1997 MERCEDES-BENZ ML500 wheel bolt torque
[x] Cancel search: wheel bolt torquePage 1471 of 4133

Basically automatic transmission 722.6 with electronic control offers the following advantages:
Reduced Fuel Consumption
Improved Shift Comfort
More Favorable Gear Steps As A Result Of 5 Gears
Enhanced Life And Reliability
Reduced Servicing Costs
The electrohydraulic control unit is bolted onto the bottom of the transmission housing. The end of the
transmission is formed by an oil pan made of sheet steel.
The oil pressure for the converter lockup clutch and center multiple-disc clutch is supplied via holes in the input
shaft. The oil pressure to the rear multiple-disc clutch is routed through the output shaft. The lubricating oil is
supplied and distributed by additional bore holes in both shafts. All bearing points of the gear sets as well as
freewheels and shift elements are supplied with lubricating oil.
The parking lock gear and drive flange are connected to the output shaft by gearing.
Freewheels F1 and F2 optimize shifting. The front freewheel (F1) rests against the stator shaft extension on the
transmission side and connects the sun gear of the front planetary gear set to the transmission housing in the
locking direction.
The torque converter housing and transmission housing are made of a metal alloy. They are bolted together and
centered via the outer multiple-disc carrier of the multiple-disc brake B1. A coated intermediate panel seals the
two components.
The oil pump and outer multiple-disc carrier of the front multiple-disc brake are bolted to the converter housing.
The mechanical part consists of the propeller shaft, output shaft, a sun gear shaft and three planetary gearsets
which are coupled together.
In transmissions for powerful engines, the planetary gearsets have 4 planetary gears, while for less powerful
engines the front and rear planetary gear system has three planetary gear wheels. The stator shaft is pressed into
this and is secured against turning by a spline.
The rear freewheel F2 connects the sun gear of the center planetary gear set to the sun gear of the rear planetary
gearset in the locking direction.
The electrohydraulic control unit consists of the shift plate made of light alloy for hydraulic control and an
electronic control unit.
The electrical control unit consists of a supporting body made of plastic in which the electrical components are
combined. The shell is screwed to the shift plate. Conductor tracks which are integrated into the shell, connect
the electric components to a plug connector. This 13-pin plug connector forms the connection with the vehicle-
side wiring harness and with the ETC 5 (electronic transmission control) control module (N15/5) via a bayonet
lock.
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-03 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Complete Transmissions - ML 320 - 722.662
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:15:30 PMPage 302 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 2526 of 4133
Front axle carrier
Wheel control, hub
Front axle torsion strut
Propeller shaft of front axle gear
Use original bolts
only.
Do not position bolts
at an angle when
screwing in.
Do not use an impact
wrench.
Observe the
tightening torque.
*BA33.10-P-1001-01C
21Lower front axle carrier
(1), pushing all hoses to
one side Installation: Contact
surfaces of front axle
carrier to longitudinal
member must be cleaned
and flat.
Insert the locating pins of
the front axle carrier into
the holes in the side
member.
22Check front axle carrier
(1) for damage
23Install in the reverse order
24Fill power steering pump
and bleedEngine 112, 113AR46.30-P-0010B
Engine 111, 612AR46.30-P-0010P
25Bleed brake system AR42.10-P-0010GH
26Perform chassis
alignment AR40.20-P-0200GH
NumberDesignationModel Series 163
BA33.10-P-1001-01CBolt of front axle carrier to frameNm200
NumberDesignationModel Series 163
BA33.20-P-1006-01DBolt, upper transverse control arm to frameNm120
NumberDesignationModel Series 163
BA32.20-P-1001-02GBolt, retaining bracket to frameNm100
NumberDesignationModel Series 163
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 DRIVELINE/AXLES Front Axle - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:38:21 PMPage 7 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3232 of 4133

Fig. 6: Removing Cooling Fans & Condenser
Courtesy of MERCEDES-BENZ OF NORTH AMERICA.
COOLING FANS
Removal & Installation
Remove headlight units. Remove upper frame crossmember, release hood release control cable and remove
crossmember. See Fig. 6
. Remove 2 cooling fans frame bolts on radiator. Disconnect cooling fan connector.
Release outside temperature sensor wiring harness. Pull up on cooling fan and remove. To install, reverse
removal procedure. Ensure cooling fan bottom guides are properly seated in lower mounts.
EVAPORATOR
Removal & Installation
Remove A/C housing unit. See A/C HOUSING UNIT . Remove expansion valve. See Fig. 5 . Discard "O"
rings. Disassemble A/C housing unit. Remove evaporator. Remove evaporator temperature sensor. To install,
reverse removal procedure. Use NEW "O" rings lubricated with refrigerant oil. If installing a new or repair
evaporator, add 1.35 ounces of NEW refrigerant oil to evaporator.
EXPANSION VALVE
Removal & Installation
1. Discharge A/C system, using approved refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment. Without disconnecting
coolant hoses, remove coolant expansion reservoir and set aside. Remove refrigerant line bracket and
loosen clamps. See Fig. 5
. Pull refrigerant lines out of expansion valve.
2. Remove expansion valve self-locking nut and discard. Remove expansion valve. Discard "O" rings. To
install, reverse removal procedure. Use NEW "O" rings lubricated with refrigerant oil. Tighten NEW self-
locking nut to specification. See TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
.
INSTRUMENT PANEL & INSTRUMENT PANEL CARRIER
Removal & Installation
1. Secure vehicle against rolling. Set transmission selector to "D" position. Obtain radio security code.
Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove driver-side air bag.
2. Place match marks on steering wheel and steering shaft. Remove steering wheel, upper steering column
covers and combination switch. Remove instrument cluster cover frame. Remove one instrument panel
lower section bolt.
3. Remove screws in footwell from left side of instrument panel bottom section. Remove instrument panel
center section. Remove 4 A/C control panel screws and remove control panel. See Fig. 1
. Release pull
cables and disconnect connectors.
4. Remove screws from center section. Remove glove box. Remove screws in footwell from right side of
instrument panel bottom section. Remove entry courtesy lights. Remove end covers and screws.
5. Release 4 "A" clips between instrument panel bottom section and upper section. See Fig. 7
. Release
parkin
g brake release cable from handle. With assistance, remove instrument panel bottom section.
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
2000-01 MANUAL A/C-HEATER SYSTEMS ML 320, ML 430 & ML 55
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:25:10 PMPage 21 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3485 of 4133

Rims
D
When changing wheels, for instance, when replacing steel
wheels with light-alloy rims, ensure that the wheel bolts
required for the spare wheel are stored in a clearly visible
location.
D
Since December 1994 models 202 and 124 with special
equipment light alloy disk wheels, are supplied with a sheet
steel spare wheel instead of a light alloy spare wheel. The
necessary wheel bolts are included with the steel spare wheel.
D
Only use approved Mercedes-Benz rims of the same version.
D
Reinforced steel rims are identified by a sticker on the wheel
disc.
D
The wheel bolts on steel and light-alloy rims should always be
tightened to the specified tightening torque using a torque
wrench.
It is not necessary to retorque the lug bolts after approximately
100 to 500 km.
D
The seat for the tire bead must display no corrosion marks.
D
Before inserting a new rubber valve, clean the contact surfaces
on the disk wheel.
On sheet steel-disk wheel wheel trims must be fitted to support
the rubber valve.
Damaged or deformed rims must not be repaired.
Tire pressure monitor
D
Before replacing a tire, check the date of manufacturer of the
wheel sensor: wheel sensors which are more than 5 years old
must be replaced.
D
Use STAR DIAGNOSIS to read out the actual values of the tire
pressure monitor. Check the remaining life of the wheel sensor
battery, replace the wheel sensor if necessary.
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 06.07.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 2
Page 3891 of 4133

Fig. 4: Connecting Hand Held Tester Scan Tool To OBD-II Data Link Connector
Courtesy of MERCEDES-BENZ OF NORTH AMERICA.
TESTING
Starter malfunctions may cause a Di agnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) to be stored in Motor Electronics
Sequential Fuel Injection (ME-SFI) sy stem. After repairs are completed check for and erase any DTCs stored in
(ME-SFI) system. See appropriate SE LF-DIAGNOSTICS article in ENGINE PERFORMANCE. If cause of
starter malfunction is not engine pe rformance related, replace starter.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
STARTER
Removal & Installation
1. Disconnect and shield negative battery cable. See BATTERY DISCONNECT/CONNECT under
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS.
2. Remove nut (2) for inner fender. See Fig. 5
. Pull front and rear section of inner fender (1) downward.
Move inner fender away inward and downward. Pull toward outside over wheel. DO NOT damage fender
cutout or paint.
3. On vehicles with 112 engine, remove nut (6) at shield (5) of left engine mount and take out shield. See
Fig. 6
.
4. On all vehicles, disconnect circuit 30 (1) and circuit 50 (2) cables from starter. See Fig. 6
. Remove bolts
(3) for starter-to-crankcase. Take starter (M1) out to the side.
5. If replacing starter on vehicles with manual transmission, check ring gear at flywheel for wear and
damage. If replacing starter on vehicles with auto matic transmission, check ring gear on drive plate for
wear and damage. Repair or repl ace damaged parts as necessary.
6. To install, reverse removal proce dure. Replace bolts with locking splines, micro-encapsulated bolts and
self-locking nuts. Mating thread of mi cro-encapsulated bolts must be cleaned to remove all residue of old
bolt locking compound. Tighten fasteners to specification. See TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
. Connect
battery. See BATTERY DISCONNECT/CONNECTunder SERVICE PRECAUTIONS.
NOTE: Numbers and letters in text refe
r to numbers and letters in figures.
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
2001-04 STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEMS Starters - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:19:47 PMPage 9 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3935 of 4133
Rear axle shock absorber
Wheel location
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
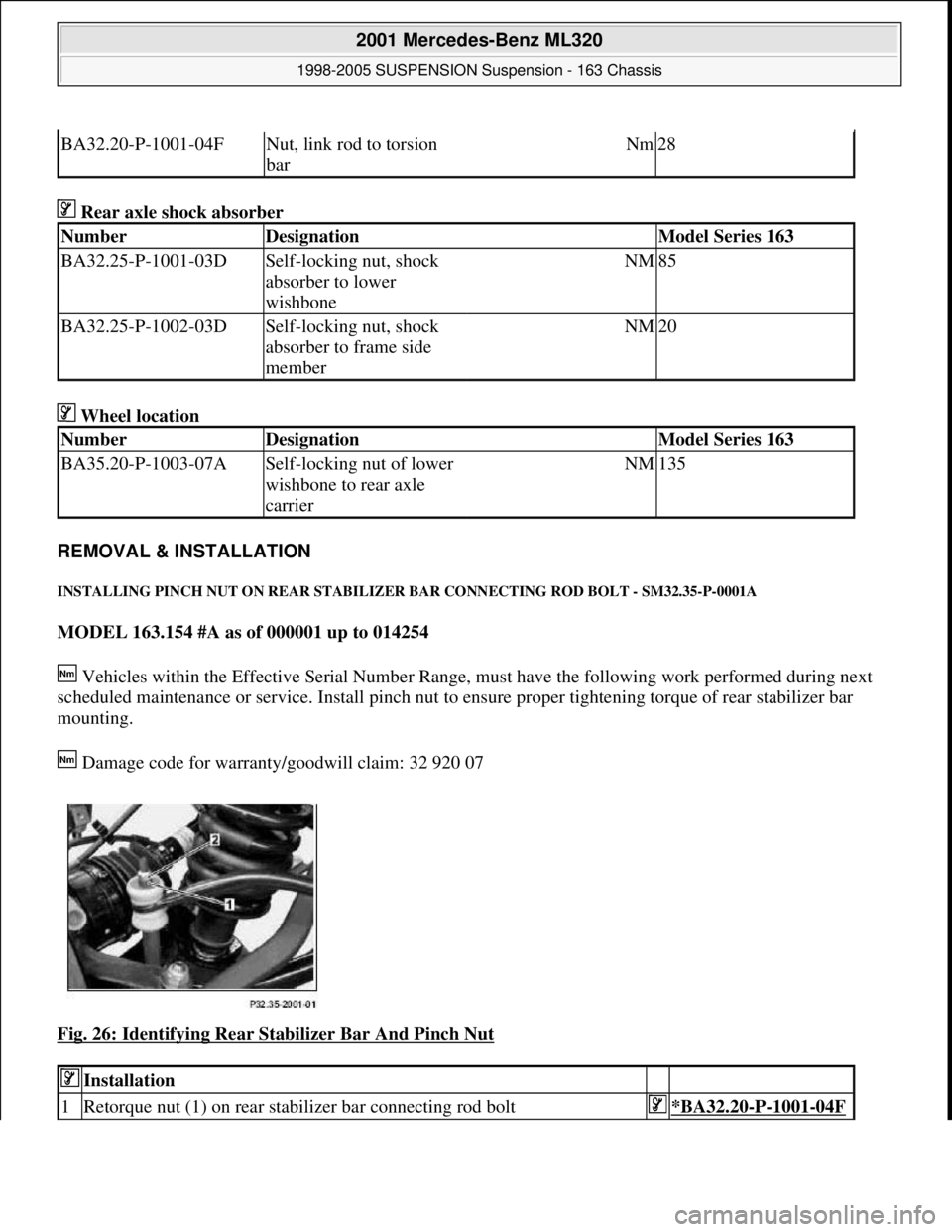
INSTALLING PINCH NUT ON REAR STABILIZER BAR CONNECTING ROD BOLT - SM32.35-P-0001A
MODEL 163.154 #A as of 000001 up to 014254
Vehicles within the Effective Serial Number Range, must have the following work performed during next
scheduled maintenance or service. Install pinch nut to ensure proper tightening torque of rear stabilizer bar
mounting.
Damage code for warranty/goodwill claim: 32 920 07
Fig. 26: Identifying Rear Stabilizer Bar And Pinch Nut
BA32.20-P-1001-04FNut, link rod to torsion
barNm28
NumberDesignationModel Series 163
BA32.25-P-1001-03DSelf-locking nut, shock
absorber to lower
wishboneNM85
BA32.25-P-1002-03DSelf-locking nut, shock
absorber to frame side
memberNM20
NumberDesignationModel Series 163
BA35.20-P-1003-07ASelf-locking nut of lower
wishbone to rear axle
carrierNM135
Installation
1Retorque nut (1) on rear stabilizer bar connecting rod bolt*BA32.20-P-1001-04F
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 SUSPENSION Suspension - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:37:36 PMPage 27 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3995 of 4133

BA40.10-P-1001-01A
Wheel bolt
Nm
150150
126 589 04 09 00
Wrench socket
Commercially available tools
(see Workshop Equipment Manual)
Number
Designation
Make (e. g.)
Order number
WH58.30-Z-1002-10A
Electric or compressed air impact wrench with limited tightening torque,
see
D
trial reports on test benches and tools for
Mercedes Benz workshops, Volume 2, 40.1
D
Workshop Equipment Manual Volume 1 "G" Group 40
651004700
6510053001
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 06.07.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 2