1998 DODGE RAM 1500 tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 1826 of 2627

SPECIFICATIONS - NV5600
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Plug, Crossover Cam and Detent 48 35 -
Bolt, Input Retainer 28 20 -
Bolt, 5-6 Crossover Bracket 28 20 -
Bolt, Clutch Housing 48 35 -
Bolt, Extension/Adapter Housing 48 35 -
Bolt, Shift Tower 9 7 80
Switch, Back-up Lamp 28 20 -
Bolt, Shift Blocker 55 41 -
Bolt, PTO Cover 40 30 -
Pivot, Clutch Release Lever 22 16 -
Plug, Fill 30 22 -
Nut, Output Shaft 339 250 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
REMOVER 8155
INSTALLER 8156
HANDLE C-4171
INSTALLER C-3972-A
INSTALLER 8154
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 21 - 123
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1832 of 2627

SHIFT COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(2) Unscrew and remove the shift lever extension
from the shift
(3) Remove screws attaching shift boot to floorpan.
Then slide boot upward on the shift lever.
(4) Remove the bolts holding the shift tower to the
isolator plate and transmission gear case.
(5) Remove the shift tower (Fig. 100) and isolator
plate (Fig. 101) from the transmission.
INSTALLATION
(1) Shift transmission into third gear.
(2) Clean the mating surfaces of shift tower, isola-
tor plate and transmission gear case with suitable
wax and grease remover.(3) Apply Mopar Gasket Maker or equivalent to
the sealing surface of the transmission. Do not over
apply sealant.
(4) Install isolator plate onto the transmission,
metal side down.
(5) Install shift tower onto the isolator plate. No
sealant is necessary between the shift tower and iso-
lator plate.
(6) Verify shift tower, isolator plate and shift tower
bushings are properly aligned.
(7) Install shift tower bolts and tighten the shift
tower bolts to 8-10 N´m (7-9 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install shift lever extension, shift boot and
bezel.
Fig. 100 SHIFT TOWER
1 - SHIFT TOWER
2 - TRANSMISSION
Fig. 101 SHIFT TOWER ISOLATOR PLATE
1 - ISOLATOR PLATE
2 - TRANSMISSION
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 21 - 129
Page 1834 of 2627

OUTPUT SHAFT FRONT BEARING
REMOVAL............................216
INSTALLATION........................216
OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING
REMOVAL............................216
INSTALLATION........................217
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION........................217
OPERATION..........................217
OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL............................218
DISASSEMBLY........................218
CLEANING...........................225
INSPECTION.........................225
ASSEMBLY...........................226
INSTALLATION........................235
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE
PISTON RETAINER
DESCRIPTION........................236
OPERATION..........................236
DISASSEMBLY........................236
CLEANING...........................236
INSPECTION.........................237
ASSEMBLY...........................237
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION........................239
OPERATION..........................239
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT
DESCRIPTION........................241
OPERATION..........................241
DISASSEMBLY........................242
INSPECTION.........................243
ASSEMBLY...........................244
REAR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION........................247
OPERATION..........................248
DISASSEMBLY........................248
CLEANING...........................248
INSPECTION.........................248
ASSEMBLY...........................249
REAR SERVO
DESCRIPTION........................251
OPERATION..........................251
DISASSEMBLY........................251
CLEANING...........................251
ASSEMBLY...........................251
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................252OPERATION..........................252
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION........................252
OPERATION..........................252
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................253
OPERATION..........................253
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION........................253
ADJUSTMENTS - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE . 254
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................255
OPERATION..........................259
REMOVAL............................260
INSTALLATION........................260
TORQUE CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................261
OPERATION..........................261
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE........261
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................261
OPERATION..........................262
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERDRIVE
ELECTRICAL CONTROLS..............262
REMOVAL............................262
INSTALLATION........................262
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................263
OPERATION..........................263
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSMISSION
RANGE SENSOR (TRS)................264
REMOVAL............................265
INSTALLATION........................266
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................267
OPERATION..........................267
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................267
OPERATION..........................272
REMOVAL............................286
DISASSEMBLY........................287
CLEANING...........................298
INSPECTION.........................298
ASSEMBLY...........................299
INSTALLATION........................309
ADJUSTMENTS - VALVE BODY...........310
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 131
Page 1842 of 2627
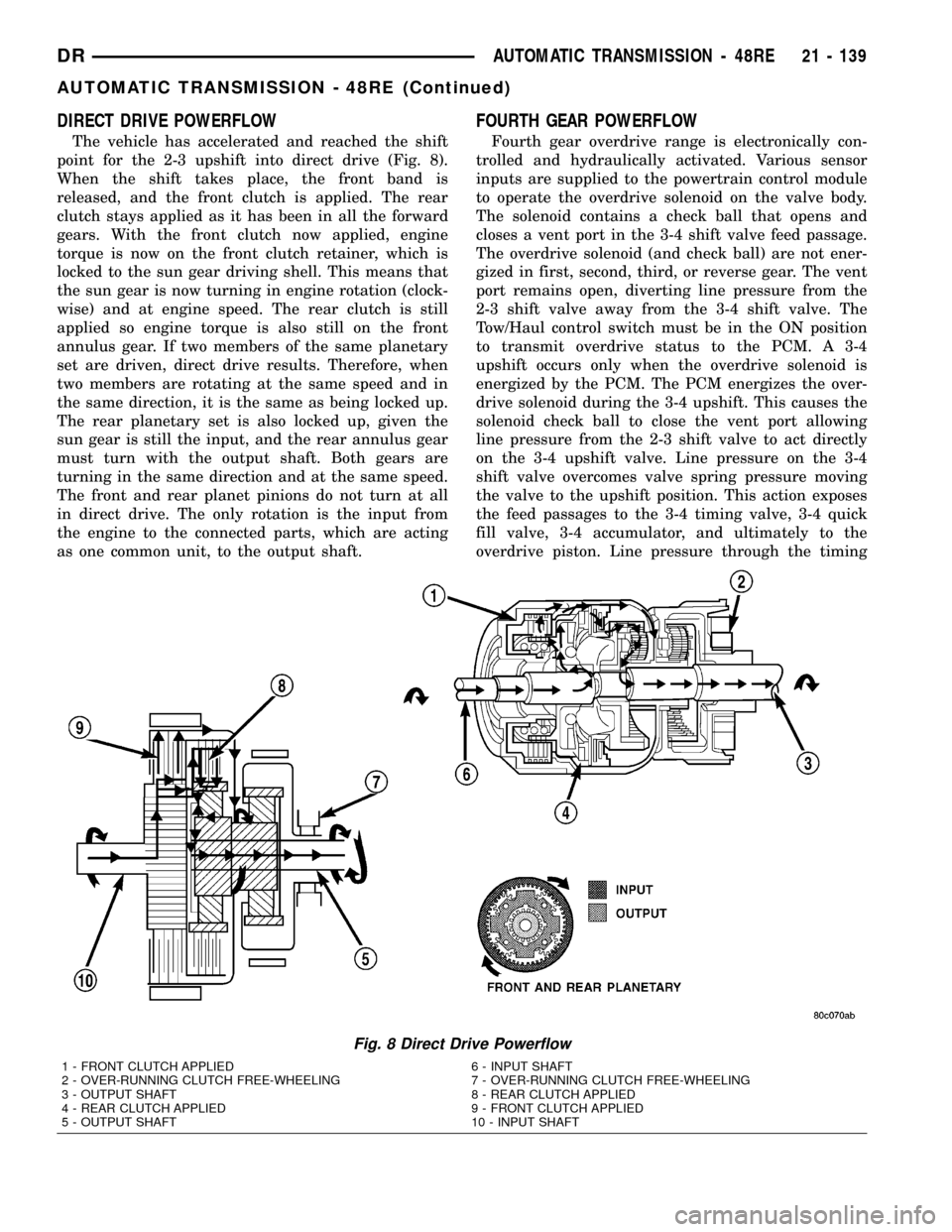
DIRECT DRIVE POWERFLOW
The vehicle has accelerated and reached the shift
point for the 2-3 upshift into direct drive (Fig. 8).
When the shift takes place, the front band is
released, and the front clutch is applied. The rear
clutch stays applied as it has been in all the forward
gears. With the front clutch now applied, engine
torque is now on the front clutch retainer, which is
locked to the sun gear driving shell. This means that
the sun gear is now turning in engine rotation (clock-
wise) and at engine speed. The rear clutch is still
applied so engine torque is also still on the front
annulus gear. If two members of the same planetary
set are driven, direct drive results. Therefore, when
two members are rotating at the same speed and in
the same direction, it is the same as being locked up.
The rear planetary set is also locked up, given the
sun gear is still the input, and the rear annulus gear
must turn with the output shaft. Both gears are
turning in the same direction and at the same speed.
The front and rear planet pinions do not turn at all
in direct drive. The only rotation is the input from
the engine to the connected parts, which are acting
as one common unit, to the output shaft.
FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
Tow/Haul control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
Fig. 8 Direct Drive Powerflow
1 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED 6 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING 7 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT 8 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED
4 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED 9 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED
5 - OUTPUT SHAFT 10 - INPUT SHAFT
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 139
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1869 of 2627

(33) Remove tools and remove servo piston and
spring.
(34) Compress rear servo piston with C-clamp and
Tool C-4470, or Valve Spring Compressor C-3422-B
(Fig. 39). Compress servo spring retainer only
enough to permit snap-ring removal.
(35) Remove servo piston snap-ring (Fig. 39). Start
one end of ring out of bore. Then carefully work
removal tool around back of snap-ring until free of
ring groove.Exercise caution when removing
snap-ring. Servo bore can be scratched or
nicked if care is not exercised.
(36) Remove tools and remove rear servo retainer,
spring and piston assembly.
CLEANING
Clean the case in a solvent tank. Flush the case
bores and fluid passages thoroughly with solvent.
Dry the case and all fluid passages with compressed
air. Be sure all solvent is removed from the case and
that all fluid passages are clear.
NOTE: Do not use shop towels or rags to dry the
case (or any other transmission component) unless
they are made from lint-free materials. Lint will stick
to case surfaces and transmission components and
circulate throughout the transmission after assem-
bly. A sufficient quantity of lint can block fluid pas-
sages and interfere with valve body operation.
Lubricate transmission parts with MopartATF +4,
Automatic Transmission fluid, during overhaul and
assembly. Use petroleum jelly to prelubricate seals,
O-rings, and thrust washers. Petroleum jelly can also
be used to hold parts in place during reassembly.
INSPECTION
Inspect the case for cracks, porous spots, worn
bores, or damaged threads. Damaged threads can be
repaired with Helicoil thread inserts. However, the
case will have to be replaced if it exhibits any type of
damage or wear.
Lubricate the front band adjusting screw threads
with petroleum jelly and thread the screw part-way
into the case. Be sure the screw turns freely.
Inspect the transmission bushings during overhaul.
Bushing condition is important as worn, scored bush-
ings contribute to low pressures, clutch slip and
accelerated wear of other components. However, do
not replace bushings as a matter of course. Replace
bushings only when they are actually worn, or
scored.
The use of crocus cloth is permissible where neces-
sary, providing it is used carefully. When used on
shafts, or valves, use extreme care to avoid rounding
off sharp edges. Sharp edges are vital as they pre-
vent foreign matter from getting between the valve
and valve bore.
Do not reuse oil seals, gaskets, seal rings, or
O-rings during overhaul. Replace these parts as a
matter of course. Also do not reuse snap rings or
E-clips that are bent or distorted. Replace these parts
as well.
ASSEMBLY
Do not allow dirt, grease, or foreign material to
enter the case or transmission components during
assembly. Keep the transmission case and compo-
nents clean. Also make sure the tools and workbench
area used for reassembly operations are equally
clean.
Shop towels used for wiping off tools and your
hands must be made fromlint freematerials. Lint
will stick to transmission parts and could interfere
with valve operation or even restrict fluid passages.
Lubricate transmission clutch and gear compo-
nents with MopartATF +4 during reassembly. Soak
clutch discs in transmission fluid before installation.
Use petroleum jelly on piston seals and o-rings to
ease installation. Petroleum jelly can also be used to
lubricate and hold thrust washers and plates in posi-
tion during assembly.
Do not use chassis grease, bearing grease,
white grease, or similar lubricants on any part.
These types of lubricants can eventually block or
restrict fluid passages and valve operation. Use
petroleum jelly only.
Do not force parts into place. The transmission
components and sub-assemblies are easily installed
by hand when properly aligned. If a part seems dif-
ficult to install, it is either misaligned or incorrectly
Fig. 39 Rear Servo Retaining Snap-Ring
1 - TOOL C-4470
2 - C-CLAMP
3 - REAR SERVO SPRING RETAINER
4 - RETAINER SNAP-RING
21 - 166 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1874 of 2627

(11) Slide front band over front clutch retainer and
install front band strut and anchor (Fig. 52).
(12) Tighten front band adjusting screw until band
is tight on clutch retainer. This will hold clutches in
place while oil pump is being installed.Verify that
front/rear clutch assembly is still properly
seated before tightening band.
OIL PUMP
(1) Install oil pump Pilot Studs C-3288-B in case
(Fig. 53).(2) Install new oil pump gasket on pilot studs and
seat it in case. Be sure gasket is properly aligned
with fluid passages in case (Fig. 53).
(3) Coat the reaction shaft thrust washer with
petroleum jelly to hold it in place. Then install
washer over reaction shaft hub and seat it on pump
(Fig. 54).
CAUTION: The thrust washer bore (I.D.), is cham-
fered on one side. Make sure the chamfered side is
installed so it faces the pump.
Fig. 53 Oil Pump Gasket And Pilot Studs
1 - OIL PUMP GASKET
2 - PILOT STUDS C-3288-B
Fig. 54 Front Clutch Thrust Washer Installation
1 - THRUST WASHER
2 - CHAMFERED SIDE OF WASHER BORE GOES TOWARD
PUMP
Fig. 55 Reaction Shaft Seal Ring And Thrust Washer
1 - SEAL RINGS
2 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - THRUST WASHER (FIBER)
Fig. 52 Front Band And Linkage
1 - LEVER
2 - STRUT
3 - ANCHOR
4 - FRONT BAND
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 171
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1905 of 2627

(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, thegeartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
vehicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to NEUTRAL.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep
dirt from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick (Fig. 87) and check fluid level
as follows:
(a) Correct acceptable level is in crosshatch area.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN line.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough MopartAT F
+4 to restore correct level. Do not overfill.
Fig. 87 Dipstick Fluid Level Marks - Typical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
21 - 202 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1919 of 2627
(4) Align and install reaction shaft support on
pump body.
(5) Install bolts attaching reaction shaft support to
pump. Tighten bolts to 20 N´m (175 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install new pump seal with Installer Tool
C-3860-A (Fig. 114). Use hammer or mallet to tap
seal into place.
(7) Install new o-ring on pump body. Lubricate oil
seal and o-ring with petroleum jelly.
(8) Cover pump assembly to prevent dust entry
and set aside for assembly installation.
OUTPUT SHAFT FRONT
BEARING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove overdrive unit from the vehicle.
(2) Remove overdrive geartrain from housing.
(3) Remove snap-ring holding output shaft front
bearing to overdrive geartrain. (Fig. 115).
(4) Pull bearing from output shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place replacement bearing in position on
geartrain with locating retainer groove toward the
rear.
(2) Push bearing onto shaft until the snap-ring
groove is visible.
(3) Install snap-ring to hold bearing onto output
shaft.
(4) Install overdrive geartrain into housing.
(5) Install overdrive unit in vehicle.
OUTPUT SHAFT REAR
BEARING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove overdrive unit from the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/OVERDRIVE
- REMOVAL)
(2) Remove overdrive geartrain from housing.
(3) Remove snap-ring holding output shaft rear
bearing into overdrive housing (Fig. 116).
(4) Using a suitable driver inserted through the
rear end of housing, drive bearing from housing.
Fig. 114 Oil Pump Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3860-A
2 - PUMP BODY
3 - PUMP SEAL
Fig. 115 Output Shaft Front Bearing
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT FRONT BEARING
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
4 - GROOVE TO REAR
5 - OVERDRIVE GEARTRAIN
Fig. 116 Output Shaft Rear Bearing
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING
2 - OVERDRIVE HOUSING
3 - SNAP-RING
21 - 216 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
OIL PUMP (Continued)