1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Electronic
[x] Cancel search: ElectronicPage 1641 of 2627

is the primary engine speed indicator for the engine
after the engine is running.
REMOVAL
The Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) on the 5.9L
diesel engine is located below the fuel injection
pump. It is bolted to the back of the timing gear
housing (Fig. 9).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at CMP sensor
(Fig. 9).
(2) Remove sensor mounting bolt.
(3) Carefully twist sensor from timing gear hous-
ing.
(4) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean out machined hole in back of timing gear
housing (cover).
(2) Apply a small amount of engine oil to sensor
o-ring.
(3) Install sensor into timing gear housing (cover)
with a slight rocking action. Do not twist sensor into
position as damage to o-ring may result.
CAUTION: Before tightening sensor mounting bolt,
be sure sensor is completely flush to back of timingchain housing (cover). If sensor is not flush, dam-
age to sensor mounting tang may result.
(4) Install mounting bolt and tighten. Refer to
Torque Specifications.
(5) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) on the die-
sel engine is attached at the front / left side of the
engine next to the engine harmonic balancer (crank-
shaft damper).
OPERATION
The Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) is the pri-
mary engine speed indicator for the engine after the
engine is running (Fig. 10). The CKP contains a hall
effect device. A rotating, notched target wheel (tone-
wheel) for the CKP is located on the engine harmonic
balancer (Fig. 11). This hall effect device detects
notches located on the tonewheel. As the tonewheel
rotates, the notches pass the tip of the CKP.
Fig. 8 5.9L DIESEL CMP
1 - CMP
2 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP (BOTTOM)
3 - ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
4 - ECM ELEC. CONNECTOR
5 - CMP ELEC. CONNECTOR
6 - CMP MOUNTING BOLT
7 - BACK OF TIMING GEAR HOUSING
Fig. 9 5.9L DIESEL CMP
1 - CMP
2 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP (BOTTOM)
3 - ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
4 - ECM ELEC. CONNECTOR
5 - CMP ELEC. CONNECTOR
6 - CMP MOUNTING BOLT
7 - BACK OF TIMING GEAR HOUSING
14 - 72 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELDR
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1664 of 2627

(17) Remove the steering column assembly from
the vehicle. (Fig. 7)
INSTALLATION
WARNING: BEFORE SERVICING THE STEERING
COLUMN THE AIRBAG SYSTEM MUST BE DIS-
ARMED. REFER TO ELECTRICAL RESTRAINT SYS-
TEM FOR SERVICE PROCEDURES. FAILURE TO DO
SO MAY RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT OF
THE AIRBAG AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION: All fasteners must be torqued to specifi-
cation to ensure proper operation of the steering
column.
(1) Position the steering column on the dash panel
support and loosely install the mounting nuts.
(2) Firmly slide the steering column upward
against the studs in dash panel and hand tighten the
nuts.
(3) Install the steering shaft coupler on the steer-
ing shaft and loosely install anewbolt.
(4) Center steering column in dash opening and
tighten mounting nuts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
NOTE: Torque the upper left nut first then the lower
right nut. Then torque the lower left nut then the
upper right nut.
NOTE: A new bolt must be used for reinstallation.
(5) Tighten the coupler bolt to 57 N´m (42 ft. lbs.).(6) Install a new brake light switch (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL).
(7) Install the shifter cable. (Refer to 21 - TRANS-
MISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 32RH/GEAR
SHIFT CABLE - INSTALLATION)
(8) Connect the wiring harness to the column.
(9) Install the SKIM module.
(10) Install the clockspring(Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL).
(11) Install the shrouds.
(12) Install the steering column opening cover
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTALLA-
TION).
(13) Align the spline on the wheel hub to shaft.
(14) Then install the steering wheel and install a
newbolt. Tighten the bolt to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(15) Install the airbag (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
(16) Install the two steering wheel switches.
(17) Install the tilt lever handle.
(18) Install the negative battery terminal.
(19) Test the operation of the horn, Electronic
PRNDL Indicator, lights and any other functions that
are steering column operated.
IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The ignition switch is located on the steering col-
umn. It is used as the main on/off switching device
for most electrical components. The mechanical key
cylinder is used to engage/disengage the electrical
ignition switch.
OPERATION
Vehicles equipped with an automatic trans-
mission and a steering column mounted shifter:
an interlock device is located within the shift cable.
This interlock device is used to lock the transmission
shifter in the PARK position when the key cylinder is
in any position and the brake pedal is not depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - IGNITION SWITCH
TEST AND REPAIR
If the key removal effort is excessive on a vehicle
with a automatic transmission first adjust the shift
linkage, (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 46RE/GEAR SHIFT CABLE -
ADJUSTMENTS).
If the ignition switch effort is excessive remove the
ignition key cylinder from the steering column. (Refer
to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOCK CYLINDER
Fig. 7 STEERING COLUMN
1 - Steering Wheel
2 - Key Cylinder
3 - Gear Shift Lever
4 - Steering Column
5 - Tilt Lever Cable
DRCOLUMN 19 - 9
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1833 of 2627

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE
DESCRIPTION........................132
OPERATION..........................134
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.....................140
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY . 140
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING...........................140
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST....................141
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR TESTING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH AND BAND
OPERATION........................144
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK................144
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIAGNOSIS
CHARTS...........................145
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR.....................158
REMOVAL............................158
DISASSEMBLY........................160
CLEANING...........................166
INSPECTION.........................166
ASSEMBLY...........................166
INSTALLATION........................174
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS.............176
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION.....................189
SPECIAL TOOLS
RE TRANSMISSION..................191
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION........................193
OPERATION..........................193
INSPECTION.........................194
BANDS
DESCRIPTION........................194
OPERATION..........................194
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - BANDS...............195
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION........................196
OPERATION..........................196
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK......196
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK...................196ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION........................197
OPERATION..........................198
REMOVAL............................199
INSTALLATION........................200
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL............................201
INSTALLATION........................201
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL.............201
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID.......................201
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION....................202
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK............................202
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER REPLACEMENT...............203
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL...............................204
FRONT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION........................205
OPERATION..........................205
DISASSEMBLY........................205
INSPECTION.........................206
ASSEMBLY...........................207
FRONT SERVO
DESCRIPTION........................208
OPERATION..........................208
DISASSEMBLY........................209
CLEANING...........................209
INSPECTION.........................209
ASSEMBLY...........................209
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE.............................210
REMOVAL............................210
INSTALLATION........................211
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE..................212
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................213
OPERATION..........................213
DISASSEMBLY........................214
CLEANING...........................214
INSPECTION.........................214
ASSEMBLY...........................214
21 - 130 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
Page 1835 of 2627

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
48RE
DESCRIPTION
The 48RE (Fig. 1) is a four speed fully automatic
transmissions with an electronic governor. The 48RE
is equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.
The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and thelow/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
21 - 132 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
Page 1842 of 2627
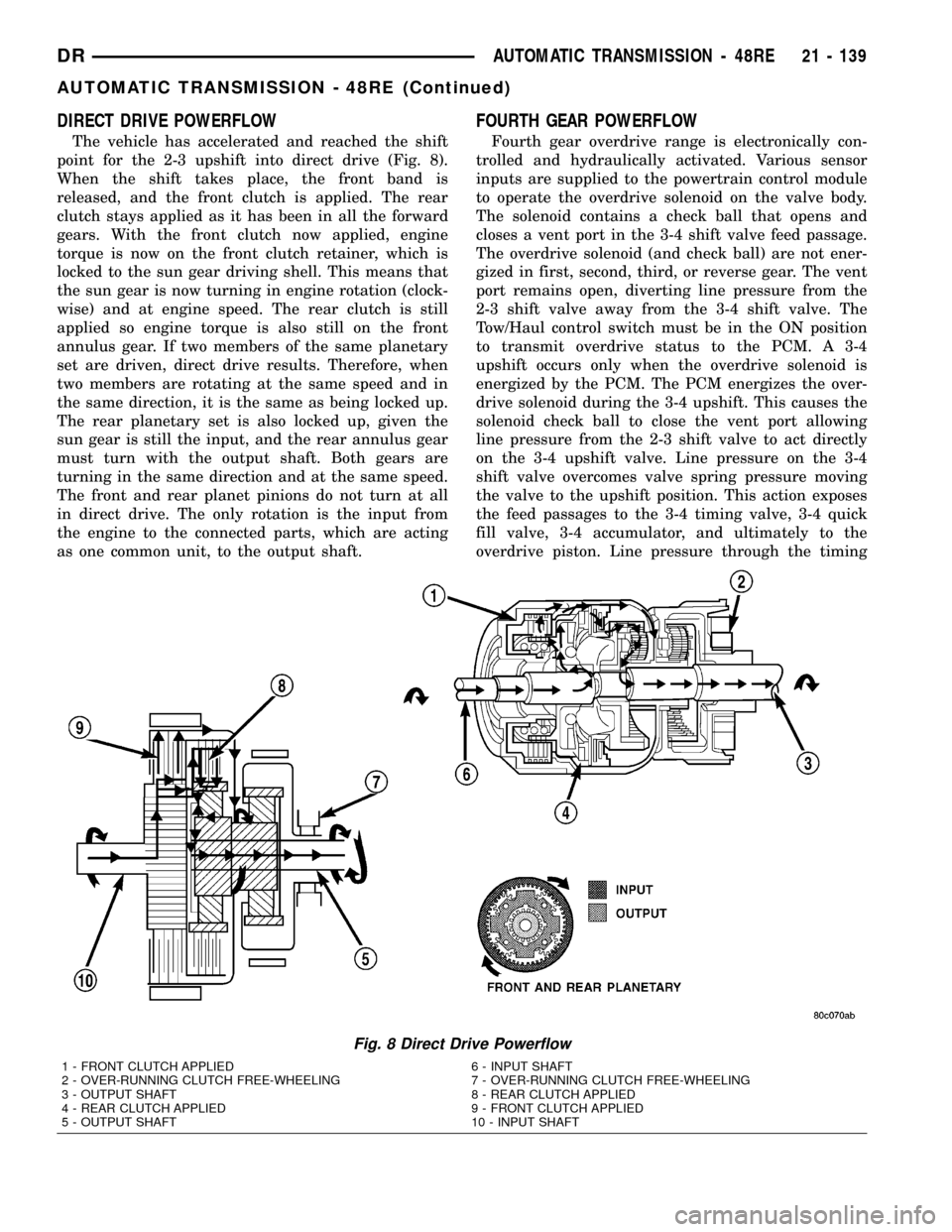
DIRECT DRIVE POWERFLOW
The vehicle has accelerated and reached the shift
point for the 2-3 upshift into direct drive (Fig. 8).
When the shift takes place, the front band is
released, and the front clutch is applied. The rear
clutch stays applied as it has been in all the forward
gears. With the front clutch now applied, engine
torque is now on the front clutch retainer, which is
locked to the sun gear driving shell. This means that
the sun gear is now turning in engine rotation (clock-
wise) and at engine speed. The rear clutch is still
applied so engine torque is also still on the front
annulus gear. If two members of the same planetary
set are driven, direct drive results. Therefore, when
two members are rotating at the same speed and in
the same direction, it is the same as being locked up.
The rear planetary set is also locked up, given the
sun gear is still the input, and the rear annulus gear
must turn with the output shaft. Both gears are
turning in the same direction and at the same speed.
The front and rear planet pinions do not turn at all
in direct drive. The only rotation is the input from
the engine to the connected parts, which are acting
as one common unit, to the output shaft.
FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
Tow/Haul control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
Fig. 8 Direct Drive Powerflow
1 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED 6 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING 7 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT 8 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED
4 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED 9 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED
5 - OUTPUT SHAFT 10 - INPUT SHAFT
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 139
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1900 of 2627

BTSI FUNCTION CHECK
(1) Verify removal of ignition key allowed in PARK
position only.
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK, the ignition
key cylinder should rotate freely from off to lock.
When the shifter is in any other position, the ignition
key should not rotate from off to lock.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should be possible when
the ignition key cylinder is in the off position.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal force, and ignition key cylin-
der is in the run or start positions, unless the foot
brake pedal is depressed approximately 1/2 inch
(12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the accessory or
lock position.
(6) Shifting between any gear and NEUTRAL, or
PARK, may be done without depressing foot brake
with ignition switch in run or start positions.
(7) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL positions only. Engine
starts must not be possible in any position other than
PARK or NEUTRAL.
(8) With shifter lever in the:
²PARK position - Apply upward force on the shift
arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must be
possible.²PARK position - Apply downward force on the
shift arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must
be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Normal position. Engine
starts must be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Engine running and brakes
applied, apply upward force on the shift arm. Trans-
mission shall not be able to shift from neutral to
reverse.
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION
Governor pressure is controlled electronically. Com-
ponents used for governor pressure control include:
²Governor body
²Valve body transfer plate
²Governor pressure solenoid valve
²Governor pressure sensor
²Fluid temperature thermistor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Transmission speed sensor
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The solenoid valve is a duty-cycle solenoid which
regulates the governor pressure needed for upshifts
and downshifts. It is an electro-hydraulic device
located in the governor body on the valve body trans-
fer plate (Fig. 76).
Fig. 75 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
Fig. 76 Governor Pressure Solenoid Valve
1 - SOLENOID FILTER
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 197
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1901 of 2627

GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The governor pressure sensor measures output
pressure of the governor pressure solenoid valve (Fig.
77).
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate is designed to supply transmis-
sion line pressure to the governor pressure solenoid
valve and to return governor pressure.
The governor pressure solenoid valve is mounted in
the governor body. The body is bolted to the lower
side of the transfer plate (Fig. 77).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absenceof sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher
than normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
Fig. 77 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 198 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1902 of 2627

sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
heavily loaded vehicle or on steep grades. When
hunting occurs, it is very objectionable because shifts
are frequent and accompanied by large changes in
noise and acceleration.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive mem-
ory in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the
preprogrammed optimum speed. WOT operation is
determined from the throttle position sensor, which
is also a part of the emission control system. The ini-
tial setting for the WOT upshift is below the opti-
mum engine speed. As WOT shifts are repeated, the
PCM learns the time required to complete the shifts
by comparing the engine speed when the shifts occur
to the optimum speed. After each shift, the PCM
adjusts the shift point until the optimum speed is
reached. The PCM also considers vehicle loading,
grade and engine performance changes due to high
altitude in determining when to make WOT shifts. It
does this by measuring vehicle and engine accelera-
tion and then factoring in the shift time.
TRANSFER CASE LOW RANGE OPERATION
On four-wheel drive vehicles operating in low
range, the engine can accelerate to its peak more
rapidly than in Normal range, resulting in delayed
shifts and undesirable engine9flare.9The low range
governor pressure curve is also higher than normal
to initiate upshifts sooner. The PCM compares elec-
tronic vehicle speed signal used by the speedometer
to the transmission output shaft speed signal to
determine when the transfer case is in low range.REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Remove transmission fluid pan and filter.
(3) Disengage wire connectors from pressure sen-
sor and solenoid (Fig. 78).
(4) Remove screws holding pressure solenoid
retainer to governor body.
(5) Separate solenoid retainer from governor (Fig.
79).
Fig. 78 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 79 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 199
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)