1996 LAND ROVER DEFENDER coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 66 of 455

ENGINE
7
REPAIR Refit
12.Lightly grease pulley spigot and locate pulley
onto cranshaft.
13.Fit pulley retaining bolt.
14.Fit pulley retainerLRT-12-080and secure with 4
bolts.
15.Tighten pulley nut to
80 Nm (59 lbf/ft)+90°.
16.Remove pulley retainer.
17.Fit drive belt.
See ELECTRICAL, Repair,
Auxiliary drive belt; Refit
18.Fit fan cowl.See COOLING SYSTEM, Repair,
Fan cowl
19.Fit viscous coupling and fan.See COOLING
SYSTEM, Repair, Viscous coupling and fan
20.Fit intercooler to induction manifold hose.
21.Fit radiator top hose.
22.Refill cooling system.
See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair, Drain and refill cooling system
23.Reconnect battery.FRONT COVER PLATE AND SEAL
Service repair no - 12.65.01
Remove
1.Disconnect battery.
2.Drain coolant.
See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair, Drain and refill cooling system
3.Remove top hose from radiator.
4.Remove intercooler to induction manifold hose.
5.Remove viscous coupling and fan.
See
COOLING SYSTEM, Repair, Viscous
coupling and fan
6.Remove fan cowl.See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair, Fan cowl
7.Remove drive belt.See ELECTRICAL, Repair,
Auxiliary drive belt
8.Remove crankshaft pulley.See Crankshaft
pulley
9.Remove 14 bolts securing front cover plate. Note
that top 2 bolts also retain thermostat hose clips.
10.Remove cover plate complete with gasket.
11.Remove small gasket from centre bolt boss.
Seal replacement
12.Remove worn seal from cover and clean recess.
13.Support cover and fit new seal, open side fitted
into recess, using special toolLRT-12-077.
Page 79 of 455
12ENGINE
20
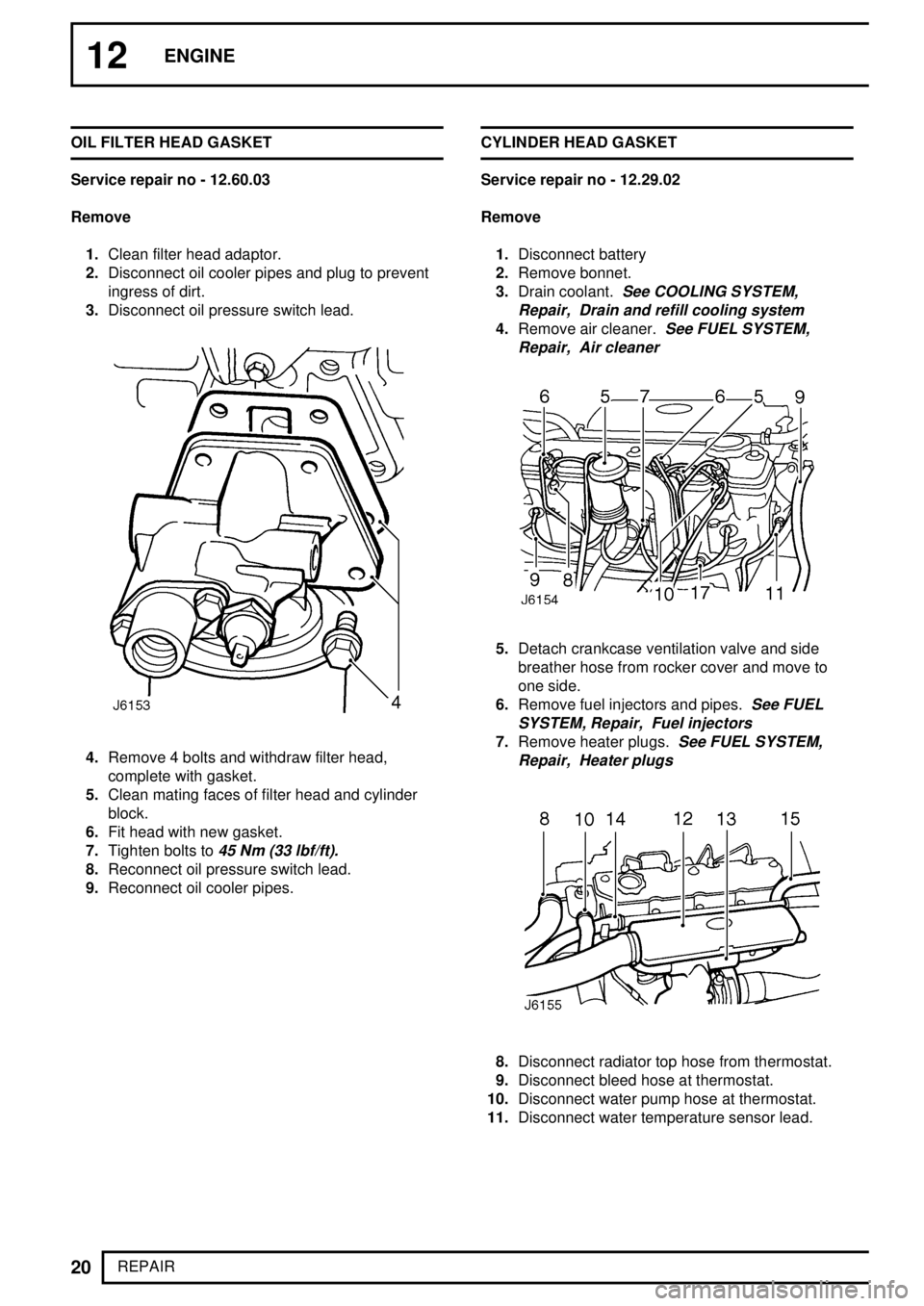
REPAIR OIL FILTER HEAD GASKET
Service repair no - 12.60.03
Remove
1.Clean filter head adaptor.
2.Disconnect oil cooler pipes and plug to prevent
ingress of dirt.
3.Disconnect oil pressure switch lead.
4.Remove 4 bolts and withdraw filter head,
complete with gasket.
5.Clean mating faces of filter head and cylinder
block.
6.Fit head with new gasket.
7.Tighten bolts to
45 Nm (33 lbf/ft).
8.Reconnect oil pressure switch lead.
9.Reconnect oil cooler pipes.CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
Service repair no - 12.29.02
Remove
1.Disconnect battery
2.Remove bonnet.
3.Drain coolant.
See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair, Drain and refill cooling system
4.Remove air cleaner.See FUEL SYSTEM,
Repair, Air cleaner
5.Detach crankcase ventilation valve and side
breather hose from rocker cover and move to
one side.
6.Remove fuel injectors and pipes.
See FUEL
SYSTEM, Repair, Fuel injectors
7.Remove heater plugs.See FUEL SYSTEM,
Repair, Heater plugs
8.Disconnect radiator top hose from thermostat.
9.Disconnect bleed hose at thermostat.
10.Disconnect water pump hose at thermostat.
11.Disconnect water temperature sensor lead.
Page 89 of 455

19FUEL SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION A mechanical lift pump, with a hand priming facility, is
driven by the camshaft, and is mounted on the RH
side of the engine.
A fuel filter, with a replaceable element and
incorporating a water separator, is mounted on the
front RH side of the engine compartment.
A fuel sedimentor may be fitted when the vehicle is
operating in more arduous conditions, and is used to
minimise water deposits in the fuel system before
reaching the fuel pump and filter.
Fuel injection is carried out by a Bosch direct injection
pump, incorporating a cold start advance unit and a
high idle setting. The pump is mounted on the RH side
of the engine and is driven directly by gears in the
front cover from the crankshaft. The pump meters and
distributes fuel to 4 pintle type injectors located in
pre-combustion chambers in the cylinder head. Four
heater plugs, located in the cylinder head directly
below each injector, are fitted to improve cold starting.
An optional hand throttle, for use with a centre power
take off, is located on the fascia to the LH side of the
fuse box, and is linked independently to the fuel
injection pump throttle lever.
Air intake
The air cleaner is mounted on the RH side of the
engine and is connected by hoses to the cold air
intake duct and turbocharger inlet. Fitted between the
air cleaner and turbocharger is the crankcase breather
hose which connects to a breather filter on the rocker
cover.
A single stage turbocharger, fitted between the
exhaust manifold and exhaust down pipe, is
connected by hoses to the air cleaner and an
intercooler which is mounted on the LH side of the
radiator. The intercooler is connected by a hose to the
inlet manifold. When an EGR valve is fitted to the
turbocharger, additional pipes/hoses are used to
connect the components.Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), when fitted.
Exhaust gas recirculation is controlled by an ECU
mounted under the front centre seat or cubby box and
receives the following inputs:
·Engine temperature from coolant temperature
sender unit on LH side of cylinder head.
·Throttle position from potentiometer on injection
pump.
·Engine speed from speedometer.
When all correct signals are received, the EGR
solenoid allows vacuum to open EGR valve and
recirculate a portion of the exhaust gas. See J6196 for
the EGR system component location and 'Operation'
for full system function.
Page 94 of 455
FUEL SYSTEM
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
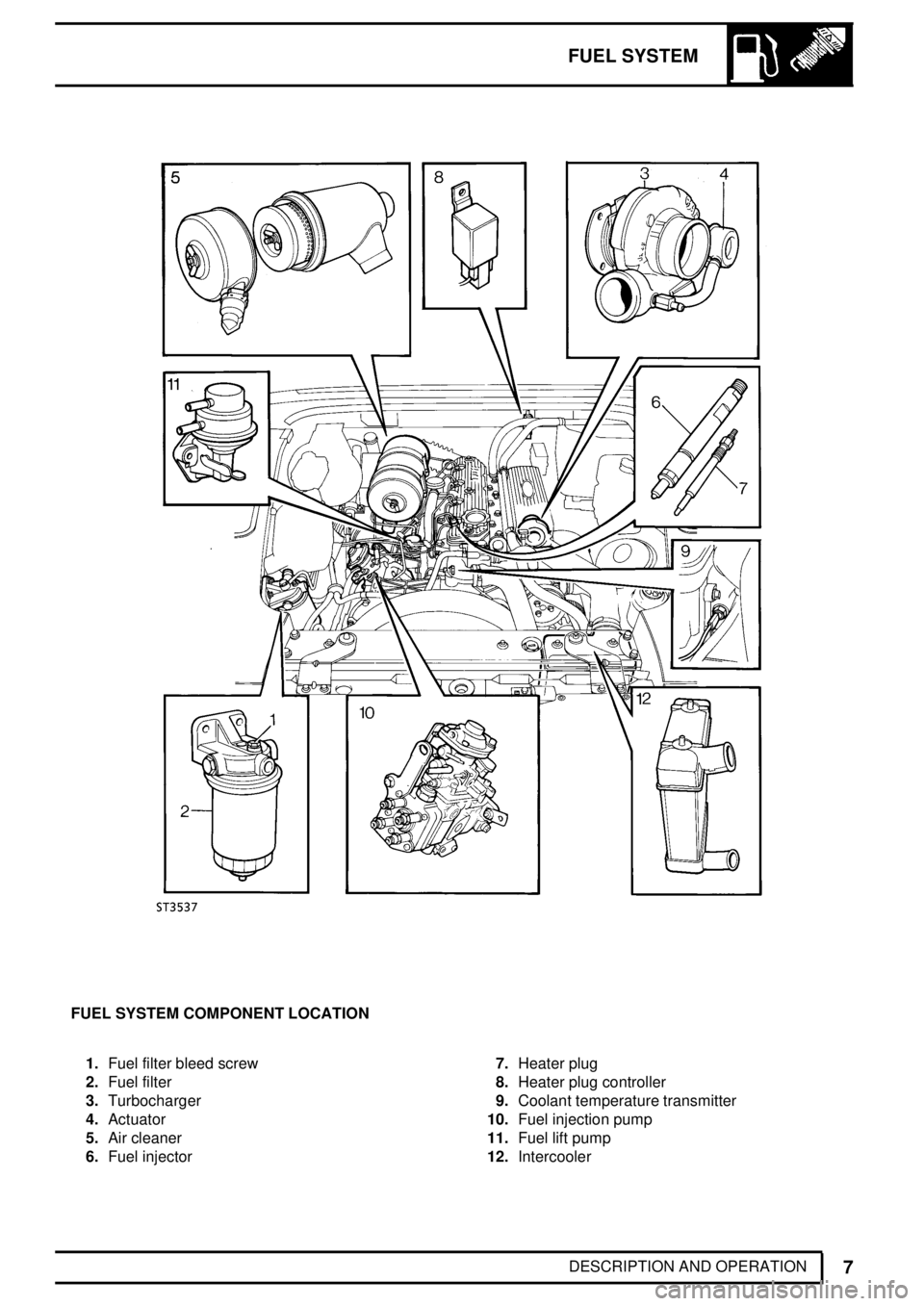
FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT LOCATION
1.Fuel filter bleed screw
2.Fuel filter
3.Turbocharger
4.Actuator
5.Air cleaner
6.Fuel injector7.Heater plug
8.Heater plug controller
9.Coolant temperature transmitter
10.Fuel injection pump
11.Fuel lift pump
12.Intercooler
Page 96 of 455

FUEL SYSTEM
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OPERATION
Diesel engines operate by compression ignition. The
rapid compression of air in the cylinder during the
compression cycle heats the air and when fuel is
injected into the heated air, it ignites instantaneously.
During cold tarting, automatically controlled heater
plugs assist in raising the temperature of the
compressed air to ignition point.
A cold start advance unit advances the injection timing
to further assist starting. Idle quality is improved by
the high idle setting.
The engine is supplied with pre-compressed air by a
single stage turbocharger.
Exhaust gases passing over a turbine cause it to
rotate, driving a compressor mounted on the turbine
shaft. Air drawn from the cold air intake passes, via
the air cleaner, to the turbocharger where it is
compressed. Compression in the turbocharger warms
up the air considerably, so that it expands. As a result
the air mass per cylinder is reduced, having a
negative effect on power output. By fitting a charge-air
intercooler, located on the LH side of the radiator, the
air is cooled before reaching the cylinders. This
increases power output through increased mass of
oxygen in the combustion process, as well as
maximising engine durability, through maintaining
lower piston and head temperatures.
Fuel is drawn from the tank by a mechanical lift pump
and passes to the injection pump via a filter. In
addition to removing particle contamination from the
fuel, the filter incorporates a water separator, which
removes and stores water.
The sedimentor/s, when fitted, is located adjacent to
the fuel tank/s and separates contamination and water
particles in the fuel before reaching the fuel lift pump.
The injection pump meters a precisely timed, exact
quantity of fuel to the injectors in response to throttle
variations, injection timing varying with engine speed.
Any excess fuel delivered to the injection pump is
passed back to the tank via the spill return line.
Fuel is injected in a finely atomised form into the main
combustion chamber, the burning fuel expands
rapidly, creating extreme turbulence which mixes the
burning fuel thoroughly with the compressed air,
providing complete combustion.Cold Starting is assisted by heater plugs, a cold start
advance unit and a high idle setting.
Heater plugs
Heater plug operation is controlled by a timer unit,
start relay and resistor. When the ignition is turned on
the timer unit is energised, the heater plugs start to
operate and a warning light on the dashboard
illuminates, remaining on until the heater plugs are
automatically switched off.
The length of time the heater plugs will operate is
dependent on under bonnet temperature, which is
monitored by a sensor located in the timer unit.
Starting the engine results in the power supply to the
heater plugs passing through the resistor, which
reduces their operating temperature. The heater plugs
are cut out either by the temperature sensor in the
timer, or by a microswitch on the injection pump which
operates when the throttle is depressed.
Cold start advance
The cold start advance unit is connected to the engine
cooling system via hoses. It contains a temperature
sensitive element which is retracted when cold and
pulls the advance lever, via cable, towards the rear of
the pump against spring pressure. As coolant
temperature rises, the cold start element expands
releasing tension on the cable and allowing spring
pressure to move the advance lever forwards.
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), when fitted
Operation of the EGR system is dependent on the
following:
·Engine temperature - must be between 20°C and
100°C approx.
·Engine speed - must be between 630 and 2850
rev/min.
·Engine load - calculated by throttle position
sensor.
·EGR valve lift position.
·Duration of engine idling.
Page 97 of 455

19FUEL SYSTEM
10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Under varying engine speed and load condition the
control unit sends a signal to open the vacuum
modulator which allows a vacuum to be applied above
the EGR diaphragm. The vacuum supply is taken from
a 'T' connector in the brake servo hose. This process
is controlled by an engine speed/load map stored in
the EGR control unit memory.
Engine speed is measured by monitoring the
waveform present on one phase of the generator.
Throttle position is measured via a sensor mounted on
the fuel injection pump throttle lever. Closed loop
control is achieved by allowing the control unit (ECU)
to continually monitor EGR valve lift via the sensor
mounted on the valve; this valve lift is compared with
the actual valve lift required on the control unit map
and adjusted, if necessary.
With coolant temperature between 20°C and 100°C,
the engine having just returned to idle, EGR will shut
off after 25-30 seconds idling.
Page 121 of 455

COOLING SYSTEM
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
Description
The complete cooling system of the 300Tdi engine
incorporates three independent functions:- Engine
(coolant) cooling; Turbo (charge air) intercooling;
Engine oil cooling.The intercooler is a separate aluminium unit, located
on the LH side of the engine compartment adjacent to
the radiator, sharing the same upper and lower
mountings. For details of turbo intercooling
See
FUEL SYSTEM, Description and operation,
Operation
. The oil cooler matrix is an integral part of
the radiator. Pre-formed pipes/hoses are used to link
the components within the separate systems as
shown below.
Engine cooling system
1.Radiator
2.Thermostat housing
3.Radiator bottom hose
4.Viscous fan
5.Water pump
6.Radiator top hose
7.Heater return hose
8.Coolant supply hose
9.By-pass hose
10.Radiator bleed (purge) hose
11.Bleed (purge) hose, thermostat housing
12.'Y' piece ejector
13.Expansion tank14.Heater rail
15.Heater unit
16.Heater feed hose
17.Intercooler
18.Air cleaner
19.Air feed hose
20.Turbocharger
21.Charge air supply pipe/hose
22.Cooled charge air supply hose
23.Exhaust manifold
24.Engine oil cooler
25.Feed pipe, engine oil cooler
26.Return pipe, engine oil cooler
27.Oil filter
Page 122 of 455

26COOLING SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE (COOLANT) COOLING
Description
The 300Tdi engine uses a pressurised cooling system
and cross flow radiator which is supplied with coolant
from an expansion tank mounted on the RH side of
the engine compartment. A belt driven centrifugal
water pump, fitted to an auxiliary mounting assembly,pumps coolant to the engine crankcase, cylinder head
and vehicle heater unit.
An eleven bladed fan, incorporating a viscous
coupling, is driven by an independent pulley secured
to the front cover plate. The thermostat housing,
bolted to the front of the cylinder head, is fitted with a
vent valve that purges excessive air pressure and
coolant back to the expansion tank.
Engine coolant circulation (engine warm - thermostat open).
1.Radiator
2.Thermostat/housing
3.Radiator bottom hose
4.Viscous fan
5.Water pump
6.Radiator top hose
7.Heater return hose
8.Coolant supply hose9.By-pass hose
10.Radiator bleed (purge) hose
11.Thermostat housing bleed (purge) hose
12.'Y' piece ejector
13.Expansion tank
14.Heater rail
15.Heater unit
16.Heater feed hose