Page 49 of 72

50
SSP 198/16
Sensors
The hot-film air mass meter
operates on the same principle as
before.
In certain engine operating states,
pulsations occur in the intake tract,
reversing the air flow - and this
gives rise to measurement errors.
The hot-film air mass meter is designed in such
a way that it is able to recognise this returning
air flow (pulsation fault).
This more exact method of intake air
measurement in all operating states improves
engine management and reduces exhaust
emissions.
The hot-film air mass meter is a thermal
flowmeter. A partial airflow from the
measuring pipe is fed past the sensor element
through a measuring channel in the air mass
meter housing.
The ascertained temperature values are
evaluated in the evaluation electronics. The
Motronic applies a voltage proportional to the
air mass to the air mass meter. This voltage is
needed to calculate the injection period and of
actual engine torque.
Substitute function and self-diagnosis:
The air mass meter detects air masses above
or below predefined limits. If the air mass
meter fails, the air mass is calculated on the
basis of a characteristic curve (throttle valve
angle and engine speed).
Hot-film air mass meter
Sensor element
Meas.
channel
Evaluation electronics
Hot-film air mass meter G70
Page 50 of 72
51
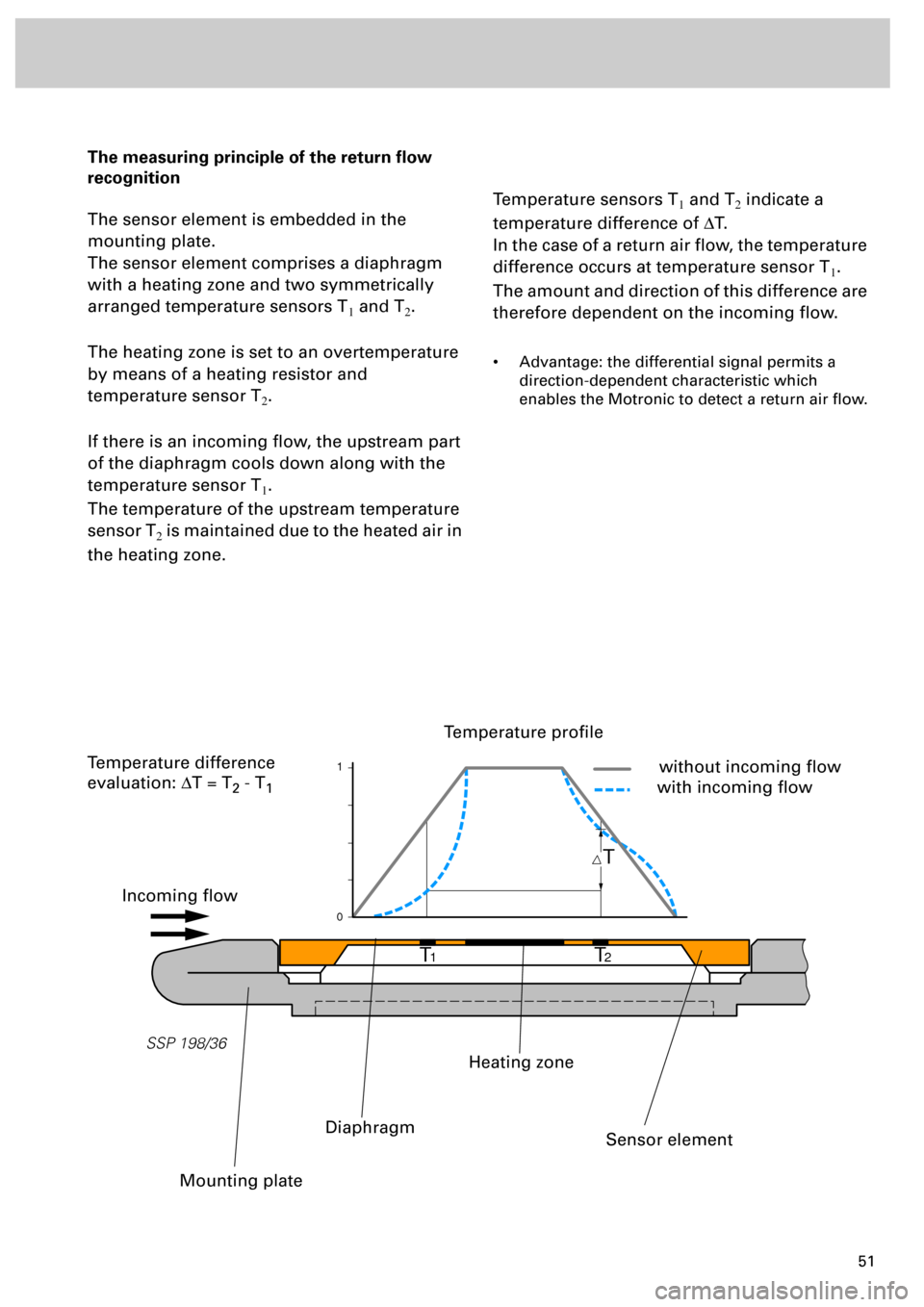
The measuring principle of the return flow
recognition
The sensor element is embedded in the
mounting plate.
The sensor element comprises a diaphragm
with a heating zone and two symmetrically
arranged temperature sensors T
1 and T2.
The heating zone is set to an overtemperature
by means of a heating resistor and
temperature sensor T
2.
If there is an incoming flow, the upstream part
of the diaphragm cools down along with the
temperature sensor T
1.
The temperature of the upstream temperature
sensor T
2 is maintained due to the heated air in
the heating zone.
Temperature sensors T1 and T2 indicate a
temperature difference of DT.
In the case of a return air flow, the temperature
difference occurs at temperature sensor T
1.
The amount and direction of this difference are
therefore dependent on the incoming flow.
• Advantage: the differential signal permits a
direction-dependent characteristic which
enables the Motronic to detect a return air flow.
T
T
1T2
1
0
SSP 198/36
Incoming flow
Temperature profile
without incoming flow
with incoming flow
Mounting plate
Diaphragm
Heating zone
Sensor element
Temperature difference
evaluation: DT = T
2 - T1
Page 66 of 72
67
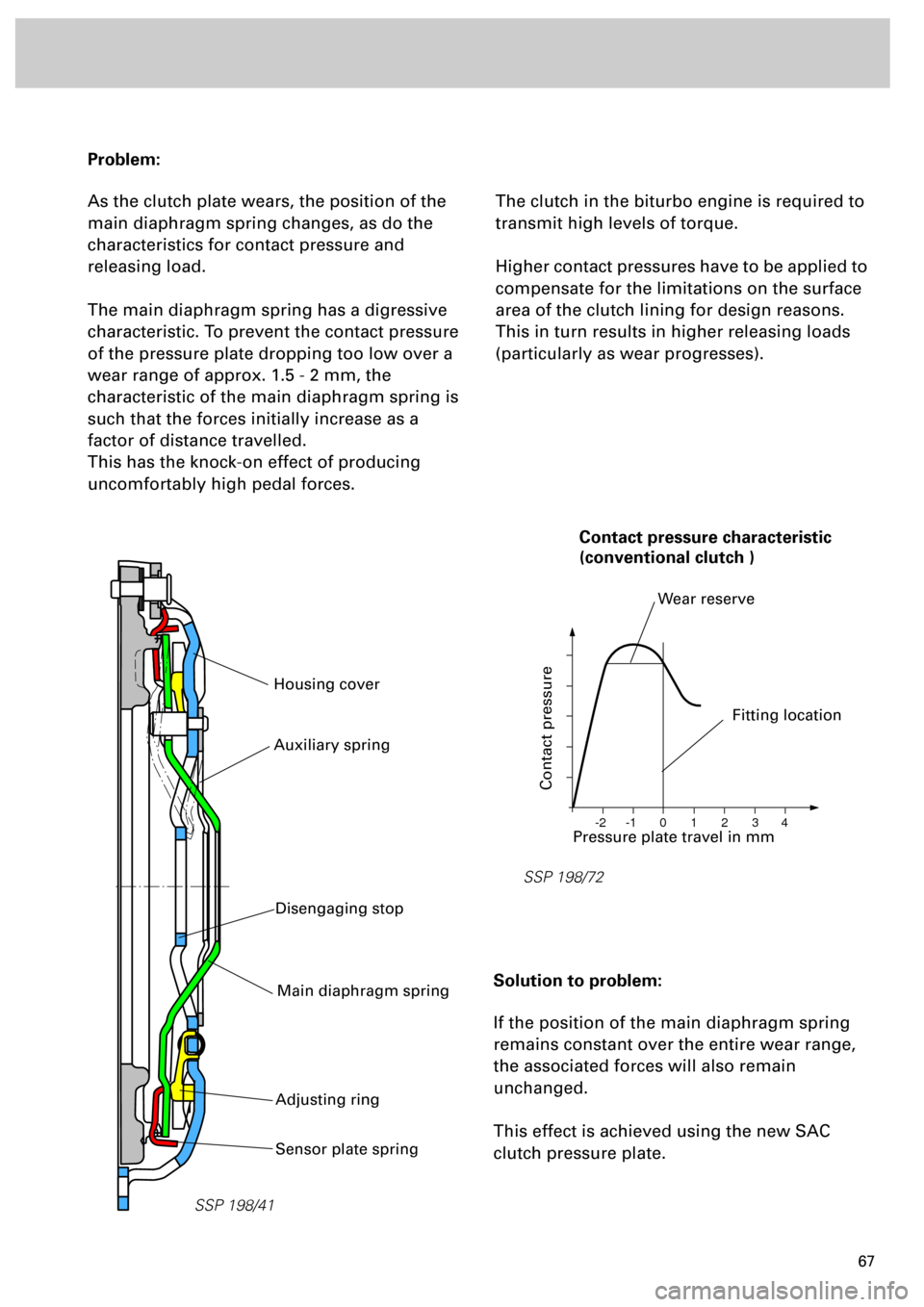
Problem:
As the clutch plate wears, the position of the
main diaphragm spring changes, as do the
characteristics for contact pressure and
releasing load.
The main diaphragm spring has a digressive
characteristic. To prevent the contact pressure
of the pressure plate dropping too low over a
wear range of approx. 1.5 - 2 mm, the
characteristic of the main diaphragm spring is
such that the forces initially increase as a
factor of distance travelled.
This has the knock-on effect of producing
uncomfortably high pedal forces.
The clutch in the biturbo engine is required to
transmit high levels of torque.
Higher contact pressures have to be applied to
compensate for the limitations on the surface
area of the clutch lining for design reasons.
This in turn results in higher releasing loads
(particularly as wear progresses).
Solution to problem:
If the position of the main diaphragm spring
remains constant over the entire wear range,
the associated forces will also remain
unchanged.
This effect is achieved using the new SAC
clutch pressure plate.
SSP 198/41
Housing cover
SSP 198/72
0 -1 -2 1 2 3 4
Pressure plate travel in mm
Contact pressure
Fitting location
Wear reserve
Contact pressure characteristic
(conventional clutch )
Sensor plate spring
Main diaphragm spring
Adjusting ring
Auxiliary spring
Disengaging stop
Page 68 of 72
69
Unlike conventional pressure plates, the main
diaphragm spring mounting of the SAC clutch
is non-rigid.
When the clutch plate is renewed, the
adjusting ring must be turned back
(refer to Workshop Manual).
The adjusting ring on new SAC clutch
pressure plates is already reset.
The sensor plate spring and the adjusting ring
locate (mounting) the main diaphragm spring.
SSP 198/73
after wear
after wear
Position as newPosition after
wearPosition as newPosition after
wear
Main plate
spring mounting
Main plate
spring mounting
Conventional clutch
SAC clutch
Adjusting ring