1997 CHEVROLET TAHOE 4 wheel drive
[x] Cancel search: 4 wheel drivePage 104 of 433
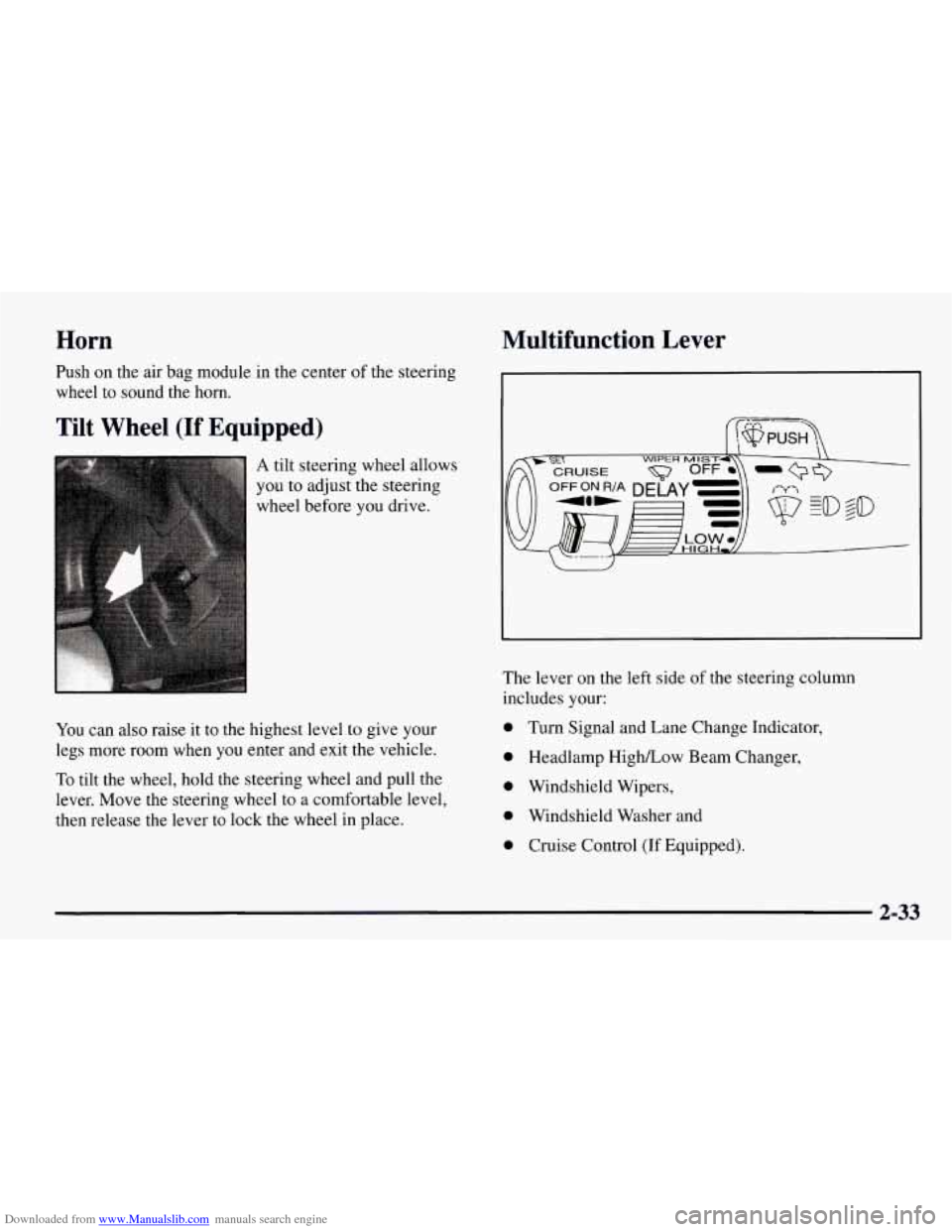
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Horn Multifunction Lever
Push
on the air bag module in the center of the steering
wheel to sound the horn.
Tilt Wheel (If Equipped)
A tilt steering wheel allows
you to adjust the steering
wheel before you drive.
You can
also raise it to the highest level to give your
legs more room when you enter and exit the vehicle.
To tilt the wheel, hold the steering wheel and pull the
lever. Move the steering wheel to
a comfortable level,
then release the lever to lock the wheel in place. The lever
on the left side of the steering column
includes your:
0 Turn Signal and Lane Change Indicator,
0 Headlamp HighLow Beam Changer,
0 Windshield Wipers,
0 Windshield Washer and
0 Cruise Control (If Equipped).
2-33
Page 108 of 433

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Washer fluid will spray as long as you push the paddle.
When you let
go of the paddle, the wipers will continue
to wipe for a few seconds and then either stop or return
to the preset speed.
The use of hood mounted air deflectors may adversely
affect windshield wiper and washer performance.
Cruise Control (If Equipped)
When you apply your brakes, cruise control shuts off.
0 Cruise control can be dangerous where you
can’t drive safely at a steady speed.
So,
don’t use your cruise control on winding
roads or in heavy traffic.
slippery roads. On such roads, fast changes
in tire traction can cause needless wheel
spinning, and you could lose control. Don’t
use cruise control on slippery roads.
0 Cruise control can be dangerous on
Setting Cruise Control
-
If you leave your cruise control switch on when
you’re not using cruise, you might hit
a button and
go into cruise when you don’t want to. You could
be startled and even lose control. Keep the cruise
control switch
OFF until you want to use it.
I I
2-37
Page 111 of 433

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Erasing Speed Memory
When you turn off the cruise control or the ignition,
your cruise control set speed memory is erased.
Lamps
Your parkingheadlamp knob is on the driver’s side of
your instrument panel.
Rotate the knob clockwise to the parking lamp symbol
to turn on the following:
0 Parking Lamps,
Sidemarker Lamps,
Clearance Lamps (if you have them),
0 Taillamps,
0 License Plate Lamps and
0 Instrument Panel Lights.
Rotate the knob clockwise again to the master lighting
symbol to turn on all the lamps listed as well as
the headlamps.
Rotate the knob counterclockwise to
OFF to turn off
your lamps.
Rotate the thumb wheel next to the knob up to adjust
instrument panel lights. Rotate the thumb wheel up to
the first notch to return the radio display and gearshift
indicator LED display to full intensity when the
headlamps or parking lamps are on.
To turn on the dome
lamps (with the vehicle doors closed) rotate the thumb
wheel up to the second notch position.
You can switch your headlamps from high to low beam
by pulling on the turn signal/high beam lever.
A circuit breaker protects your headlamps. If you have
an electrical overload, your headlamps will flicker
on
and off. Have your headlamp wiring checked right away
if this happens.
2-40
Page 187 of 433

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Here’s how anti-lock works. Let’s say the road is wet.
You’re driving safely. Suddenly an animal jumps out in
front
of you.
You slam on the brakes. Here’s what happens with ABS.
A computer senses that wheels are slowing down. If one
of the wheels is about to stop rolling, the computer will
separately work the brakes at each front wheel and at the
rear wheels. The
anti-lock system can change the brake pressure
faster than any driver could. The computer is
programmed to make the most of available tire and
road conditions.
You can steer around the obstacle while braking hard. As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates on
wheel speed and controls braking pressure accordingly.
4-8
Page 188 of 433

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need
to get your foot up to the brake pedal or always decrease
stopping distance. If you get too close to the vehicle in
front of you, you won’t have time to apply your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or stops. Always leave
enough room up ahead
to stop, even though you have
anti-lock brakes.
Using Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down
and let anti-lock work for
you. You may feel the brakes
vibrate, or you may notice some noise, but this is
normal. On vehicles with four-wheel drive, your
anti-lock brakes work at all times
-- whether you are in
two-wheel drive or four-wheel drive.
Braking in Emergencies
With anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the same
time. In many emergencies, steering can help you more
than even the very best braking.
Steering
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system is not functioning, you can steer but
it will take much more effort.
Variable Effort Steering
This system varies the amount of steering effort
proportionate to your vehicle speed. Steering is easier at
lower speeds for maneuvering and parking ease. As your
vehicle speed increases, the steering effort also
increases. At highway speeds, the amount
of steering
effort is increased for vehicle control and stability.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot
of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each
of us is subject to
the same laws of physics when driving on curves. The
traction of the tires against the road surface makes it
possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels. If there’s no traction, inertia will keep
the vehicle going in the same direction. If you’ve ever
tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll understand this.
The traction you can get
in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle at
which the curve is banked, and your speed. While you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.
Page 189 of 433

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve.
Then you suddenly accelerate. Both control
systems
-- steering and acceleration -- have to do their
work where the tires meet the road. Adding the sudden
acceleration can demand too much of those places. You
can
lose control.
What should you do if
this ever happens? Ease up on the
accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the way you want it
to
go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should
adjust your speed. Of course, the posted speeds are
based on good weather and road conditions. Under less
favorable conditions you’ll want to
go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a
curve, do it before you enter the curve, while your front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed
so you can “drive” through the
curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait to
accelerate until you are out
of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into the straightaway.
Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective than
braking. For example, you come over a hill and find a truck stopped in your lane, or a car suddenly pulls out
from nowhere, or a child darts out from between parked
cars and stops right in front
of you. You can avoid these
problems by braking
-- if you can stop in time. But
sometimes you can’t; there isn’t room. That’s the time \
for
evasive action
-- steering around the problem.
Your vehicle can perform very well in emergencies like
these. First apply your brakes. (See “Braking in
Emergencies’’ earlier in this section.) It is better to
remove as much speed
as you can from a possible
collision. Then steer around the problem, to the left or
right depending on the space available.
4-10
Page 192 of 433

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0
0
0
0
Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder and
start your left lane change signal before moving out
of the right lane to pass. When you are far enough
ahead of the passed vehicle to see its front in your
inside mirror, activate your right lane change signal
and move back into the right lane. (Remember that if
your right outside mirror is convex, the vehicle you
just passed may seem to be farther away from you
than it really is.)
Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time
on two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
Don’t overtake a slowly moving vehicle
too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps are not flashing, it may
be slowing down or starting
to turn.
If you’re being passed, make it easy for the
following driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little to the right.
Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes, steering
and acceleration) don’t have enough friction where the
tires meet the road to
do what the driver has asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep
trying to steer and
constantly seek
an escape route or area of less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not
“overdriving” those conditions. But skids are
always possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling. In the steering or cornering skid, too
much speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip and
lose cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving wheels to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid are best
handled by easing your foot
off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want the
vehicle
to go. If you start steering quickly enough, your
vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second skid if
it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel or other material is
on the road. For safety, you’ll
want to slow down and adjust your driving
to these
conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
4-13
Page 193 of 433

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine While driving on a surface with reduced traction, try
your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration
or
braking (including engine braking by shifting to a lower
gear). Any sudden changes could cause the tires to slide.
You may not realize the surface is slippery until your
vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning
clues
-- such as enough water, ice or packed snow on
the road to make a “mirrored surface”
-- and slow down
when you have any doubt.
Remember:
Any anti-lock brake system (ABS) helps
avoid only the braking skid.
Driving Guidelines
This multipurpose passenger vehicle is defied as a utility
vehicle in Consumer Information Regulations issued by
the National Highway Trafpc Safety Administration
(NHTSA) of the United States Department of
Transportation. Utility vehicles have higher ground
clearance and a narrower track to make them capable of
performing in a wide variety of off-road applications.
Specific design characteristics give them a higher center of
gravity than ordinary cars.
An advantage of the higher
ground clearance is a better view of the road allowing you
to anticipate problems. They are not designed for
cornering at the same speeds as conventional
two-wheel-drive vehicles any more than low-slung
sports
cars are designed to perform satisfactorily under off-road conditions.
If at
all possible, avoid sharp turns or abrupt
maneuvers. As with other vehicles of this type, failure to
operate
this vehicle correctly may result in loss of control
or vehicle rollover.
Off-Road Driving with Your
Four-Wheel-Drive Vehicle
This off-road guide is for vehicles that have
four-wheel drive.
Also, see “Anti-Lock Brakes”
in the Index.
If your vehicle doesn’t have four-wheel drive, you
shouldn’t drive off-road unless you’re on
a level,
solid surface.
Off-road driving can
be great fun. But it does have some
definite hazards. The greatest of these is the terrain itself.
“Off-roading” means you’ve left the great North
American road system behind. Traffic lanes aren’t
marked. Curves aren’t banked. There are no road signs.
Surfaces can be slippery, rough, uphill or downhill. In
short, you’ve gone right back to nature.
Off-road driving involves some new skills.
And that’s
why it’s very important that you read this guide. You’ll
find many driving tips
and suggestions. These will help
make your off-road driving safer and more enjoyable.
4-14