1997 JAGUAR XJ6 handbrake
[x] Cancel search: handbrakePage 30 of 227

16 Spark plug renewal
2
Refer to Section 4, renewing the plugs
regardless of their apparent condition.
17 Air cleaner element renewal
1
1The air filter is located inside a housing at
the left side of the engine compartment. To
remove the air filter, release the four spring
clips that secure the two halves of the air
cleaner housing together, then lift the cover
up and remove the air filter element (see
illustration).
Caution: Never drive the car with the air
cleaner removed. Excessive engine wear
could result and backfiring could even
cause a fire under the bonnet.
2Wipe out the inside of the air cleaner
housing.
3Place the new filter into the air cleaner
housing, making sure it seats properly.
4Refitting the cover is the reverse of removal.
18 Fuel filter renewal
2
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke or allow open flames or bare
light bulbs near the work area, and don’t
work in a garage where a natural gas-typeappliance (such as a water heater or
clothes dryer) with a pilot light is present.
Since petrol is carcinogenic, wear latex
gloves when there’s a possibility of being
exposed to fuel, and, if you spill any fuel on
your skin, rinse it off immediately with soap
and water. Mop up any spills immediately
and do not store fuel-soaked rags where
they could ignite. The fuel system is under
constant pressure, so, if any fuel lines are
to be disconnected, the fuel pressure in
the system must be relieved first (see
Chapter 4 for more information). When you
perform any kind of work on the fuel
system, wear safety glasses and have a
Class B type fire extinguisher on hand.
1The canister type filter is mounted
underneath the car on the passenger’s side
frame rail just in front of the left rear tyre.
2Depressurise the fuel system (refer to
Chapter 4), then disconnect the cable from
the negative terminal of the battery.
3On 1988 to 1990 models, detach the banjo
bolt from the outlet side of the filter then
remove the union from the inlet side of the
filter. Unscrew the filter mounting bolt and
remove the filter (see illustration).
4On 1991 to 1994 models, the fuel filter has
quick-disconnect fittings that do not require 8Clean and lubricate the handbrake cable,
along with the cable guides and levers. This
can be done by smearing some of the chassis
grease onto the cable and its related parts
with your fingers.
9Open the bonnet and smear a little chassis
grease on the bonnet latch mechanism. Have
an assistant pull the bonnet release lever from
inside the car as you lubricate the cable at the
latch.
10Lubricate all the hinges (door, bonnet,
etc.) with engine oil to keep them in proper
working order.
11The key lock cylinders can be lubricated
with spray graphite or silicone lubricant, which
is available at motor factors.12Lubricate the door weather-stripping with
silicone spray. This will reduce chafing and
retard wear.
15 Road test
1
Instruments and electrical
equipment
1Check the operation of all instruments and
electrical equipment.
2Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn, to check that it functions
properly.
Steering and suspension
3Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
4Drive the car, and check that there are no
unusual vibrations or noises.
5Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive “sloppiness”, or roughness, and
check for any suspension noises when
cornering and driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
6Check the performance of the engine and
transmission, listening for any unusual noises.7Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
8Check that the gear changing action of the
transmission is smooth and progressive and
that the drive is taken up smoothly from a
standing start.
Braking system
9Make sure that the car does not pull to one
side when braking, and that the wheels do not
lock prematurely when braking hard.
10Check that there is no vibration through
the steering when braking.
11Check that the handbrake operates
correctly without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the car stationary on a
slope.
12Test the operation of the brake servo unit
as follows. With the engine off, depress the
footbrake four or five times to exhaust the
vacuum. Hold the brake pedal depressed, then
start the engine. As the engine starts, there
should be a noticeable “give” in the brake
pedal as vacuum builds up. Allow the engine to
run for at least two minutes, and then switch it
off. If the brake pedal is depressed now, it
should be possible to detect a hiss from the
servo as the pedal is depressed. After about
four or five depressions, no further hissing
should be heard, and the pedal should feel
considerably harder.
1•14Every 7500 miles or 6 months
17.1 Detach the clips and separate the
cover, then slide the filter element out of
the housing
3261 Jaguar XJ6
14.6 Grease fittings for the rear
driveshafts are located in the centre
on each U-joint
Every 15 000 miles (24 000 km) or 12 months
Page 35 of 227

26 Automatic transmission fluid
and filter renewal
2
1At the specified time intervals, the
transmission fluid should be drained and
renewed. Since the fluid will remain hot long
after driving, perform this procedure only after
the engine has cooled down completely.
2Before beginning work, purchase the
specified transmission fluid and a new filter.
3Other tools necessary for this job include
axle stands to support the vehicle in a raised
position, a drain pan capable of holding at
least eight pints, newspapers and clean rags.4Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
5Place the drain pan under the drain plug in
the bottom of the transmission sump pan.
Remove the plug and allow the fluid to drain
(see illustration).
6Refit the drain plug, then move the drain
pan underneath the dipstick tube. Loosen the
dipstick tube collar and let the remaining fluid
drain (see illustrations).
7Remove the sump pan mounting bolts and
brackets (see illustration).
8Detach the sump pan from the transmission
and lower it, keeping it as horizontal as
possible in order not to spill too much of the
remaining fluid (see illustration).9Drain the remaining fluid from the
transmission sump pan, clean it with solvent
and dry it with compressed air. Be sure to
clean the metal filings from the magnet, if
equipped.
10Remove the screws and detach the filter
from the valve body (see illustrations).
11Refit the new O-ring and filter, being sure
to tighten the bolts securely.
12Carefully clean the fluid pan-to-
transmission sealing surface.
13Make sure the gasket surface on the
transmission sump pan is completely clean,
then refit the gasket. Put the sump pan in
place against the transmission and refit the
brackets and bolts. working around the sump
pan, tighten each bolt a little at a time until the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications
is reached. Don’t overtighten the bolts!
Connect the dipstick tube and tighten the
collar securely.
14Lower the vehicle and add the specified
amount of fluid through the filler tube (see
Section 8).
15With the transmission in Park and the
handbrake set, run the engine at fast idle, but
don’t race it.
16Move the gear selector through each
position, and then back to Park. Check the
fluid level.
17Be sure to check underneath the car for
any leaks after the first few miles of driving.
Every 30 000 miles (48 000 km) or 2 years
Every 30 000 miles or 2 years 1•19
1
26.6a Unscrew the dipstick tube collar26.6b Detach the tube and let the
remaining fluid drain
26.7 Use a socket and extension to
remove the transmission sump pan bolts
and brackets26.8 Lower the sump pan from the
transmission
26.10a Use a Torx-head driver to remove
the filter bolts (arrowed) . . .
3261 Jaguar XJ6
26.5 Using an Allen spanner remove the
drain plug located in the bottom of the
transmission sump pan
26.10b . . . then remove the fluid filter from
the transmission26.10c Be sure to remove the old O-ring
from the transmission - always use a new
O-ring when replacing the filter
Page 36 of 227

30 Coolant renewal
2
Warning: Do not allow engine
coolant (antifreeze) to come in
contact with your skin or painted
surfaces of the vehicle. Rinse off
spills immediately with plenty of water.
Antifreeze is highly toxic if ingested. Never
leave antifreeze laying around in an open
container or in puddles on the floor;
children and pets are attracted by it’s
sweet smell and may drink it. Check with
local authorities about disposing of used
antifreeze. Your local authority may have
collection centres which will see that
antifreeze is disposed of safely.1Periodically, the cooling system should be
drained, flushed and refilled to replenish the
antifreeze mixture and prevent formation of
rust and corrosion, which can impair the
performance of the cooling system and
cause engine damage. When the cooling
system is serviced, all hoses and the radiator
cap should be checked and renewed if
necessary.
Draining
2Apply the handbrake and block the wheels.
If the vehicle has just been driven, wait several
hours to allow the engine to cool down before
beginning this procedure.
3Remove the expansion tank pressure cap
(see illustration).
4Move a large container under the radiator
drain to catch the coolant. Then using a largescrewdriver, open the radiator drain plug and
direct the coolant into the container (see
illustration).
27 Differential oil renewal
2
1Drive the car for several miles to warm up
the differential lubricant, then raise the car
and support it securely on axle stands.
2Move a drain pan, rags, newspapers and
the required tools under the car.
3Remove the check/fill plug from the
differential. If necessary refer to Section 9 for
the check/fill plug location.
4With the drain pan under the differential,
use a ratchet and socket to loosen the drain
plug (see illustration). Note:A special pipe
plug socket may be required to complete this
procedure.
5Once loosened, carefully unscrew it with
your fingers until you can remove it from the
case. Since the lubricant will be hot, wear a
rubber glove to prevent burns.
6Allow all of the oil to drain into the pan, then
replace the drain plug and tighten it securely.
7Refer to Section 9 and fill the differential
with lubricant.
8Refit the fill plug and tighten it securely.
9Lower the vehicle. Check for leaks at the
drain plug after the first few miles of driving.
28 Brake fluid renewal
2
Warning: Brake fluid can harm
your eyes and damage painted
surfaces, so use extreme
caution when handling or
pouring it. Do not use brake fluid that has
been standing open or is more than oneyear old. Brake fluid absorbs moisture from
the air. Excess moisture can cause a
dangerous loss of braking effectiveness.
1At the specified time intervals, the brake
fluid should be drained and renewed. Since
the brake fluid may drip or splash when
pouring it, place plenty of rags around the
master cylinder to protect any surrounding
painted surfaces.
2Before beginning work, purchase the
specified type of brake fluid.
3Remove the cap from the master cylinder
reservoir.
4Using a hand suction pump or similar
device, withdraw the fluid from the master
cylinder reservoir.
5Add new fluid to the master cylinder until it
rises to the base of the filler neck.
6Bleed the brake system as described in
Chapter 9 at all four brakes until new and
uncontaminated fluid flows from the bleed
screw.
7Refill the master cylinder with fluid and
check the operation of the brakes. The pedal
should feel solid when depressed, with no
sponginess.
Warning: Do not drive the car if
you are in any doubt about the
braking system.
1•20Every 30 000 miles or 2 years
27.4 The differential drain plug (arrowed)
is accessible through a hole located in the
middle of the differential support brace
30.3 Push the expansion tank pressure
cap downward and rotate anti-clockwise -
never remove it when the engine is hot!
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Every 60 000 miles (96 000 km)
29 Handbrake shoes check
2
1Remove the rear discs and inspect the
handbrake shoes as described in Chapter 9. If
the shoes are worn or damaged they must be
renewed.Warning: The dust created by
the brake system may contain
asbestos, which is harmful to
your health. Never blow it out
with compressed air and don’t inhale any
of it. An approved filtering mask should be
worn when working on the brakes. Do not,
under any circumstances, use petroleum-
based solvents to clean brake parts. Usebrake system cleaner only! Try to use non-
asbestos replacement parts whenever
possible.
Every 2 years, regardless of mileage
Page 39 of 227

Torque wrench settings*Nm lbf ft
Camshaft bearing cap bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Camshaft sprocket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Crankshaft damper-to-crankshaft bolt
3.2 and 3.6 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204 151
4.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180 to 220 133 to 162
Crankshaft pulley to damper bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Crankshaft rear oil seal retainer bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Crankshaft sensor bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Cylinder head bolts
Step 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60 44
Step 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Tighten an additional 90° (1/4 turn)
Driveplate bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123 to 149 91 to 110
Engine mounts
To engine block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 to 66 36 to 39
To chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 24 16 to 18
Exhaust manifold heat shield fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Exhaust manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Intake manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Oil pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Sump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Sump bolts, adapter to pan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 to 54 36 to 40
Timing chain cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Valve cover screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 to 12 7 to 9
*Note:Refer to Part B for additional specifications
2A•2 Engine in-car repair procedures
3261 Jaguar XJ6
1 General information
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to in-car
repair procedures for the in-line six-cylinder
engines. All information concerning engine
removal and refitting and engine block and
cylinder head overhaul can be found in Part B
of this Chapter.
The following repair procedures are based
on the assumption that the engine is installed
in the car. If the engine has been removed
from the car and mounted on a stand, many of
the steps outlined in this Part of Chapter 2 will
not apply. We have photographed some in-
car engine procedures with the engine on a
stand for photographic purposes.
The Specifications included in this Part of
Chapter 2 apply only to the procedures
contained in this Part. Part B of Chapter 2
includes the Specifications necessary for
cylinder head and engine block rebuilding.
2 Repair operations possible
with the engine in the car
Many repair operations can be
accomplished without removing the engine
from the car.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier and help keep dirt out of
the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, itmay be helpful to remove the bonnet to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (refer to Chapter 11 if necessary).
Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint. Special pads are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for gasket or seal
renewal, the repairs can generally be made
with the engine in the car. The intake and
exhaust manifold gaskets, crankshaft oil seals
and cylinder head gasket are all accessible
with the engine in place (although rear oil seal
renewal involves removal of the transmission).
The sump is difficult for a home mechanic to
replace without a hoist and other specialised
equipment, since the front suspension,
steering and crossmember must be lowered
to allow enough clearance for sump removal.
If such equipment is not available, the
alternative would be to remove the engine for
renewal of the sump or oil pump. Note:We
assume that the home mechanic does not
have access to the specialised equipment,
and have photographed our subject engine
out of the car for some procedures.
Exterior engine components, such as the
intake and exhaust manifolds, the water
pump, the starter motor, the alternator, the
distributor and the fuel system components
can be removed for repair with the engine in
place.
Since the cylinder head can be removed
with the engine in-car, camshaft and valve
component servicing can also be
accomplished. Renewal of the timing chains
and sprockets is also possible with the engine
in-car.
3 Top Dead Centre (TDC) for
number one piston- locating
1
Note:The following procedure is based on the
assumption that the distributor is correctly
installed. If you are trying to locate TDC to refit
the distributor correctly, piston position must
be determined by feeling for compression at
the number one spark plug hole, then aligning
the ignition timing marks (see paragraph 8).
1Top Dead Centre (TDC) is the highest point
in the cylinder that each piston reaches as it
travels up the cylinder bore. Each piston
reaches TDC on the compression stroke and
again on the exhaust stroke, but TDC
generally refers to piston position on the
compression stroke.
2Positioning the piston(s) at TDC is an
essential part of many procedures such as
camshaft and timing chain/sprocket removal
and distributor removal.
3Before beginning this procedure, be sure to
place the transmission in Neutral and apply
the handbrake or block the rear wheels. Also,
disable the ignition system by detaching the
coil wire from the centre terminal of the
distributor cap and grounding it on the engine
block with a jumper wire. Remove the spark
plugs (see Chapter 1).
4In order to bring any piston to TDC, the
crankshaft must be turned using one of the
methods outlined below. When looking at the
timing chain end of the engine, normal
crankshaft rotation is clockwise.
a) The preferred method is to turn the
crankshaft with a socket and ratchet
Page 43 of 227

damage the crankshaft in the process (if the
crankshaft is damaged, the new seal will end
up leaking).
9The crankshaft seal rides on a spacer that
slips over the front of the crankshaft. Slip the
spacer off and clean the varnish off the seal
surface (see illustration).
10Clean the bore in the cover and coat the
outer edge of the new seal with engine oil or
multi-purpose grease. Apply moly-base
grease to the seal lip.
11Lubricate the spacer with clean engine oil
and refit it onto the crankshaft. Using a socket
with an outside diameter slightly smaller than
the outside diameter of the seal, carefully
drive the new seal into place with a hammer
(see illustration). Make sure it’s installed
squarely and driven in to the same depth as
the original. If a socket isn’t available, a short
section of large-diameter pipe will also work.
Note:The new seal comes with a plastic
installer guide. Do not remove this guide until
refitting is completed. The guide keeps the
seal lip properly oriented over the crankshaft.
12Refit the Woodruff key, then refit the
damper. Tighten the damper bolt to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
Note:The damper bolt can be used to pull the
damper back onto the crankshaft, but make
sure the damper is perfectly aligned with the
Woodruff key.
13The rest of the assembly is the reverse of
the removal procedure.
14Run the engine and check for oil leaks at
the front seal.
8 Timing chains
and sprockets- removal,
inspection and refitting
3
Caution: If the timing chain broke during
engine operation, the valves may have
come in contact with the pistons, causingdamage. Check the valve clearance (see
Section 10) before removal of the cylinder
head - bent valves usually will have
excessive clearance, indicating damage
that will require machine workshop work to
repair.
Note 1:This procedure requires that the sump
be removed (see Section 12).In a professional
workshop, this would be performed as an in-
car procedure with specialised tools to
remove the front suspension. Given the
equipment available to the average home
mechanic, this alternate procedure requires
removal of the engine from the car.
Note 2:If your engine is a 4.0 litre, built after
serial number 9J160552, and you’re
experiencing an engine rattle on cold starts
that disappears after the engine is warmed up,
the problem could be a defective upper
tensioner. A newly designed replacement
upper tensioner is available from the dealer
and should solve the problem. It can be
installed easily without pulling the cylinder
head or front cover, or can be installed during
a chain removal procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the negative cable from the
battery.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
2Block the rear wheels and set the
handbrake.
3Refer to Part B of this Chapter for engine
removal procedures.
4Refer to Section 4 and remove the valve
cover.
5Refer to Section 3 and position the engine
at TDC for cylinder number 1, then mark and
remove the distributor (see Chapter 5).
6Refer to Section 11 and remove the cylinder
head. After cylinder head removal, the uppertiming chain will be loosely retained by the
two upper chain guides, which are retained by
refitting a large rubber band (see Section 10).
Caution: Do not rotate the crankshaft with
the upper timing chain disconnected and
the cylinder head and camshafts in place,
or damage could result from piston-to-
valve contact.
7Some models may be equipped with a
hydraulic pump used for the brake
servo/hydraulic self-levelling suspension
system. If equipped, it will be mounted to the
front cover. Models not equipped with this
option will have a flat block-off plate over the
hole. If equipped with the pump, refer to
Chapters 9 and 10 for procedures to reduce
the high pressure in the brake servo system
and to depressurise the self-levelling system.
Before removing the engine, unbolt the pump
from the front cover and set it aside without
disconnecting the hoses (see illustration).
8Refer to Section 7 and remove the
crankshaft pulley and damper. Refer to
Section 12 for removal of the sump.
9If equipped with the hydraulic pump,
remove the coupling disc and unbolt the drive
coupling from the intermediate shaft (see
illustrations).
2A•6 Engine in-car repair procedures
8.7 Unbolt the hydraulic pump (arrowed)
from the front cover, without
disconnecting the hoses
3261 Jaguar XJ6 7.9 Remove the spacer from the end of the crankshaft
and clean it thoroughly
7.11 Drive the new seal squarely into the front cover with a large
socket or section of pipe - do not remove the plastic refitting
guide (arrowed) until the seal is installed
Page 58 of 227

rebuilt engine or short block, some rebuilders
will not warranty their engines unless the
radiator has been professionally flushed. Also,
we don’t recommend overhauling the oil
pump - always refit a new one when an engine
is rebuilt.
Before beginning the engine overhaul, read
through the entire procedure to familiarise
yourself with the scope and requirements of
the job. Overhauling an engine isn’t difficult,
but it is time-consuming. Plan on the vehicle
being tied up for a minimum of two weeks,
especially if parts must be taken to an
automotive machine workshop for repair or
reconditioning. Check on availability of parts
and make sure that any necessary special
tools and equipment are obtained in advance.
Most work can be done with typical hand
tools, although a number of precision
measuring tools are required for inspecting
parts to determine if they must be renewed.
Often an automotive machine workshop will
handle the inspection of parts and offer
advice concerning reconditioning and
renewal. Note:Always wait until the engine
has been completely dismantled and all
components, especially the engine block,
have been inspected before deciding what
service and repair operations must be
performed by an automotive machine
workshop. Since the engine block’s condition
will be the major factor to consider when
determining whether to overhaul the original
engine or buy a rebuilt one, never purchase
parts or have machine work done on other
components until the engine block has been
thoroughly inspected. As a general rule, time
is the primary cost of an overhaul, so it
doesn’t pay to refit worn or substandard
parts.
If it turns out that a number of major
components are beyond reconditioning, it
may be cost effective to buy a factory-rebuilt
engine from a Jaguar dealership.
As a final note, to ensure maximum life and
minimum trouble from a rebuilt engine,
everything must be assembled with care in a
spotlessly-clean environment.
3 Vacuum gauge
diagnostic checks
2
A vacuum gauge provides valuable
information about what is going on in the
engine at a low cost. You can check for worn
rings or cylinder walls, leaking cylinder head or
intake manifold gaskets, incorrect carburettor
adjustments, restricted exhaust, stuck or
burned valves, weak valve springs, improper
ignition or valve timing and ignition problems.
Unfortunately, vacuum gauge readings are
easy to misinterpret, so they should be used
with other tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Both the absolute readings and the rate of
needle movement are important for accurate
interpretation. Most gauges measure vacuumin inches of mercury (in-Hg). As vacuum
increases (or atmospheric pressure decreases),
the reading will decrease. Also, for every
1000 foot increase in elevation above sea level;
the gauge readings will decrease about one
inch of mercury.
Connect the vacuum gauge directly to
intake manifold vacuum, not to ported (above
the throttle plate) vacuum (see illustration).
Be sure no hoses are left disconnected during
the test or false readings will result.
Before you begin the test, allow the engine
to warm up completely. Block the wheels and
set the handbrake. With the transmission in
Park, start the engine and allow it to run at
normal idle speed.
Warning: Carefully inspect the
fan blades for cracks or damage
before starting the engine. Keep
your hands and the vacuum
tester clear of the fan and do not stand in
front of the vehicle or in line with the fan
when the engine is running.
Read the vacuum gauge; an average,
healthy engine should normally produce
between 17 and 22 inches of vacuum with a
fairly steady needle.
Refer to the following vacuum gauge
readings and what they indicate about the
engines condition:
1A low steady reading usually indicates a
leaking gasket between the intake manifold
and carburettor or throttle body, a leaky
vacuum hose, late ignition timing or incorrect
camshaft timing. Check ignition timing with a
timing light and eliminate all other possible
causes, utilising the tests provided in this
Chapter before you remove the timing belt
cover to check the timing marks.
2If the reading is three to eight inches below
normal and it fluctuates at that low reading,
suspect an intake manifold gasket leak at an
intake port or a faulty injector.
3If the needle has regular drops of about two
to four inches at a steady rate the valves are
probably leaking. Perform a compression or
leak-down test to confirm this.
4An irregular drop or down-flick of the
needle can be caused by a sticking valve or
an ignition misfire. Perform a compression or
leak-down test and read the spark plugs.5A rapid vibration of about four in-Hg
vibration at idle combined with exhaust
smoke indicates worn valve guides. Perform a
leak-down test to confirm this. If the rapid
vibration occurs with an increase in engine
speed, check for a leaking intake manifold
gasket or cylinder head gasket, weak valve
springs, burned valves or ignition misfire.
6A slight fluctuation, say one inch up and
down, may mean ignition problems. Check all
the usual tune-up items and, if necessary, run
the engine on an ignition analyser.
7If there is a large fluctuation, perform a
compression or leak-down test to look for a
weak or dead cylinder or a blown cylinder
head gasket.
8If the needle moves slowly through a wide
range, check for a clogged PCV system,
incorrect idle fuel mixture, throttle body or
intake manifold gasket leaks.
9Check for a slow return after revving the
engine by quickly snapping the throttle open
until the engine reaches about 2,500 rpm and
let it shut. Normally the reading should drop to
near zero, rise above normal idle reading
(about 5 in.-Hg over) and then return to the
previous idle reading. If the vacuum returns
slowly and doesn’t peak when the throttle is
snapped shut, the rings may be worn. If there
is a long delay, look for a restricted exhaust
system (often the silencer or catalytic
converter). An easy way to check this is to
temporarily disconnect the exhaust ahead of
the suspected part and redo the test.
4 Cylinder compression check
2
1A compression check will tell you what
mechanical condition the upper end (pistons,
rings, valves, cylinder head gasket) of your
engine is in. Specifically, it can tell you if the
compression is down due to leakage caused
by worn piston rings, defective valves and
seats or a blown cylinder head gasket. Note:
The engine must be at normal operating
temperature and the battery must be fully
charged for this check.
2Begin by cleaning the area around the
spark plugs before you remove them
(compressed air should be used, if available,
otherwise a small brush or even a bicycle tyre
pump will work). The idea is to prevent dirt
from getting into the cylinders as the
compression check is being done.
3Remove all of the spark plugs from the
engine (see Chapter 1).
4Block the throttle wide open.
5Detach the coil wire from the centre of the
distributor cap and ground it on the engine
block. Use a jumper wire with alligator clips on
each end to ensure a good earth. Also,
remove the fuel pump relay (see Chapter 4) to
disable the fuel pump during the compression
test.
Engine removal and overhaul procedures 2B•3
2B
3.4 The vacuum gauge is easily attached
to a port on the intake manifold, and can
tell a lot about an engine’s state of tune
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 123 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
9
Chapter 9
Braking system
General
Brake fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Minimum brake pad thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc minimum permissible thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cast into disc
Parallelism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch) maximum
Runout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.102 mm (0.004 inch) maximum
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Brake servo mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Caliper bolts (front and rear) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 to 40 23 to 29
Caliper bracket bolts
Front bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102 to 128 75 to 94
Rear bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 to 62 40 to 45
Master cylinder-to-brake servo nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 28 16 to 20
Wheel nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Specifications Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Brake check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Brake fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake hoses and lines - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Brake hydraulic system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Brake light switch - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Brake servo - general information, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 7Disc brake caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Disc brake pads - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Handbrake cable - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Handbrake cables - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Handbrake shoes - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Master cylinder - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
9•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
1 General information
All models covered by this manual are
equipped with hydraulically operated front
and rear disc brake systems. Both front and
rear brakes are self adjusting.
Hydraulic system
The hydraulic system is divided into
two separate circuits. The master cylinder has
separate reservoirs for the two circuits, and, in
the event of a leak or failure in one hydraulic
circuit, the other circuit will remain operative.
All models are equipped with an Anti-lock
Braking System (ABS).
Brake servo
A hydraulic brake servo system is used on
all models covered by this manual. Thissystem uses hydraulic pressure from an
engine-driven pump on models equipped with
a power hydraulic system, and an electric
pump on models without the power hydraulic
system.
Handbrake
The handbrake lever operates the rear
brakes through cable actuation. It’s activated
by a lever mounted in the centre console. The
handbrake assembly uses a pair of brake
shoes located inside the rear hub/brake disc.
Brake pad wear warning system
The brake pad wear warning system turns
on a red light in the instrument cluster when
the brake pads have worn down to the point
at which they must be replaced. Do NOT
ignore this reminder. If you don’t renew the
pads shortly after the brake pad wear warning
light comes on, the brake discs will be
damaged.The wear sensors are attached to the brake
pads. Once the pads wear down to the point
at which they’re flush with the sensor, the disc
grinds away the side of the sensor facing the
disc, the wire inside the sensor is broken, the
circuit is opened and the red light on the
instrument panel comes on.
Always check the sensor(s) when replacing
the pads. If you change the pads before the
warning light comes on, the sensor(s) may still
be good; once the light has come on, renew
the sensor.
Service
After completing any operation involving
dismantling of any part of the brake system,
always test drive the vehicle to check for
proper braking performance before resuming
normal driving. When testing the brakes,
perform the tests on a clean, dry, flat surface.
Conditions other than these can lead to
inaccurate test results.
Page 126 of 227
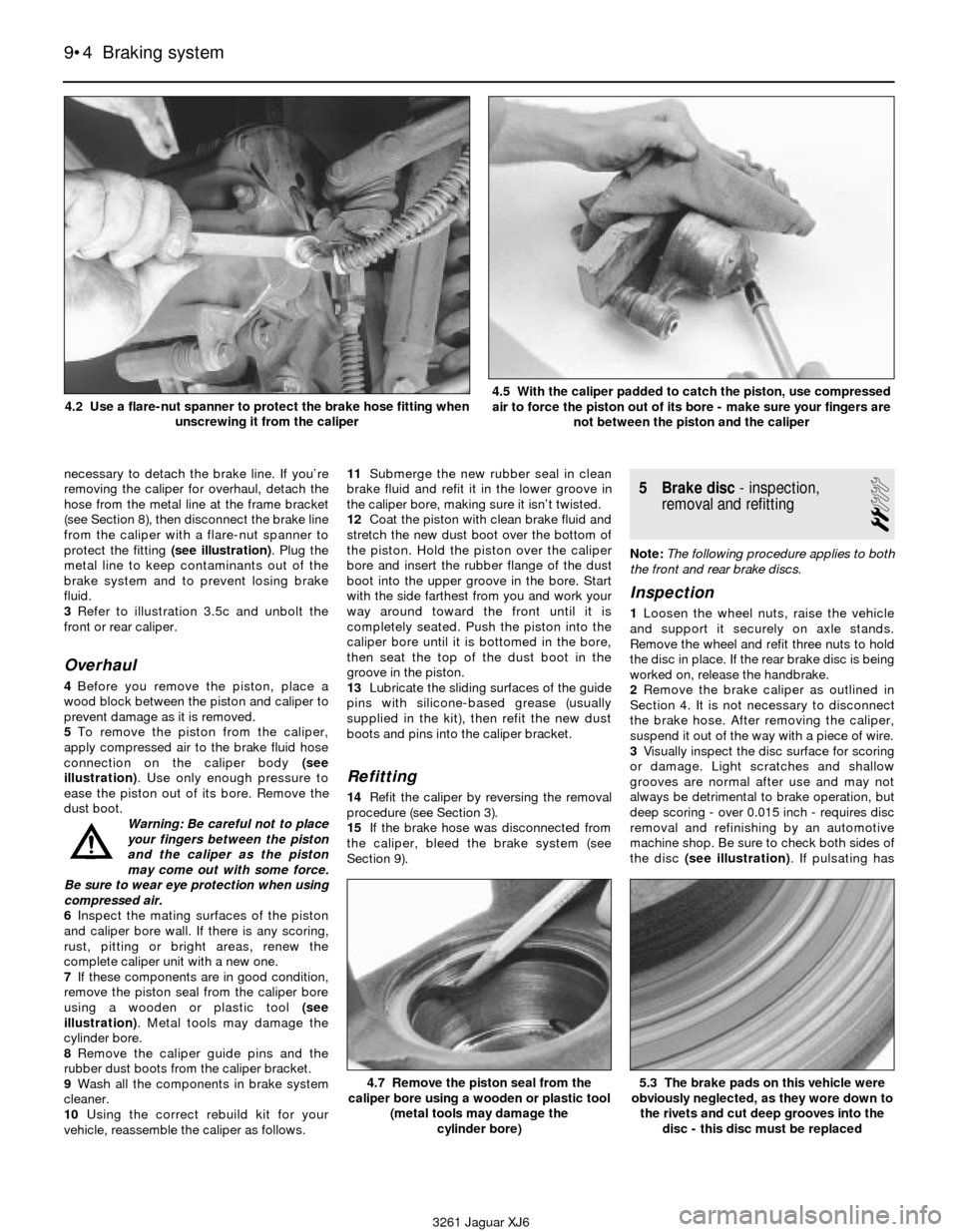
necessary to detach the brake line. If you’re
removing the caliper for overhaul, detach the
hose from the metal line at the frame bracket
(see Section 8), then disconnect the brake line
from the caliper with a flare-nut spanner to
protect the fitting (see illustration). Plug the
metal line to keep contaminants out of the
brake system and to prevent losing brake
fluid.
3Refer to illustration 3.5c and unbolt the
front or rear caliper.
Overhaul
4Before you remove the piston, place a
wood block between the piston and caliper to
prevent damage as it is removed.
5To remove the piston from the caliper,
apply compressed air to the brake fluid hose
connection on the caliper body (see
illustration). Use only enough pressure to
ease the piston out of its bore. Remove the
dust boot.
Warning: Be careful not to place
your fingers between the piston
and the caliper as the piston
may come out with some force.
Be sure to wear eye protection when using
compressed air.
6Inspect the mating surfaces of the piston
and caliper bore wall. If there is any scoring,
rust, pitting or bright areas, renew the
complete caliper unit with a new one.
7If these components are in good condition,
remove the piston seal from the caliper bore
using a wooden or plastic tool (see
illustration). Metal tools may damage the
cylinder bore.
8Remove the caliper guide pins and the
rubber dust boots from the caliper bracket.
9Wash all the components in brake system
cleaner.
10Using the correct rebuild kit for your
vehicle, reassemble the caliper as follows.11Submerge the new rubber seal in clean
brake fluid and refit it in the lower groove in
the caliper bore, making sure it isn’t twisted.
12Coat the piston with clean brake fluid and
stretch the new dust boot over the bottom of
the piston. Hold the piston over the caliper
bore and insert the rubber flange of the dust
boot into the upper groove in the bore. Start
with the side farthest from you and work your
way around toward the front until it is
completely seated. Push the piston into the
caliper bore until it is bottomed in the bore,
then seat the top of the dust boot in the
groove in the piston.
13Lubricate the sliding surfaces of the guide
pins with silicone-based grease (usually
supplied in the kit), then refit the new dust
boots and pins into the caliper bracket.
Refitting
14Refit the caliper by reversing the removal
procedure (see Section 3).
15If the brake hose was disconnected from
the caliper, bleed the brake system (see
Section 9).
5 Brake disc- inspection,
removal and refitting
2
Note:The following procedure applies to both
the front and rear brake discs.
Inspection
1Loosen the wheel nuts, raise the vehicle
and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel and refit three nuts to hold
the disc in place. If the rear brake disc is being
worked on, release the handbrake.
2Remove the brake caliper as outlined in
Section 4. It is not necessary to disconnect
the brake hose. After removing the caliper,
suspend it out of the way with a piece of wire.
3Visually inspect the disc surface for scoring
or damage. Light scratches and shallow
grooves are normal after use and may not
always be detrimental to brake operation, but
deep scoring - over 0.015 inch - requires disc
removal and refinishing by an automotive
machine shop. Be sure to check both sides of
the disc (see illustration). If pulsating has
9•4 Braking system
4.7 Remove the piston seal from the
caliper bore using a wooden or plastic tool
(metal tools may damage the
cylinder bore)5.3 The brake pads on this vehicle were
obviously neglected, as they wore down to
the rivets and cut deep grooves into the
disc - this disc must be replaced
3261 Jaguar XJ6 4.2 Use a flare-nut spanner to protect the brake hose fitting when
unscrewing it from the caliper
4.5 With the caliper padded to catch the piston, use compressed
air to force the piston out of its bore - make sure your fingers are
not between the piston and the caliper