The overdrive
clutch pressure port is at the left rear of the case.
Test One - Transmission In Manual Low
This test checks pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of the rear clutch and servo circuit.
Both test gauges are required for this test.
(1) Connect tachometer to engine. Position tachom-
eter so it can be observed from driver seat if helper
will be operating engine. Raise vehicle on hoist that
will allow rear wheels to rotate freely.
(2) Connect 100 psi Gauge C-3292 to accumulator
port. Then connect 300 psi Gauge C-3293-SP to rear
servo port.
(3) Disconnect throttle and gearshift cables from
levers on transmission valve body manual shaft.
(4) Have helper start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(5) Move transmission shift lever fully forward
into 1 range.
(6) Gradually move transmission throttle lever
from full forward to full rearward position and note
pressures on both gauges:²Line pressure at accumulator port should be
54-60 psi (372-414 kPa) with throttle lever forward
and gradually increase to 90-96 psi (621-662 kPa) as
throttle lever is moved rearward.
²Rear servo pressure should be same as line pres-
sure within 3 psi (20.68 kPa).
Test Two - Transmission In 2 Range
This test checks pump output, line pressure and
pressure regulation. Use 100 psi Test Gauge C-3292
for this test.
(1) Leave vehicle in place on hoist and leave Test
Gauge C-3292 connected to accumulator port.
(2) Have helper start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(3) Move transmission shift lever one detent rear-
ward from full forward position. This is 2 range.
(4) Move transmission throttle lever from full for-
ward to full rearward position and read pressure on
gauge.
(5) Line pressure should be 54-60 psi (372-414
kPa) with throttle lever forward and gradually
increase to 90-96 psi (621-662 kPa) as lever is moved
rearward.
Test Three - Transmission In D Range Third Gear
This test checks pressure regulation and condition
of the clutch circuits. Both test gauges are required
for this test.
(1) Turn OD switch off.
(2) Leave vehicle on hoist and leave Gauge C-3292
in place at accumulator port.
(3) Move Gauge C-3293-SP over to front servo port
for this test.
(4) Have helper start and run engine at 1600 rpm
for this test.
(5) Move transmission shift lever two detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is D range.
(6) Read pressures on both gauges as transmission
throttle lever is gradually moved from full forward to
full rearward position:
²Line pressure at accumulator in D range third
gear, should be 54-60 psi (372-414 kPa) with throttle
lever forward and increase as lever is moved rear-
ward.
²Front servo pressure in D range third gear,
should be within 3 psi (21 kPa) of line pressure up to
kickdown point.
Test Four - Transmission In Reverse
This test checks pump output, pressure regulation
and the front clutch and rear servo circuits. Use 300
psi Test Gauge C-3293-SP for this test.
(1) Leave vehicle on hoist and leave gauge C-3292
in place at accumulator port.
(2) Move 300 psi Gauge C-3293-SP back to rear
servo port.
Fig. 9 Pressure Test Port Locations
1 - REAR SERVO TEST PORT
2 - GOVERNOR TEST PORT
3 - ACCUMULATOR TEST PORT
4 - FRONT SERVO TEST PORT
5 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH TEST PORT
21 - 142 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)