1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Electronic
[x] Cancel search: ElectronicPage 2245 of 2627

TRANSFER CASE - NV273
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV273
DESCRIPTION........................542
OPERATION..........................543
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV273.......................543
REMOVAL............................544
DISASSEMBLY........................544
CLEANING...........................554
INSPECTION.........................554
ASSEMBLY...........................556
INSTALLATION........................568
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV273.............568
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE NV271/NV273.........569
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL AND DUST BOOT
REMOVAL............................571
INSTALLATION........................571FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN AND
REFILL............................571
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................572
INSTALLATION........................572
MODE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................573
OPERATION..........................573
SELECTOR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................574
OPERATION..........................574
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION........................575
OPERATION..........................575
REMOVAL............................575
INSTALLATION........................575
TRANSFER CASE - NV273
DESCRIPTION
The NV273 is an electronically controlled part-time
transfer case with a low range gear reduction system.
The NV273 has three operating ranges plus a NEU-
TRAL position. The low range system provides a gear
reduction ratio for increased low speed torque capa-
bility.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum case halves.
OPERATING RANGES
Transfer case operating ranges are:
²2WD (2-wheel drive)
²4HI (4-wheel drive)
²4LO (4-wheel drive low range)
²NEUTRAL
The 2WD range is for use on any road surface at
any time.The 4HI and 4LO ranges are for off road use only.
They are not for use on hard surface roads. The only
exception being when the road surface is wet or slip-
pery or covered by ice and snow.
The low range reduction gear system is operative
in 4LO range only. This range is for extra pulling
power in off road situations. Low range reduction
ratio is 2.72:1.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a dash
mounted shift selector switch. The shift selector
switch provides a input to the Transfer Case Control
Module (TCCM) to indicate the driver's desire to
change operating ranges. The TCCM uses this input,
along with input from the transfer case mounted
mode sensor and information from the vehicle's bus,
to determine if a shift is permitted. If the TCCM
decides the shift is permitted, the TCCM controls the
shift motor, mounted to the exterior of the transfer
case, to perform the shift.
21 - 542 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
Page 2246 of 2627
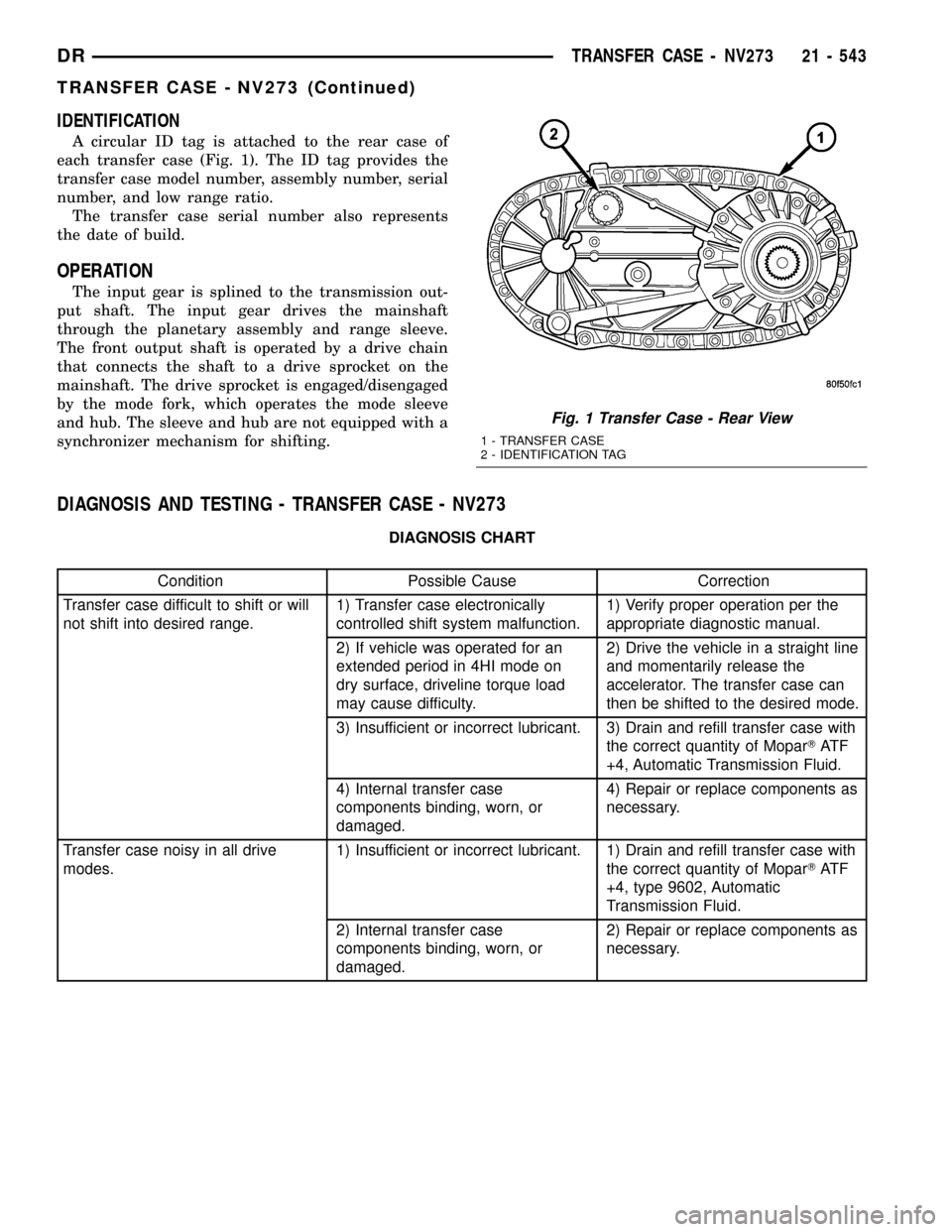
IDENTIFICATION
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 1). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.
The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission out-
put shaft. The input gear drives the mainshaft
through the planetary assembly and range sleeve.
The front output shaft is operated by a drive chain
that connects the shaft to a drive sprocket on the
mainshaft. The drive sprocket is engaged/disengaged
by the mode fork, which operates the mode sleeve
and hub. The sleeve and hub are not equipped with a
synchronizer mechanism for shifting.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV273
DIAGNOSIS CHART
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case electronically
controlled shift system malfunction.1) Verify proper operation per the
appropriate diagnostic manual.
2) If vehicle was operated for an
extended period in 4HI mode on
dry surface, driveline torque load
may cause difficulty.2) Drive the vehicle in a straight line
and momentarily release the
accelerator. The transfer case can
then be shifted to the desired mode.
3) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 3) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct quantity of MoparTAT F
+4, Automatic Transmission Fluid.
4) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.4) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct quantity of MoparTAT F
+4, type 9602, Automatic
Transmission Fluid.
2) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.2) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Fig. 1 Transfer Case - Rear View
1 - TRANSFER CASE
2 - IDENTIFICATION TAG
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 543
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2278 of 2627

have not been met. This is in an attempt to notify
the driver that the transmission needs to be put into
NEUTRAL, the vehicle speed is too great, or some
other condition outlined (other than a diagnostic fail-
ure that would prevent this shift) elsewhere (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/TRANSFER CASE CONTROL MODULE -
OPERATION) is not met. Note that this flashing will
continue indefinitely until the conditions are eventu-
ally met, or the selector switch position is changed,
or if diagnostic routines no longer allow the
requested shift.
²
If the driver attempts to make a shift into transfer
case NEUTRAL, and any of the driver controllable con-
ditions are not met, the request will be ignored until all
of the conditions are met or until the NEUTRAL select
button is released. Additionally the neutral lamp will
flash, or begin to flash while the button is depressed
and operator controllable conditions are not being met.
All of the LED's except the Neutral will flash if any of
the operator controllable conditions for shifting are not
met while the Neutral button is depressed. This9toggle9
type of feature is necessary because the TCCM would
interpret another request immediately after the shift
into transfer case NEUTRAL has completed.
²No LED's illuminated indicate a fault in the
transfer case control system.
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (Fig. 96) consists of a permanent
magnet D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a
high speed-low torque device into a low speed-high
torque device. The output of the device is coupled to
a shaft which internally moves the mode and range
forks that change the transfer case operating ranges.
The motor is rated at 25 amps maximum at 72É F
with 10 volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the
Transfer Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to
move the transfer case shift sector bi-directionally, as
required, to obtain the transfer case operating mode
indicated by the instrument panel mounted selector
switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in
the 2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assem-
bly will be installed, it will be necessary to shift the
transfer case to the 2WD/AWD position prior to
motor removal.(1) Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
(2) Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift
motor and mode sensor.
(3) Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and
mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
(4) Separate the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and
properly positioned over the shift sector and against
the transfer case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sec-
tor shaft orientation are aligned. It may be neces-
sary to manually shift the transfer case if the shift
motor and sector shaft are not aligned.
(2) Position the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly onto the transfer case.
(3) Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the
transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 N´m (12-18
ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sen-
sor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use
MoparTLock & Seal or LoctiteŸ 242 to replenish
the lock patch material originally found on the bolts
(4) Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor
and mode sensor.
(5) Refill the transfer case as necessary.
(6) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case
operation.
Fig. 96 Shift Motor - Shown Inverted - Typical
1 - SHIFT MOTOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 575
SELECTOR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2497 of 2627

and coil are the only serviced parts on the compres-
sor.
A/C compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the A/C-heater control, A/C pres-
sure transducer, A/C compressor clutch relay, evapo-
rator temperature sensor and the powertrain control
module (PCM). The PCM may delay compressor
clutch engagement for up to thirty seconds (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information). The battery must
be fully-charged before performing the following
tests. Refer to Battery for more information.
(1) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale) in
series with the clutch coil terminal. Use a voltmeter
(0 to 20 volt scale) with clip-type leads for measuring
the voltage across the battery and the compressor
clutch coil.
(2) With the A/C-heater controls in any A/C mode,
and the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, start the engine and run it at normal idle.
(3) The compressor clutch coil voltage should read
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage. If there is
voltage at the clutch coil, but the reading is not
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage, test the clutch
coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop and repair
as required. If there is no voltage reading at the
clutch coil, use a DRB IIItscan tool and (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information) for testing of thecompressor clutch circuit and PCM control. The fol-
lowing components must be checked and repaired as
required before you can complete testing of the clutch
coil:
²Fuses in the junction block and the power distri-
bution center (PDC)
²A/C-heater control
²A/C compressor clutch relay
²A/C pressure transducer
²Evaporator temperature sensor
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
(4) The compressor clutch coil is acceptable if the
current draw measured at the clutch coil is within
specifications with the electrical system voltage at
11.5 to 12.5 volts (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - SPECIFICATIONS). This should
only be checked with the work area temperature at
21É C (70É F). If system voltage is more than 12.5
volts, add electrical loads by turning on electrical
accessories until the system voltage drops below 12.5
volts.
(a) If the clutch coil current reading is above
specifications, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced.
(b) If the clutch coil current reading is zero, the
coil is open and should be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C-heater control to the
Recirculation Mode, the blower motor switch in the
highest speed position, and the engine speed at 1500
to 2000 rpm. This procedure (burnishing) will seat
the opposing friction surfaces and provide a higher
compressor clutch torque capability.
REMOVAL
The refrigerant system can remain fully-charged
during compressor clutch, rotor, or coil replacement.
The compressor clutch can be serviced in the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the compressor clutch coil wire har-
ness connector.
(4) Remove the bolts that secure the compressor to
the mounting bracket.
(5) Remove the compressor from the mounting
bracket. Support the compressor in the engine com-
partment while servicing the clutch.
Fig. 1 Compressor Clutch - Typical
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SHAFT KEY (not used on KJ)
3 - ROTOR
4 - COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
24 - 10 CONTROLSDR
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)
Page 2501 of 2627

spikes and electromagnetic interference that can be
generated as the electromagnetic field of the relay
coil collapses.
The A/C compressor clutch relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the integrated power module (IPM). The
inputs and outputs of the A/C compressor clutch
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from a fuse in the IPM through a
fused B(+) circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (86) receives a ground
input from the PCM/ECM through the A/C compres-
sor clutch relay control circuit only when the PCM/
ECM electronically pulls the control circuit to
ground.
²The coil battery terminal (85) receives a battery
current input from PTC 1 in the IPM through a
fused ignition switch output (run) circuit only when
the ignition switch is in the On position.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the compressor clutch coil
through the A/C compressor clutch relay output cir-
cuit only when the A/C compressor clutch relay coil is
energized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the A/C compres-
sor clutch relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
module (IPM) (Fig. 11).
(3) Refer to the fuse and relay layout label on the
IPM cover for compressor clutch relay identification
and location.
(4) Remove the A/C compressor clutch relay from
the IPM.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout label affixed to
the underside of the IPM cover for A/C compressor
clutch relay location.
(2) Position the A/C compressor clutch relay in the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the A/C compressor clutch relay termi-
nals with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(4) Push down firmly on the A/C compressor clutch
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the IPM.(6) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The heater and air conditioning systems use elec-
trical controls. These controls provide the vehicle
operator with a number of setting options to help
control the climate and comfort within the vehicle.
The A/C-heater control for the Single Zone system
(Fig. 12) or Dual Zone system (Fig. 13) is located to
the right of the instrument cluster on the instrument
panel.
The Single Zone control panel contains a rotary-
type temperature control switch, a rotary-type mode
control switch and a rotary-type blower motor speed
switch. The A/C-heater control also has a push but-
ton to activate the optional heated side view mirror
defroster elements and to turn the A/C on.
The Dual Zone control panel contains a pair of slid-
er-type temperature control switches, a rotary-type
mode control switch and a rotary-type blower motor
speed switch. The control also has buttons to activate
the optional heated sideview mirror defroster ele-
ments, turn the A/C on and set the system to Max
A/C.
The A/C-heater control panel cannot be repaired. If
faulty or damaged, the entire unit must be replaced.
Fig. 11 Integrated Power Module (IPM)
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
24 - 14 CONTROLSDR
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2504 of 2627

(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION
The blend door actuators are reversible, 12-volt
Direct Current (DC), servo motors. Models with the
single zone heater and air conditioner system have a
single blend door, which is controlled by a single
blend door actuator. Models with the optional dual
zone front heater and air conditioner system have
dual blend doors, which are controlled by two blend
door actuators. The single zone blend door actuator is
located on the driver side end of the HVAC housing,
close to the dash panel. In the dual zone system, the
same blend door actuator used for the single zone
system becomes the driver side blend door actuator,
and is mechanically connected to only the driver side
blend door. In the dual zone system, a second sepa-
rate blend door actuator is also located on the top of
the HVAC housing and is mechanically connected to
only the passenger side blend door.
The blend door actuators are interchangeable with
each other, as well as with the actuators for the
mode door, defrost door and the recirculation door.
Each actuator is contained within an identical blackmolded plastic housing with an integral wire connec-
tor receptacle. Integral mounting tabs allow the
actuator to be secured with three screws to the
HVAC housing. Each actuator also has an identical
output shaft with splines that connects it to the link-
age that drives the proper door. The blend door
actuators do not require mechanical indexing to the
blend door linkage, as they are electronically cali-
brated by the heater-A/C control module. The blend
door actuators cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if
damaged or faulty, they must be replaced.
OPERATION
Each blend door actuator is connected to the A/C-
heater control through the vehicle electrical system by a
dedicated two-wire lead and connector from the HVAC
wire harness. The blend door actuator can move the
blend-air door in two directions. When the A/C-heater
control pulls the voltage on one side of the motor con-
nection high and the other connection low, the blend-air
door will move in one direction. When the A/C-heater
control reverses the polarity of the voltage to the motor,
the blend-air door moves in the opposite direction.
When the A/C-heater control makes the voltage to both
connections high or both connections low, the blend-air
door stops and will not move. The motor connections
also provide a feedback signal to the A/C-heater control.
This feedback signal allows the A/C-heater control to
monitor the operation and relative positions of the blend
door actuator and the blend-air door. The A/C-heater
control learns the blend door stop positions during the
calibration procedure and will store a diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) for any problems it detects in the blend door
actuator circuits.
The blend door actuator can be diagnosed using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to Body Diagnostic Proce-
dures for more information. The blend door actuators
cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if damaged or
faulty, they must be replaced.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
Fig. 15 A/C Pressure Transducer - 3.7L Shown
1 - NUT
2 - FRONT UPPER CROSSMEMBER
3 - A/C CONDENSER
4 - NUT (2)
5 - SUCTION LINE
6 - A/C COMPRESSOR
7 - A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
8 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
9 - A/C DISCHARGE LINE
DRCONTROLS 24 - 17
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (Continued)
Page 2508 of 2627

cal indexing to the defrost door, as it is electronically
calibrated by the heater-A/C control module. The
defrost door actuator cannot be adjusted or repaired
and, if damaged or faulty, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The defrost door actuator is connected to the heat-
er-A/C control module through the vehicle electrical
system by a dedicated two-wire lead and connector
from the HVAC wire harness. The defrost door actua-
tor can move the defrost door in two directions.
When the heater-A/C control module pulls the volt-
age on one side of the motor connection high and the
other connection low, the defrost door will move in
one direction. When the module reverses the polarity
of the voltage to the motor, the defrost door moves in
the opposite direction. When the module makes the
voltage to both connections high or both connections
low, the defrost door stops and will not move. These
same motor connections also provide a feedback sig-
nal to the heater-A/C control module. This feedback
signal allows the module to monitor the operation
and relative positions of the defrost door actuator
and the defrost door. The heater-A/C control module
learns the defrost door stop positions during the cal-
ibration procedure and will store a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC) for any problems it detects in the
defrost door actuator circuits. The defrost door actua-
tor can be diagnosed using a DRBIIItscan tool.
Refer to Body Diagnostic Procedures.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
defrost door actuator (Fig. 19).
(4) Remove the screws that secure the defrost door
actuator to the HVAC housing.(5) Remove the defrost door actuator from the
HVAC housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the defrost door actuator into the
HVAC housing. If necessary, rotate the actuator
slightly to align the splines on the actuator output
sleeve with those on the defrost door linkage.
(2) Install and tighten the screws that secure the
defrost door actuator to the HVAC housing. Tighten
the screws to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the HVAC wire harness connector to
the defrost door actuator.
(4) Install the instrument panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
Fig. 19 HVAC Housing - Dual Zone Shown, Single
Zone Typical
1 - NUT
2 - PASSENGER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - NUT
4 - INLET BAFFLE
5 - RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
6 - RECIRCULATION DOOR
7 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
8 - HVAC HOUSING
9 - BOLT
10 - DEFROSTER DOOR ACTUATOR
11 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
DRCONTROLS 24 - 21
DEFROST DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 2511 of 2627

RECIRCULATION DOOR
ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION
The recirculation door actuator is a reversible
12-volt Direct Current (DC) servo motor. The single
recirculation door actuator is located on the passen-
ger side end of the HVAC housing, on the top of the
air inlet housing. The recirculation door actuator is
mechanically connected to the recirculation air door.
The recirculation door actuator is interchangeable
with the actuators for the blend door(s), defrost door
and the mode door. Each actuator is contained within
an identical black molded plastic housing with an
integral wire connector receptacle. Integral mounting
tabs allow the actuator to be secured with three
screws to air inlet housing. Each actuator also has an
identical output shaft with splines that connects it tothe linkage that drives the proper door. The recircu-
lation door actuator does not require mechanical
indexing to the recirculation door linkage, as it is
electronically calibrated by the heater-A/C control
module. The recirculation door actuator cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if damaged or faulty, it
must be replaced.
OPERATION
The recirculation door actuator is connected to the
heater-A/C control module through the vehicle elec-
trical system by a dedicated two-wire lead and con-
nector of the HVAC wire harness. The recirculation
door actuator can move the recirculation door in two
directions. When the heater-A/C control module pulls
the voltage on one side of the motor connection high
and the other connection low, the recirculation air
door will move in one direction. When the module
reverses the polarity of the voltage to the motor, the
recirculation air door moves in the opposite direction.
When the module makes the voltage to both connec-
tions high or both connections low, the recirculation
air door stops and will not move. These same motor
connections also provide a feedback signal to the
heater-A/C control module. This feedback signal
allows the module to monitor the operation and rela-
tive position of the recirculation door actuator and
the recirculation air door. The heater-A/C control
module learns the recirculation air door stop posi-
tions during the calibration procedure and will store
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) for any problems it
detects in the recirculation door actuator circuits.
The recirculation door actuator can be diagnosed
using a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to Body Diagnostic
Procedures for more information. The recirculation
door actuator cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if
damaged or faulty, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
Fig. 22 HVAC Housing - Dual Zone Shown, Single
Zone Typical
1 - NUT
2 - PASSENGER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - NUT
4 - INLET BAFFLE
5 - RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
6 - RECIRCULATION DOOR
7 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
8 - HVAC HOUSING
9 - BOLT
10 - DEFROSTER DOOR ACTUATOR
11 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
24 - 24 CONTROLSDR
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)