1998 DODGE RAM 1500 drive shaft
[x] Cancel search: drive shaftPage 1367 of 2627

VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Remove radiator upper hose.
(5) Remove upper fan shroud.
(6) Using Special Tools 6958 Spanner with Adapter
Pins 8346, loosen fan and viscous assembly from
water pump (Fig. 81).
(7) Remove fan and viscous assembly.
(8) Disconnect electrical connector for fan mounted
inside radiator shroud.
NOTE: Transmission cooler line snaps into shroud
lower right hand corner.
(9) Remove crankshaft damper bolt.
(10) Remove damper using Special Tools 8513
Insert and 1026 Three Jaw Puller (Fig. 82).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: To prevent severe damage to the Crank-
shaft, Damper or Special Tool 8512±A, thoroughlyclean the damper bore and the crankshaft nose
before installing Damper.
(1) Align crankshaft damper slot with key in
crankshaft. Slide damper onto crankshaft slightly.
CAUTION: Special Tool 8512±A, is assembled in a
specific sequence. Failure to assemble this tool in
this sequence can result in tool failure and severe
damage to either the tool or the crankshaft.
(2) Assemble Special Tool 8512±A as follows, The
nut is threaded onto the shaft first. Then the roller
bearing is placed onto the threaded rod (The hard-
ened bearing surface of the bearingMUSTface the
nut). Then the hardened washer slides onto the
threaded rod (Fig. 83). Once assembled coat the
threaded rod's threads with MopartNickel Anti-
Seize or equivalent.
(3) Using Special Tool 8512±A, press damper onto
crankshaft (Fig. 84).
(4) Install then tighten crankshaft damper bolt to
175 N´m (130 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install fan blade assembly (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
INSTALLATION).
(6) Install radiator upper shroud and tighten fas-
teners to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.).
(7) Connect electrical connector for shroud fan.
(8) Install radiator upper hose.
Fig. 81 FAN ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL/ASSEMBLY
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6958 SPANNER WRENCH WITH ADAPTER
PINS 8346
2-FAN
Fig. 82 CRANKSHAFT DAMPER - REMOVAL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8513 INSERT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 1026
9 - 144 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
Page 1368 of 2627

(9) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
(10) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Connect negative cable to battery.
STRUCTURAL COVER
DESCRIPTION
The structural dust cover is made of die cast alu-
minum and joins the lower half of the transmission
bell housing to the engine bedplate.
OPERATION
The structural cover provides additional power-
train stiffness and reduces noise and vibration.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove the left hand exhaust pipe from
exhaust manifold.
(3) Loosen the right hand exhaust manifold-to-ex-
haust pipe retaining bolts.
(4) Remove the eight bolts retaining structural
cover (Fig. 85) in the sequence shown.
(5) Pivot the exhaust pipe downward and remove
the structural cover.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The structural cover must be installed as
described in the following steps. Failure to do so
will cause severe damage to the cover.
(1) Position the structural cover in the vehicle.
(2) Install all four bolts retaining the cover-to-en-
gine. DO NOT tighten the bolts at this time.
(3) Install the four cover-to-transmission bolts. Do
NOT tighten at this time.
Fig. 83 PROPER ASSEMBLY METHOD FOR
SPECIAL TOOL 8512±A
1 - BEARING
2 - NUT
3 - THREADED ROD
4 - BEARING HARDENED SURFACE (FACING NUT)
5 - HARDENED WASHER
Fig. 84 Crankshaft Damper Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8512
Fig. 85 Structural Cover
1 - BOLT
2 - BOLT
3 - BOLT
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 145
VIBRATION DAMPER (Continued)
Page 1375 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHECKING
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit (Fig. 93)and
install gauge assembly C-3292.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
(3) Oil Pressure:
²Curb Idle - 25 kPa (4 psi) minimum
²3000 rpm - 170 - 758 kPa (25 - 110 psi)
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle, shut off engine.
Check for a clogged oil pick-up screen or a pressure
relief valve stuck open.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.If the oil leak source is not posi-
tively identified at this time, proceed with the air
leak detection test method.
Air Leak Detection Test Method
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kPa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(4) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(5) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply
and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
Fig. 93 OIL PRESSURE SENDING UNIT -TYPICAL
1 - BELT
2 - OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
9 - 152 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1389 of 2627
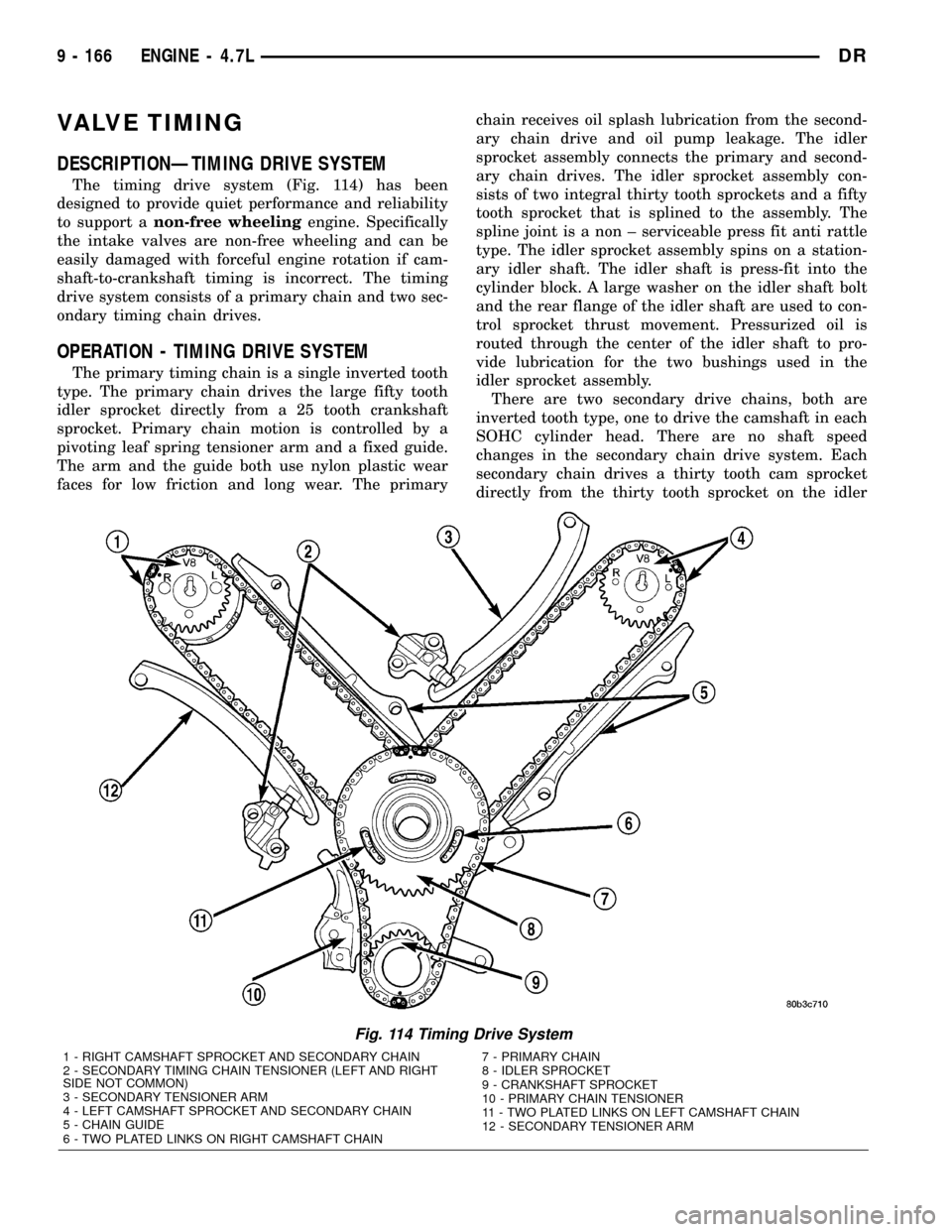
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTIONÐTIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The timing drive system (Fig. 114) has been
designed to provide quiet performance and reliability
to support anon-free wheelingengine. Specifically
the intake valves are non-free wheeling and can be
easily damaged with forceful engine rotation if cam-
shaft-to-crankshaft timing is incorrect. The timing
drive system consists of a primary chain and two sec-
ondary timing chain drives.
OPERATION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The primary timing chain is a single inverted tooth
type. The primary chain drives the large fifty tooth
idler sprocket directly from a 25 tooth crankshaft
sprocket. Primary chain motion is controlled by a
pivoting leaf spring tensioner arm and a fixed guide.
The arm and the guide both use nylon plastic wear
faces for low friction and long wear. The primarychain receives oil splash lubrication from the second-
ary chain drive and oil pump leakage. The idler
sprocket assembly connects the primary and second-
ary chain drives. The idler sprocket assembly con-
sists of two integral thirty tooth sprockets and a fifty
tooth sprocket that is splined to the assembly. The
spline joint is a non ± serviceable press fit anti rattle
type. The idler sprocket assembly spins on a station-
ary idler shaft. The idler shaft is press-fit into the
cylinder block. A large washer on the idler shaft bolt
and the rear flange of the idler shaft are used to con-
trol sprocket thrust movement. Pressurized oil is
routed through the center of the idler shaft to pro-
vide lubrication for the two bushings used in the
idler sprocket assembly.
There are two secondary drive chains, both are
inverted tooth type, one to drive the camshaft in each
SOHC cylinder head. There are no shaft speed
changes in the secondary chain drive system. Each
secondary chain drives a thirty tooth cam sprocket
directly from the thirty tooth sprocket on the idler
Fig. 114 Timing Drive System
1 - RIGHT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET AND SECONDARY CHAIN
2 - SECONDARY TIMING CHAIN TENSIONER (LEFT AND RIGHT
SIDE NOT COMMON)
3 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
4 - LEFT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET AND SECONDARY CHAIN
5 - CHAIN GUIDE
6 - TWO PLATED LINKS ON RIGHT CAMSHAFT CHAIN7 - PRIMARY CHAIN
8 - IDLER SPROCKET
9 - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET
10 - PRIMARY CHAIN TENSIONER
11 - TWO PLATED LINKS ON LEFT CAMSHAFT CHAIN
12 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
9 - 166 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
Page 1390 of 2627

sprocket assembly. A fixed chain guide and a hydrau-
lic oil damped tensioner are used to maintain tension
in each secondary chain system. The hydraulic ten-
sioners for the secondary chain systems are fed pres-
surized oil from oil reservoir pockets in the block.
Each tensioner also has a mechanical ratchet system
that limits chain slack if the tensioner piston bleeds
down after engine shut down. The tensioner arms
and guides also utilize nylon wear faces for low fric-
tion and long wear. The secondary timing chains
receive lubrication from a small orifice in the ten-
sioners. This orifice is protected from clogging by a
fine mesh screen which is located on the back of the
hydraulic tensioners.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐMEASURING
TIMING CHAIN WEAR
NOTE: This procedure must be performed with the
timing chain cover removed.
(1) Remove the timing chain cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) To determine if the secondary timing chains
are worn, rotate the engine clockwise until maximum
tensioner piston extension is obtained. Measure the
distance between the secondary timing chain ten-
sioner housing and the step ledge on the piston (Fig.
115). The measurement at point (A) must be less
than 15mm (0.5906 inches).
(3) If the measurement exceeds the specification
the secondary timing chains are worn and require
replacement. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
REMOVAL).
NOTE: If the secondary chains are to be replaced
the primary chain must also be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE TIMING -
VERIFICATION
CAUTION: The 4.7L is a non free-wheeling design
engine. Therefore, correct engine timing is critical.NOTE: Components referred to as left hand or right
hand are as viewed from the drivers position inside
the vehicle.
NOTE: The blue link plates on the chains and the
dots on the camshaft drive sprockets may not line
up during the timing verification procedure. The
blue link plates are lined up with the sprocket dots
only when re-timing the complete timing drive.
Once the timing drive is rotated blue link-to-dot
alignment is no longer valid.
Engine base timing can be verified by the following
procedure:
(1) Remove the cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
Fig. 115 Measuring Secondary Timing Chains For
Wear
1 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
2 - SECONDARY CHAIN TENSIONER PISTON
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 167
VALVE TIMING (Continued)
Page 1391 of 2627

(2) Using a mirror, locate the TDC arrow on the
front cover (Fig. 116). Rotate the crankshaft until the
mark on the crankshaft damper is aligned with the
TDC arrow on the front cover. The engine is now at
TDC.
(3) Note the location of the V8 mark stamped into
the camshaft drive gears (Fig. 117). If the V8 mark
on each camshaft drive gear is at the twelve o'clock
position, the engine is at TDC (cylinder #1) on the
exhaust stroke. If the V8 mark on each gear is at the
six o'clock position, the engine is at TDC (cylinder
#1) on the compression stroke.
(4) If both of the camshaft drive gears are off in
the same or opposite directions, the primary chain or
both secondary chains are at fault. Refer to Timing
Chain and Sprockets procedure in this section.
(5) If only one of the camshaft drive gears is off
and the other is correct, the problem is confined to
one secondary chain. Refer to Single camshaft tim-
ing, in this procedure.
(6) If both camshaft drive gear V8 marks are at
the twelve o'clock or the six o' clock position the
engine base timing is correct. Reinstall the cylinder
head covers.
Fig. 116 Engine Top Dead Center (TDC) Indicator
Mark
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - CRANKSHAFT TIMING MARKS
Fig. 117 Camshaft Sprocket V8 Marks
1 - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD2 - RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD
9 - 168 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
VALVE TIMING (Continued)
Page 1392 of 2627

SINGLE CAMSHAFT TIMING
NOTE: to adjust the timing on one camshaft, pre-
form the following procedure.
(1) Using Chain Tensioner Wedge, special tool
8350, stabilize the secondary chain drive (Fig. 118).
For reference purposes, mark the chain-to-sprocket
position (Fig. 118).
(2) Remove the camshaft drive gear retaining bolt.
(3) Carefully remove the camshaft drive gear from
the camshaft.
(4) Re-index the camshaft drive gear in the chain
until the V8 mark is at the same position as the V8
mark on the opposite camshaft drive gear.
NOTE: When gripping the camshaft, place the pliers
on the tube portion of the camshaft only. Do not
grip the lobes or the sprocket areas.
(5) Using a suitable pair of adjustable pliers,
rotate the camshaft until the alignment dowel on the
camshaft is aligned with the slot in the camshaft
drive gear (Fig. 119).
CAUTION: Remove excess oil from camshaft
sprocket retaining bolt before reinstalling bolt. Fail-
ure to do so may cause over-torqueing of bolt
resulting in bolt failure.
Fig. 118 Securing Timing Chain Tensioners Using Timing Chain Wedge
1 - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD
2 - RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD3 - SPECIAL TOOL 8350 WEDGE
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8350 WEDGE
Fig. 119 Camshaft Dowel
1 - ADJUSTABLE PLIERS
2 - CAMSHAFT DOWEL
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 169
VALVE TIMING (Continued)
Page 1393 of 2627

(6)Position the camshaft drive gear onto the camshaft,
remove oil from bolt then install the retaining bolt. Using
Special Tools, Spanner Wrench 6958 with Adapter Pins
8346 and a suitable torque wrench, Tighten retaining bolt
to 122N´m (90 ft. Lbs.) (Fig. 120) (Fig. 121).
(7) Remove special tool 8350.
(8) Rotate the crankshaft two full revolutions, then
reverify that the camshaft drive gear V8 marks are
in fact aligned.
(9) Install the cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Disconnect both heater hoses at timing cover.(4) Disconnect lower radiator hose at engine.
(5) Remove crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(6) Remove accessory drive belt tensioner assembly
(Fig. 122).
Fig. 120 Camshaft Sprocket Left Cylinder Head
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
3 - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 6958 SPANNER WITH ADAPTER PINS 8346
Fig. 121 Camshaft Sprocket InstallationÐRight
Cylinder Head
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6958 WITH ADAPTER PINS 8346
3 - LEFT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
4 - RIGHT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
Fig. 122 Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner
1 - TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
2 - FASTENER TENSIONER TO FRONT COVER
9 - 170 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
VALVE TIMING (Continued)