1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO traction control
[x] Cancel search: traction controlPage 952 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4D-2 FRONT BRAKES
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
When the brakes are applied, fluid pressure is sent to
each brake caliper. The pressure at the caliper is ex-
erted equally against the caliper piston. The pressure
applied to the piston is transmitted directly to the
inboard brake pad. This forces the pad against the inner
surface of the brake rotor. At the same time, fluid
pressure within the caliper piston bore forces the caliper
to slide inward on its guide pins. This action brings the
outboard pad into contact with the outer surface of the
brake rotor. This pressure on both sides of the brake
rotor causes friction, bringing the vehicle to a stop.
BRAKE CALIPER
The caliper has a single bore and is mounted to the
steering knuckle with two mounting bolts. Hydraulic
pressure, created by applying the brake pedal, is con-
verted by the caliper to a stopping force. This force
acts equally against the piston and the bottom of the
caliper bore to move the piston outward and to slide
the caliper inward, resulting in a clamping action on
the rotor. This clamping action forces the linings against
the rotor, creating friction to stop the vehicle.Important:
•Replace all components included in the repair kits
used to service the caliper.
Lubricate the rubber parts with clean brake fluid to
ease assembly.
Do not use lubricated shop air on brake parts, as
damage to the rubber components may result.
If any hydraulic component is removed or discon-
nected, it may be necessary to bleed all or part of
the brake system. Refer to Section 4F, Antilock
Brake System And Traction Control System.
Replace the pads in axle sets only.
The torque values specified are for dry, unlubricated
fasteners.
Perform the service operations on a clean bench,
free from all oily material.
BRAKE PADS
There are two brake pads mounted to each caliper, one
inboard and one outboard. As front disc brake pad wear,
master cylinder reservoir brake fluid level will drop. Fluid
level should be checked after replacing pads.
BRAKE ROTOR
Each front disc brake rotor is vented to help cool it dur-
ing and after brake applications.
Page 985 of 2053

SECTION 4F
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM AND
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
General Description and System Opertion..........4F-3
Basic Knowledge Required...................................4F-3
ABS System Components...................................4F-3
Traction Control System (TCS) Description...........4F-3
EBD System........................................................4F-5
EBD Failure Matrix...............................................4F-6
Tires and ABS/TCS..............................................4F-7
Hydraulic Circuit...................................................4F-8
ABS 5.3...............................................................4F-8
ABS/TCS 5.3.....................................................4F-11
Component Locator...........................................4F-14
ABS, ABS/TCS 5.3............................................4F-14
Diagnosis............................................................4F-15
Diagnostic Circuit Check....................................4F-15
ABS Indicator Lamp Inoperative.........................4F-18
Traction Control System (TCS) Indicator Lamp
Inoperative.....................................................4F-22
EBD Indicator Lamp Inoperative.........................4F-26
Power Supply to Control Module,
No DTCs Stored..............................................4F-30
ABS Indicator Lamp Illuminated Continuously,
No DTCs Stored..............................................4F-34
Self-Diagnostics................................................4F-36
Displaying DTCs................................................4F-36
Clearing DTCs...................................................4F-36
Intermittents and Poor Connections....................4F-36
DTC 03 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault ...4F-38
DTC 07 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-40
DTC 04 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Fault...............................................................4F-42DTC 08 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-44
DTC 05 - Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault....4F-46
DTC 09 - Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-48
DTC 06 - Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault .4F-50
DTC 10 - Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-52
DTC 11 - Wheel Speed Sensor Frequency Error ..4F-54
DTC 42 - Acceleration Sensor Fault....................4F-58
DTC 43 - Acceleration Sensor Continuity Fault.....4F-60
DTC 13/14 - Left Front Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-62
DTC 15/16 - Right Front Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-64
DTC 17/18 - Left Rear Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-66
DTC 19/20 - Right Rear Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-68
DTC 21/22 - Left Rear Prime Line and Traction
Control System (TCS) Pilot Valve Fault............4F-70
DTC 23/24 - Right Rear Prime Line and Traction
Control System (TCS) Pilot Valve Fault............4F-72
DTC 12 - Valve Relay Circuit Fault......................4F-74
DTC 24 - Pump Motor or Pump Motor
Relay Fault.....................................................4E-76
DTC 27 - Stoplamp Switch Fault.........................4E-80
DTC 28 - Low Voltage Fault................................4E-84
DTC 02 - ABS Control Module Internal Fault........4E-88
Scheatic and Routing Diagrams........................4E-90
ABS Circuit (Without TCS): Gasoline...................4E-90
ABS/TCS Circuit: Gasoline.................................4E-91
ABS/ABD (Automatic Brake
Differential Lock): Diesel.................................4E-93
Page 987 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM OPERATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section, it is important that you have
a basic knowledge of the following items. Without this
knowledge, it will be difficult to use the diagnostic
procedures contained in this section.
•Basic Electrical Circuits - You should understand
the basic theory of electricity and know the meaning
of voltage, current (amps), and resistance (ohms).
You should understand what happens in a circuit
with an open or shorted wire. You should be able to
read and understand a wiring diagram.
Use of Circuit Testing Tools - You should know
how to use a test light and how to bypass
components to test circuits using fused jumper
wires. You should be familiar with a digital
multimeter. You should be able to measure voltage,
resistance, and current, and be familiar with the
controls and how to use them correctly.
ABS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The ABS 5.3 Antilock Braking System (ABS) consists
of a conventional hydraulic brake system plus antilock
components. The conventional brake system includes
a vacuum booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes,
rear disc brakes, interconnecting hydraulic brake pipes
and hoses, brake fluid level switch and the BRAKE
indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM), two system fuses,
four wheel speed sensors (one at each wheel), intercon-
necting wiring, the ABS indicator, the EBD indicator
and the TCS indicator. See “ABS Component Locator”
in this section for the general layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located
between the surge tank and the bulkhead on the left
side of the vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hy-
draulic check valves, two solenoid valves for each
wheel, a hydraulic pump, and two accumulators. The
hydraulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front
calipers and rear calipers by modulating hydraulic
pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
Units equipped with TCS add two more valves for each
drive wheel for the purpose of applying the brake to a
wheel that is slipping. This is done with pressure from
the hydraulic pump in the unit. There is also a TCS
indicator lamp on the instrument panel to alert the driver
to the fact that the TCS system is active. The
components identified in the drawing are those added
to the basic ABS 5.3 system to provide traction control.
Nothing in the hydraulic unit or the EBCM is serviceable.
In the event of any failure, the entire ABS unit withattached EBCM must be replaced. For more
information, refer to “Base Braking Mode” and
“Antilock Braking Mode” in this section.
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
(TCS) DESCRIPTION
General Information
The traction control system (TCS) is a traction system
by means of brake intervention only, available in a low
speed range (< 60kph).
It workes on µ - split roads with sidewise different friction
coefficients.
The spinning driven wheel is braked and the drive
torque can be transferred to the wheel on the high-µ
side. During TCS active, the TCS information lamp is
blinking.
The temperature of the brakes is calculated by a mathe-
matical model and TCS is switched passive if the calcu-
lated temperature is greater than a threshold value (500
°C).
TCS is permitted again, when the calculated tempera-
ture is less than 350 °C.
Control Algorithm
The input signals for the control algorithm are the
filtered wheel speed signals from the ABS speed
processing.
With the speed difference of the driven wheels, the
control deviation is calculated.
If the control deviation exceeds a certain threshold
value, the wheel with the greater slip is braked actively.
The threshold value depends on the vehicle speed:
It is reduced with increasing vehicle speed down to a
constant value.
KAA4F010
Page 999 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-16 ABS AND TCS
1. Install the scan tool.
2. Turn ignition switch to ON.
3. Select the Data List mode.
Is the scan tool receiving data from the electronic
brake control module (EBCM)?
Check the display.
Are there any current DTCs displayed?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK for 10 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition to ON and observe the ABS
indicator.
Does the indicator light for 2 seconds and then go off?
Check the ABS indicator.
Did the ABS indicator turn on and stay on?
Check whether the vehicle is equipped with traction
control.
Is the vehicle equipped with traction control?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK for 10 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition to ON and observe the TCS
indicator.
Does the indicator light for 2 seconds and then go off?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the EBCM harness connector.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Use a digital voltmeter (DVM) to measure the
voltage from ground to terminal 1 and 50 of the
EBCM harness connector.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Use a DVM to measure the resistance from the EBCM
harness connector, terminals 28 and 29 to ground.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Repair the open in the circuit that failed.
Is the repair complete?
Use a DVM to measure the resistance between
terminal 46 of the EBCM harness connector and
terminal 8 of the data link connector (DLC).
Is the resistance below the specified value?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the open or high resistance in circuit BrG
between terminal 11 of the EBCM harness connector
and terminal 13 of the DLC.
Is the repair complete?
Perform the road test described above.
Are any DTCs set? Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Diagnostic Circuit Check
Action Yes
Go to Step 2
Refer to the
applicable DTC
table
Go to Step 5
Go to “ABS
Indicator Lamp
Illuminated
Constantly”
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 13
Go to Step 8
Go to Step 10
System OK
Go to Step 11
System OK
Go to Step 1
Go to the table
for the DTCNo
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 3
Go to Step 4
Go to
“ABS Indicator
Lamp Inopera-
tive
Go to Step 13
Go to “Traction
Control System
Indicator Lamp
Inoperative”
Go to “Power
Supply to
Control Mod-
ule, No DTCs
Stored
Go to Step 9
-
Go to Step 12
-
-
System OK Value(s)
-
-
-
-
-
-
11 - 14 v
≈ 0 Ω
-
2 Ω
-
-
-
Page 1005 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-22 ABS AND TCS
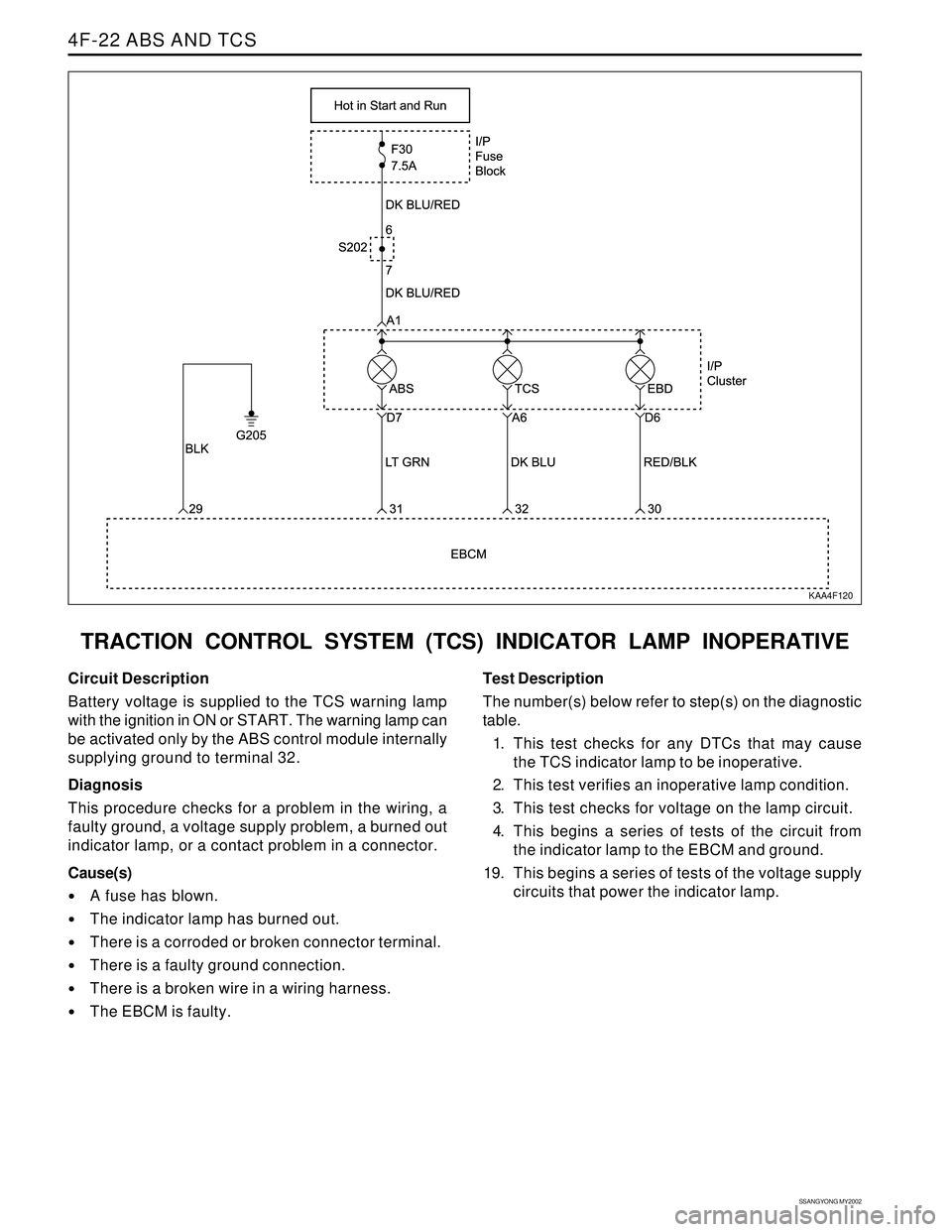
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCS) INDICATOR LAMP INOPERATIVE
KAA4F120
Circuit Description
Battery voltage is supplied to the TCS warning lamp
with the ignition in ON or START. The warning lamp can
be activated only by the ABS control module internally
supplying ground to terminal 32.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a problem in the wiring, a
faulty ground, a voltage supply problem, a burned out
indicator lamp, or a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
A fuse has blown.
The indicator lamp has burned out.
There is a corroded or broken connector terminal.
There is a faulty ground connection.
There is a broken wire in a wiring harness.
The EBCM is faulty.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This test checks for any DTCs that may cause
the TCS indicator lamp to be inoperative.
2. This test verifies an inoperative lamp condition.
3. This test checks for voltage on the lamp circuit.
4. This begins a series of tests of the circuit from
the indicator lamp to the EBCM and ground.
19. This begins a series of tests of the voltage supply
circuits that power the indicator lamp.
Page 1006 of 2053
ABS AND TCS 4F-23
SSANGYONG MY2002
Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
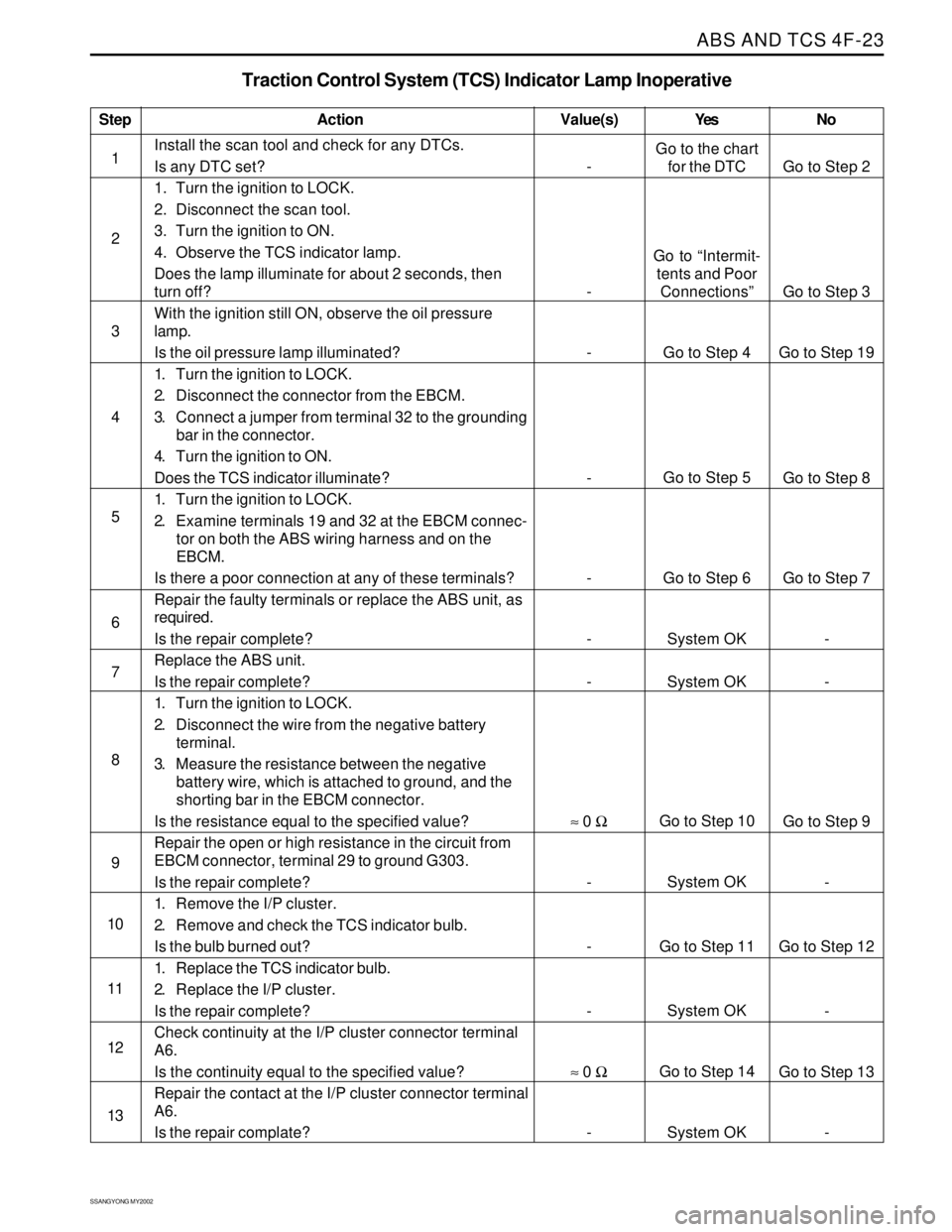
Traction Control System (TCS) Indicator Lamp Inoperative
Action Yes NoValue(s)
Install the scan tool and check for any DTCs.
Is any DTC set?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the scan tool.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Observe the TCS indicator lamp.
Does the lamp illuminate for about 2 seconds, then
turn off?
With the ignition still ON, observe the oil pressure
lamp.
Is the oil pressure lamp illuminated?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the connector from the EBCM.
3. Connect a jumper from terminal 32 to the grounding
bar in the connector.
4. Turn the ignition to ON.
Does the TCS indicator illuminate?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Examine terminals 19 and 32 at the EBCM connec-
tor on both the ABS wiring harness and on the
EBCM.
Is there a poor connection at any of these terminals?
Repair the faulty terminals or replace the ABS unit, as
required.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the wire from the negative battery
terminal.
3. Measure the resistance between the negative
battery wire, which is attached to ground, and the
shorting bar in the EBCM connector.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Repair the open or high resistance in the circuit from
EBCM connector, terminal 29 to ground G303.
Is the repair complete?
1. Remove the I/P cluster.
2. Remove and check the TCS indicator bulb.
Is the bulb burned out?
1. Replace the TCS indicator bulb.
2. Replace the I/P cluster.
Is the repair complete?
Check continuity at the I/P cluster connector terminal
A6.
Is the continuity equal to the specified value?
Repair the contact at the I/P cluster connector terminal
A6.
Is the repair complate?
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
≈ 0 Ω
-
-
-
≈ 0 Ω
-Go to the chart
for the DTC
Go to “Intermit-
tents and Poor
Connections”
Go to Step 4
Go to Step 5
Go to Step 6
System OK
System OK
Go to Step 10
System OK
Go to Step 11
System OK
Go to Step 14
System OKGo to Step 2
Go to Step 3
Go to Step 19
Go to Step 8
Go to Step 7
-
-
Go to Step 9
-
Go to Step 12
-
Go to Step 13
-
Page 1007 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-24 ABS AND TCS
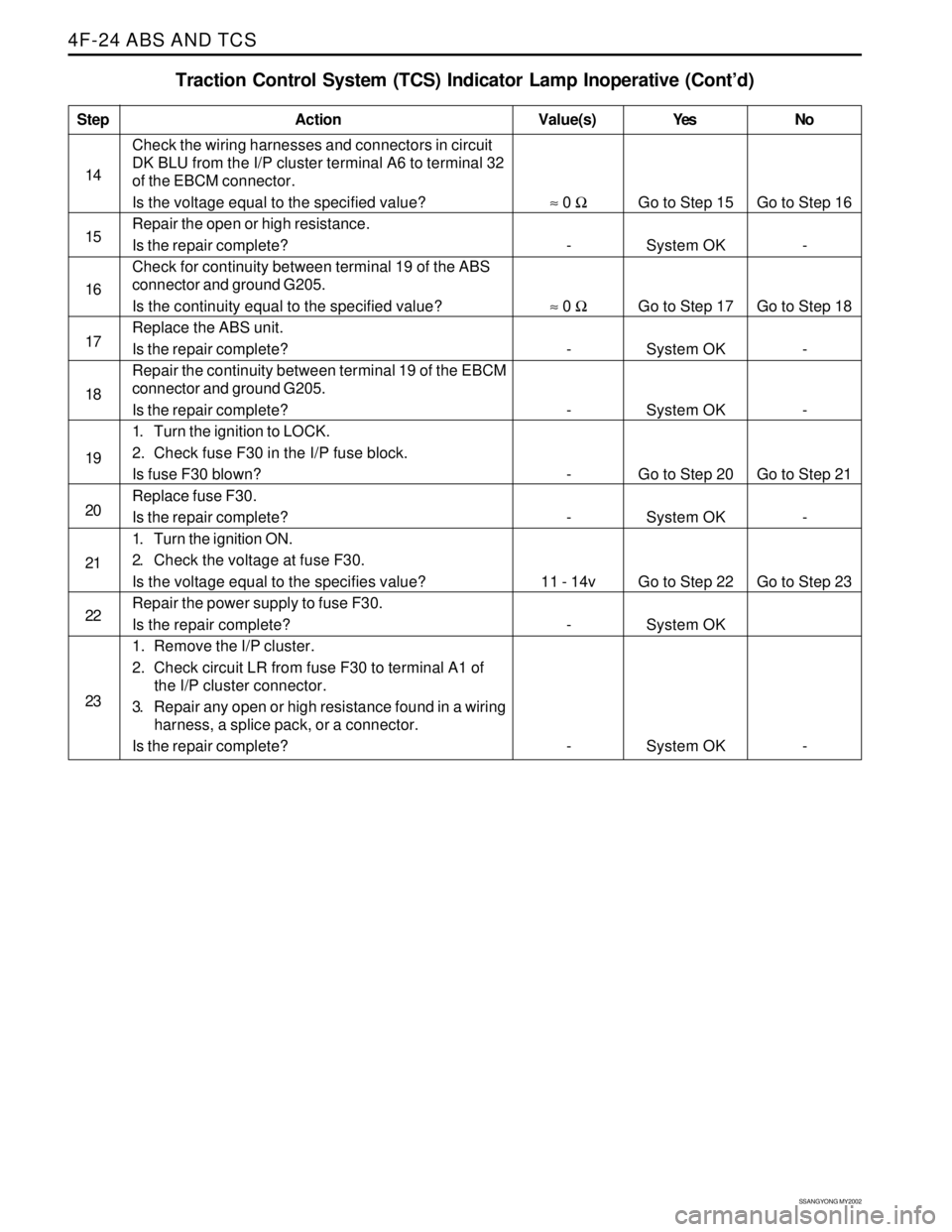
Check the wiring harnesses and connectors in circuit
DK BLU from the I/P cluster terminal A6 to terminal 32
of the EBCM connector.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
Repair the open or high resistance.
Is the repair complete?
Check for continuity between terminal 19 of the ABS
connector and ground G205.
Is the continuity equal to the specified value?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the continuity between terminal 19 of the EBCM
connector and ground G205.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Check fuse F30 in the I/P fuse block.
Is fuse F30 blown?
Replace fuse F30.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition ON.
2. Check the voltage at fuse F30.
Is the voltage equal to the specifies value?
Repair the power supply to fuse F30.
Is the repair complete?
1. Remove the I/P cluster.
2. Check circuit LR from fuse F30 to terminal A1 of
the I/P cluster connector.
3. Repair any open or high resistance found in a wiring
harness, a splice pack, or a connector.
Is the repair complete? Step
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Traction Control System (TCS) Indicator Lamp Inoperative (Cont’d)
Action Yes NoValue(s)
≈ 0 Ω
-
≈ 0 Ω
-
-
-
-
11 - 14v
-
-Go to Step 15
System OK
Go to Step 17
System OK
System OK
Go to Step 20
System OK
Go to Step 22
System OK
System OKGo to Step 16
-
Go to Step 18
-
-
Go to Step 21
-
Go to Step 23
-
Page 1010 of 2053
ABS AND TCS 4F-27
SSANGYONG MY2002
Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Traction Control System (TCS) Indicator Lamp Inoperative
Action
Go to the chart
for the DTC
Go to “Intermit-
tents and Poor
Connections”
Go to Step 4
Go to Step 5
Go to Step 6
System OK
System OK
Go to Step 10
System OK
Go to Step 11
System OK
Go to Step 14
System OKGo to Step 2
Go to Step 3
Go to Step 19
Go to Step 8
Go to Step 7
-
-
Go to Step 9
-
Go to Step 12
-
Go to Step 13
- Value(s)
Install the scan tool and check for any DTCs.
Is any DTC set?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the scan tool.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Observe the EBD indicator lamp.
Does the lamp illuminate for about 2 seconds, then
turn off?
With the ignition still ON, observe the oil pressure
lamp.
Is the oil pressure lamp illuminated?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the connector from the EBCM.
3. Connect a jumper from terminal 30 to the grounding
bar in the connector.
4. Turn the ignition to ON.
Does the EBD indicator illuminate?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Examine terminals 19 and 30 at the EBCM connec-
tor on both the ABS wiring harness and on the
EBCM.
Is there a poor connection at any of these terminals?
Repair the faulty terminals or replace the ABS unit, as
required.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the wire from the negative battery
terminal.
3. Measure the resistance between the negative
battery wire, which is attached to ground, and the
shorting bar in the EBCM connector.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Repair the open or high resistance in the circuit from
EBCM connector, terminal 19 to ground G205.
Is the repair complete?
1. Remove the I/P cluster.
2. Remove and check the TCS indicator bulb.
Is the bulb burned out?
1. Replace the EBD indicator bulb.
2. Replace the I/P cluster.
Is the repair complete?
Check continuity at the I/P cluster connector terminal
D6.
Is the continuity equal to the specified value?
Repair the contact at the I/P cluster connector terminal
D6
Is the repair complate?
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
≈ 0 Ω
-
-
-
≈ 0 Ω
-Yes No