1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Cooling system
[x] Cancel search: Cooling systemPage 1523 of 2627
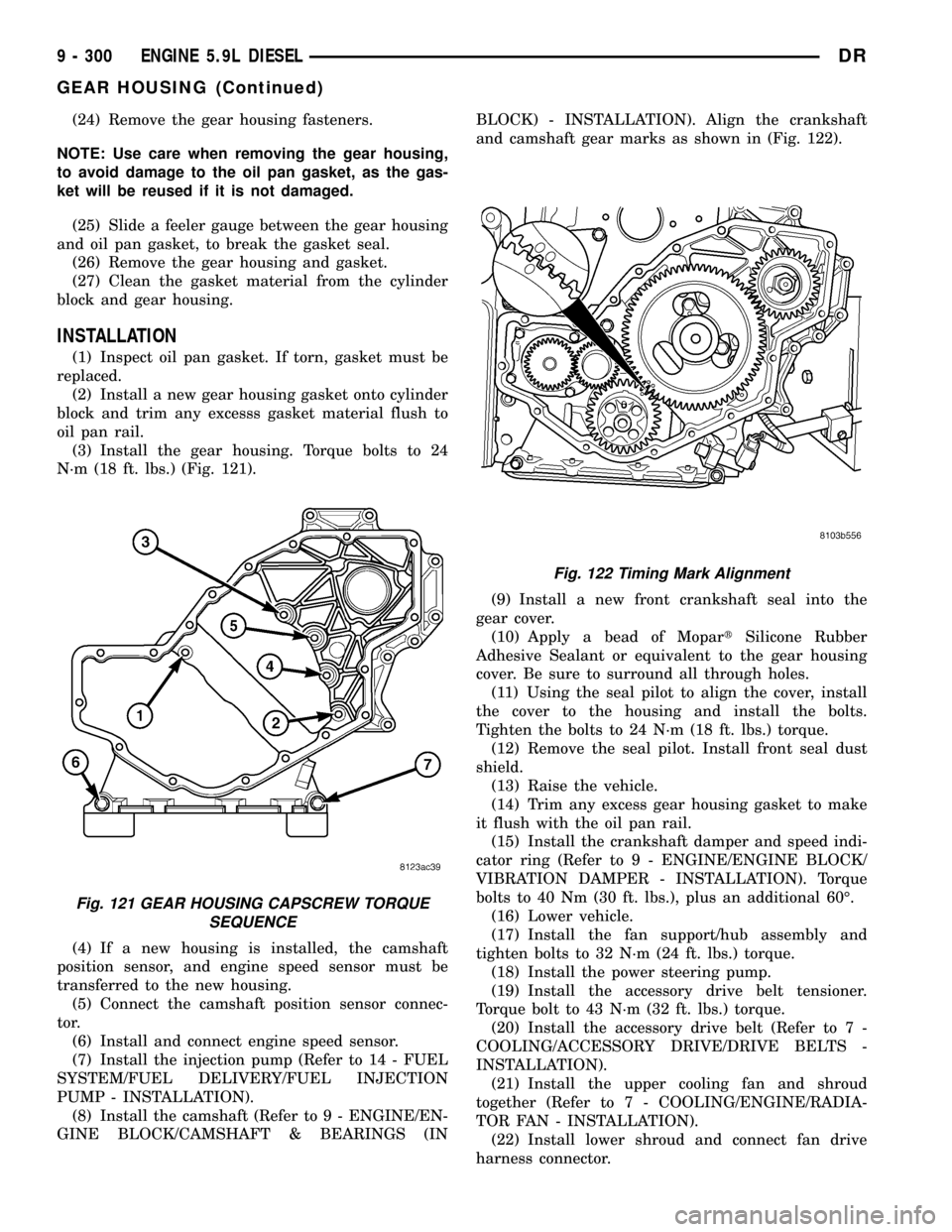
(24) Remove the gear housing fasteners.
NOTE: Use care when removing the gear housing,
to avoid damage to the oil pan gasket, as the gas-
ket will be reused if it is not damaged.
(25) Slide a feeler gauge between the gear housing
and oil pan gasket, to break the gasket seal.
(26) Remove the gear housing and gasket.
(27) Clean the gasket material from the cylinder
block and gear housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Inspect oil pan gasket. If torn, gasket must be
replaced.
(2) Install a new gear housing gasket onto cylinder
block and trim any excesss gasket material flush to
oil pan rail.
(3) Install the gear housing. Torque bolts to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 121).
(4) If a new housing is installed, the camshaft
position sensor, and engine speed sensor must be
transferred to the new housing.
(5) Connect the camshaft position sensor connec-
tor.
(6) Install and connect engine speed sensor.
(7) Install the injection pump (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL INJECTION
PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (INBLOCK) - INSTALLATION). Align the crankshaft
and camshaft gear marks as shown in (Fig. 122).
(9) Install a new front crankshaft seal into the
gear cover.
(10) Apply a bead of MopartSilicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant or equivalent to the gear housing
cover. Be sure to surround all through holes.
(11) Using the seal pilot to align the cover, install
the cover to the housing and install the bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Remove the seal pilot. Install front seal dust
shield.
(13) Raise the vehicle.
(14) Trim any excess gear housing gasket to make
it flush with the oil pan rail.
(15) Install the crankshaft damper and speed indi-
cator ring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
VIBRATION DAMPER - INSTALLATION). Torque
bolts to 40 Nm (30 ft. lbs.), plus an additional 60É.
(16) Lower vehicle.
(17) Install the fan support/hub assembly and
tighten bolts to 32 N´m (24 ft. lbs.) torque.
(18) Install the power steering pump.
(19) Install the accessory drive belt tensioner.
Torque bolt to 43 N´m (32 ft. lbs.) torque.
(20) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(21) Install the upper cooling fan and shroud
together (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIA-
TOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(22) Install lower shroud and connect fan drive
harness connector.
Fig. 121 GEAR HOUSING CAPSCREW TORQUE
SEQUENCE
Fig. 122 Timing Mark Alignment
9 - 300 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
GEAR HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1542 of 2627
CAUTION: Do not apply more than 138 kPa (20 psi)
air pressure to the charge air cooler system, sever
damage to the charge air cooler system may occur.
(3) Connect a regulated air supply to air fitting on
Tool 9022 Adapter. Set air pressure to a Maximum of
138 kPa (20 psi).
(4) Using soapy water check the rubber sleeves,
charge air cooler and intake manifold for leaks.
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF THE ENGINE WAS JUST TURNED
OFF, THE AIR INTAKE SYSTEM TUBES MAY BE
HOT.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Discharge the A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE) and remove the A/C condenser
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL) (if A/C
equipped).
(3) Remove the transmission auxiliary cooler
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION/TRANS
COOLER - REMOVAL).
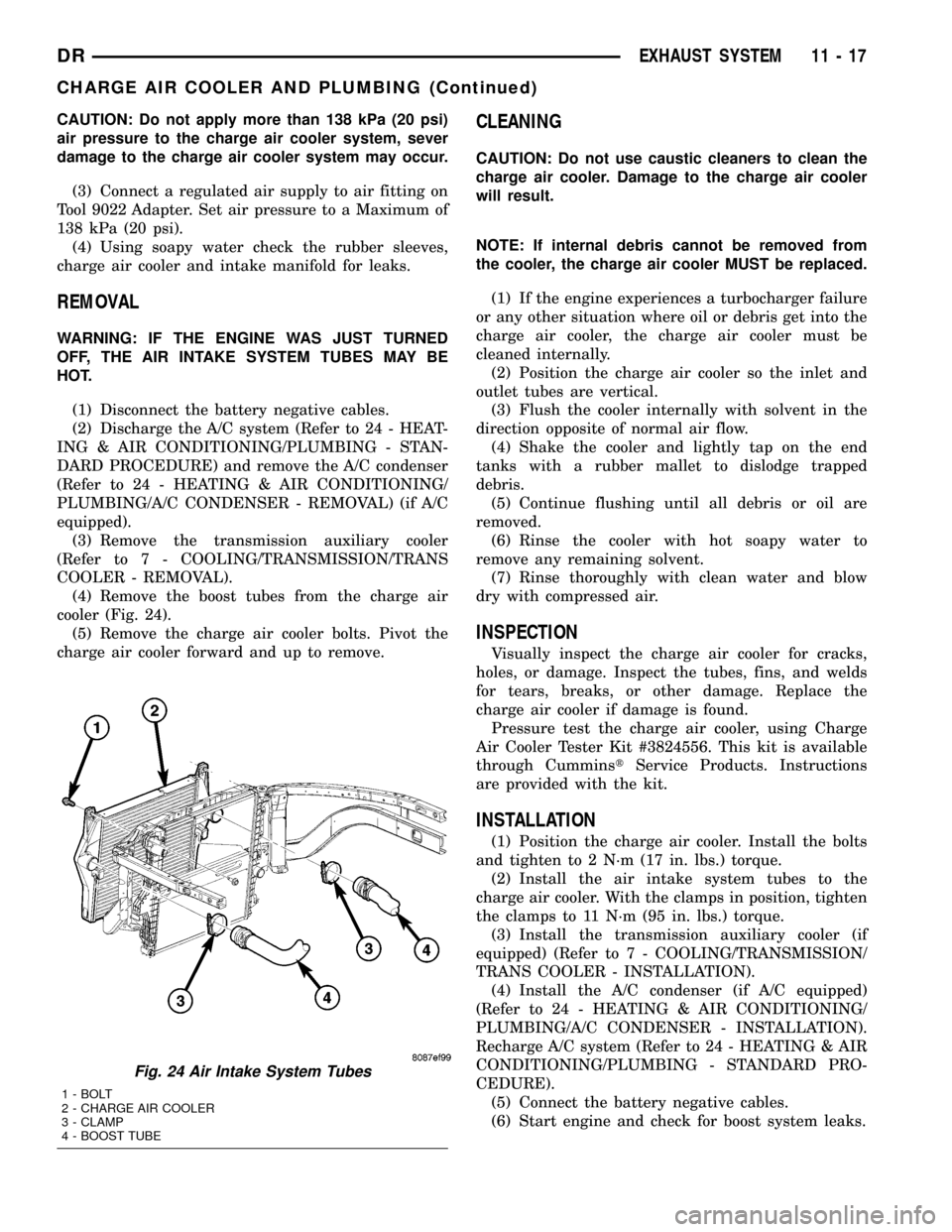
(4) Remove the boost tubes from the charge air
cooler (Fig. 24).
(5) Remove the charge air cooler bolts. Pivot the
charge air cooler forward and up to remove.
CLEANING
CAUTION: Do not use caustic cleaners to clean the
charge air cooler. Damage to the charge air cooler
will result.
NOTE: If internal debris cannot be removed from
the cooler, the charge air cooler MUST be replaced.
(1) If the engine experiences a turbocharger failure
or any other situation where oil or debris get into the
charge air cooler, the charge air cooler must be
cleaned internally.
(2) Position the charge air cooler so the inlet and
outlet tubes are vertical.
(3) Flush the cooler internally with solvent in the
direction opposite of normal air flow.
(4) Shake the cooler and lightly tap on the end
tanks with a rubber mallet to dislodge trapped
debris.
(5) Continue flushing until all debris or oil are
removed.
(6) Rinse the cooler with hot soapy water to
remove any remaining solvent.
(7) Rinse thoroughly with clean water and blow
dry with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the charge air cooler for cracks,
holes, or damage. Inspect the tubes, fins, and welds
for tears, breaks, or other damage. Replace the
charge air cooler if damage is found.
Pressure test the charge air cooler, using Charge
Air Cooler Tester Kit #3824556. This kit is available
through CumminstService Products. Instructions
are provided with the kit.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the charge air cooler. Install the bolts
and tighten to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the air intake system tubes to the
charge air cooler. With the clamps in position, tighten
the clamps to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the transmission auxiliary cooler (if
equipped) (Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION/
TRANS COOLER - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the A/C condenser (if A/C equipped)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/A/C CONDENSER - INSTALLATION).
Recharge A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(5) Connect the battery negative cables.
(6) Start engine and check for boost system leaks.
Fig. 24 Air Intake System Tubes
1 - BOLT
2 - CHARGE AIR COOLER
3 - CLAMP
4 - BOOST TUBE
DREXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 17
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 1555 of 2627

(14) Remove the bolts attaching the lower radiator
crossmember to the hydroform fender rail. (Fig. 18)
CAUTION: Do not use any flame or plasma cutting
equipment to cut the frame in this procedure. The
inaccurate and high temperatures achieved during
flame or plasma cutting will change the metal char-
acteristics and may weaken the frame and/or repair
location.
(15) Using a reciprocating saw or equivalent, cut
the fender rail and shotgun at a straight and square
section of the hydroform and remove.
(16) Smooth and square the cut edges.
(17) Using the damaged structure as a reference
cut the service part at the same location as the first
cut. Smooth and square the cut edges.
NOTE: The repair structure should butt up to the
remaining structure and provide the same overall
vehicle geometry.
(18) Fabricate 51 mm (2.0 in.) long repair inserts
using scrap from the old structure or the replacement
part. It will be necessary to split the inserts on each
of their four sides to fit into the hydroform.
(19) Remove any paint or e-coat from the inserts
and also to the interior and exterior of the hydro-
forms.
(20) Cut plug weld holes as described below.
²On the upper rail, cut one 13 mm (0.5 in.) hole
on each side of the rail, 25 mm (1.0 in.) from the butt
joint of the tubes.
²On the lower rail, cut one 13 mm (0.5 in.) hole
on the top and bottom sides of the rail 25 mm (1.0
in.) from the butt joint of the tube.
²On the lower rail, cut two 13 mm (0.5 in.) holes
on the inner and outer sides of the rail 25 mm (1.0
in.) from the butt joint of the tube.
CAUTION: Shield the surrounding area and compo-
nents from exposure to the welding spatter and
heat.
(21) Install the insert 1º into the replacement part
and tack into place with a weld. (Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME - SPECIFICATIONS -
WELDING)
(22) Insert the service part into place and using
the appropriate measuring equipment, verify the
front end sheet metal bracket's location in all three
(X,Y, and Z) planes of space. (Fig. 19)
(23) Complete all 360É plug welds.
NOTE: Before the final welding, use three dimen-
sional measuring equipment to ensure the part is in
the correct location. Verify that tap plate extrusion
at the bottom of the vertical post lines up with theisolator and hole in the frame perch mount. Also
ensure the lower radiator closure tube is bolted into
the forward shotgun ends.
(24) Complete welding by making a 360É butt weld
around the fender rails.
(25) Metal finish the exposed welds on the hydro-
forms.
(26) Dress the welded area and apply corrosion
resistant coatings inside and out.
(a) Inside the rail, inject a creeping wax based
rust inhibitor compound to the inside of the hydro-
forms ensuring 100% coverage including the mat-
ing face between the fender rail sections and insert
such that corrosion protection is restored in the
internal cavity.
(b) Apply a durable top coat to the outside of the
repair area.
(27) Install the front cab mount bolt if previously
removed and tighten to 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.).
(28) Install the lower radiator crossmember bolts
and tighten to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.).
(29) Install the headlamp unit. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/HEAD-
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION)
(30) Install the upper radiator crossmember. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/UPPER RADIATOR
CROSSMEMBER - INSTALLATION)
(31) Install the wire harness and ground if previ-
ously removed and install the bolts.
(32) Install the integrated power module, if previ-
ously removed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
DISTRIBUTION/INTEGRATED POWER MODULE -
INSTALLATION)
(33) Install the air cleaner bracket and air cleaner,
if previously removed. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT -
INSTALLATION)
(34) Install the radiator assembly. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR - INSTALLATION)
(35) Install the A/C lines, if previously removed.
Refer to the Heating and Air Conditioning section of
the manual for the recommended procedures.
(36) Install the A/C condenser, if previously
removed. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/A/C CONDENSER - INSTAL-
LATION)
(37) Install the fender. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTE-
RIOR/FRONT FENDER - INSTALLATION)
(38) Install the front wheelhouse splash shield.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLATION)
(39) Reconnect the battery ground.
13 - 12 FRAMES & BUMPERSDR
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1625 of 2627

This will ensure proper gear-to-shaft tighten-
ing.
(5) Clean pump gear and pump shaft at machined
tapers with an evaporative type cleaner such as
brake cleaner.
(6) Position injection pump to mounting flange on
gear housing while aligning injection pump shaft
through back of injection pump gear.
(7) After pump is positioned flat to mounting
flange, install 3 pump mounting nuts and tighten
finger tight only.Do not attempt a final tightening
at this time.Do not attempt to tighten (pull)
pump to gear housing using mounting nuts.
Damage to pump or gear cover may occur. The
pump must be positioned flat to its mounting
flange before attempting to tighten 3 mounting
nuts.
(8) To prevent damage or cracking of components,
install and tighten nuts in the following sequence:
(a) Install injection pump shaft washer and nut
to pump shaft. Tighten nutfinger tight only.
(b) Do preliminary (light) tightening of injection
pump shaft nut.
(c) Tighten 3 injection pump mounting nuts to
24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).(d) Do a final tightening of pump shaft nut to
105 N´m (77 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install drive gear access cover (plate) using a
3/8º drive ratchet. Plate is threaded to timing gear
cover. Tighten to 8 N´m (71 in. lbs.) torque.
(10) Install fuel line (injection pump-to-pressure
limiting valve). Tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(11) Install fuel line (injection pump-to-fuel rail).
(a) Tighten fitting at fuel pump to 37 N´m (27 ft.
lbs.) torque. Use a back-up wrench.
(b) Tighten fitting at fuel rail to 37 N´m (27 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(12) Install fuel line (injection pump-to-fuel filter
housing). Tighten to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Connect Fuel Control Actuator (FCA) electri-
cal connector to rear of injection pump.
(14) Install intake manifold air intake tube (above
injection pump). Tighten clamps.
(15) Install accessory drive belt.
(16) Install cooling fan shroud.
(17) Install cooling fan assembly.
(18) Connect both negative battery cables to both
batteries.
(19) Check system for fuel or engine oil leaks.
Fig. 12 FUEL INJECTION PUMP REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
1 - PUMP DRIVE GEAR NUT
2 - WASHER
3 - PUMP DRIVE GEAR
4 - RUBBER O-RING
5 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP6 - PUMP MOUNTING NUTS (3)
7 - PUMP MOUNTING STUDS (3)
8 - O-RING MACHINED GROOVE
9 - FRONT TIMING GEAR HOUSING
14 - 56 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELDR
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1854 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BUZZING NOISE 1. Fluid Level Low 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Mis-assembled. 2. Route cable away from engine and bell
housing.
3. Valve Body Mis-assembled. 3. Remove, disassemble, inspect valve
body. Reassemble correctly if necessary.
Replace assembly if valves or springs are
damaged. Check for loose bolts or screws.
4. Pump Passages Leaking. 4. Check pump for porous casting, scores
on mating surfaces and excess rotor
clearance. Repair as required. Loose pump
bolts.
5. Cooling System Cooler Plugged. 5. Flow check cooler circuit. Repair as
needed.
6. Overrunning Clutch Damaged. 6. Replace clutch.
SLIPS IN REVERSE ONLY 1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust linkage.
3. Rear Band Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust band.
4. Rear Band Worn. 4. Replace as required.
5. Overdrive Direct Clutch Worn. 5. Disassemble overdrive. Repair as
needed.
6. Hydraulic Pressure Too Low. 6. Perform hydraulic pressure tests to
determine cause.
7. Rear Servo Leaking. 7. Air pressure check clutch-servo operation
and repair as required.
8. Band Linkage Binding. 8. Inspect and repair as required.
SLIPS IN FORWARD
DRIVE RANGES1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Fluid Foaming. 2. Check for high oil level, bad pump
gasket or seals, dirt between pump halves
and loose pump bolts. Replace pump if
necessary.
3. Throttle Linkage Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust linkage.
4. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 4. Adjust linkage.
5. Rear Clutch Worn. 5. Inspect and replace as needed.
6. Low Hydraulic Pressure Due to
Worn Pump, Incorrect Control
Pressure Adjustments, Valve Body
Warpage or Malfunction, Sticking,
Leaking Seal Rings, Clutch Seals
Leaking, Servo Leaks, Clogged Filter
or Cooler Lines.6. Perform hydraulic and air pressure tests
to determine cause.
7. Rear Clutch Malfunction, Leaking
Seals or Worn Plates.7. Air pressure check clutch-servo operation
and repair as required.
8. Overrunning Clutch Worn, Not
Holding (Slips in 1 Only).8. Replace Clutch.
SLIPS IN LOW GEAR9D9
ONLY, BUT NOT IN
MANUAL 1 POSITIONOverrunning Clutch Faulty. Replace overrunning clutch.
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 151
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1905 of 2627

(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, thegeartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
vehicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to NEUTRAL.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep
dirt from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick (Fig. 87) and check fluid level
as follows:
(a) Correct acceptable level is in crosshatch area.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN line.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough MopartAT F
+4 to restore correct level. Do not overfill.
Fig. 87 Dipstick Fluid Level Marks - Typical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
21 - 202 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 2016 of 2627

TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS
The 45RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime...........................1.50:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
Reverse.............................3.00:1
GEAR RATIOS
The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime...........................1.50:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse.............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 45RFE/545RFE offers full electronic control of
all automatic up and downshifts, and features real-
time adaptive closed-loop shift and pressure control.
Electronic shift and torque converter clutch controls
help protect the transmission from damage due to
high temperatures, which can occur under severe
operating conditions. By altering shift schedules, line
pressure, and converter clutch control, these controls
reduce heat generation and increase transmission
cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmissions includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 45RFE/545RFE pump-pressure
control system monitors input torque and adjusts the
pump pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the
pump works continuously; the second stage is
bypassed when demand is low. The control system
also monitors input and output speed and, if incipi-
ent clutch slip is observed, the pressure control sole-
noid duty cycle is varied, increasing pressure in
proportion to demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 45RFE/545RFE is packaged in
a one-piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH,
the case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiff-
ness. It is also designed to maximize the benefit of
the structural dust cover that connects the bottom of
the bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing
overall power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRBtscan tool.
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
1 - IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS (STAMPED)
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 313
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2069 of 2627

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repairThe use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P (PARK)
and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever
in P (PARK) to be sure that the fluid level check is
accurate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.At normal operating temperature
(approximately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is cor-
rect if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on
the oil level indicator. The fluid level will be approx-
21 - 366 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR