Page 294 of 2189
|-
DI6YTengine('96mode|.,97coupe:KA,Kcmode|s,,97sedan:KA,KC,KL{Dx}modets,'gThatchback:a||models}:
COOLANT
o
l)
r.-.
.t)
a:!)
o-o
aroa1t
PRIMARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (PRIMARY HOzS,
SENSOR 1)SECONDARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR {SECONDARY
HOzS, SENSOR 2)
MANIFOLD AESOI-UTE PRESSURE IMAP) SENSOR
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE IECT) SENSOR
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT} SENSOR
CRANKSHAFT SPEED FLUCTUATION (CKF) SENSOR
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IACI VALVE
THROTTLE BOOY (TB)
FUEL INJECTORFUEL FILTERFUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
FUEL PUMP IFPIFUEL TANKFUEL TANK EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAPI VALVE
AIR CLEANERRESONATORPOSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILTATION IPCVI VALVE
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAP} PURGE CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVEEVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAP) CONTROL CANISTER
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION IEVAPI TWO WAY VALVE
THREE WAY CATALYTIC CONVERTER (TWCI
[3)@ao(o
a@
(0
@)
(cont'd)
11-25
Page 295 of 2189
![HONDA CIVIC 1996 6.G Workshop Manual System Description
Vacuum Connections (contd)
Dl6Y7 angin6 (97 coup.: KL mod€l, sedan: KL (LX) model,,9g modet):
i1] PRIMARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (PRIMARY HO2S,SENSOR 1)E) SECONDARY HEATED OXYGEN HONDA CIVIC 1996 6.G Workshop Manual System Description
Vacuum Connections (contd)
Dl6Y7 angin6 (97 coup.: KL mod€l, sedan: KL (LX) model,,9g modet):
i1] PRIMARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (PRIMARY HO2S,SENSOR 1)E) SECONDARY HEATED OXYGEN](/manual-img/13/6068/w960_6068-294.png)
System Description
Vacuum Connections (cont'd)
Dl6Y7 angin6 ('97 coup.: KL mod€l, sedan: KL (LX) model,,9g modet):
i1] PRIMARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (PRIMARY HO2S,SENSOR 1)E) SECONDARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR {SECONDARYHO2S, SENSOR 2l€l MANTFOLD ABSOT_UTE PRESSUnE tMAp) SENSOR€r ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE |ECT) SENSOR€] INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE IIAT} SENSOR6 CRANKSHAFT SPEED FLUCTUATION ICKFI SENSOR17 IOLE AIR CONTROL IIACI VALVE@ THRoTTLE BoDY {TBIO FUEL INJEGToR(9 FUE|- FTLTEFO FUEL PRESSURE REGULAToR@ FUEL PUMP {FPI(D FUEL TANK@ FIFL TANK EVAPoRATIVE EMIssIoN {EVAPIVALVE(, AIR CLEANER
(tO RESONATORl? PoSITIVE cRANKcAsE VENTILATIoN IPcv}VALVEIA EVAPORANVE EMISSION TEVAPI PURGE CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE19 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION IEVAPI CONTROL CANISTERE EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAPIBYPASS SOLENOIDVALVE€' EVAPoRATIVE EMIssIoN IEVAPI THREE wAY vALvEQ' EVAPORATIVE EMISSION IEVAPI CONTROL CANISTERVENT SHUT VALVE@ FUEL TANK PRESSURE sENsoR{?1! EVAPORANVE EMISSION IEVAPI TWO WAY VALVE?5 THREE WAY CATALYTIC CONVERTER ITWC'
11-26
Page 296 of 2189
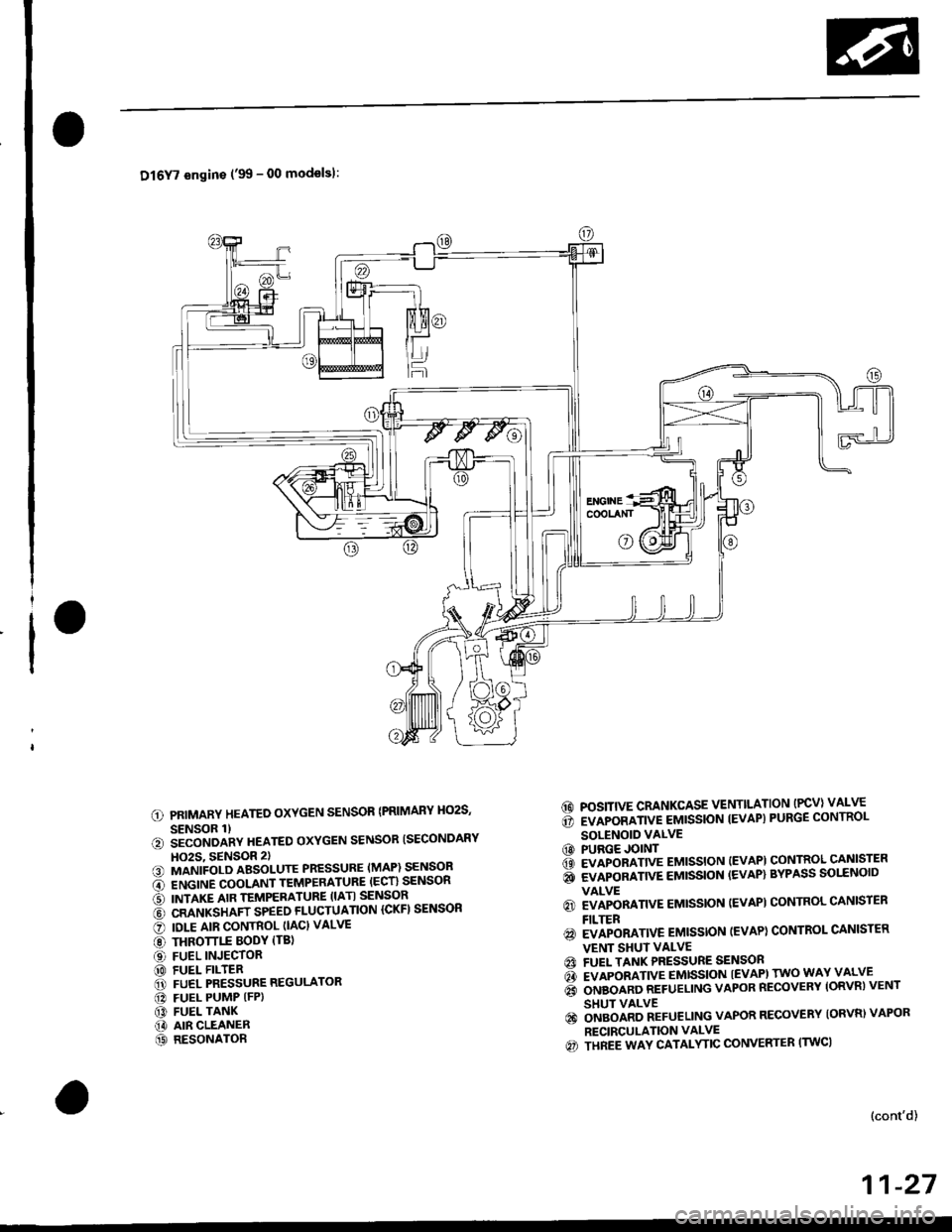
Dl6Y7 engins ('99 - 00 modelsl:
PRIMARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR {PRIMARY HO2S,
SENSOR 1)iiconoanv neareo oxYGEN sENsoR ISECoNDARY
HO2S, 9ENSOR 2)MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT} SENSOR
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IATI SENSOR
CRANKSHAFT SPEED FLUCTUATION ICKFI SENSOR
IOLE AIR CONTROL (IAC} VALVE
THROTTLE BODY (TBl
FUEL INJECTORFUEL FILTERFUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
FUEL PUMP (FP)
FUEL TANKAIR CLEANERRESONATOR
6d POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV) VALVE
6 rvapoamve eutssloN tEvAP) PURGE coNTRoL
SOLENOID VALVECO PURGE JOINT6 evlponnnve eutssloN (EvAPl coNTRoL cANlsrER
i evlponnnve eussloN {EVAP} BYPASS solrNolD
VALVE
6) EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAPI CONTROL CANISTEN
FILTER
@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSTON (EVAP) CONTROL CANISTER
VENT SHUI VALVEA FUEL TANK PRESSURE SENSON
d rvlpoamve emtsstoN tEvAPl rwo wAY vALvE
6 orueonno nerueLING vAPoR REcovERY loRvnl vENT
SHUT VALVE
€) ongolno neruellNc VAPOR RECOVERY {ORVR) VAPOR
RECIRCULATION VALVE
€) THREE WAY CATALYTIC CONVERTER (TWC)
a
6t
@!.,
o@ao
@@
(}
@@
(cont'd)
11-27
Page 297 of 2189

I
a
System Description
Vacuum Connections (cont'd)
816A2 engine:
@ EvApoRATtvE EMtsstoN tEvAp) puRGE coNTRoLSOLENOID VALVE@ PURGE JoINT€t EvApoRATtvE EMtsstoN (EVApt coNTRoL caNtsTERQA EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAP) BYPASS SOLENOIDVALVE
@ EVApoRATtvE EMtsstoN lEvApl coNTRoL caNtsrERFILTER@ EvApoRATtvE EMtsstoN {EvApt coNrRoL cANtsrERVENT SHUT VALVE@ FUEL TANK PRESSURE sENsoRGI EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAP} TWO WAY VALVE@ ONBOARD REFUETING VAPOR RECOVERY {ORVR} VENTSHUT VALVE@ oNBoAnD REFUELING vApoR REcovERy (oRvRl vApoR. RECIRCULATION VALVE(c} THREE WAY CATALYTIC CONVERTER {TWCI
(' PRIMARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR IPRIMARY HO2S.SENSOR 1l.?) SECONDARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR {SECONDARYHO2S, SENSOR 2)13] MANIFOLD ABSoLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) sENsoBi' ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE IECT) SENSORO INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE ITATI SENSORi6l KNOCK SENSOR {KS}O oRANKSHAFT SPEED FLUCTUATIoN {cKF} sENsoR@ IDLE AIR coNTRoL (IAc} VALVE€) THRoTTLE BoDy trB|(D FUEL INJECToRO FUEL PULSATIoN DAMPER[D FUEL FILTER@ FUEL PRESSURE REGULAToR!I FUEL PUMP IFP)f,' FUEL TANK(iD ArR CLEANERt' RESONAToR'.1]i POSITIVE cRANKcAsE VENTILATIoN {Pcv} VALVE
11-28
Page 350 of 2189
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedures
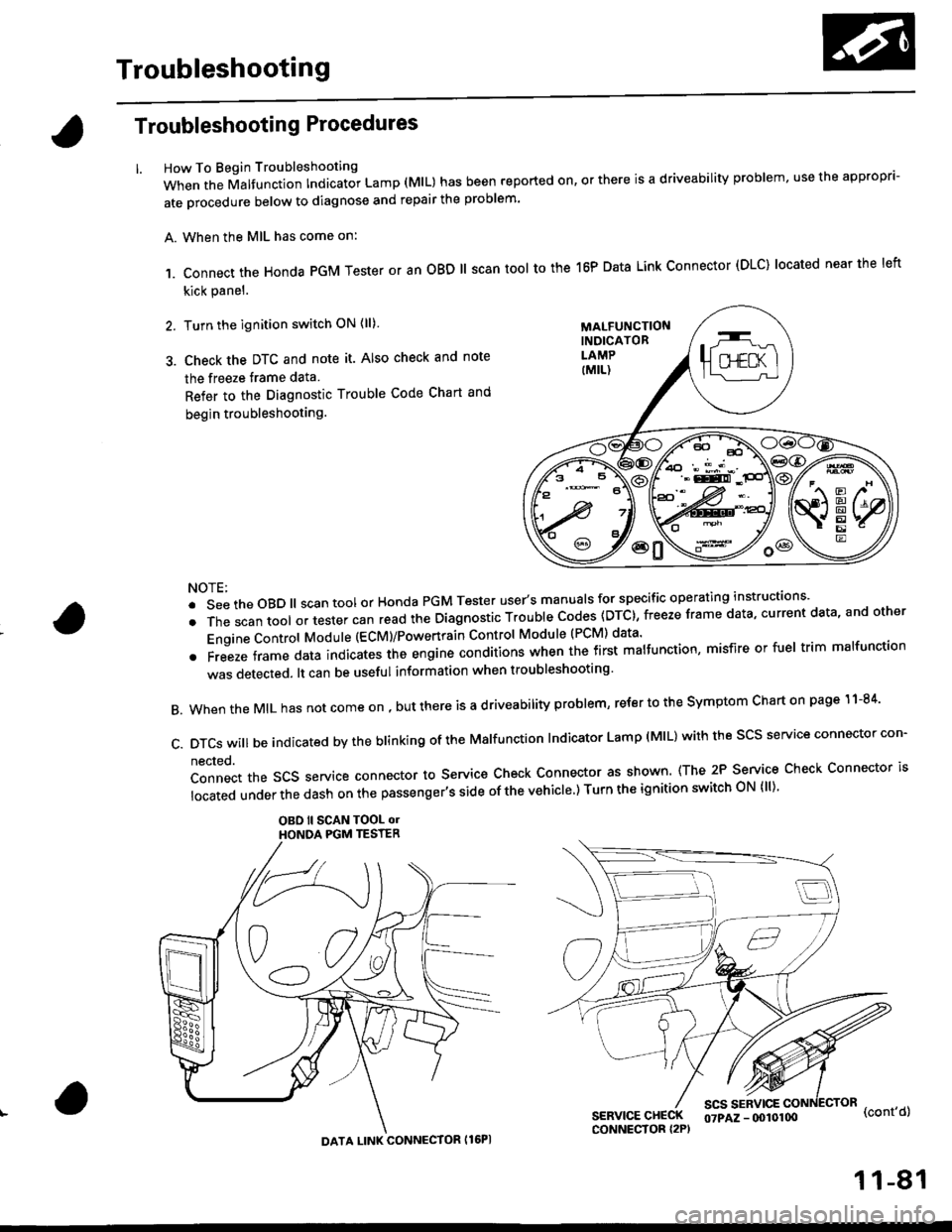
How To Begin Troubleshooting
When the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MlL) has been reported on, or there is a driveability problem, use the appropr'-
ate orocedure below to diagnose and repair the problem'
A. When the MIL has come on:
,1. connect the Honda PGM Tester or an oBD ll scan tool to the 16P Data Link connector (DLC) located near the left
kick panel.
2. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll)
3. Check the DTC and note it. Also check and note
the freeze trame data
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Code Chart and
begin troubleshooting.
NOTE:
.SeetheoBD||scantoolorHondaPGMTesteruser,smanua|sforspecificoperatinginstructions..
.Thescantoo|oltestercanreadtheDiagnosticTroub|ecodes(DTc},freezeframedata,currentdata,andother
Engine Control Module (ECM)/Powertrain Control Module (PCM) data'
oFreezeframedataindicatestheengineconditionswhenthefirstma|function,misfireorfue|trimma|function
was detected. lt can be useful information when troubleshooting'
B. When the MIL has not come on , out there is a d riveability problem, refer to the Symptom Chart on page 1 1-84'
c.DTcswi|lbeindicatedbytheb|inkingoftheMa|function|ndicatorLamp(M|L)withthescsserviceconnectorcon.
nected.
Connect the SCS service connector to Service Check Connector as shown (The 2P Service Check Connector is
|ocatedunderthedashonthepassenger,ssideofthevehic|e')TurntheignitionswitchoN{||)'
OBO ll SCAN TOOL olHONOA PGM TESTER
SERVICE CHECKCONNECTOR I2P)
scs sERvlcE(cont'd)
MALFUNCTIONINDICATORLAMP
DATA LINK CONNECTOR Il6PI
07PAZ - (x)l0100
11-81
Page 353 of 2189
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedures (cont,dl
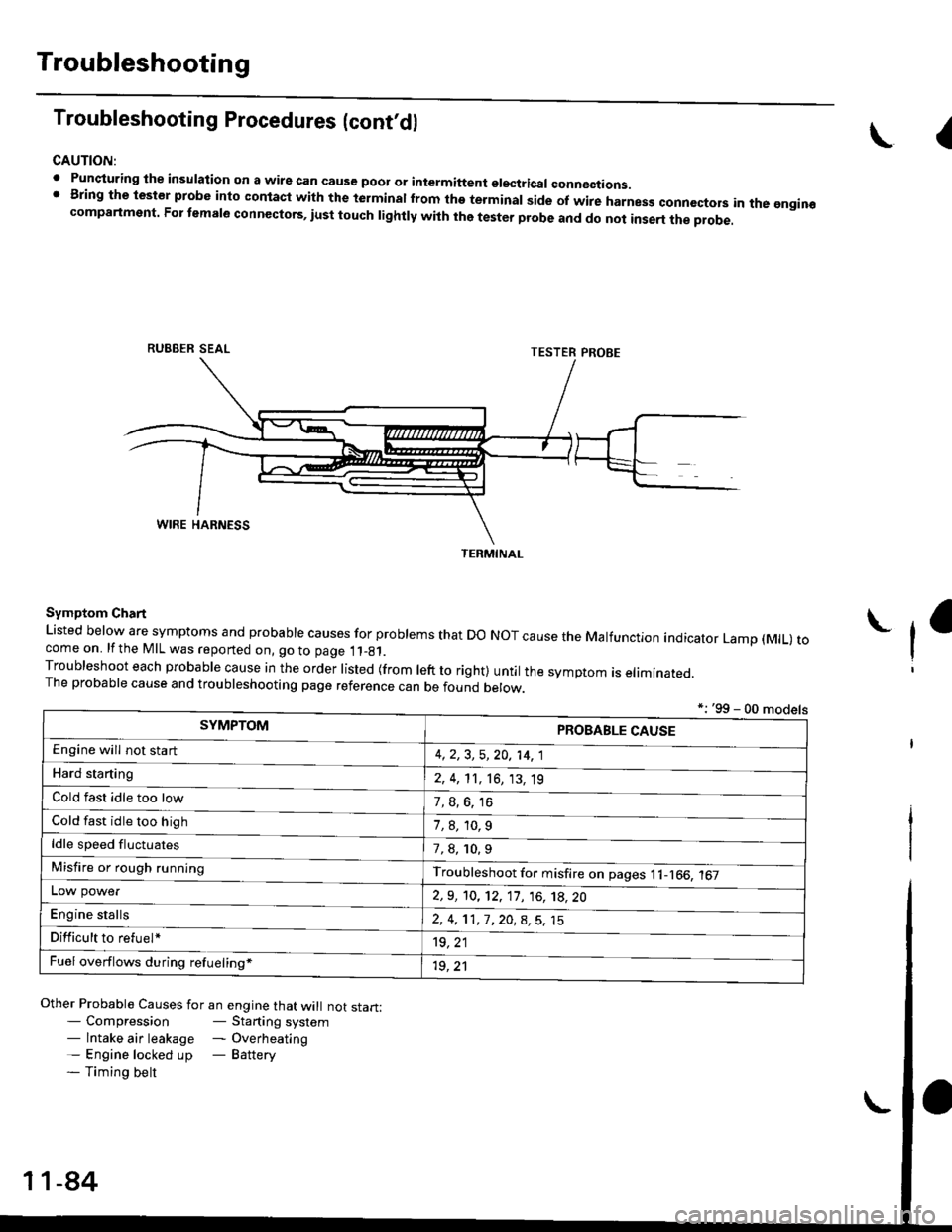
CAUTION:
. Punqturing ihe insulation on a wirs can cause poor or intermiftent electricar connections.I Bring the test€r probe into contacl with the terminatlrom the terminal side of wire harnesg conncctors in the gngin€compartment. For temale connectors, iust touch lightly with the tester probe and do not inse.t the probe.
\I
RUBBER SEAL
Other Probable Causes for an engine that will not start:- Compression- Starting system- lntake air leakage - Overheating- Engine locked up - Battery- Timing belt
TESTER PROBE
Symptom Chart
Listed below are symptoms and probable causes for problems that Do NoT cause the Malfunction indicator Lamp (MlL) tocome on. lfthe MIL was reported on, go to page 11_81.Troubleshoot each probabre cause in the order risted (from reft to right) untir the symptom is eriminated.The probable cause and troubleshooting page reference can be found berow.
L
*: '99 - 00 models
TERMINAL
SYMPTOMPROBABLE CAUSE
4,2,3, 5,20, 14, 1
2, 4, 11, 16, 13, 't9
?, s^6. 16
1,8,10.9
Engine will not sta rt
Hard starting
Cold fast idle too low
Cold fast idle too high
ldle speed fluctuates7,8, 10.9
Troubleshoot for misfire on pages l1-166, 167Misfire or rough running
LOW power
E"g|* "t"lb
2,9, 10, 12, 11, 16, 't8,20
2,4,11,7,20,8,5,15
't9, 21
1r, ,1
Difficult to refuel*
Fuel overflows during refueling*
11-84
Page 354 of 2189
Probable Cause List lFor th€ DTC Chart, see page 11-971*: '99 - 00 models
Probable GausePageSystem
11 1-107Engine Control Module (ECM)/Powertrain Control Module (l'uM)
PGM-Fl main relay
l^^iti^n cwetam
211-230,231
3't't-237
Section 23
51'�1-172,183Crankshaft Position/fop Dead Center/Cylinder Fosltlon sensor clrculr'� Lr\F selrsor
circuit
Intake Air Temperature (lAT) sensor circuit
ldle Air Control (lAC) Valve
ldle speed adjustment
Throttle bodY
Throftle cable
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor
Throftle Position (TP) sensor
Barometric pressure (BARO) senso'
Mf g"a, po"ition signal (see page 11-216) or clutch switch signal
Brake switch signal
Air Cleaner
lntake air pipe
Three Way Catalytic Converter (TWC)
Evaporative emission (EVAP) control
Contaminated fuel
ORVR vent shut valvs
't1-124
71 1-194
I11-220 - 223
11-241
'1011-244
1111-115
1211-132
13't1-178
14Section 14. 11-218
1511-210
16't1-244
1811-252
1911-261
20
21*11-296
(cont'd)
11-85
Page 355 of 2189
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedures (cont,dl
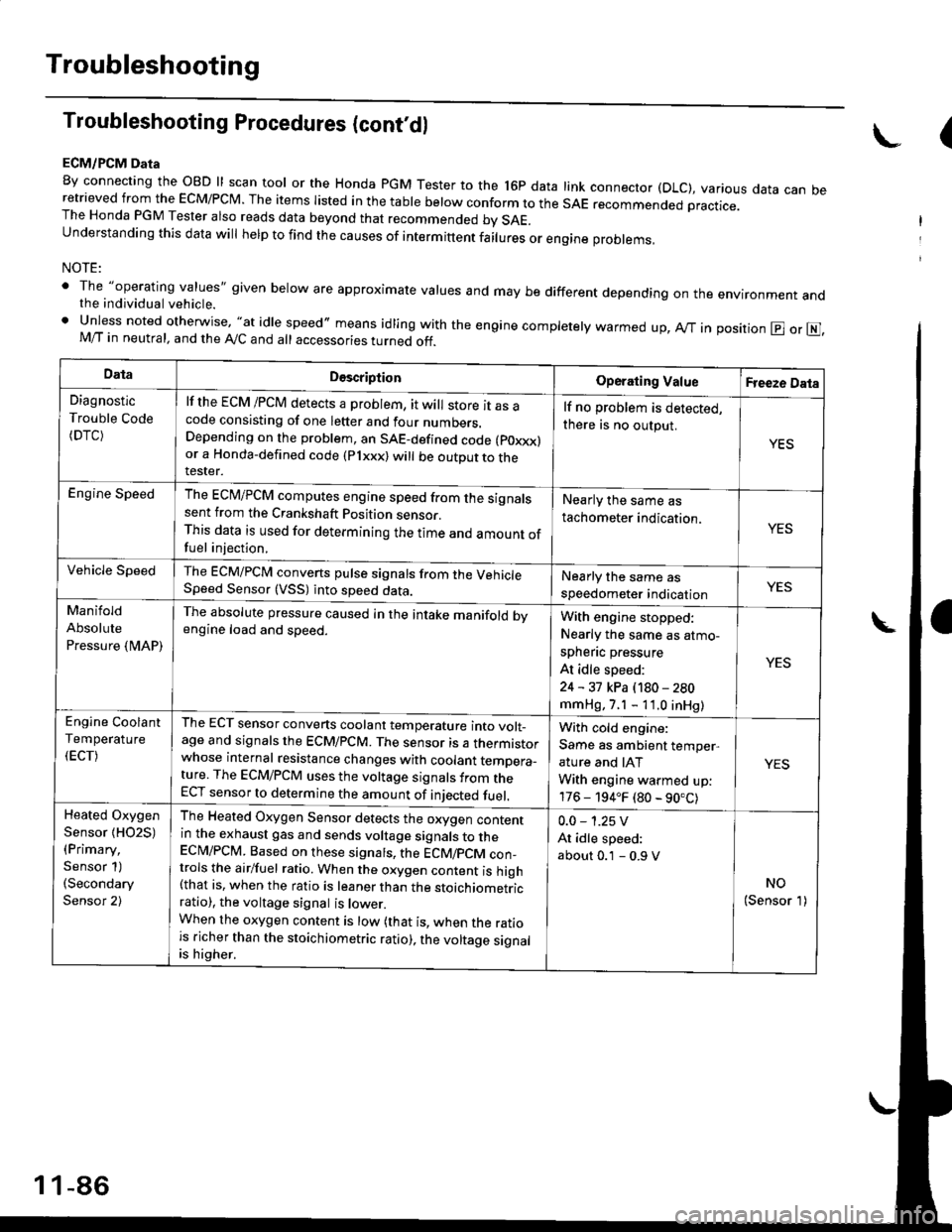
ECM/PCM Data
By connecting the OBD ll scan tool or the Honda pGM Tester to the l6p data link connector (DLC), various data can beretrieved from the EcM/PcM. The items Iisted in the table below conform to the sAE recommended practice.The Honda PGM Tester also reads data beyond that recommended bv SAE.understanding this data wil help to find the causes of intermittent fairures or engine probrems,
NOTE:
' The "operating values" given below are approximate values and may be different depending on the environment andthe individual vehicle.. Unless noted otherwise, "at idle speed,, means idling with the engine completely warmed up, Ay'T in position @ or E],M/T in neutral, and the Ay'C and all accessories turned off.
(
DataDescriptionOperating ValueFreeze Data
Diagnostic
Trouble Code(DTC)
lf the ECM /PCM detects a problem, it will store it as acode consisting of one letter and four numbers.Depending on the problem, an SAE-defined code (poxxx)or a Honda-defined code (Plxxx) will be outDut to therester.
lf no problem is detected,
there is no output.
YES
Engine SpeedThe ECM/PCM computes engine speed from the signalssent from the Crankshaft Position sensor.This data is used for determining the time and amount offuel injection,
Nearly the same as
tachometer indication.YES
Vehicle SpeedThe ECM/PCM converts pulse signals from the VehicleSpeed Sensor (VSS) into speed data.Nearly the same as
speedometer indicationYES
Manifold
Absolute
Pressure {MAP)
The absolute pressure caused in the intake manifold bvengine load and speed.With engine stopped:
Nearly the same as atmo-
spheflc pressure
At idle speed:
24 - 31 kPa (180 - 280
mmHg, 7.1 - 11.0 inHg)
YES
Engine Coolant
Temperature
(ECT)
The ECT sensor converts coolant temperature into volt_age and signals the ECM/PCM. The sensor is a thermistorwhose internal resistance changes with coolant temDera_ture. The ECM/PCM uses the voltage signals from theECT sensor to determine the amount of iniected fuel.
With cold engine:
Same as ambient temper,
ature and IAT
With engine warmed up:
176 - 194.F (80 - 90.C)
YES
Heated Oxygen
Sensor {HO2S)(Primary,
Sensor 1)(Secondary
Sensor 2)
The Heated Oxygen Sensor detects the oxygen contentin the exhaust gas and sends voltage signals to theECI\4/PCM. Based on these signats, the ECM/pCM con_trols the airlfuel ratio. When the oxygen content is high(that is, when the ratio is leaner than the stoichiometricratio), the voltage signal is lower.When the oxygen content is low (that is, when the ratiois richer than the stoichiometric ratio), the voltage signalis higher.
0.0 - 1.25 V
At idle speed:
about 0.1 - 0.9 V
NO(Sensor 1)
1 1-86