1998 DODGE RAM 1500 PCM
[x] Cancel search: PCMPage 2108 of 2627

(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal oper-
ating mode.
OPERATION
When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to the
solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset, the TCM energizes the
relay. Prior to this, the TCM verifies that the con-
tacts are open by checking for no voltage at the
switched battery terminals. After this is verified, the
voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the TCM mon-
itors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is part of
the solenoid module, which is mounted to the top of
the valve body inside the transmission.
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has five
switch contact pins that:
²Determine shift lever position
²Supply ground to the Starter Relay in Park and
Neutral only.
²
Supply +12 V to the backup lamps in Reverse only.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transmission
temperature to the TCM and PCM.
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) communi-
cates shift lever position to the TCM as a combina-
tion of open and closed switches. Each shift lever
position has an assigned combination of switch states
(open/closed) that the TCM receives from four sense
circuits. The TCM interprets this information and
determines the appropriate transmission gear posi-
tion and shift schedule.
There are many possible combinations of open and
closed switches (codes). Seven of these possible codes
are related to gear position and five are recognized
as ªbetween gearº codes. This results in many codes
which shouldnever occur. These are called
ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result in a DTC,
and the TCM will then determine the shift lever
position based on pressure switch data. This allows
reasonably normal transmission operation with a
TRS failure.
GEAR C5 C4 C3 C2 C1
ParkCL OP OP CL CL
Temp 1CL OP OP CL OP
ReverseOP OP OP CL OP
Temp 2OP OP CL CL OP
Neutral 1OP OP CL CL CL
Neutral 2OP CL CL CL CL
Temp 3OP CL CL CL OP
DriveOP CL CL OP OP
Temp 4OP CL OP OP OP
Manual 2CL CL OP OP OP
Temp 5CL OP OP OP OP
Manual 1CL OP CL OP OP
Fig. 125 Checking Torque Converter Seating-Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 405
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2145 of 2627

(4) Remove the front output shaft seal slinger by
bending (Fig. 85) the slinger ears away from the
transfer case.
(5) Using a suitable pry tool (Fig. 86), remove the
slinger from the output shaft using care not to dam-
age the shaft.(6) Using a screw and a slide hammer, remove the
front output shaft seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the new front output shaft seal with
Installer MB991168A
(2) Install the front output shaft seal slinger with
Installer 8840. Install the slinger onto the shaft until
the tool contacts the rear of the output shaft.
(3) Install a new seal boot clamp onto the seal
boot.
(4) Install the seal boot and clamp onto the slinger
hub and tighten the clamp with Crimp Tool
C-4975-A.
(5) Install front propeller shaft (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/
PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION).
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transfer case position sensor is an electronic
device whose output can be interpreted to indicate
the transfer case's current operating mode. The sen-
sor consists of a five position, resistive multiplexed
circuit which returns a specific resistance value to
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for each trans-
fer case operating mode. The sensor is located on the
top of the transfer case, just left of the transfer case
centerline and rides against the sector plate rooster-
comb. The PCM supplies 5VDC (+/- 0.5V) to the sen-
sor and monitors the return voltage to determine the
sector plate, and therefore the transfer case, position.
OPERATION
During normal vehicle operation, the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) monitors the transfer case
position sensor return voltage to determine the oper-
ating mode of the transfer case. Refer to the Operat-
ing Mode Versus Resistance table for the correct
resistance for each position (Fig. 87).
Fig. 85 Bend Slinger Ears
1 - SLINGER
2 - BEND UPWARD
Fig. 86 Remove Slinger From Shaft
1 - SLINGER
2-PRYTOOL
21 - 442 TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENIIDR
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL (Continued)
Page 2180 of 2627

(6) Fill transfer case to bottom edge of fill plug
opening with MopartATF +4, Automatic Transmis-
sion fluid.
(7) Install and tighten fill plug to 41-54 N´m
(30-40 ft. lbs.).
(8) Lower vehicle.
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the front propeller shaft (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL).
(2) Install two bolts 180É apart into the front out-
put shaft companion flange.
(3) Place holder over the bolts and against the
companion flange (Fig. 94).
(4) Remove and discard the front companion flange
nut.
(5) Remove the companion flange from the front
output shaft. It may be necessary to use Flange
puller 8992 to remove the companion flange.
(6) Using a screw and a slide hammer, remove the
front output shaft seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the new front output shaft seal with
Installer MB991168A.
(2) Install the front companion flange onto the
front output shaft.
(3) Install two bolts 180É apart into the front out-
put shaft companion flange.(4) Place holder over the bolts and against the
companion flange (Fig. 95).
(5) Install a new front companion flange nut.
Tighten the companion flange nut to 258-312 N´m
(190-230 ft.lbs.).
(6) Install front propeller shaft (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/
PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION).
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transfer case position sensor is an electronic
device whose output can be interpreted to indicate
the transfer case's current operating mode. The sen-
sor consists of a five position, resistive multiplexed
circuit which returns a specific resistance value to
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for each trans-
fer case operating mode. The sensor is located on the
top of the transfer case, just left of the transfer case
centerline and rides against the sector plate rooster-
comb. The PCM supplies 5VDC (+/- 0.5V) to the sen-
sor and monitors the return voltage to determine the
sector plate, and therefore the transfer case, position.
OPERATION
During normal vehicle operation, the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) monitors the transfer case
position sensor return voltage to determine the oper-
ating mode of the transfer case. Refer to the Operat-
ing Mode Versus Resistance table for the correct
resistance for each position (Fig. 96).
Fig. 94 Remove Companion Flange Nut
1 - HOLDER 6719
2 - BOLTS
Fig. 95 Install Companion Flange Nut
1 - HOLDER 6719
2 - BOLTS
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV271 21 - 477
FLUID (Continued)
Page 2491 of 2627
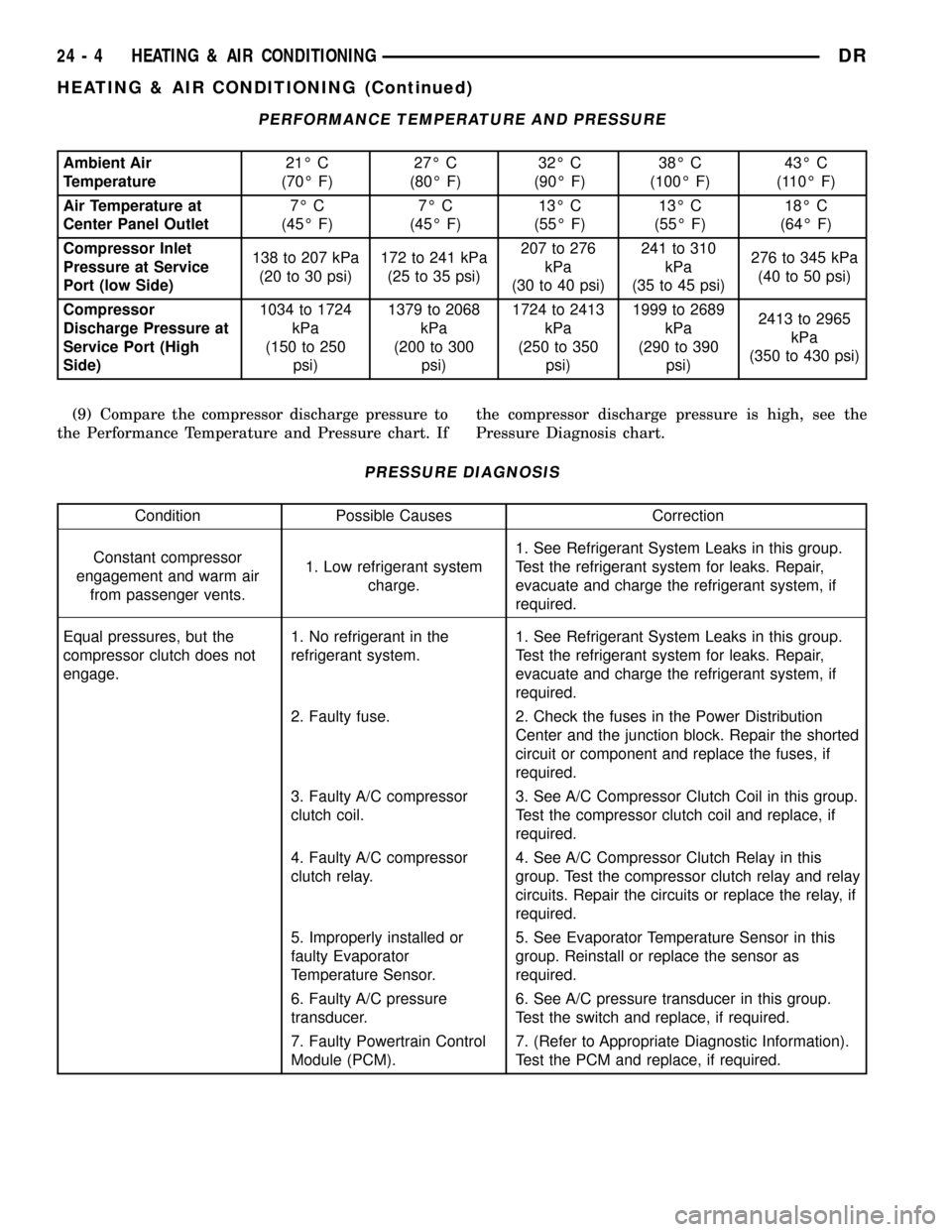
PERFORMANCE TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE
Ambient Air
Temperature21É C
(70É F)27É C
(80É F)32É C
(90É F)38É C
(100É F)43É C
(110É F)
Air Temperature at
Center Panel Outlet7É C
(45É F)7É C
(45É F)13É C
(55É F)13É C
(55É F)18É C
(64É F)
Compressor Inlet
Pressure at Service
Port (low Side)138 to 207 kPa
(20 to 30 psi)172 to 241 kPa
(25 to 35 psi)207 to 276
kPa
(30 to 40 psi)241 to 310
kPa
(35 to 45 psi)276 to 345 kPa
(40 to 50 psi)
Compressor
Discharge Pressure at
Service Port (High
Side)1034 to 1724
kPa
(150 to 250
psi)1379 to 2068
kPa
(200 to 300
psi)1724 to 2413
kPa
(250 to 350
psi)1999 to 2689
kPa
(290 to 390
psi)2413 to 2965
kPa
(350 to 430 psi)
(9) Compare the compressor discharge pressure to
the Performance Temperature and Pressure chart. Ifthe compressor discharge pressure is high, see the
Pressure Diagnosis chart.
PRESSURE DIAGNOSIS
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Constant compressor
engagement and warm air
from passenger vents.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
Equal pressures, but the
compressor clutch does not
engage.1. No refrigerant in the
refrigerant system.1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
2. Faulty fuse. 2. Check the fuses in the Power Distribution
Center and the junction block. Repair the shorted
circuit or component and replace the fuses, if
required.
3. Faulty A/C compressor
clutch coil.3. See A/C Compressor Clutch Coil in this group.
Test the compressor clutch coil and replace, if
required.
4. Faulty A/C compressor
clutch relay.4. See A/C Compressor Clutch Relay in this
group. Test the compressor clutch relay and relay
circuits. Repair the circuits or replace the relay, if
required.
5. Improperly installed or
faulty Evaporator
Temperature Sensor.5. See Evaporator Temperature Sensor in this
group. Reinstall or replace the sensor as
required.
6. Faulty A/C pressure
transducer.6. See A/C pressure transducer in this group.
Test the switch and replace, if required.
7. Faulty Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).7. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information).
Test the PCM and replace, if required.
24 - 4 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGDR
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2497 of 2627

and coil are the only serviced parts on the compres-
sor.
A/C compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the A/C-heater control, A/C pres-
sure transducer, A/C compressor clutch relay, evapo-
rator temperature sensor and the powertrain control
module (PCM). The PCM may delay compressor
clutch engagement for up to thirty seconds (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information). The battery must
be fully-charged before performing the following
tests. Refer to Battery for more information.
(1) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale) in
series with the clutch coil terminal. Use a voltmeter
(0 to 20 volt scale) with clip-type leads for measuring
the voltage across the battery and the compressor
clutch coil.
(2) With the A/C-heater controls in any A/C mode,
and the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, start the engine and run it at normal idle.
(3) The compressor clutch coil voltage should read
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage. If there is
voltage at the clutch coil, but the reading is not
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage, test the clutch
coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop and repair
as required. If there is no voltage reading at the
clutch coil, use a DRB IIItscan tool and (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information) for testing of thecompressor clutch circuit and PCM control. The fol-
lowing components must be checked and repaired as
required before you can complete testing of the clutch
coil:
²Fuses in the junction block and the power distri-
bution center (PDC)
²A/C-heater control
²A/C compressor clutch relay
²A/C pressure transducer
²Evaporator temperature sensor
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
(4) The compressor clutch coil is acceptable if the
current draw measured at the clutch coil is within
specifications with the electrical system voltage at
11.5 to 12.5 volts (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - SPECIFICATIONS). This should
only be checked with the work area temperature at
21É C (70É F). If system voltage is more than 12.5
volts, add electrical loads by turning on electrical
accessories until the system voltage drops below 12.5
volts.
(a) If the clutch coil current reading is above
specifications, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced.
(b) If the clutch coil current reading is zero, the
coil is open and should be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C-heater control to the
Recirculation Mode, the blower motor switch in the
highest speed position, and the engine speed at 1500
to 2000 rpm. This procedure (burnishing) will seat
the opposing friction surfaces and provide a higher
compressor clutch torque capability.
REMOVAL
The refrigerant system can remain fully-charged
during compressor clutch, rotor, or coil replacement.
The compressor clutch can be serviced in the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the compressor clutch coil wire har-
ness connector.
(4) Remove the bolts that secure the compressor to
the mounting bracket.
(5) Remove the compressor from the mounting
bracket. Support the compressor in the engine com-
partment while servicing the clutch.
Fig. 1 Compressor Clutch - Typical
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SHAFT KEY (not used on KJ)
3 - ROTOR
4 - COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
24 - 10 CONTROLSDR
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)
Page 2500 of 2627

NOTE: The air gap is determined by the spacer
shims. When installing an original, or a new clutch
assembly, try the original shims first. When install-
ing a new clutch onto a compressor that previously
did not have a clutch, use a 1.0, 0.50, and 0.13 mil-
limeter (0.040, 0.020, and 0.005 inch) shims from the
new clutch hardware package that is provided with
the new clutch.
(9) To complete the procedure (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The A/C compressor clutch relay (Fig. 10) is a
International Standards Organization (ISO) micro-re-
lay. Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO
micro-relay terminal functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the ISO micro-relay
terminal pattern (or footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the physical dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is located in the
intergrated power module (IPM) in the engine com-
partment. See the fuse and relay layout label affixed
to the inside surface of the IPM cover for A/C com-
pressor clutch relay identification and location.
The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the A/C compressor clutch relay. Fivemale spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of
the base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical
system, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
OPERATION
The A/C compressor clutch relay is an electrome-
chanical switch that uses a low current input from
the powertrain control module (PCM) or engine con-
trol module (ECM) depending on engine application,
to control the high current output to the compressor
clutch electromagnetic coil. The movable common
feed contact point is held against the fixed normally
closed contact point by spring pressure. When the
relay coil is energized, an electromagnetic field is
produced by the coil windings. This electromagnetic
field draws the movable relay contact point away
from the fixed normally closed contact point, and
holds it against the fixed normally open contact
point. When the relay coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns the movable contact point back
against the fixed normally closed contact point. The
resistor or diode is connected in parallel with the
relay coil in the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage
Fig. 9 Check Clutch Air Gap - Typical
1 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 10 A/C Compressor Clutch Micro-Relay
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
DRCONTROLS 24 - 13
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)
Page 2501 of 2627

spikes and electromagnetic interference that can be
generated as the electromagnetic field of the relay
coil collapses.
The A/C compressor clutch relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the integrated power module (IPM). The
inputs and outputs of the A/C compressor clutch
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from a fuse in the IPM through a
fused B(+) circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (86) receives a ground
input from the PCM/ECM through the A/C compres-
sor clutch relay control circuit only when the PCM/
ECM electronically pulls the control circuit to
ground.
²The coil battery terminal (85) receives a battery
current input from PTC 1 in the IPM through a
fused ignition switch output (run) circuit only when
the ignition switch is in the On position.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the compressor clutch coil
through the A/C compressor clutch relay output cir-
cuit only when the A/C compressor clutch relay coil is
energized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the A/C compres-
sor clutch relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
module (IPM) (Fig. 11).
(3) Refer to the fuse and relay layout label on the
IPM cover for compressor clutch relay identification
and location.
(4) Remove the A/C compressor clutch relay from
the IPM.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout label affixed to
the underside of the IPM cover for A/C compressor
clutch relay location.
(2) Position the A/C compressor clutch relay in the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the A/C compressor clutch relay termi-
nals with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(4) Push down firmly on the A/C compressor clutch
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the IPM.(6) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The heater and air conditioning systems use elec-
trical controls. These controls provide the vehicle
operator with a number of setting options to help
control the climate and comfort within the vehicle.
The A/C-heater control for the Single Zone system
(Fig. 12) or Dual Zone system (Fig. 13) is located to
the right of the instrument cluster on the instrument
panel.
The Single Zone control panel contains a rotary-
type temperature control switch, a rotary-type mode
control switch and a rotary-type blower motor speed
switch. The A/C-heater control also has a push but-
ton to activate the optional heated side view mirror
defroster elements and to turn the A/C on.
The Dual Zone control panel contains a pair of slid-
er-type temperature control switches, a rotary-type
mode control switch and a rotary-type blower motor
speed switch. The control also has buttons to activate
the optional heated sideview mirror defroster ele-
ments, turn the A/C on and set the system to Max
A/C.
The A/C-heater control panel cannot be repaired. If
faulty or damaged, the entire unit must be replaced.
Fig. 11 Integrated Power Module (IPM)
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
24 - 14 CONTROLSDR
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2503 of 2627

The A/C pressure transducer cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The A/C pressure transducer monitors the pres-
sures in the high side of the refrigerant system
through its connection to a fitting on the discharge
line. The transducer will change its internal resis-
tance in response to the pressures it monitors. The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or the Engine
Control Module (ECM) depending on engine applica-
tion, provides a five volt reference signal and a sen-
sor ground to the transducer, then monitors the
output voltage of the transducer on a sensor return
circuit to determine refrigerant pressure. The PCM/
ECM is programmed to respond to this and other
sensor inputs by controlling the operation of the air
conditioning compressor clutch and the radiator cool-
ing fan to help optimize air conditioning system per-
formance and to protect the system components from
damage. The A/C pressure transducer input to the
PCM/ECM will also prevent the air conditioning com-
pressor clutch from engaging when ambient temper-
atures are below about 10É C (50É F) due to the
pressure/temperature relationship of the refrigerant.
The Schrader-type valve in the discharge line fitting
permits the A/C pressure transducer to be removed
or installed without disturbing the refrigerant in the
system. The A/C pressure transducer is diagnosed
using a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
The A/C pressure transducer is tested using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information. Before testing the A/C pressure
transducer, be certain that the transducer wire har-
ness connection is clean of corrosion and properly
connected. For the air conditioning system to operate,
an A/C pressure transducer voltage reading between
0.451 and 4.519 volts is required. Voltages outside
this range indicate a low or high refrigerant system
pressure condition to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) or Engine Control Module (ECM) depending
on engine application. The PCM/ECM is programmed
to respond to a low or high refrigerant system pres-
sure by suppressing operation of the compressor.
Refer to the A/C Pressure Transducer Voltage chart
for the possible conditions indicated by the trans-
ducer voltage reading.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER VOLTAGE
CHART
Voltage Possible Indication
0.0 1. No sensor supply voltage from
PCM/ECM.
2. Shorted sensor circuit.
3. Faulty transducer.
0.150 TO 0.450 1. Ambient temperature below
10É C (50É F).
2. Low refrigerant system
pressure.
0.451 TO 4.519 1. Normal refrigerant system
pressure.
4.520 TO 4.850 1. High refrigerant system
pressure.
5.0 1. Open sensor circuit.
2. Faulty transducer.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Note: It is not necessary to discharge the
refrigerant system to replace the A/C pressure
transducer.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
A/C pressure transducer.
(3) Remove the A/C pressure transducer from the
fitting on the discharge line (Fig. 15).
(4) Remove the O-ring seal from the A/C pressure
transducer fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Replace the O-ring seal before installing the
A/C pressure transducer.
(1) Lubricate a new rubber O-ring seal with clean
refrigerant oil and install it on the A/C pressure
transducer fitting. Use only the specified O-rings as
they are made of a special material for the R-134a
system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type recom-
mended for the A/C compressor in the vehicle.
(2) Install and tighten the A/C pressure transducer
onto the discharge line fitting. The transducer should
be hand-tightened securely onto the discharge line
fitting.
(3) Connect the wire harness connector to the A/C
pressure transducer.
24 - 16 CONTROLSDR
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (Continued)