1997 HONDA CIVIC Sensors
[x] Cancel search: SensorsPage 537 of 2189

Emission Control System
Evaporative Emission IEVAPI Controls (cont'd)
'96 D16Y8 ongins (coupol.'97 D16Y8 €ngino (coups: all mod€ls, sedan: KL model),'98 D16Y5 engine (all mod6lsl,'98
Dl5YB engine {all modols):
{BLK/YEL
From
< No. 15
FUELTANKPRESSURESENSOR
EVAP PURG€CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE
.� LT GRN
GRN/BLK
ALTERNATORSP SENSOR(7.5 A)
VARIOUSSENSORS
YEL/BLU
V€NT SHUT
EVAPBYPASSSOLENOIDVALVEL BLU
WHTRED/YEL
L __ LT GRN/
EVAPTWO WAYVALVE
INTAKEMANIFOI.I'
'97 D16Y7 engin. (coupa: KL model, sedan: KL {LX) model},38 Dl6
/ engine:
?:y- -<
FromNo. 15ALTERNATORSP SENSOR17.5 A)
FUELTANKPRESSURESENSOR
YEL/BLULT G]GRN/BLK
LT GRN/WHT
BLU
YEL
EVAPBYPASSRED/
VALVE
EVAPTWO WAVALVE
EVAP CONTROLCANISTER
FUEL FILLCAP
BLK
11-268
FUEL TANK
Page 538 of 2189

J
'96 Dl6Y5 engine,'96 D16Y8 engine (sodanl,'97 Dl6Y5 sngino,'97 Dl6Y8 sngine (sedan: KA, KC modols):
EVAPTWO WAY
EVAPPURGECONYROLSOLENOIDVALVEVALFromNo. 15
BLK/YEL__ _ < ALTERNATOR- SP SENSOR
FUELFILLCAP
VARIOUSSENSORS
(cont'd)
11-269
I
'96 D16Y' engin.,.9? D16Y7 engine {coupe: KA, KC models, sedan: KA. KC, Kl- IDX) modols, hatchback: all models}:
FromNo. 15
3lI/- - - -{ ALTERNAT'RSP SENSORRED/YEL
EVAPPUBGECONTROLSOLENOIDVALVE
FUELFILLCAP
8LK
+
t\,"ro*,
MANIFOLD
Page 546 of 2189

\
'99 - 00 models excepi Dl6Y5 engine with M/T:
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0452: A low voltage problem in the Fuel Tank Pressure
sensor.
The fuel tank pressure sensor converts fuel tank absolute pressure into electrical signals and inputs the ECM/PCM
OUTPUTVOLTAGE(vlt.5
0.5-7 kP.(-g) mmHg,-2 in.Hgl
+7 kP.
150 mmHg,2 in.Hgl
PRESSURE
I
Wire side of lemale terminals
FUEL TANKPRESSURE SENSORSUB.HARNESS6P CONNECTOR (C574 (C568)rl
vcc2(YEL/BLUIsG2{GRN/BLK}
Wire side o{ temale terminals
The MIL has been .eported on.
DTC P0452 is stored
Check the vacuum lines:
Check the vacuum lines of the
fuel tank pressure sensor lor mis-
routing, leakage, breakage and
cloggrng.
Are the vacuum hnes OK?
Problem veritication:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Proce-
du re,2. Bemove the fuel fill caP.
3. Turn the ignition switch ON {ll)
4. Monitorthe FTP Sensor voltage
with the Honda PGM Tester' or
measure voltage between body
groLrnd and ECM/PCM connec_
tor terminalA29.
lntermitlent tailure, 3Ystem b OK
at this time. Check for Poor con'
nections or loose wire3 at C131
{located under right side of dash},
C401 {located above under'dash
tuse/relay box), C574 (C568)*
llocdted under access Panel),C792 (tuel rank Prcssure sensorl
and ECM/PCM.
ls there approx.2 5 V?
Check for an open in wire {VCC2
line):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2. Reinstall the ltrel fill caP
3, Remove the access Panel from
the floor.4. Disconnect the fuel tank Pres'sure sensor sub-harness 6P
5. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll).
6. At the access Panel side, mea_
sure voltage between the fuel
tank Pressure sensor sub-nar-
ness 6P connector No 5termi
nal and No. 6 termlnal.
Repair open in tho wire between
th6 fu€l tank Prossuro sen3oa and
the ECM/PCM lc28).ls there approx 5 V?
ECM/PCM CONNECTOR A (32P)
PTANK {LT BLUI
I
ll
(To page '11-278)
(cont'd)
Page 547 of 2189

Emission Control System
Evaporative Emission (EVAPI Controls {cont,dlJ
FUEL TANKPRESSURE SENSORSU8-HABNESS6P CONNECTOR 1C574 tC568)rt
PTANK
{LT GRN}
PTANK
ILT GRN}
Wire side of female terminals
(From page 11-277)
Check for a short in the wire{PTANK line):At the access panel side, measure voltage between the fueltank pressure sensor sub-harness6P connector No. 2 terminal andNo. 6 terminal.
ls there approx. 5 V?
Chock lor a Short in the wi.e(PTANK line):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the ECM/PCM con-nector A (32P).
3. Check for continuity betweenthe fuel tank pressure sensorsub-harness 6P connector No.2 terminals and body ground.
Repair short in the wi.e betwsenthe luel tank pressure sensor andECM/PCM {A291.
Subsiitute a known-good ECM/PCM and rechock. lf symptom/indication goes away, replac€ theoriginal ECM/PCM.
11-278
Page 681 of 2189

Description
The automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides
4 soeeds forward and 1 reverse.
Torque Convertel, Geats, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear
which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly seryes as a
flywheel while transmiuing power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in Iine with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, gears tor 2nd, 4th, reverse and lst (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch, and
gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse. 1st and park. The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the counter-
shaft. When certain combinations of gears in transmission are engaged by clutches. power is transmitted from the main-
shaft to the countershaft to provide E, ld, E, and E positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Powertrain Control Module {PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenojd valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comtonable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main vatve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body and the
lock-up valve body through the respective separator plates, They are bolted on the torque converter housang
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve, the CPB {Clutch Pressure
Back-up) valve, the modulator valve. the servo control valve, the relief valve, and ATF pump gears The secondary valve
body contains the 2-3 shift valve. the 3-4 shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch
pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve,
the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the
reverse shift fork, and the accumulators. The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing
valve. The linear solenoid and the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid from regulator
passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective teed pipes
or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will activate
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a line
to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear, The shift control solenoid valves A and B are con-
trolled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
In ,Dt1 position, in 3rd and 4th. and in E position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the timing of
the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and
B, and linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 691 of 2189

Electronic Control SYstem
The electronac controt system consrsts of a Powertrain control Module (PcM), sensors, a Iinear solenoid and four solenoid
valves, shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions The PCM is located
below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
PGM-FIControl Sy3tem
A/T Control SYstom
Shift Control
Lock-uD Control
14-13
Page 692 of 2189
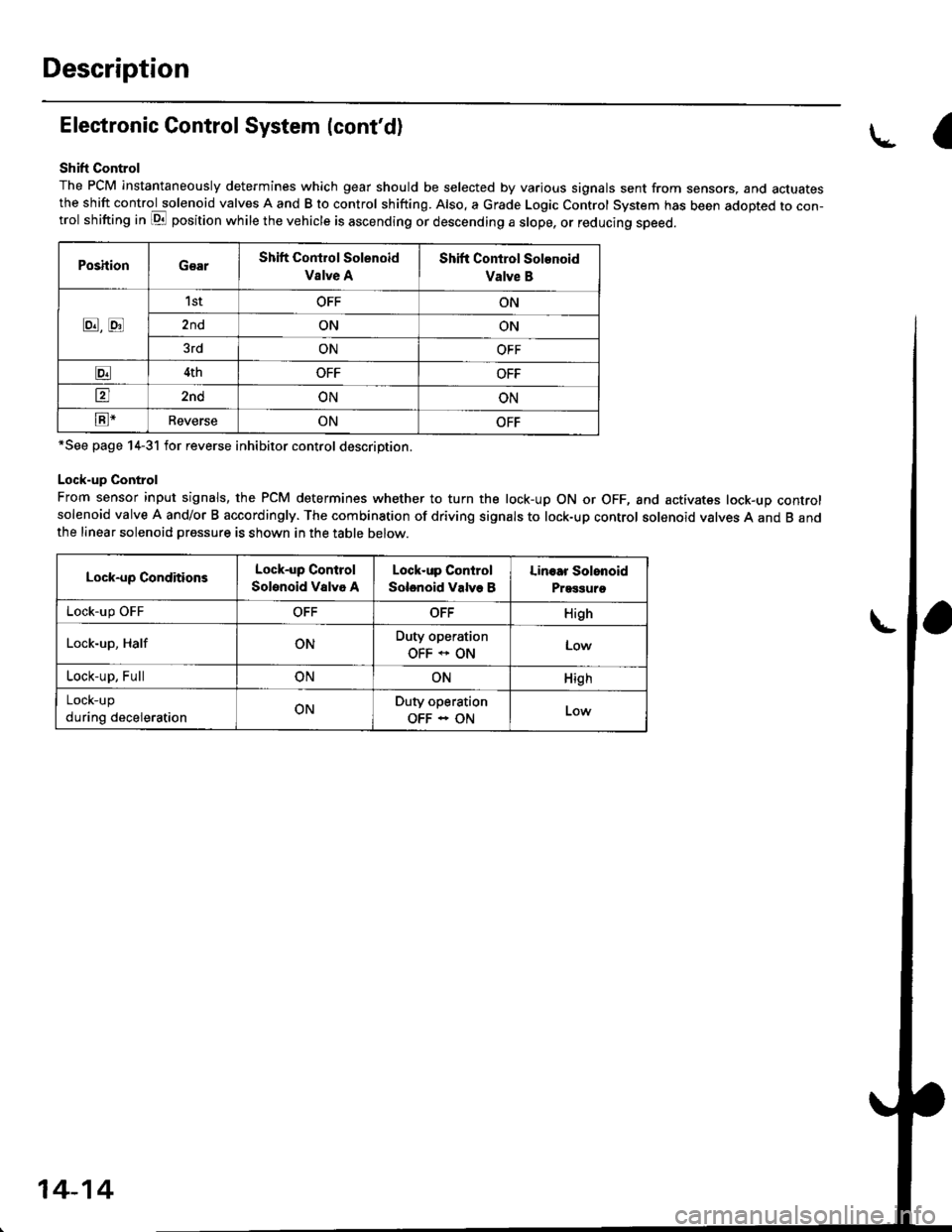
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
Shift Control
The PCM instantaneously determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuatesthe shift control solenoid valves A and B to control shifting. Also. a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to con-trol shifting in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speed.
PoshionGearShift Control Solenoid
Vslve A
Shift Control Solenoid
Valve B
8,tr
1stOFFON
2ndONON
3rdONOFF
E4thOFFOFF
tr2ndONON
E-ReverseONOFF
*See page 14-31 for reverse inhibitor control description.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the PCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up controlsolenoid valve A and/or B accordingly. The combination of driving signals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B andthe linear solenoid pressure is shown in the table below.
Lock-up ConditionsLock-up Control
Solenoid Valvo A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Linoar Solonoid
Prggguro
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF * ONLow
Lock-up, FullONONHigh
LOCK-Up
during decelerationONDuty operation
OFF - ON
a
14-14
Page 773 of 2189

Troubleshooting Flowchart - Mainshaft Speed Sensor
NOTE: Record all freeze data before you troubleshoot.
Possible Causg
. Diaconn€cted mainshaft spoed
sen3or connector'Short or open in mainshaft
sDeed sen3or wile. Faulty main3halt speed sensor
NOTE: Code P0715 (15) on the PCM doesn't
always mean there's an electrrcal problem in
the mainshaft or countershaft speed sensor
circuit; code P0715 {15) may also indicate a
mechanical problem in the transmissjon Any
problem causing irregular countershaft to
mainshalt speed difference can cause thls
code.
lll ,..TT
(ol-i-l
tl
side oI male terminals
MAINSI{AFT SPEEDSENSOR CONNECTOR
Terminal
PCM CONNECTOR D (16P)
NMSG (WHT)
Wire side of female terminals
(cont'd)
14-95
. OBD ll Scan Tool indicates Codem715.. Sell-diagno3is E indicator indi-
cates Code 15.
Check the mainshaft and counter-
shatt speed sensors installation,
and check them for damage.
Are the mainshaft and countershaft
speed sensor installed properly,
and not damaged?
Rsinalall or replace and rocheck.
Mea3u.e Meinshalt SPeod
Sensor Residance al the Sen3or
Connector:1. Disconnect the 2P connectorfrom the mainshaft sPeedsensor.2, Nreasure mainshaft speed sen_sor resistance at the sensorconnector.
ls the resistance 400 - 600 O?
Check Mainshaft Sp.ed Sen3o.
for a Short Circult:1. Disconnect the D (16P) con-nector trom the PCM.2. Check lor continuity betweenbody ground and the D11 ter'minal and D12 terminal indi
vidually.
Bopair 3hort in the wiros b€twe€nthe 011 and D12 termin.ls rndth€ main3hett sp€€d aensoa.ls there continuity?
To page 14 96