1998 DODGE RAM 1500 light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 1405 of 2627
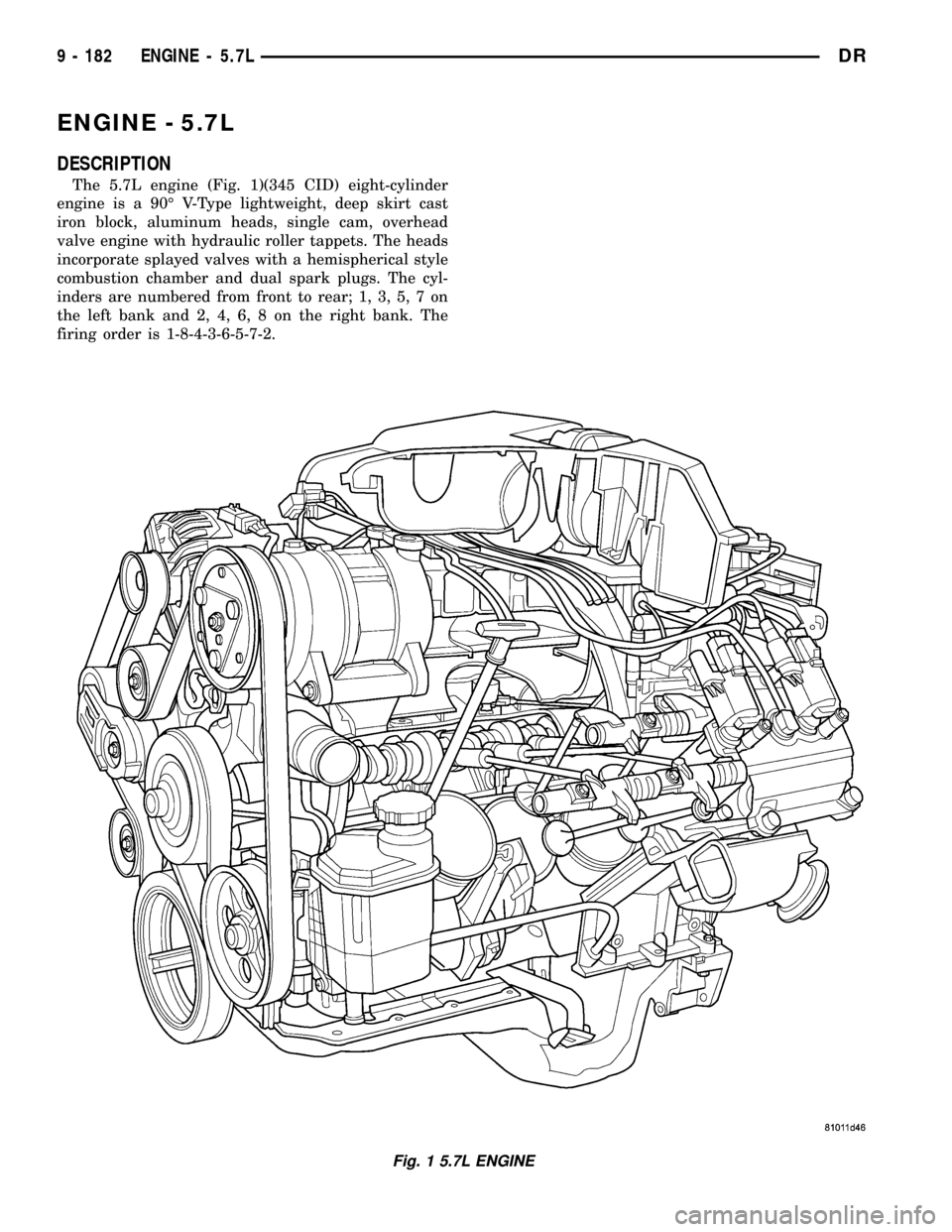
ENGINE - 5.7L
DESCRIPTION
The 5.7L engine (Fig. 1)(345 CID) eight-cylinder
engine is a 90É V-Type lightweight, deep skirt cast
iron block, aluminum heads, single cam, overhead
valve engine with hydraulic roller tappets. The heads
incorporate splayed valves with a hemispherical style
combustion chamber and dual spark plugs. The cyl-
inders are numbered from front to rear; 1, 3, 5, 7 on
the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right bank. The
firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2.
Fig. 1 5.7L ENGINE
9 - 182 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
Page 1406 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL
- REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
6. Dirt or water in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 7. Repair or replace as necessary.
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 183
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1425 of 2627

INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powered metal and
are pressed into the cylinder head. The guides are
not replaceable or serviceable, and valve guide ream-
ing is not recommended. If the guides are worn
beyond acceptable limits, replace the cylinder heads.
DESCRIPTION
Both the intake and exhaust valves are made of
steel. The intake valve is 50.93 mm (2.00 inches) in
diameter and the exhaust valve is 39.53 mm (1.55
inches) in diameter. All valves use three bead lock
keepers to retain the springs and promote valve rota-
tion.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING
NOTE: Valve seats that are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise the cylinder head
must be replaced.
NOTE: When refacing valves and valve seats, it is
important that the correct size valve guide pilot be
used for reseating stones. A true and complete sur-
face must be obtained.
(1) Using a suitable dial indicator measure the
center of the valve seat Total run out must not
exceed 0.051 mm (0.002 in).
(2) Apply a small amount of Prussian blue to the
valve seat, insert the valve into the cylinder head,
while applying light pressure on the valve rotate the
valve. Remove the valve and examine the valve face.
If the blue is transferred below the top edge of the
valve face, lower the valve seat using a 15 degree
stone. If the blue is transferred to the bottom edge of
the valve face, raise the valve seat using a 65 degree
stone.
(3) When the seat is properly positioned the width
of the intake seat must be 1.018 - 1.62 mm (0.0464 -
0.0637 in.) and the exhaust seat must be 1.48 - 1.92
mm (0.058 - 0.075 in.).
(4) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat. The installed height for
both intake and exhaust valve springs must not
exceed 46.0 mm (1.81 in.).
VALVE FACE AND VALVE SEAT ANGLE CHART
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
SEAT WIDTH
INTAKE 1.018 - 1.62 mm
(0.0464 - 0.0637 in.)
EXHAUST 1.48 - 1.92 mm
(0.058 - 0.075 in.)
FACE ANGLE
(INT. AND EXT.) 45É - 45
1¤2É
SEAT ANGLE
(INT. AND EXT.) 44
1¤2É - 45É
(5)
The valve seat must maintain an angle of 44.5 ±
45.0 degrees angle.
(6) The valve face must maintain a face angle of
45.0 ± 45.5 degrees angle (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 Valve Assembly Configuration
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
9 - 202 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
Page 1428 of 2627

ENGINE BLOCK
CLEANING
Thoroughly clean the oil pan and engine block gas-
ket surfaces.
Use compressed air to clean out:
²The galley at the oil filter adaptor hole.
²The front and rear oil galley holes.
²The feed holes for the crankshaft main bearings.
Once the block has been completely cleaned, apply
Loctite PST pipe sealant with Teflon 592 to the
threads of the front and rear oil galley plugs. Tighten
the 1/4 inch NPT plugs to 20 N´m (177 in. lbs.)
torque. Tighten the 3/8 inch NPT plugs to 27 N´m
(240 in. lbs.) torque.
INSPECTION
(1) It is mandatory to use a dial bore gauge to
measure each cylinder bore diameter. To correctly
select the proper size piston, a cylinder bore gauge,
capable of reading in 0.003 mm (.0001 in.) INCRE-
MENTS is required. If a bore gauge is not available,
do not use an inside micrometer (Fig. 7).
(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at three levels below top of bore. Start perpen-
dicular (across or at 90 degrees) to the axis of the
crankshaft and then take two additional reading.
(3) Measure the cylinder bore diameter crosswise
to the cylinder block near the top of the bore. Repeatthe measurement near the middle of the bore, then
repeat the measurement near the bottom of the bore.
(4) Determine taper by subtracting the smaller
diameter from the larger diameter.
(5) Rotate measuring device 90É and repeat steps
above.
(6) Determine out-of-roundness by comparing the
difference between each measurement.
(7) If cylinder bore taper does not exceed 0.025
mm (0.001 inch) and out-of-roundness does not
exceed 0.025 mm (0.001 inch), the cylinder bore can
be honed. If the cylinder bore taper or out- of-round
condition exceeds these maximum limits, the cylinder
block must be replaced. A slight amount of taper
always exists in the cylinder bore after the engine
has been in use for a period of time.CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK)
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE PLUG
CAUTION: Do not damage the rear surface of the
camshaft or the core plug sealing surface, when
removing the core plug.
(1) Remove the rear cam bearing core plug.
REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT
(1) Remove the battery negative cable.
(2) Remove the air cleaner assembly.
(3) Drain coolant.
(4) Remove the accessory drive belt.
(5) Remove the generator.
(6) Remove the A/C compressor, and set aside
(7) Remove the radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove intake manifold(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove cylinder head covers(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove both left and right cylinder heads(Re-
fer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL) .
(11) Remove the oil pan(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(12) Remove timing case cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove the oil pick up tube.
(14) Remove the oil pump(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL).
Fig. 7 BORE GAUGE-TYPICAL
1 - FRONT
2 - BORE GAUGE
3 - CYLINDER BORE
4 - 38 MM (1.5 in)
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 205
Page 1432 of 2627

CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL -
REAR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL AREA
LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, camshaft bore
cup plugs, oil galley pipe plugs, oil filter runoff,
and main bearing cap to cylinder block mating sur-
faces. See Engine, for proper repair procedures of
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in the section, Inspection (Engine oil
Leaks in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING), under the Oil Leak row, for components
inspections on possible causes and corrections.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL
SEAL - REAR - REMOVAL).
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure can be performed in vehicle.
(1) If being preformed in vehicle, remove the
transmission.
(2) Remove the flexplate (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/FLEX PLATE - REMOVAL).
NOTE: The crankshaft oil seal CAN NOT be reused
after removal.
NOTE: The crankshaft rear oil seal remover Special
Tool 8506 must be installed deeply into the seal.
Continue to tighten the removal tool into the seal
until the tool can not be turned farther. Failure to
install tool correctly the first time will cause tool to
pull free of seal without removing seal from engine.
(3) Using Special Tool 8506, remove the crankshaft
rear oil seal.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The rear seal must be installed dry for
proper operation. Do not lubricate the seal lip or
outer edge.
(1) Position the plastic seal guide onto the crank-
shaft rear face. Then position the crankshaft rear oil
seal onto the guide.
(2) Using Special Tools 8349 Crankshaft Rear Oil
Seal Installer and C-4171 Driver Handle, with a
hammer, tap the seal into place. Continue to tap on
the driver handle until the seal installer seats
against the cylinder block crankshaft bore.
(3) Install the flexplate.
(4) Install the transmission.
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL
RETAINER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the transmission.
(3) Remove the drive plate / flywheel.
(4) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the rear oil seal retainer mounting
bolts.
(6) Carefully remove the retainer from the engine
block.
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 209
Page 1433 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Throughly clean all gasket resdue from the
engine block.
(2) Use extream care and clean all gasket resdue
from the retainer.
(3) Position the gasket onto the retainer.
(4) Position the retainer onto the engine block.
(5) Install the retainer mounting bolts. Tighten the
bolts to 15 N´m (132 in. lbs.) using a crisscross pat-
tern, starting with the bolt on the lower right.
(6) Install a new rear seal(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
- INSTALLATION).
(7) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the drive plate / flywheel.
(9) Install the transmission.
(10) Check and verify engine oil level.
(11) Start engine and check for leaks.
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the transmission.
(2) Remove the bolts and flexplate.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the flexplate or flywheel onto the
crankshaft and install the bolts hand tight.
(2)For automatic transmissions:Tighten the
flexplate retaining bolts to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(3)For manual transmissions:Tighten the fly-
wheel retaining bolts to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the transmission.
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-70 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air. When
air is fed to the tappets, they lose length, which allows
valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake side of oil
pump through which air can be drawn will create the
same tappet action. Check the lubrication system from
the intake strainer to the pump cover, including the
relief valve retainer cap. When tappet noise is due to
aeration, it may be intermittent or constant, and usu-
ally more than one tappet will be noisy. When oil level
and leaks have been corrected, operate the engine at
fast idle. Run engine for a sufficient time to allow all of
the air inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3)
Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by excessive
leak-down around the unit plunger, or by the plunger
partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder. The tap-
pet should be replaced. A heavy click is caused by a tap-
pet check valve not seating, or by foreign particles
wedged between the plunger and the tappet body. This
will cause the plunger to stick in the down position.
This heavy click will be accompanied by excessive clear-
ance between the valve stem and rocker arm as valve
closes. In either case, tappet assembly should be
removed for inspection and cleaning.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
ing the noise. If more than one tappet seems to be
noisy, it's probably not the tappets.
9 - 210 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1435 of 2627

(5) Piston installation into the cylinder bore
requires slightly more pressure than that required
for non-coated pistons. The bonded coating on the
piston will give the appearance of a line-to-line fit
with the cylinder bore.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the following components:
²Oil pan and gasket/windage tray (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
²Timing chain cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head(s) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) If necessary, remove top ridge of cylinder bores
with a reliable ridge reamer before removing pistons
from cylinder block.Be sure to keep tops of pis-
tons covered during this operation.Pistons and
connecting rods must be removed from top of cylinder
block. When removing piston and connecting rod
assemblies from the engine, rotate crankshaft so the
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.CAUTION: DO NOT use a number stamp or a punch
to mark connecting rods or caps, as damage to
connecting rods could occur
NOTE: Connecting rods and bearing caps are not
interchangeable and should be marked before
removing to ensure correct reassembly.
(4)
Mark connecting rod and bearing cap positions
using a permanent ink marker or scribe tool (Fig. 12).
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to damage the
fractured rod and cap joint face surfaces, as engine
damage may occur.
(5) Remove connecting rod cap. Install Special Tool
8507 Connecting Rod Guides into the connecting rod
being removed. Remove piston from cylinder bore.
Repeat this procedure for each piston being removed.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to nick crank-
shaft journals, as engine damage may occur
(6) Immediately after piston and connecting rod
removal, install bearing cap on the mating connect-
ing rod to prevent damage to the fractured cap and
rod surfaces.
(7) Carefully remove piston rings from piston(s),
starting from the top ring down.
CLEANING
CAUTION: DO NOT use a wire wheel or other abra-
sive cleaning devise to clean the pistons or con-
necting rods. The pistons have a Moly coating, this
coating must not be damaged.
(1) Using a suitable cleaning solvent clean the pis-
tons in warm water and towel dry.
(2) Use a wood or plastic scraper to clean the ring
land grooves.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove the piston pin from the
piston and connecting rod assembly.
Fig. 11 BORE GAUGE - TYPICAL
1 - FRONT
2 - BORE GAUGE
3 - CYLINDER BORE
4-38MM
(1.5 in)
Fig. 12 IDENTIFY CONN ROD TO CYLINDER
9 - 212 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1438 of 2627

(10) Install No. 2 intermediate piston ring using a
piston ring installer (Fig. 16).
(11) Install No. 1 upper piston ring using a piston
ring installer (Fig. 16).
(12) Position piston ring end gaps as shown in
(Fig. 17). It is important that expander ring gap is at
least 45É from the side rail gaps, but not on the pis-
ton pin center or on the thrust direction.
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).(4) Remove radiator upper hose.
(5) Remove upper fan shroud.
(6) Using Special Tools 6958 Spanner with Adapter
Pins 8346, loosen fan and viscous assembly from
water pump.
(7) Remove fan and viscous assembly.
(8) Remove crankshaft damper bolt.
(9) Remove damper using Special Tools 8513A
Insert and 8454 Three Jaw Puller.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: To prevent severe damage to the Crank-
shaft, Damper or Special Tool 8512±A, thoroughly
clean the damper bore and the crankshaft nose
before installing Damper.
(1) Slide damper onto crankshaft slightly.
CAUTION: Special Tool 8512±A, is assembled in a
specific sequence. Failure to assemble this tool in
this sequence can result in tool failure and severe
damage to either the tool or the crankshaft.
(2) Assemble Special Tool 8512±A as follows, The
nut is threaded onto the shaft first. Then the roller
bearing is placed onto the threaded rod (The hard-
ened bearing surface of the bearingMUSTface the
nut). Then the hardened washer slides onto the
threaded rod (Fig. 18). Once assembled coat the
threaded rod's threads with MopartNickel Anti-
Seize or (Loctite No. 771).
Fig. 16 UPPER AND INTERMEDIATE RINGS
Fig. 17 PISTON RING END GAP POSITION
1 - SIDE RAIL UPPER
2 - NO. 1 RING GAP
3 - PISTON PIN
4 - SIDE RAIL LOWER
5 - NO. 2 RING GAP AND SPACER EXPANDER GAP
Fig. 18 Proper Assembly Method for Special Tool
8512
1 - BEARING
2 - NUT
3 - THREADED ROD
4 - BEARING HARDENED SURFACE (FACING NUT)
5 - HARDENED WASHER
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 215
PISTON RINGS (Continued)