1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Cylinder
[x] Cancel search: CylinderPage 1376 of 2627

camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
SERVICE
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied. MOPARtprovides engine oils that conform to
this service grade.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. Use only engine oils with multi-
ple viscosities such as 5W-30 or 10W-30 in the 3.7L
engines. These are specified with a dual SAE viscos-
ity grade which indicates the cold-to-hot temperature
viscosity range. Select an engine oil that is best
suited to your particular temperature range and vari-
ation (Fig. 94).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. The designation of ENERGY CON-
SERVING is located on the label of an engine oil con-
tainer.
CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 95).
Fig. 94 TEMPERATURE/ENGINE OIL VISCOSITY -
3.7L ENGINE
Fig. 95 Engine Oil Container Standard Notations
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 153
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1377 of 2627

OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located at the right
rear of the engine on the 3.7L engines. (Fig. 96).
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
pressure loss or oil foaming can result.
Inspect engine oil level approximately every 800
kilometers (500 miles). Unless the engine has exhib-
ited loss of oil pressure, run the engine for about five
minutes before checking oil level. Checking engine oil
level on a cold engine is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4)
Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in Maintenance Schedules.Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4)
Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase drain.
(5)Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow oil
to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for stretch-
ing or other damage. Replace drain plug if damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7)
Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil described in this section.
(8) Install oil fill cap.
(9) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(10) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
USED ENGINE OIL DISPOSAL
Care should be exercised when disposing used engine
oil after it has been drained from a vehicle engine.
Refer to the WARNING at beginning of this section.
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-flow,
disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Corporation
recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise (Fig. 97)to
remove it from the cylinder block oil filter boss.
Fig. 96 ENGINE OIL DIPSTICK 3.7L ENGINE
1 - TRANSMISSION DIPSTICK
2 - ENGINE OIL DIPSTICK
3 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP
Fig. 97 Oil Filter - 4.7L Engine
1 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
9 - 154 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
OIL (Continued)
Page 1378 of 2627

(4) When filter separates from cylinder block oil
filter boss, tip gasket end upward to minimize oil
spill. Remove filter from vehicle.
NOTE: Make sure filter gasket was removed with fil-
ter.
(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface of oil and grime.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 98) hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.
(3) Add oil, verify crankcase oil level and start
engine. Inspect for oil leaks.
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Install engine support fixture special tool #
8534.Do not raise engine at this time.
(3) Loosen both left and right side engine mount
through bolts. Do not remove bolts.
(4)
(5) Remove the structural dust cover, if equipped.
(6) Drain engine oil.
(7) Remove the front crossmember(Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/FRONT CROSS-
MEMBER - REMOVAL).
CAUTION: Only raise the engine enough to provide
clearance for oil pan removal. Check for proper
clearance at fan shroud to fan and cowl to intake
manifold.(8) Raise engine using special tool # 8534 to pro-
vide clearance to remove oil pan.
NOTE: Do not pry on oil pan or oil pan gasket. Gas-
ket is integral to engine windage tray and does not
come out with oil pan.
(9) Remove the oil pan mounting bolts and oil pan.
(10) Unbolt oil pump pickup tube and remove
tube.
(11) Inspect the integral windage tray and gasket
and replace as needed.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the oil pan gasket mating surface of the
bedplate and oil pan.
(2) Position the oil pan gasket and pickup tube
with new o-ring. Install the mounting bolt and nuts.
Tighten bolt and nuts to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Position the oil pan and install the mounting
bolts. Tighten the mounting bolts to 15 N´m (11 ft.
lbs.) in the sequence shown (Fig. 99).
(4) Lower the engine into mounts using special
tool # 8534.
(5) Install both the left and right side engine
mount through bolts. Tighten the nuts to 68 N´m (50
ft. lbs.).
(6) Remove special tool # 8534.
(7) Install structural dust cover, if equipped.
(8) Install the front crossmember(Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/FRONT CROSS-
MEMBER - INSTALLATION).
(9) Fill engine oil.
(10) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
(11) Start engine and check for leaks.
Fig. 98 Oil Filter Sealing Surface-Typical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 99 Oil Pan Mounting Bolts and Oil Pan
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 155
OIL FILTER (Continued)
Page 1382 of 2627
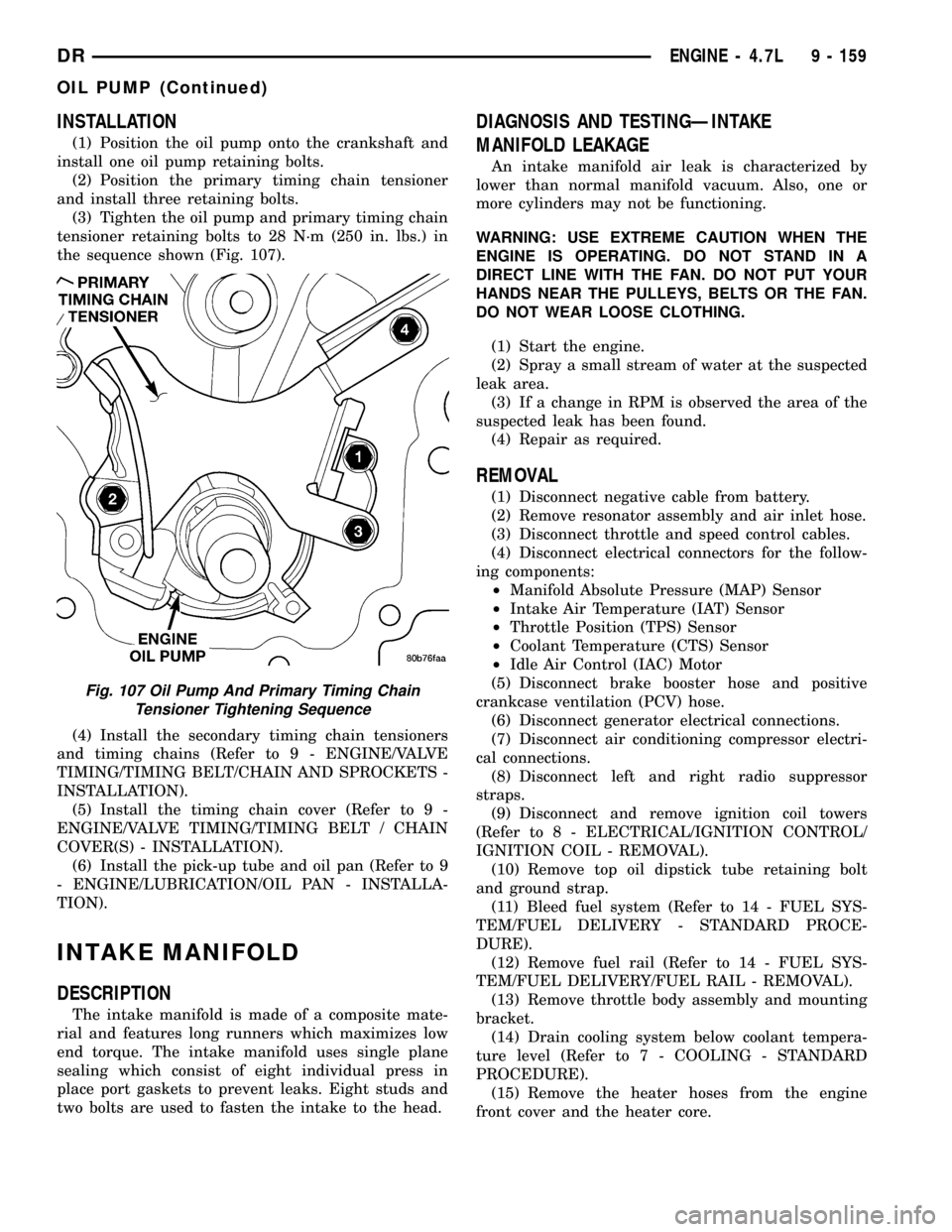
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the oil pump onto the crankshaft and
install one oil pump retaining bolts.
(2) Position the primary timing chain tensioner
and install three retaining bolts.
(3) Tighten the oil pump and primary timing chain
tensioner retaining bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in
the sequence shown (Fig. 107).
(4) Install the secondary timing chain tensioners
and timing chains (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the pick-up tube and oil pan (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold is made of a composite mate-
rial and features long runners which maximizes low
end torque. The intake manifold uses single plane
sealing which consist of eight individual press in
place port gaskets to prevent leaks. Eight studs and
two bolts are used to fasten the intake to the head.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐINTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water at the suspected
leak area.
(3) If a change in RPM is observed the area of the
suspected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove resonator assembly and air inlet hose.
(3) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
(4) Disconnect electrical connectors for the follow-
ing components:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
(5) Disconnect brake booster hose and positive
crankcase ventilation (PCV) hose.
(6) Disconnect generator electrical connections.
(7) Disconnect air conditioning compressor electri-
cal connections.
(8) Disconnect left and right radio suppressor
straps.
(9) Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt
and ground strap.
(11) Bleed fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(12) Remove fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove throttle body assembly and mounting
bracket.
(14) Drain cooling system below coolant tempera-
ture level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(15) Remove the heater hoses from the engine
front cover and the heater core.
Fig. 107 Oil Pump And Primary Timing Chain
Tensioner Tightening Sequence
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 159
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1384 of 2627

EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The exhaust manifolds are log style with a pat-
ented flow enhancing design to maximize perfor-
mance. The exhaust manifolds are made of high
silicon molybdenum cast iron. A perforated core
graphite exhaust manifold gasket is used to improve
sealing to the cylinder head. The exhaust manifolds
are covered by a three layer laminated heat shield
for thermal protection and noise reduction. The heat
shields are fastened with a torque prevailing nut
that is backed off slightly to allow for the thermal
expansion of the exhaust manifold.
REMOVAL
RIGHT EXHAUST MANIFOLD
(1) Disconnect negative cable for battery.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly, resonator assem-
bly and air inlet hose.
(3) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove A/C compressor (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove A/C accumulator support bracket fas-
tener.(6) Drain coolant below heater hose level (Refer to
7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Remove heater hoses at engine.
(8) Remove fasteners attaching exhaust manifold
heat shield.
(9) Remove heat shield.
(10) Remove upper exhaust manifold attaching fas-
teners.
(11) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(12) Disconnect exhaust pipe from manifold.
(13) Remove fasteners attaching starter. Move
starter aside.
(14) Remove lower exhaust manifold attaching fas-
teners.
(15) Remove exhaust manifold and gasket (Fig.
110). Manifold is removed from below the engine
compartment.
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 161
Page 1389 of 2627
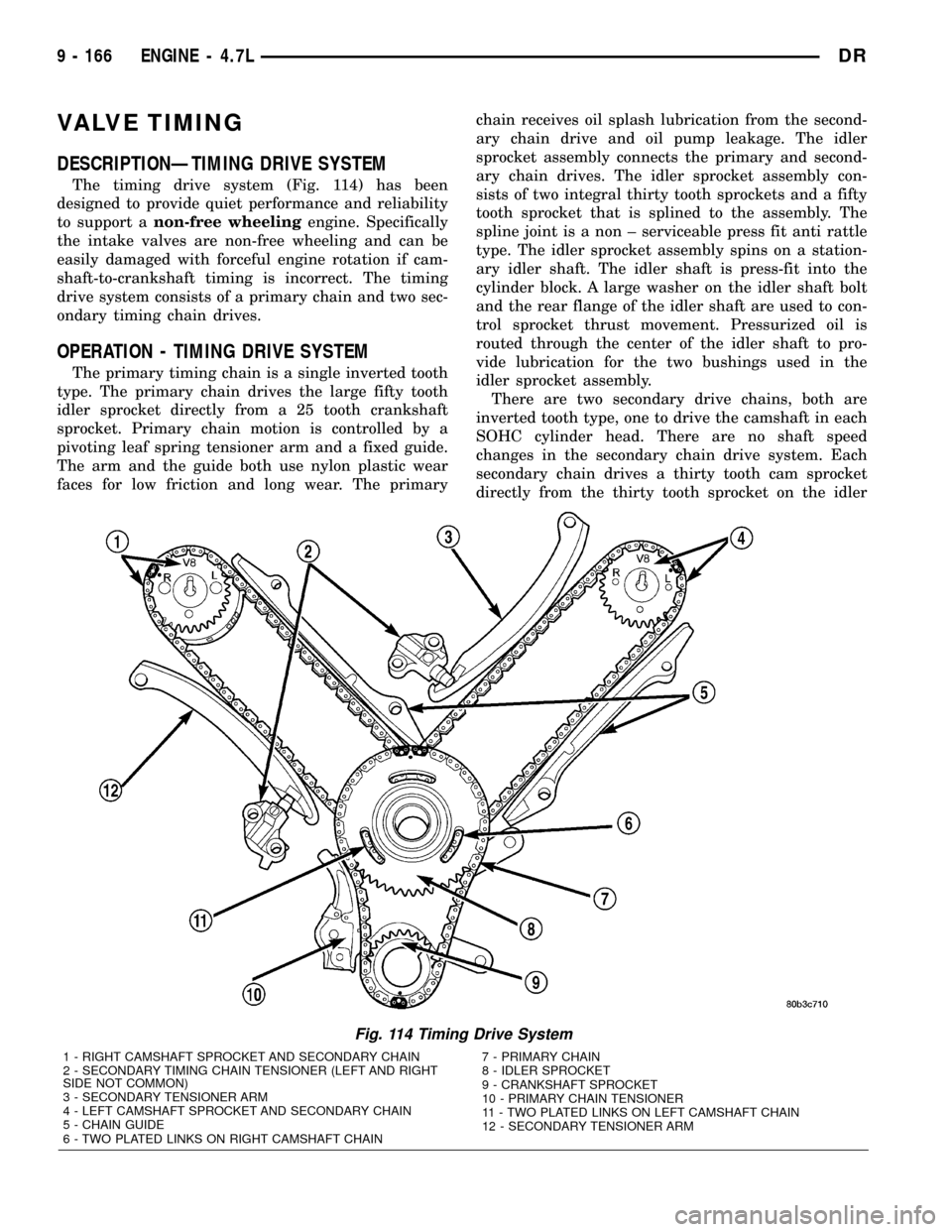
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTIONÐTIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The timing drive system (Fig. 114) has been
designed to provide quiet performance and reliability
to support anon-free wheelingengine. Specifically
the intake valves are non-free wheeling and can be
easily damaged with forceful engine rotation if cam-
shaft-to-crankshaft timing is incorrect. The timing
drive system consists of a primary chain and two sec-
ondary timing chain drives.
OPERATION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The primary timing chain is a single inverted tooth
type. The primary chain drives the large fifty tooth
idler sprocket directly from a 25 tooth crankshaft
sprocket. Primary chain motion is controlled by a
pivoting leaf spring tensioner arm and a fixed guide.
The arm and the guide both use nylon plastic wear
faces for low friction and long wear. The primarychain receives oil splash lubrication from the second-
ary chain drive and oil pump leakage. The idler
sprocket assembly connects the primary and second-
ary chain drives. The idler sprocket assembly con-
sists of two integral thirty tooth sprockets and a fifty
tooth sprocket that is splined to the assembly. The
spline joint is a non ± serviceable press fit anti rattle
type. The idler sprocket assembly spins on a station-
ary idler shaft. The idler shaft is press-fit into the
cylinder block. A large washer on the idler shaft bolt
and the rear flange of the idler shaft are used to con-
trol sprocket thrust movement. Pressurized oil is
routed through the center of the idler shaft to pro-
vide lubrication for the two bushings used in the
idler sprocket assembly.
There are two secondary drive chains, both are
inverted tooth type, one to drive the camshaft in each
SOHC cylinder head. There are no shaft speed
changes in the secondary chain drive system. Each
secondary chain drives a thirty tooth cam sprocket
directly from the thirty tooth sprocket on the idler
Fig. 114 Timing Drive System
1 - RIGHT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET AND SECONDARY CHAIN
2 - SECONDARY TIMING CHAIN TENSIONER (LEFT AND RIGHT
SIDE NOT COMMON)
3 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
4 - LEFT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET AND SECONDARY CHAIN
5 - CHAIN GUIDE
6 - TWO PLATED LINKS ON RIGHT CAMSHAFT CHAIN7 - PRIMARY CHAIN
8 - IDLER SPROCKET
9 - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET
10 - PRIMARY CHAIN TENSIONER
11 - TWO PLATED LINKS ON LEFT CAMSHAFT CHAIN
12 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
9 - 166 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
Page 1390 of 2627

sprocket assembly. A fixed chain guide and a hydrau-
lic oil damped tensioner are used to maintain tension
in each secondary chain system. The hydraulic ten-
sioners for the secondary chain systems are fed pres-
surized oil from oil reservoir pockets in the block.
Each tensioner also has a mechanical ratchet system
that limits chain slack if the tensioner piston bleeds
down after engine shut down. The tensioner arms
and guides also utilize nylon wear faces for low fric-
tion and long wear. The secondary timing chains
receive lubrication from a small orifice in the ten-
sioners. This orifice is protected from clogging by a
fine mesh screen which is located on the back of the
hydraulic tensioners.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐMEASURING
TIMING CHAIN WEAR
NOTE: This procedure must be performed with the
timing chain cover removed.
(1) Remove the timing chain cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) To determine if the secondary timing chains
are worn, rotate the engine clockwise until maximum
tensioner piston extension is obtained. Measure the
distance between the secondary timing chain ten-
sioner housing and the step ledge on the piston (Fig.
115). The measurement at point (A) must be less
than 15mm (0.5906 inches).
(3) If the measurement exceeds the specification
the secondary timing chains are worn and require
replacement. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
REMOVAL).
NOTE: If the secondary chains are to be replaced
the primary chain must also be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE TIMING -
VERIFICATION
CAUTION: The 4.7L is a non free-wheeling design
engine. Therefore, correct engine timing is critical.NOTE: Components referred to as left hand or right
hand are as viewed from the drivers position inside
the vehicle.
NOTE: The blue link plates on the chains and the
dots on the camshaft drive sprockets may not line
up during the timing verification procedure. The
blue link plates are lined up with the sprocket dots
only when re-timing the complete timing drive.
Once the timing drive is rotated blue link-to-dot
alignment is no longer valid.
Engine base timing can be verified by the following
procedure:
(1) Remove the cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
Fig. 115 Measuring Secondary Timing Chains For
Wear
1 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
2 - SECONDARY CHAIN TENSIONER PISTON
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 167
VALVE TIMING (Continued)
Page 1391 of 2627

(2) Using a mirror, locate the TDC arrow on the
front cover (Fig. 116). Rotate the crankshaft until the
mark on the crankshaft damper is aligned with the
TDC arrow on the front cover. The engine is now at
TDC.
(3) Note the location of the V8 mark stamped into
the camshaft drive gears (Fig. 117). If the V8 mark
on each camshaft drive gear is at the twelve o'clock
position, the engine is at TDC (cylinder #1) on the
exhaust stroke. If the V8 mark on each gear is at the
six o'clock position, the engine is at TDC (cylinder
#1) on the compression stroke.
(4) If both of the camshaft drive gears are off in
the same or opposite directions, the primary chain or
both secondary chains are at fault. Refer to Timing
Chain and Sprockets procedure in this section.
(5) If only one of the camshaft drive gears is off
and the other is correct, the problem is confined to
one secondary chain. Refer to Single camshaft tim-
ing, in this procedure.
(6) If both camshaft drive gear V8 marks are at
the twelve o'clock or the six o' clock position the
engine base timing is correct. Reinstall the cylinder
head covers.
Fig. 116 Engine Top Dead Center (TDC) Indicator
Mark
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - CRANKSHAFT TIMING MARKS
Fig. 117 Camshaft Sprocket V8 Marks
1 - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD2 - RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD
9 - 168 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
VALVE TIMING (Continued)